Reconstitution of Soils [อิตาลี]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Chiara Cassinari
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Ricostituzione
technologies_7346 - อิตาลี
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
วิทยากรหลัก
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Manfredi Paolo
mcm Ecosistemi
อิตาลี
co-compiler:
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
NEW LIFE Project (NEW LIFE)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
m.c.m Ecosistemi (m.c.m Ecosistemi)1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Reconstitution is a technology that counters land degradation and according to the theory of "Circular Economy" it's a sustainable land management technology
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [อิตาลี]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Chiara Cassinari
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
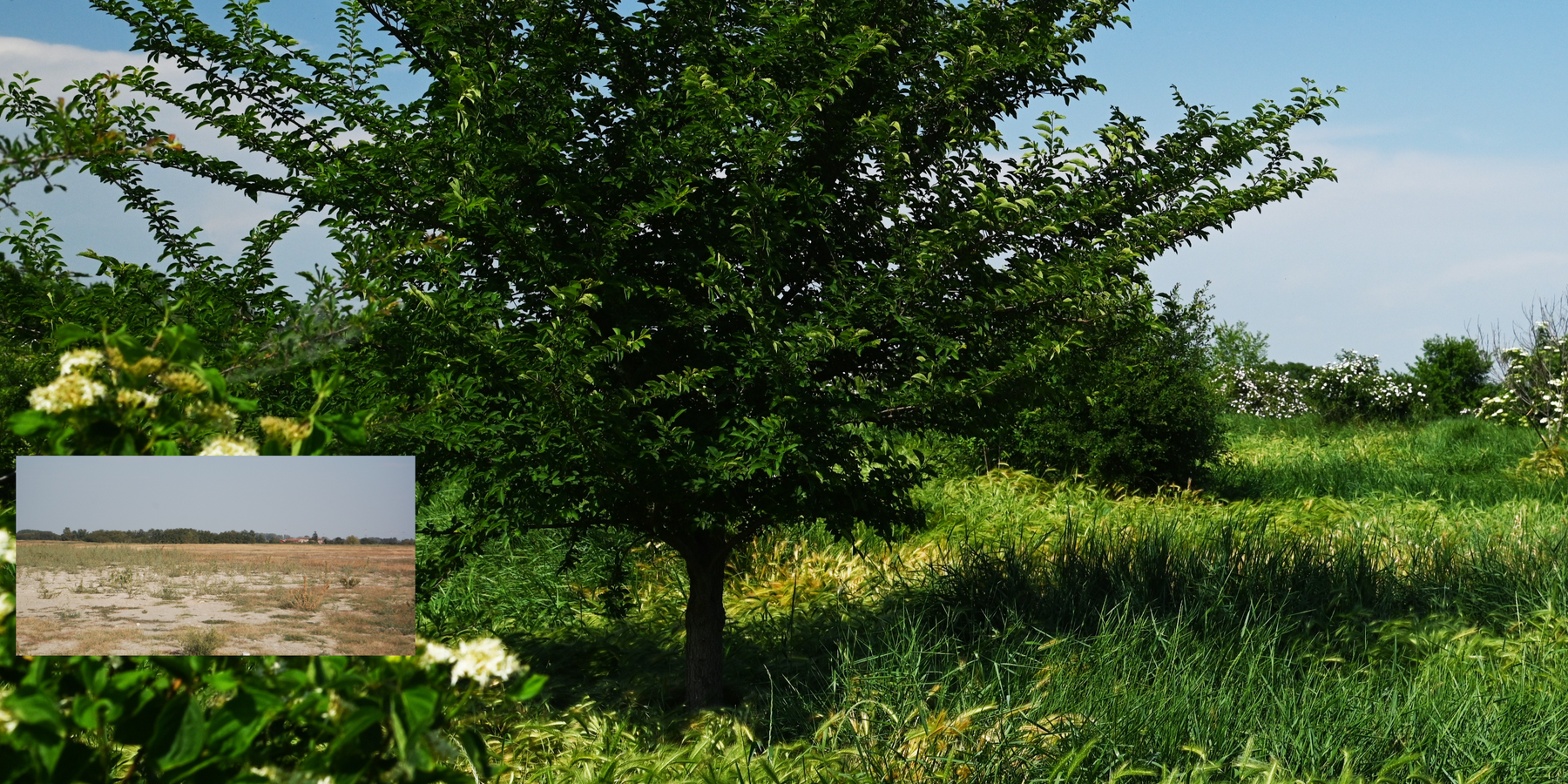
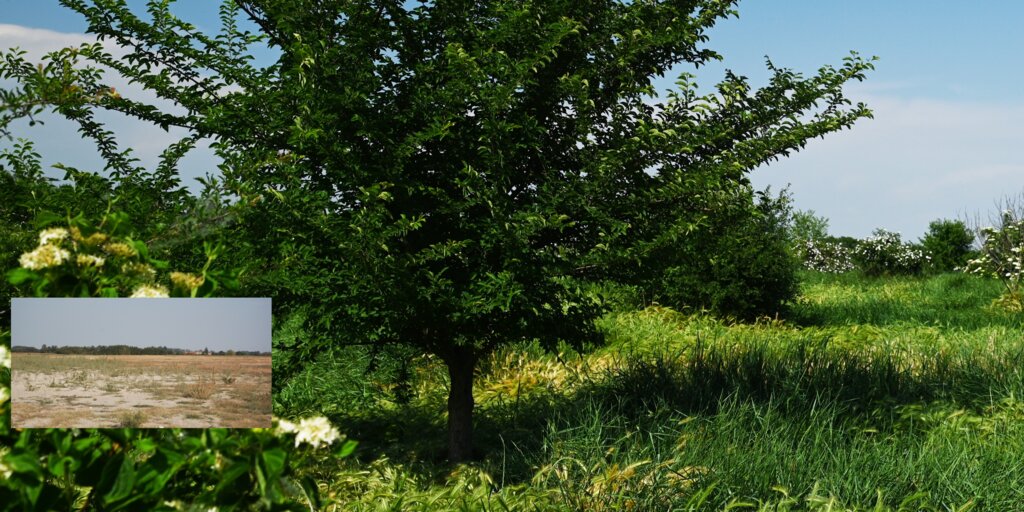
Reconstitution of soils is a pedotechnique based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials to achieve benefits in areas with barren, degraded, desertified and/ or sealed soils.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
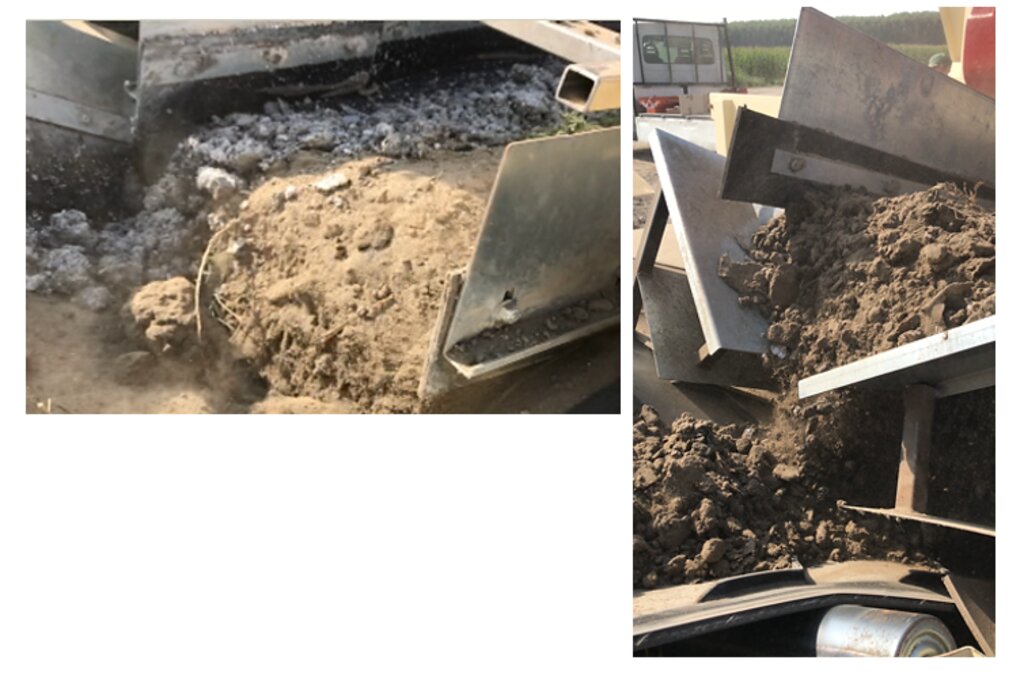
Reconstitution of soils to generate an Anthroposol is a technology based on the treatment of organic and non-organic pedomaterials or “matrices” (from “matrix” in Latin: everything that is the foundation of something) to achieve ecosystem benefits, especially in areas with degraded, desertified, barren and/or sealed soils. The technology applies a conceptual model based on the production of new soil aggregates with targeted environmental and soil characters generated via a chemico-mechanical process that entails reusing residues of specific origin. The activity is consistent with the principles of a “Circular Economy”, applying restoration ecology, use of compatible waste and saving the non-renewable resource of soil. Reconstitution is covered by two patents of the mcm Ecosistemi s.r.l. company.
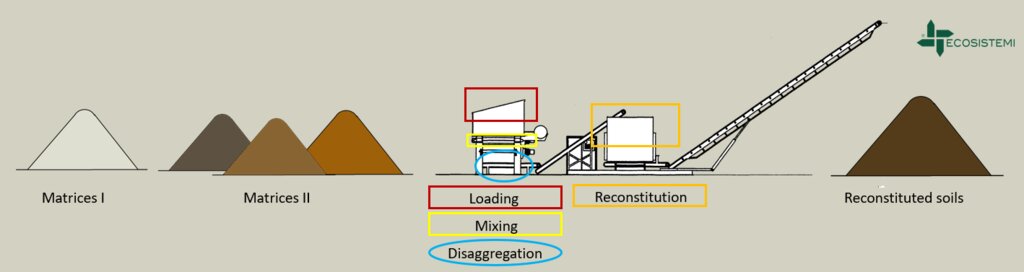
Reconstitution applies the process to two groups of pedomaterials. Firstly, primary matrices (matrices I), represent the main material to be converted into fertile soil. These could be degraded soil itself or inorganic mineral pedomaterials. Secondly, secondary matrices (matrices II) refer to byproducts and waste from production activities. Secondary matrices are divided into two. First, organic - from wood and cellulose processing production activities and from textile and agro-food industries. These are characterized by a high organic component with a high carbon/nitrogen ratio, and a high presence of plant fibres. Second, mineral matrices - especially from mining, the preparation of drinking and industrial water and the management of hydroelectric reservoirs and internal canals. There are four stages.
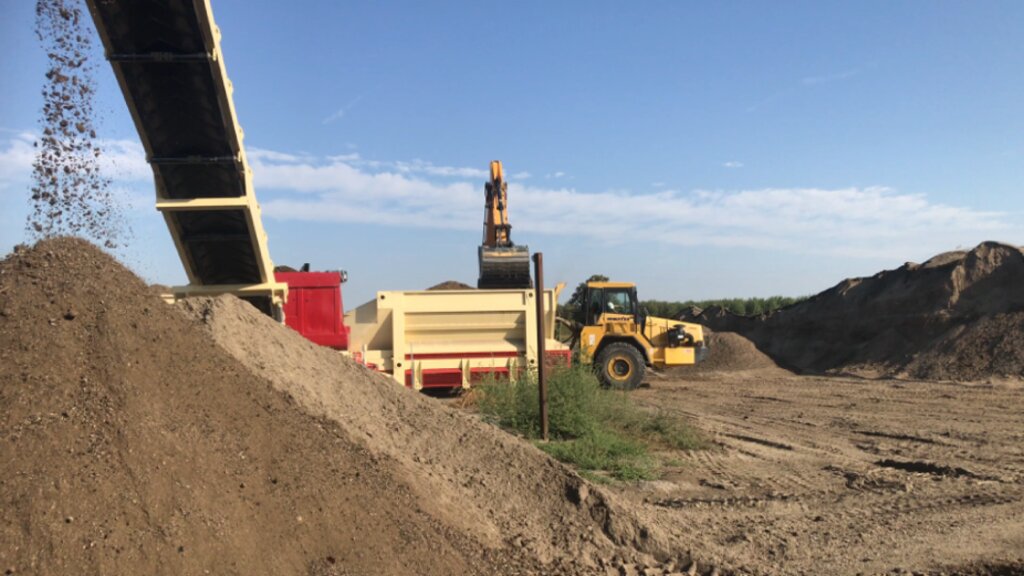
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected according to the type of soil desired and then loaded in the plant. Dosage is calculated through an application program (PEDOGÉNIA), which estimates the chemical properties of the finished product.
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity.
3) Disaggregation: Breakup and defibering through rotating movements at variable power.
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
The treatment generates an Anthroposol whose characters and properties are different from the materials of origin.
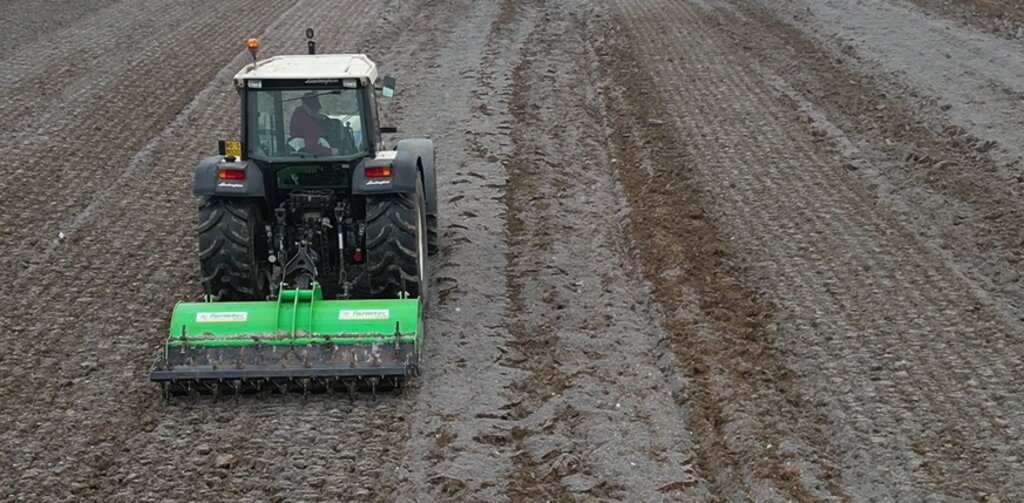
The properties of the reconstituted soils and the technical-economic sustainability of the pedotechnology have been demonstrated over the years with agronomical tests and experiments, as well as comparative analysis between degraded soils and reconstituted soils. This demonstrates the reconstituted soil’s ability to create a stable pedosystem to carry out its basic functions - storage, filtration, transformation of nutrients and biodiversity pools - for various forms of land use, and ecosystem benefits. Agroforestry restoration with reconstitution has social impact, as it is demonstrated by a EU project (“New Life”), where the Park of Trebbia river has increased utility to people after restoration. Agronomic restoration allows farmers to increase yields using less fertilizer and water. Another environmental and economic advantage is that manufacturing companies which produce waste can reduce costs through the recycling process of reconstitution. For reconstitution, a plant has to be installed near the land to be restored; an overview is presented in 4.1. In addition, earth moving vehicles are needed for the transport and placement of reconstituted soil.
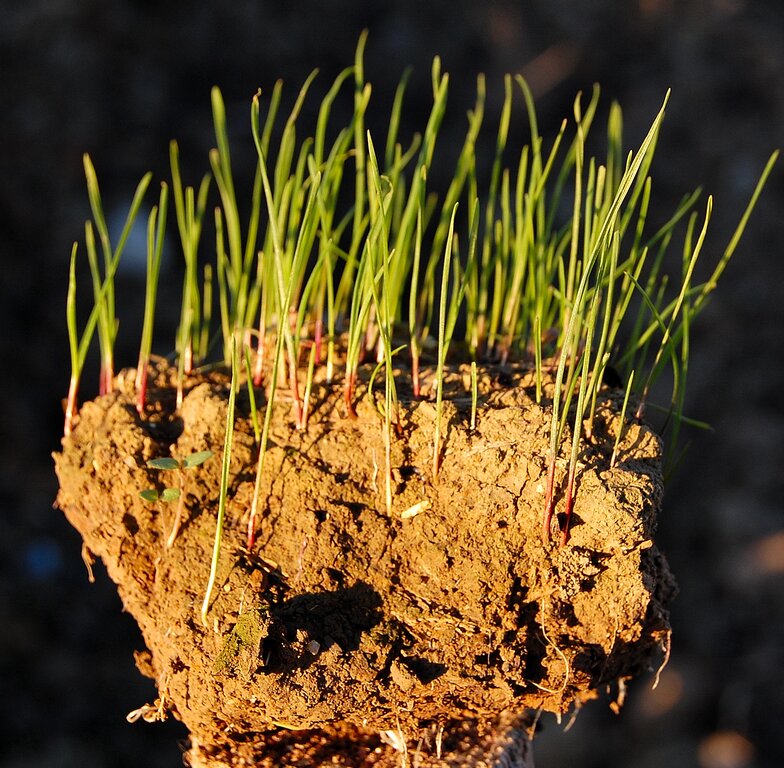
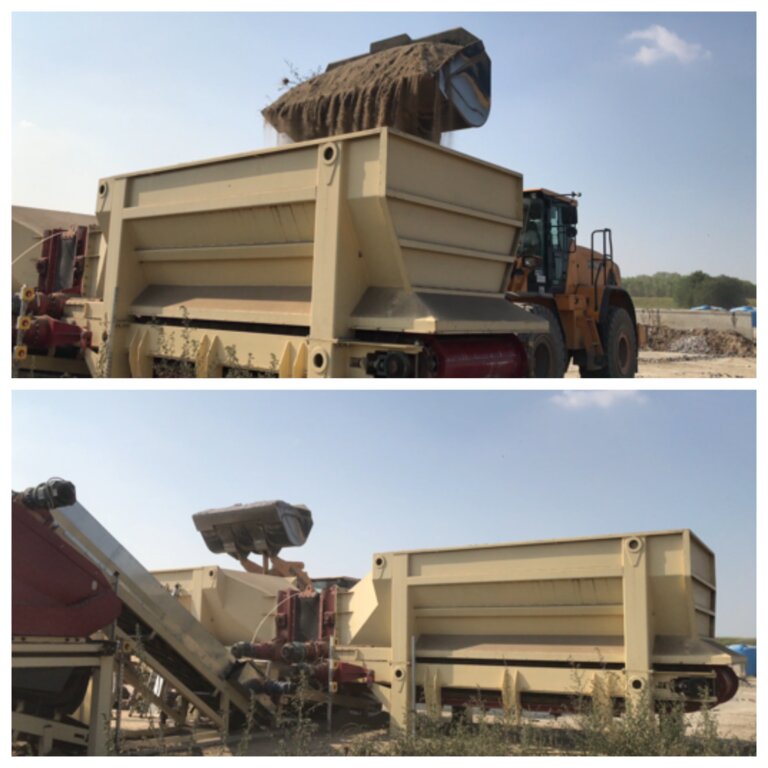
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=nF3nl4S5X8M
Reconstitution plant
วันที่:
18/12/2024
สถานที่:
Piacenza, Loc. Mortizza
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Paolo Manfredi
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
youtube video
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kjy95Kz-e70
Construction site: collection of degraded soil to be reconstituted
วันที่:
18/12/2018
สถานที่:
Piacenza, Gossolengo
ชื่อผู้ถ่ายวีดีโอ:
Paolo Manfredi
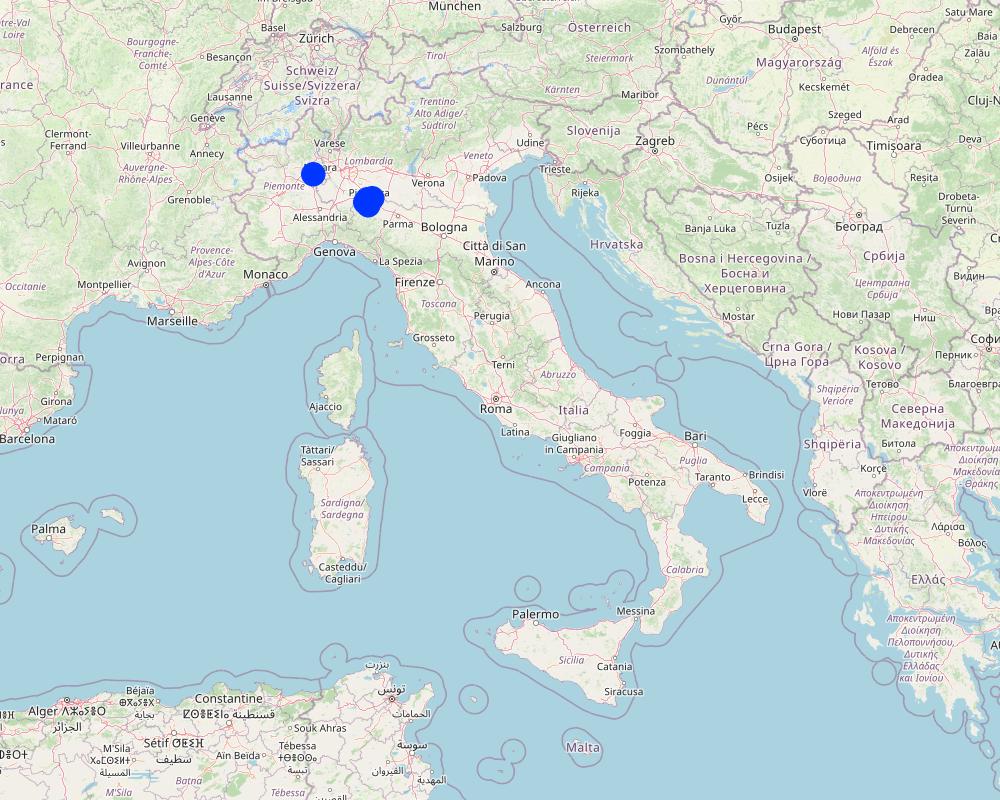
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อิตาลี
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Emilia Romagna, Piacenza; Piemonte, Vicolungo
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 1-10 ตร.กม.
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- น้อยกว่า 10 ปี (ไม่นานนี้)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
Regional, National and International projects
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านสังคมที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- tomato, fodder crops
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
maize - wheat - tomato

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
Type of (semi-)natural forest:
- subtropical dry forest natural vegetation
Tree plantation, afforestation: Specify origin and composition of species:
- การปลูกหลายพันธุ์รวมกัน
Type of tree plantation, afforestation:
- subtropical dry forest plantation
Type of tree:
- Acacia species
- Populus species
- Salix species
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- mixed deciduous/ evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- การอนุรักษ์ / ป้องกันธรรมชาติ
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- วนเกษตร (Agroforestry)
เหมืองแร่ อุตสาหกรรมจากธรรมชาติ

ที่ดินที่ไม่ให้ผลผลิต
ระบุ:
degraded, desertified and sealed soils
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
- การจัดการของเสีย / การจัดการน้ำเสีย
- ecosystem rehabilitation
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
- A4: การรักษาดินชั้นล่าง

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S11: อื่น ๆ

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M6: การจัดการของเสีย (การทำ รีไซเคิล การเอากลับมาใช้ใหม่หรือการลดปริมาณ)
- M7: อื่นๆ

มาตรการอื่น ๆ
ระบุ:
addition of organic matter, new soil aggregates, increase water holding capacity
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน
- Wo (Offsite degradation): ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านเคมี
- Cn (Fertility decline): ความอุดมสมบูรณ์และปริมาณอินทรียวัตถุในดินถูกทำให้ลดลงไป (ไม่ได้เกิดจากสาเหตุการกัดกร่อน)
- Ca (Acidification): การเกิดกรด
- Cs (Salinization/alkalinization): การสะสมเกลือหรือการทำให้เป็นด่าง

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านกายภาพ
- Pc (Compaction): การอัดแน่น
- Pk (Slaking and crusting): การอุดตันของช่องว่างในดินหรือรูพรุน
- Pi (Soil sealing)

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bq (Quantity/biomass decline): การลดลงของปริมาณหรือมวลชีวภาพ
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง
- Bl (Loss of soil life): การสูญเสียสิ่งมีชีวิตในดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Ha (Aridification): การเกิดความแห้งแล้ง
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ลดความเสื่อมโทรมของดิน
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Reconstituted technology: phases of work:
1) Loading: After the chemico-physico-environmental and rheological characterization of matrices I and II, the materials are selected and dosed
2) Mixing: The matrices undergo mechanical mixing under controlled humidity
3) Disaggregation through rotating movements at variable power
4) Reconstitution: Specifically calibrated cyclic compression and formation of reconstituted soil aggregates.
ผู้เขียน:
Paolo Manfredi
วันที่:
12/04/2023
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
10 hectares
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
EUR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.89
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
123.00, gross income
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | characterization of the intervention site | no timing |
| 2. | morphological planning | no timing |
| 3. | environmental planning | no timing |
| 4. | pedo-agronomic planning | no timing |
| 5. | moving-plant placement only if the area to be restored is distant from the area where the permanent plant is located | no timing |
| 6. | degraded soil removal and collect | after harvest of crops, if there are |
| 7. | reconstitution | no timing |
| 8. | replacement of reconstituted soil | no timing |
| 9. | final soil placement | no timing |
| 10. | site-specific planting to make soil ready for use | dependence of plants species |
| 11. | land use | no timing |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The reconstitution plants are 2: one is fixed that is located in an area, the other is a moving-plant: that is it can be located near the area to be restored.
According to the distance between the intervention site and the fixed plant it can be more useful using the moving-plant
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | 3 Workers | person/day | 232.0 | 123.0 | 28536.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Construction area - mobile plant | number | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Earth moving vehicles | number | 2.0 | 20000.0 | 40000.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Matrices to be used | m3 | 75000.0 | 15.0 | 1125000.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Reconstitution | m3 | 100000.0 | 2.5 | 250000.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 1473536.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 1655658.43 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
Costs related to the matrices to be used and transport (1125000.00 EUR) are covered by company producing waste used. The costs to dispose of matrices II are much higher than taking them to the reconstitution plant.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
degraded land value 0 EUR
restored area value 390000 EUR
restoration using allocation of natural soil (8 EUR/m3, cost of natural soil in Piacenza) added to transport costs = 2100000.00 EUR
restoration using reconstituted soil technology = 28536 + 30000 + 40000 + 250000.00 EUR because 1125000.00 EUR are covered by company producing waste and so not spent for restoration.
Cost related to construction area and mobile plant are the costs for the set up of the area where to put the mobile plant and for it' transport to the intervention site.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ordinary plant maintenance | every 6 months or when needed |
| 2. | Reconstituted soil analysis | every 6 months |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | 1 Worker | person/day | 20.0 | 123.0 | 2460.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | 3 Laboratory staff | person/day | 100.0 | 115.0 | 11500.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 13960.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 15685.39 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The most important factor affecting costs could be the transport of degraded soil or matrices I to be used to the restoration site in the case of soil sealed
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุปริมาณน้ำฝนเฉลี่ยรายปี (ถ้ารู้) :หน่วย ม.ม.
891.02
ข้อมูลจำเพาะ/ความคิดเห็นเรื่องปริมาณน้ำฝน:
May: average monthly regionally anomaly +230% (heavy rains); October: heavy rains
February 2023 is the month with less rain 27.6 mm; in May is the rainiest 250.7 mm
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
Bulletin ARPAE 2023
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
mean annual temperature 14.4 °C Bulletin ARPAE 2023
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- หยาบ/เบา (ดินทราย)
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
- ละเอียด/หนัก (ดินเหนียว)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ปานกลาง (1-3%)
- ต่ำ (<1%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Following the soil characterization (data are mean of 30 soil samples) of the last area of intervention with reconstitution; the data describes soil condition before reconstitution.
The soil texture is silty-loam
The aggregate stability index describes soils with poor stability
pH (1:2.5 in H2O) 6.98 ± 0.37
EC (saturated paste) 0.93 ± 0.41 dS m-1
tot CaCO3 10.33 ± 4.36 g kg-1 SS
active CaCO3 3.08 ± 1.24 g kg-1 SS
tot C 10.62 ± 3.68 g kg-1 SS
organic C 10.26 ± 3.44 g kg-1 SS
tot N 1.47 ± 0.43 g kg-1 SS
HA + FA 2.54 ± 1.26 g kg-1 SS
Olsen P 87.83 ± 44.19 mg kg-1 SS
available Fe 74.68 ± 32.97 mg kg-1 SS
available Mn 27.92 ± 15.78 mg kg-1 SS
available Zn 2.30 ± 1.72 mg kg-1 SS
available Cu 4.32 ± 1.34 mg kg-1 SS
soluble B 0.71 ± 0.25 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable K 21.61 ± 34.72 mg kg-1 SS
assimilable Mg 92.68 ± 28.13 mg kg-1 SS
CEC 26.22 ± 4.42 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Mg2+ 2.39 ± 0.50 cmol(+) kg-1
exch K+ 0.42 ± 0.33 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Na+ 0.48 ± 0.22 cmol(+) kg-1
exch Ca2+ 11.82 ± 4.75 cmol(+) kg-1
Chemical fertility is low, intrinsec fertility is poor, global fertility lower-intermidiate
In the link other data about soil analysis https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-Hb0PcmSYGY&list=PLXcG4R_rAdFaqGnKCa0qaL6FcrafvU0VE
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ปานกลาง
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำใช้เพื่อการเกษตรเท่านั้น (การชลประทาน)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ต่ำ
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ต่ำ
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เข้าถึงได้แบบเปิด (ไม่ได้จัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=OKrAG6jrqXA
คุณภาพพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
70%
หลังจาก SLM:
95%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 70% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that wheat quality. in terms of proteins, increased in reconstituted soils
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
65%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
these increment are estimation
การเสี่ยงต่อความล้มเหลวในการผลิต
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
0
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 0: this decreasing is an estimation, it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=D0II3SGNhKo
การจัดการที่ดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40
หลังจาก SLM:
100
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
simplified from 40% to 100%; because of the physical properties of reconstituted soils; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ld8YzGcx6Qw
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 60% to 10%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils also using less fertilizers and water
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 60% to 100%; in field trials, comparing low fertility soils and reconstituted soils, we tested that maize and wheat yields increased in reconstituted soils and so also farm income increases
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
ความมั่นคงด้านอาหาร / พึ่งตนเองได้
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 60% to 100%; because of it's quite impossible a production failure using reconstituted soils because of their high fertility
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in a EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=BJ8gFmV1Onc
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 10% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) we tested that as a consequence the agroforestry restoration with reconstitution, the area of Park of Trebbia river has increased its social usability
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
15%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 15%, this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils for example a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils, reduction of soil compaction and soil skeleton
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rMazUuMaa6o
การระบายน้ำส่วนเกิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; some laboratory tests demonstrated that reconstitution improves soils permeability
https://www.youtube.com/shorts/oDhW-YlBjHA
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 40% to 100%; analyzing the water retention curves in many experimentation sites and comparing them with degraded soils, reconstituted soils has demonstrated to have better water holding capacity
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Yqtl4-xYMeo
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Qy_B3oCyIAM
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species were sprouted naturally
การสูญเสียดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils as soil stability index
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g1GhoyIy4sk
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50%
หลังจาก SLM:
0%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 50% to 0%; we tested a reduction of soil crusting index in clay silty soils
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aPQRoaYmrIQ
การอัดแน่นของดิน
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 50% to 100%; because of the high organic carbon content and the mechanical treatment there is for example a reduction of soil compaction in reconstituted soils
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
60%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 60% to 100%; the high chemical fertility of reconstituted soils has been demonstrated in a lot of field tests
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
80%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 10% to 80%; reconstituted soils has high organic carbon with a high C/N ratio; the SOC/clay is optimal
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 100% in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QFnUsjYLwfw
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
100%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 100%; in the EU project (New Life) after reconstituted soils replacement a lot of diversified herbaceous species sprouted naturally
ชนิดพันธุ์ที่ให้ประโยชน์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
80%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4Q8tqJNai3o
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
10%
หลังจาก SLM:
80%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 80%; in the EU project (New Life) after we planted over than 3,000 trees and shrubs of 16 indigenous species we recreated an ecological niche
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, physical reconstituted soil properties
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40%
หลังจาก SLM:
0%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 0%; because of high water holding capacity, high permeability, phisical reconstituted soil properties
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
40
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 40% to 10%; this is an estimation considering reconstituted soils microbial activity (tests about biological fertility), soil water content (humidity), soil temperature, nutrient availability and pH-value
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ag5wzRVFg9s
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Anetp8gKaQg
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
20%
หลังจาก SLM:
50%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increasing from 20% to 50%; because of the CaCO3 content of some matrices II
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
50%
หลังจาก SLM:
10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
decreasing from 50% to 10%; this is an estimation considering physical properties of reconstituted soils
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูฝน | ลดลง | ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุฝนประจำท้องถิ่น | ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| สภาพอากาศฤดูหนาวที่รุนแรง | ปานกลาง |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวก
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The recycle of suitable waste materials used defrays the reconstitution technology in short and long term
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 91-100%
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ใช่
อื่น ๆ (ระบุ):
the Technology is partly modified to face every restoration project
ให้ระบุการปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี (การออกแบบ วัสดุหรือชนิดพันธุ์ เป็นต้น):
design, matrices to be used
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Strengths: to change soil class in Land Capability Classification, to improve soil workability, to create new soil aggregates (the organic matter is covered by fine soil mineral fractions) |
| Advantages: to increase soil fertility, to implement Circular Economy |
| Opportunities: to create a non-renewable resource (soil) and/or to restore it, to implement Circular Economy |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Strengths: to produce the suitable soil for the environment where it will be placed |
| Advantages: to reduce the use of fertilizers |
| Opportunities: to restore soil using suitable waste, Circular Economy |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: demand exceed supply, concerning current number of workers employed in the reconstituted plant | formation of new workers |
| Risks: crisis of industries producing suitable waste | non-stop search for suitable waste to use |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Weaknesses: restoration of soil in very steep slope | studies about the physical behavior of reconstituted soil in steep slope |
| Disadvantages: contamined soils | studies about possibility of using reconstitution to clean soils |
|
Risks: the pedotechniques include all the anthropic activities that determine a growing influence of man on pedogenesis and pedolandscapes; they have to satisfy man needs while avoiding any undesirable environmental consequences (Dazzi et al., 2010). This is the main core of reconstitution of soils, but sometimes, the use of waste material, even if, environmental suitable, isn't understood because of waste are considered materials only for disposal. |
Dissemination concerning the laboratory analysis before the waste use, studies and research projects with University to test environmental suitability of reconstituted soils |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
2 visits/survey a year
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
each land user where technology was adopted
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
15/03/2023
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The reconstitution pedotechnique: Applications, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., 10.1016/j.eti.2021.102246
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
The reconstitution: environmental restoration assessment by means of LCC and FCC, 10.6092/issn.2281-4485/8500
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Trees and shrubs monitoring using an ecological approach: the conclusion of the restoration project of Borgotrebbia landfill (Northern Italy), Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Meloni F., Stragliati L., Trevisan M., Giupponi L., 10.31031/EAES.2019.06.000635
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
A new technology to restore soil fertility: Reconstitution, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Francaviglia R., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201933
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Growth and yield response of tomato (Solarium lycopersicum L.) to soil reconstitution technology, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Gatti M., Trevisan M., 10.12871/00021857201916
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Test on the effects of reconstituted soil on emergency speed and root growth in maize, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Salvi R., Battaglia R., Marocco A., Trevisan M., 10.1515/contagri-2018-0035
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Osservazione di Lycogala terrestre Fr. e Stemonitis axifera (Bull.) T. Macr. su suoli ricostituiti sabbiosi, Manfredi P., Salvi R., Bersan M., Cassinari C., Marocco A., Trevisan M.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Relationship between hydraulic properties and plant coverage of the closed-landfill soils in Piacenza (Po Valley, Italy), Cassinari C., Manfredi P., Giupponi L., Trevisan M., Piccini C., 10.5194/se-6-929-2015
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Soil temperature fluctuations in a degraded and in a reconstituted soil, Manfredi P., Cassinari C., Trevisan M., ISBN 20385625
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
Confronto tra dati produttivi di mais coltivato su terre ricostituite e terre naturali, Manfredi P., Tassi D., Cassinari C.
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
Scientific Journal
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Ecosistemi web site
URL:
https://www.mcmecosistemi.com/
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Paolo Manfredi ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Paolo-Manfredi-2
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Chiara Cassinari ResearchGate
URL:
https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Chiara-Cassinari
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
All the publications with DOI mentioned above
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Ecosistemi YouTube channel
URL:
https://www.youtube.com/channel/UCOloFv-BLgvIVt9kBZuZyZg
7.4 General comments
Very useful questionnaire
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Reconstitution of Soils Approach [อิตาลี]
Reconstitution of soils is a patented pedotechnology that brings benefits to degraded soils. Simultaneously, it raises awareness of the potential of restoring soil fertility through recycling. The approach starts with the identification of the soil issue, and the technology is then planned, implemented and promoted through a consortium.
- ผู้รวบรวม: Chiara Cassinari
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล