Learning Site to promote Sustainable Land and Forest Management Practices in Khost [อัฟกานิสถาน]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mohammad Arif
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Megha bajaj, Mohammad Aslam Hasand, Afghanistan Safi
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: Rima Mekdaschi Studer, Illias Animon, Muhammad Ishaq Safi
په خوست ولایت کی د ځنګل او ځمکی بنسټیزه مدیریت عملی کارونو د پاره دزده کړی ساحی رامینځ ته کول
technologies_7460 - อัฟกานิสถาน
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Akbar Muhajir
Sparkai Forest and Rangeland Management Association
อัฟกานิสถาน
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistanชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
FAO Afghanistan (FAO Afghanistan) - อัฟกานิสถาน1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [อัฟกานิสถาน]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mohammad Arif
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
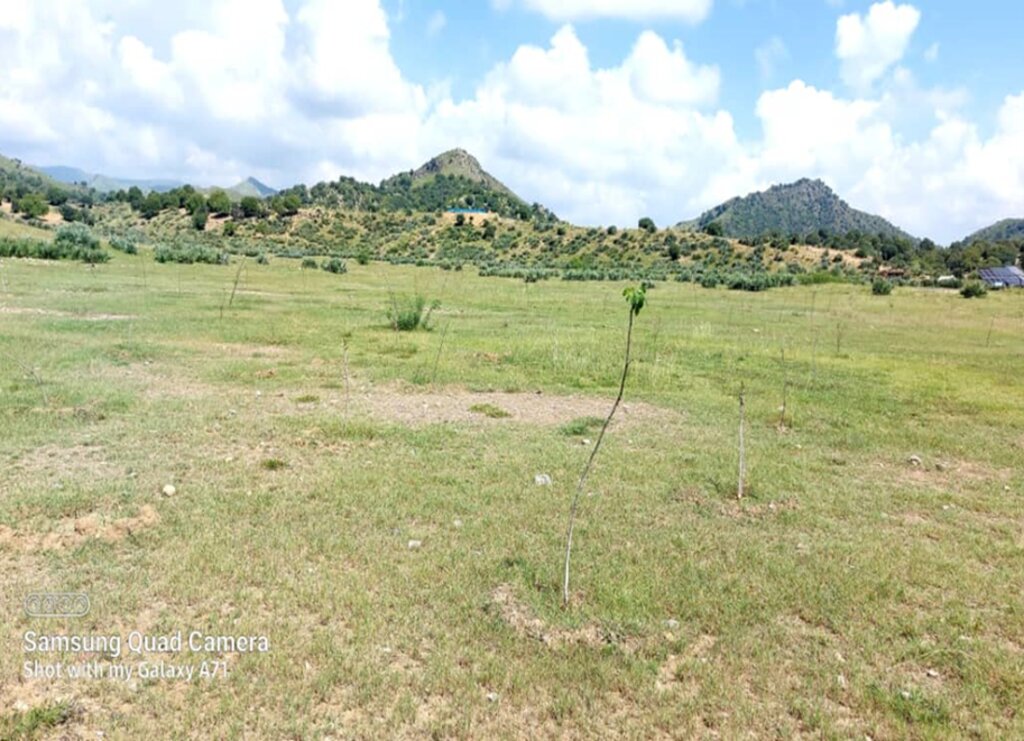
The learning site incorporates several key elements of the technology including a solar-powered water lifting system, three reservoirs and an adopted irrigation system. It features demonstration plots for various initiatives, such as tree planting (walnut, almond, pomegranate and mulberry, the cultivation of fodder (alfalfal Mazari palm) and and medicinal plants (e,g, cumin), and a nursery (walnut) established through the community’s own contributions.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
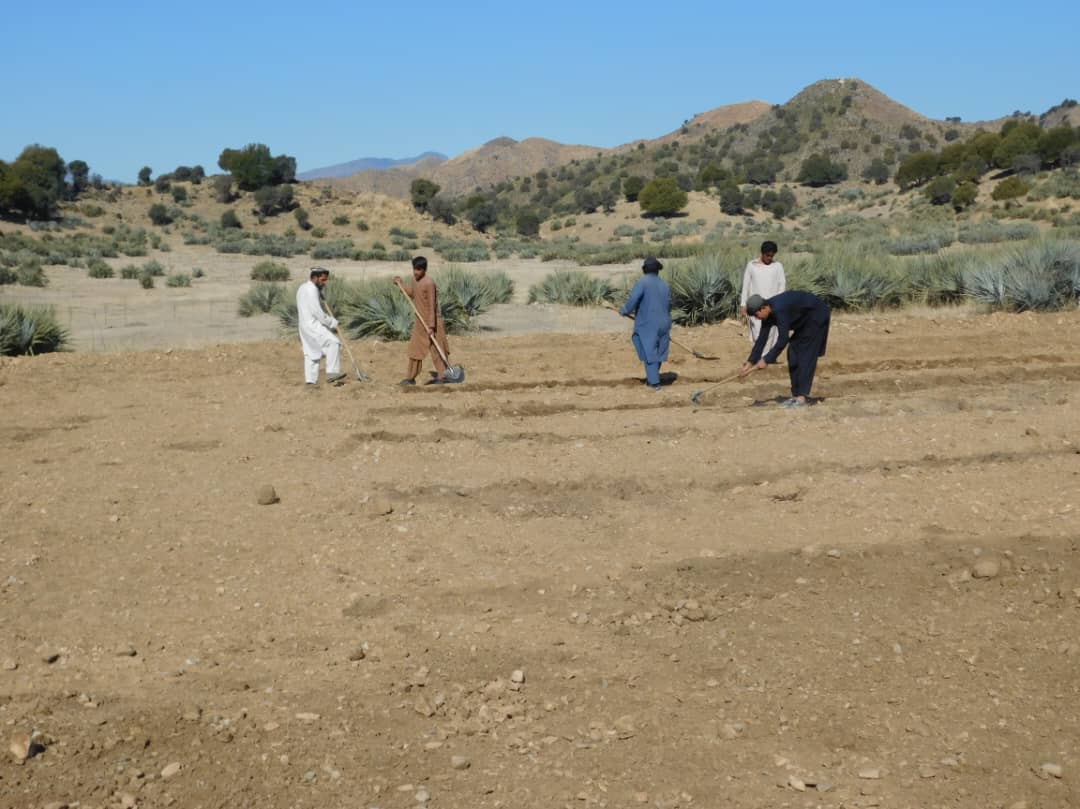
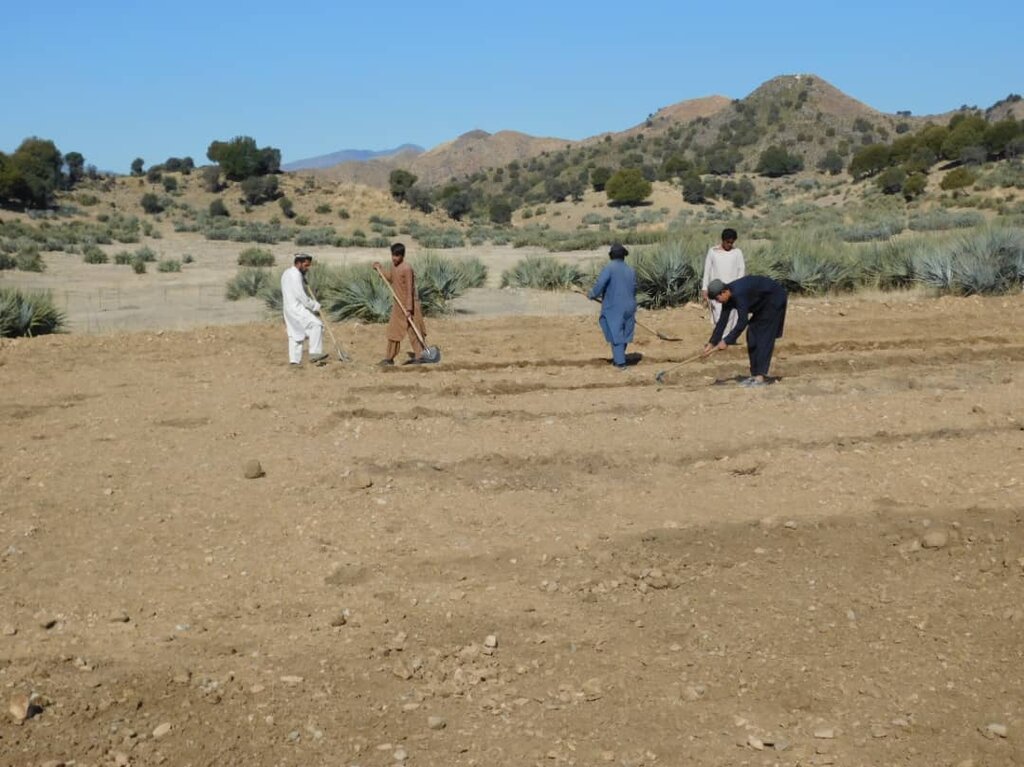
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging. The degradation of natural resources, particularly forests and rangelands, has significantly impacted local communities in Khost. Many residents rely on these resources for fuel, heating, and grazing livestock. However, challenges such as overgrazing, the uprooting of bushes and shrubs, and deforestation for fuel have led to considerable environmental degradation. The lack of proper management of these natural resources has resulted in consistent flooding, which erodes and pollutes agricultural lands. Additionally, local communities often do not recognize the value of these resources, leading to unsustainable land-use practices. Poverty, ongoing conflicts, political instability, and unemployment have driven residents to cut down trees for sale in local markets to support their livelihoods.
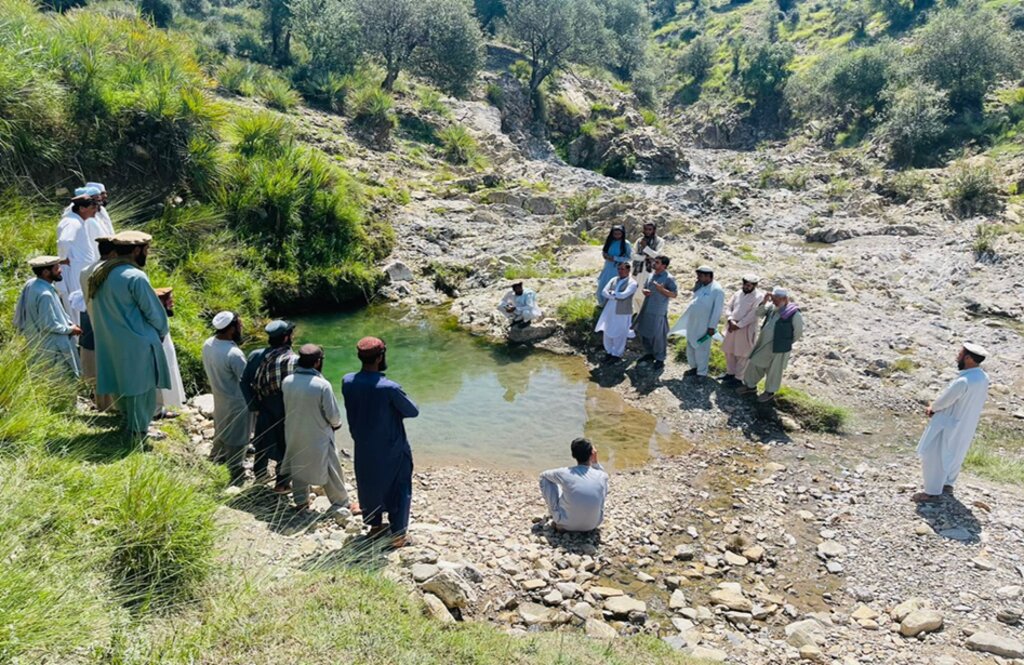
To address these challenges, we conducted a participatory assessment involving local communities and stakeholders, aiming to establish a learning site for sustainable land and forest management practices. Our assessment revealed that many local residents were unaware of sustainable practices or the ecological significance of these resources, contributing to ongoing environmental degradation.
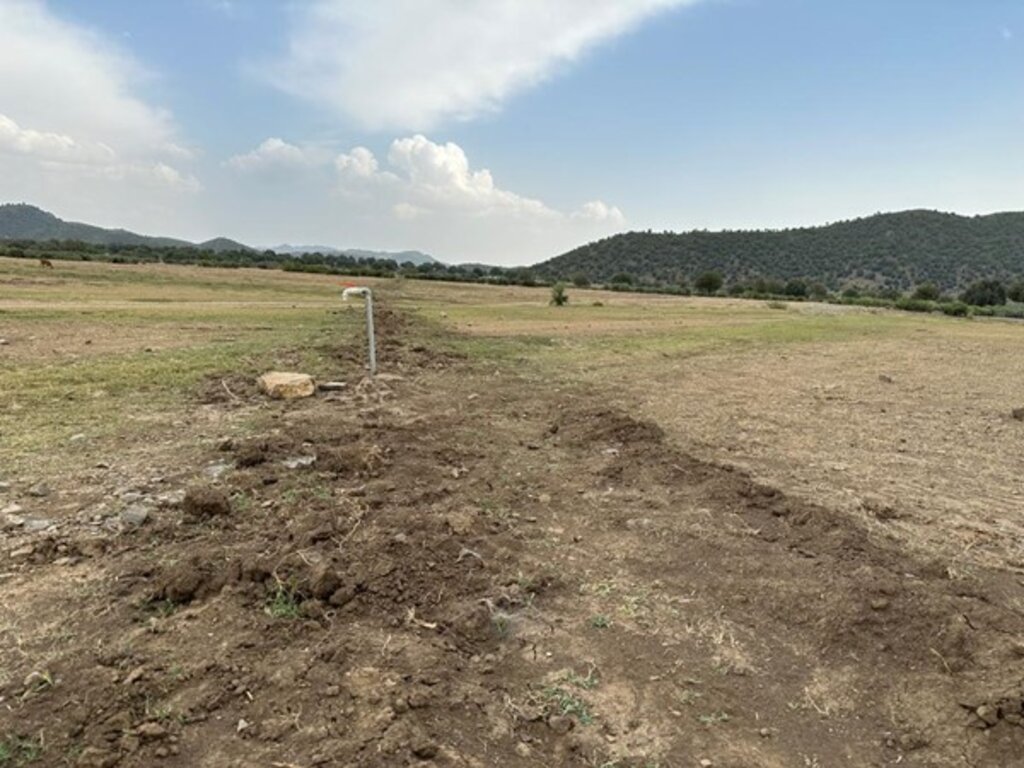
After assessing the natural resources and community needs, we established a learning site for sustainable forest and rangeland management. Feasibility studies helped us identify available water sources, assess community interest, and select suitable land next to forests and rangelands. The site selected is easily accessible, located about 10 kilometers from the main road.
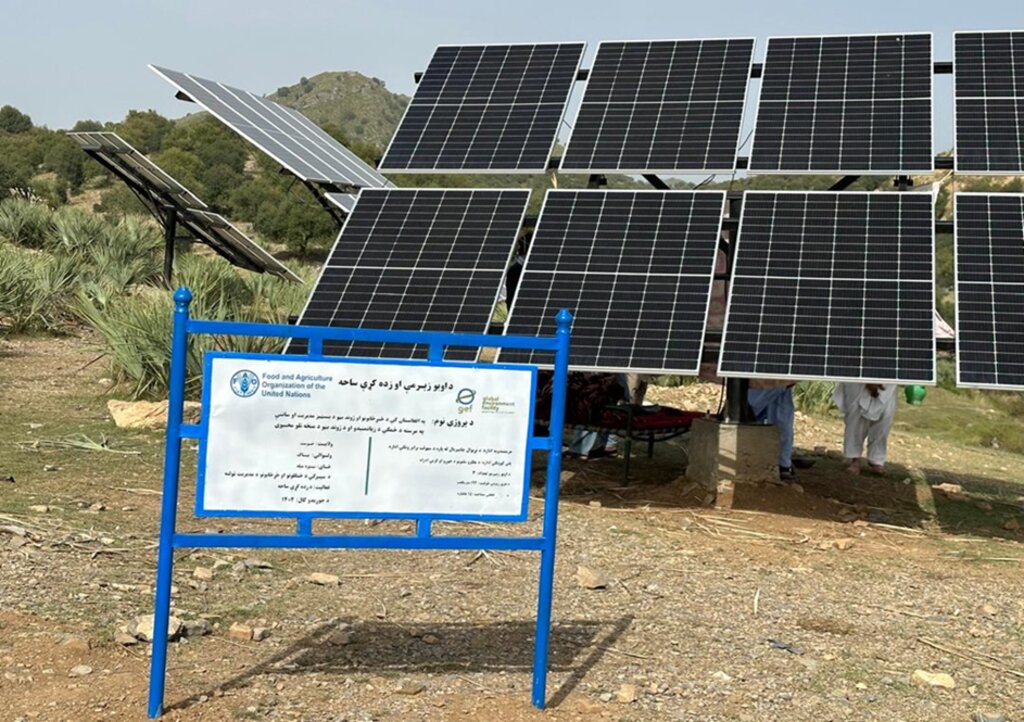
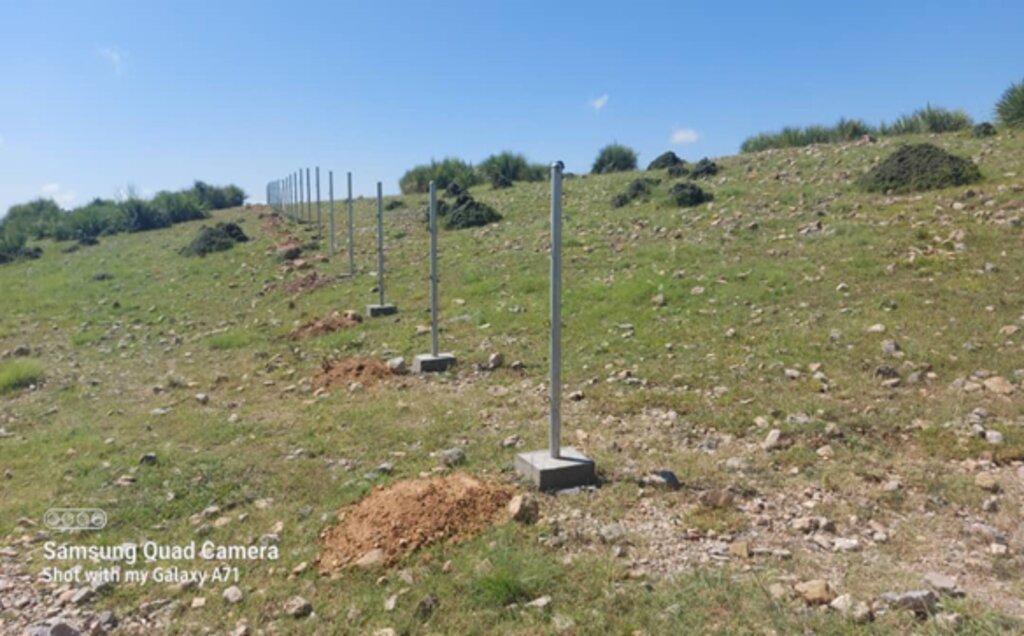
In the initial phase, we installed 26 solar panels on three metal stands, each with a capacity of 400 watts, positioned 200 meters from the water source. At the water source, we installed a 2-inch submersible pump to lift water to the learning site, which encompasses approximately 20 hectares of land across three small hills, each situated 300 meters apart.
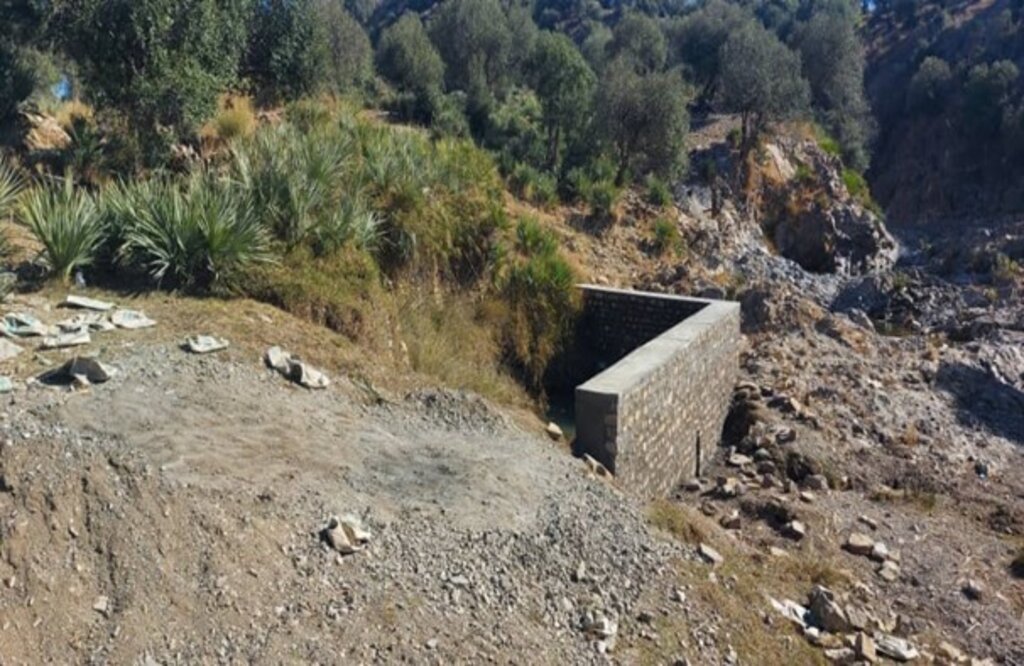
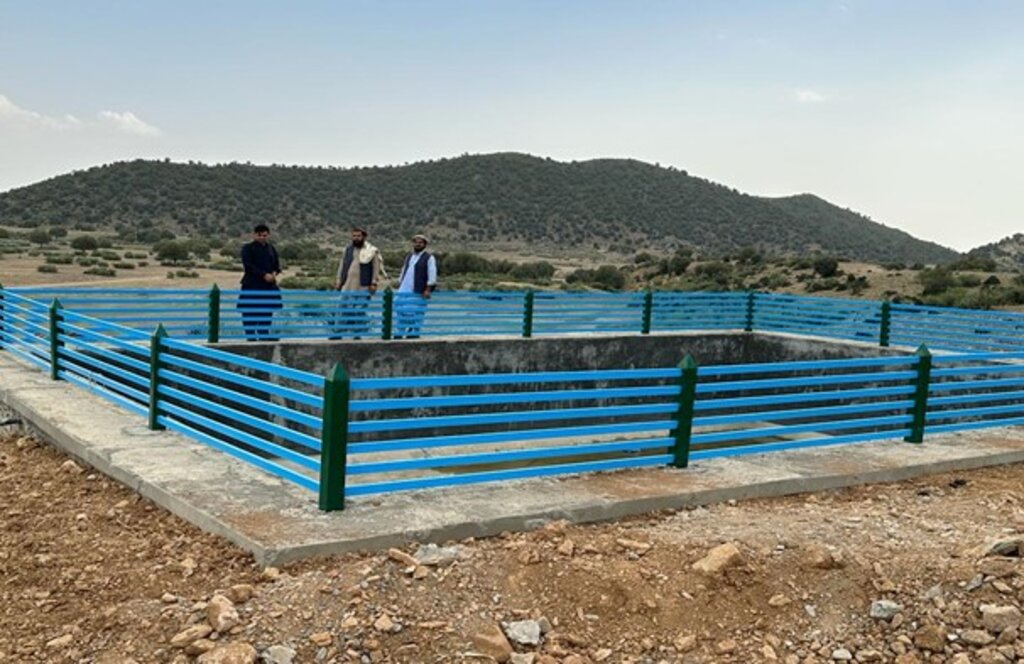
We constructed three reservoirs, each with a capacity of 192 cubic meters. The first reservoir is located 300 meters from the water source and is fed by the solar system. A pipe network system utilizing 2-inch pipes connects the water source to the first reservoir and the other two reservoirs. This system allows the reservoirs to supply water to lower fields or demonstration plots via gravity.
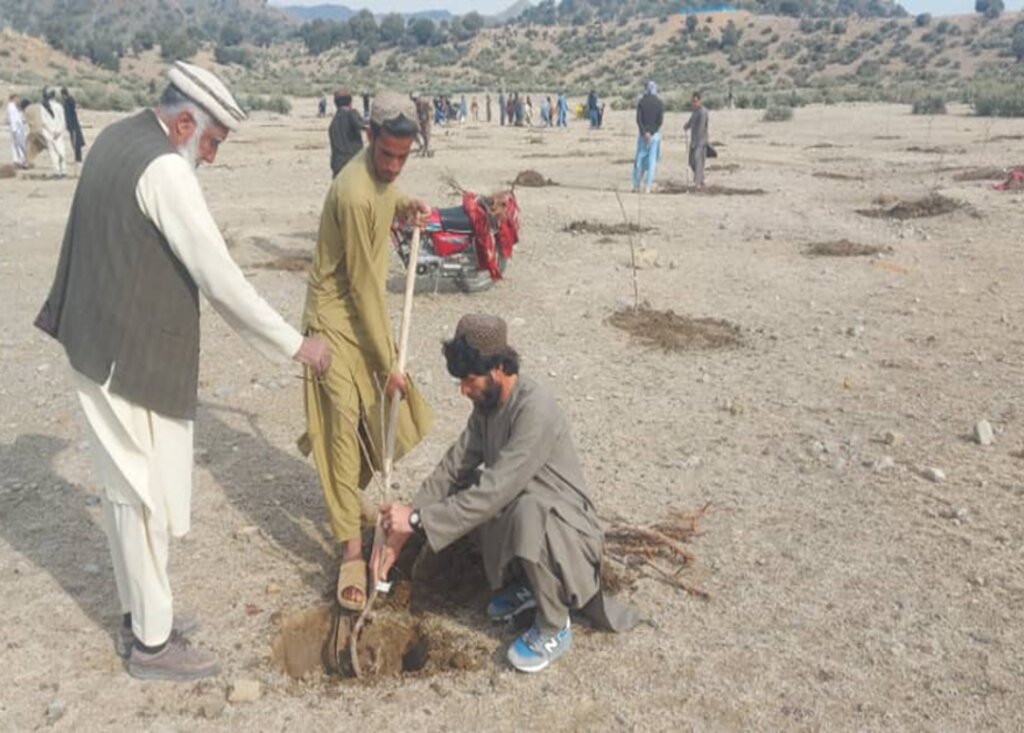
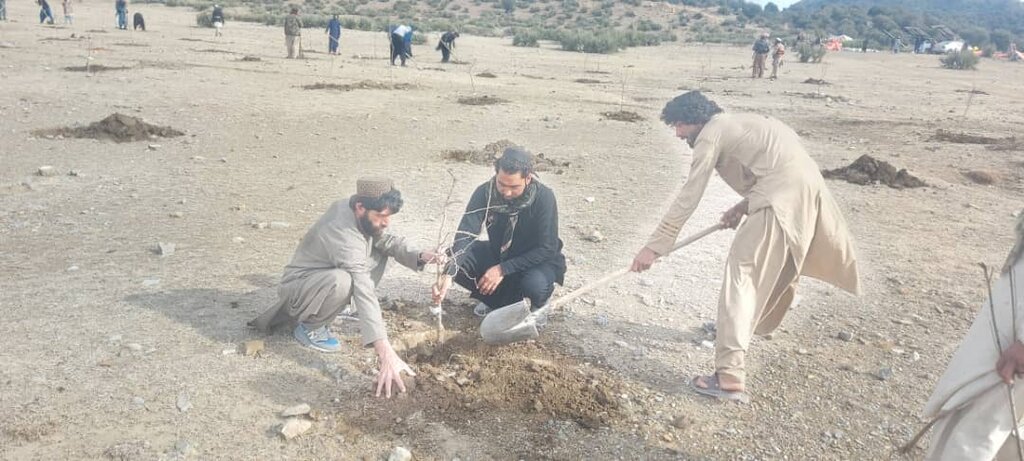
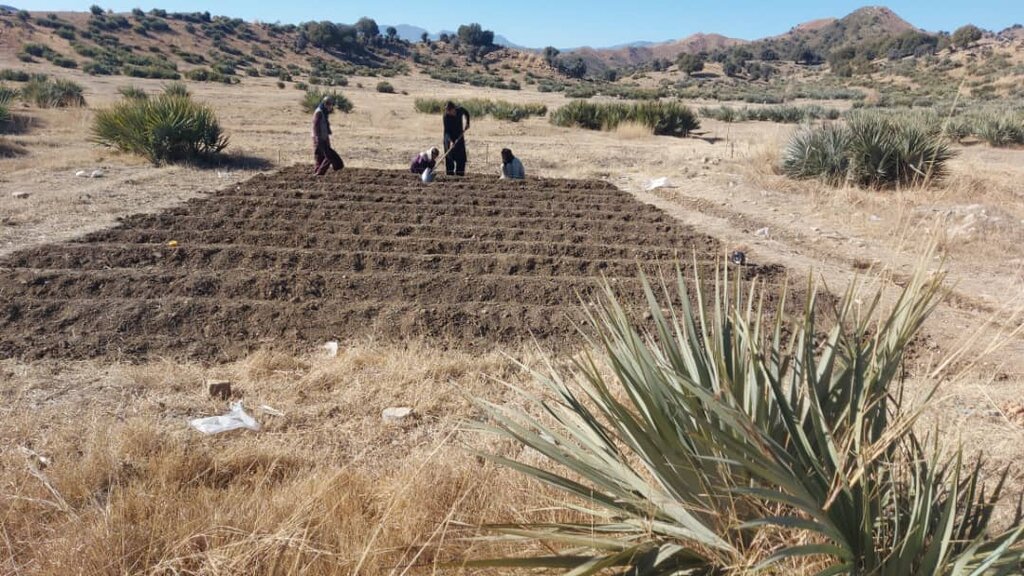
In the demonstration plots, a network of pipes was installed every 50 meters, with taps placed accordingly. We established a 20-hectare learning site focused on sustainable forest and rangeland management practices, featuring demonstration plots for reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant production, reseeding, and a forest nursery. The dimensions of these plots include 10 hectares for reforestation, 2 hectares for fodder production, 0.5 hectares for medicinal plants, and 0.1 hectares for the walnut nursery. A total of 3,000 forest species were planted in the reforestation plot, along with alfalfa and Mazari palm in the fodder plots, and black cumin in the medicinal plot.
These plots are irrigated using flexible 1-inch pipes connected to the taps installed every 50 meters. Given Khost Province's favorable weather conditions, the plants require irrigation primarily from April to August; outside of this interval, the irrigation system provides sufficient water to sustain the site. The site were fenced with barbed wire for protection.
The technology is applied to communal land adjacent to forests and rangelands. It serves as an educational center for the local community, focusing on sustainable landscape restoration and management. A savings box was created, and a Forest and Rangeland Management Association was established. Social funds were set up, along with fencing and hiring guards for the maintenance of the technology.
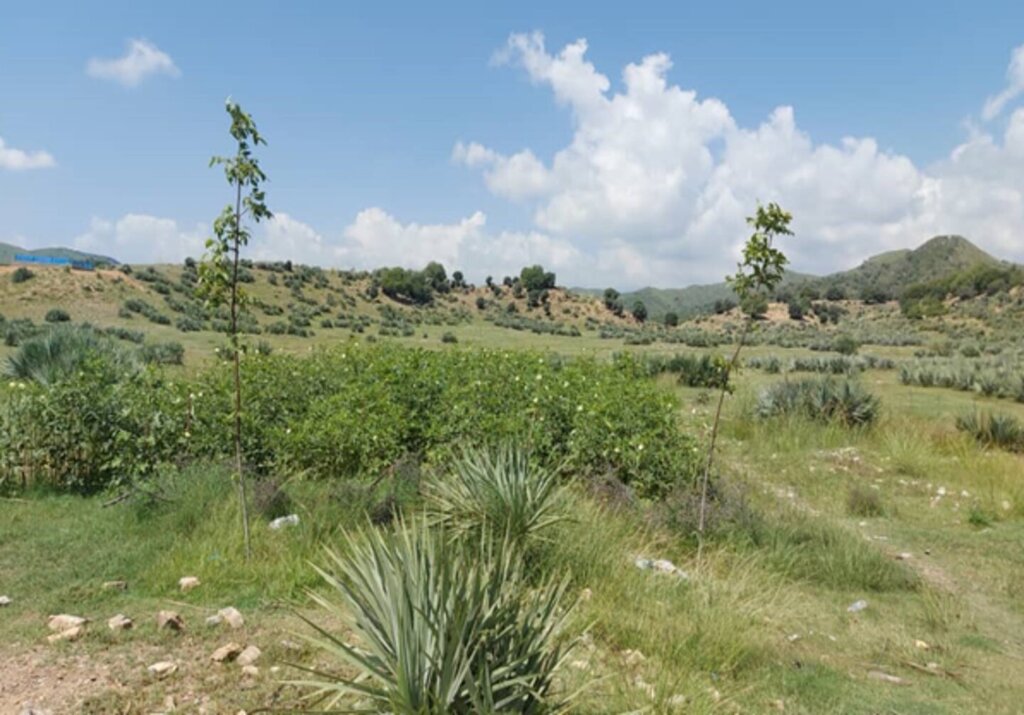
Key infrastructure was established, including a solar-powered lifting system, constructed reservoirs, and a piping network for irrigation. Various forest species were planted in reforestation plots, while local seeds were planted in fodder and medicinal plots. Additionally, walnut seeds were sown in a nursery for diverse restoration practices. These efforts have revitalized the land. Barbed wire fencing was installed for protection, and the site is now fully operational as a learning site.
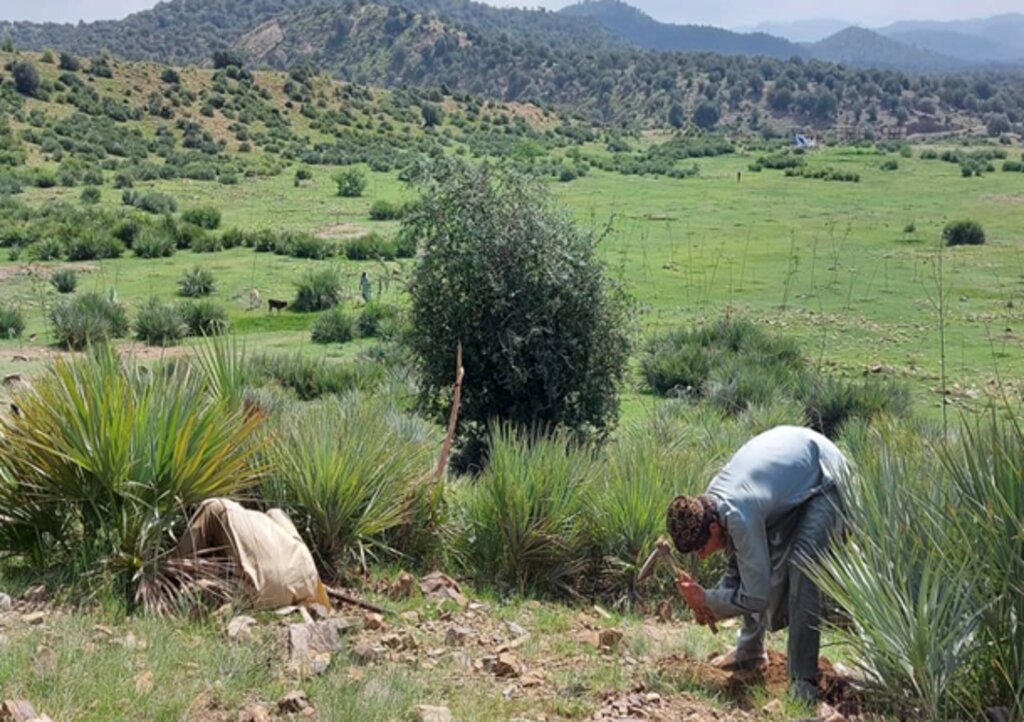
The introduction of this technology led to positive changes in the local community. They have successfully quarantined forest and rangeland, implemented rotational grazing, and collected local seeds and cuttings to plant on degraded lands and riverbanks. Community-based nurseries were also established to transplant seedlings into degraded forest areas, helping to revitalize natural resources.
The local community is optimistic about the technology, particularly the reservoir construction and solar-powered lifting systems that ensure water availability, as well as the restoration techniques employed. However, they expressed concerns about interference from neighbors, livestock grazing, floods that can clog pumps, and damage from hail and windstorms to solar panels.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.4 วีดีโอของเทคโนโลยี
ความคิดเห็น/อธิบายสั้นๆ:
N/A
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
อัฟกานิสถาน
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Khost
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Stara Mila, Sparkai village of Baak district
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- ใช้ ณ จุดที่เฉพาะเจาะจงหรือเน้นไปยังบริเวณพื้นที่ขนาดเล็ก
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, approximately 20 km from the Baak main road, extending towards the Zazi Maidan district. It is classified as communal land
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2023
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
FAO- GEF-07 Combating land degradation and biodiversity loss by promoting sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation in Afghanistan (GEF7)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- อนุรักษ์ระบบนิเวศน์
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- serves as educational centre for the local community on sustainable landscape restoration and management
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- ปศุสัตว์ร่วมกับการทำป่าไม้ (Silvo-pastoralism)

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกไม้ยืนต้น ไม้พุ่ม
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- fruits, other
- tree nuts (brazil nuts, pistachio, walnuts, almonds, etc.)
- walnut, almond, pomegranate, mulberry
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ไม่ใช่

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- goats
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
510

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การเอาไม้ที่ตายแล้วออกไปหรือการตัดแต่งกิ่ง
- การใช้ประโยชน์จากป่า ยกเว้นไม้
Type of (semi-)natural forest:
- subtropical mountain systems natural vegetation
- wild olive, black thorn, hop bush, Mazari palm, cumin
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- mixed deciduous/ evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ผลิตภัณฑ์อื่น ๆ จากป่า
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to poor management, the land has been overgrazed. To address this, we established a learning site focused on restoration through various interventions: reforestation, fodder and medicinal plant demonstration plots, and a 50-square-meter nursery for sapling production. The site is protected by fencing to prevent herders from grazing, allowing them to collect fodder instead. Some fodder is left in the field to produce seeds for natural regeneration.
Forest and Rangeland Management Association focuses on:
Local seed collection: Gathering native seeds to enhance biodiversity and ensure ecosystem resilience.
Ecotourism development: Encouraging visitors to explore the sites, fostering appreciation for local flora and fauna while supporting conservation efforts.
Regeneration of native species: Implementing strategies to restore and regenerate various native plant species, which play crucial roles in maintaining ecological balance.
Fodder production for silage: Cultivating high-quality fodder crops that contribute to livestock nutrition and support sustainable agriculture.
Sapling production through nurseries: Establishing nurseries dedicated to growing saplings of native forest species as well as fruit and nut trees, which can be used for reforestation, habitat restoration efforts and generating income.
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ใช่
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agro-pastoralism (incl. integrated crop-livestock)

ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์
Extensive grazing:
- การเลี้ยงสัตว์แบบเร่ร่อนไปตามที่ต่าง ๆ (Nomadism)
- กึ่งโนแมนดิซึ่มหรือแพสโตแรลลิซึ่ม (Semi-nomadism/pastoralism)
ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่มีการจัดการแบบเข้มข้นหรือการผลิตอาหารสัตว์:
- ตัดแล้วขนไป / ไม่มีการปล่อยแทะเล็มเอง (Cut-and-carry / zero grazing)
- ทุ่งหญ้าเลี้ยงสัตว์ที่ได้มีการปรับปรุง (Improved pastures)
Animal type:
- cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
- goats
- sheep
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
ไม่ใช่
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- meat
- milk
Species:
cattle - dairy and beef (e.g. zebu)
Count:
510

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การเอาไม้ที่ตายแล้วออกไปหรือการตัดแต่งกิ่ง
Type of (semi-)natural forest:
- subtropical mountain systems natural vegetation
- wild olive, Mazari palm, hop bush, black thorn and grasses
Are the trees specified above deciduous or evergreen?
- mixed deciduous/ evergreen
ผลิตภัณฑ์และบริการ:
- ไม้ซุง
- ไม้ที่นำมาทำเป็นเชื้อเพลิง
- นันทนาการ / การท่องเที่ยว
- การป้องกันภัยธรรมชาติ
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The area is a dry mountainous terrain with natural vegetation including wild olive, mazari palm, hopbush, and grasses. It supports nomadic and semi-nomadic pastoralism, primarily grazing goats, sheep, and cows.
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Near the learning site, a gully and springs provide a year-round water source. We have installed a solar-powered lifting system and constructed three reservoirs to distribute water across 20 hectares, including the planted areas and demonstration plots. A network of pipes and taps with flexible hoses ensures efficient water distribution. This water source is exclusively for this site and does not affect neighboring villages or farmers.
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การจัดการสวนป่า
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการด้านชลประทาน (รวมถึงการลำเลียงส่งน้ำ การระบายน้ำ)
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
- V2: หญ้าและไม้ยืนต้น

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยโครงสร้าง
- S6: กำแพง สิ่งกีดขวาง รั้วไม้ รั้วต่างๆ
- S7: การกักเก็บน้ำ/การส่งลำเลียง/อุปกรณ์การชลประทาน
- S10: มาตรการในการประหยัดพลังงาน

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยการจัดการ
- M2: การเปลี่ยนแปลงของการจัดการหรือระดับความเข้มข้น
- M3: การวางผังตามสิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและสิ่งแวดล้อมของมนุษย์
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The whole area 20 hectares have been fenced with barbed wire, under the structure measures, reservoirs have been constructed and dug pits for plants.
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
- Bh (Loss of habitat): การสูญเสียแหล่งที่อยู่
- Bs (Quality and species composition): องค์ประกอบหรือความหลากหลายทางคุณภาพและชนิดพันธุ์ลดลง

การเสื่อมโทรมของน้ำ
- Hs (Change in quantity of surface water): การเปลี่ยนแปลงปริมาณของน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hg (Change in groundwater): การเปลี่ยนแปลงของน้ำบาดาลหรือระดับน้ำในแอ่งน้ำบาดาล
- Hp (Decline of surface water quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำที่ผิวดิน
- Hq (Decline of groundwater quality): การลดลงของคุณภาพน้ำบาดาล
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The local community relies on natural resources for their livelihoods, leading to deforestation, overgrazing, and the uprooting of shrubs and bushes for fuel. Severe runoff, droughts, and climate change have further contributed to environmental degradation.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ฟื้นฟูบำบัดที่ดินที่เสื่อมโทรมลงอย่างมาก
- ปรับตัวกับสภาพความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
An educational center (learning site) has been established on degraded land to enhance the capacity of the local community and other stakeholders about best practices for landscape restoration.
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
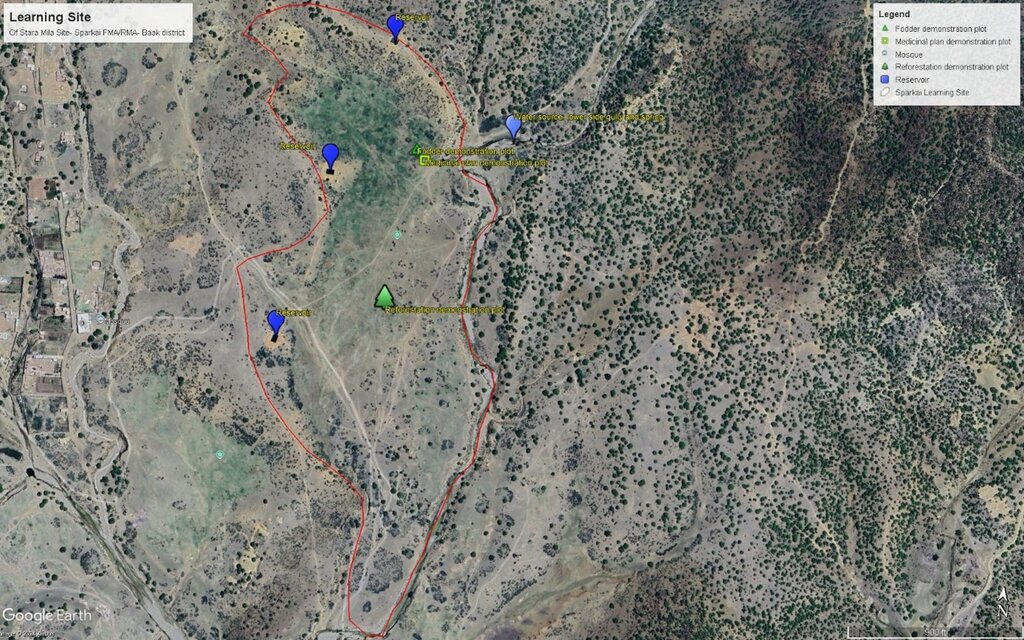
This GIS map highlights learning site elements. The blue pins indicate water source and reservoirs, while the green rectangular pins represent fodder demonstration plot. Yellow squire pin mark area dedicated to medicinal plants, and green tree-shaped pin indicate reforestation plot. Finally, the red track pin indicates location of barbed wire fencing. The site map has been prepared after the completion of intervention.
ผู้เขียน:
Mohammad Omar Dost
วันที่:
17/09/2024
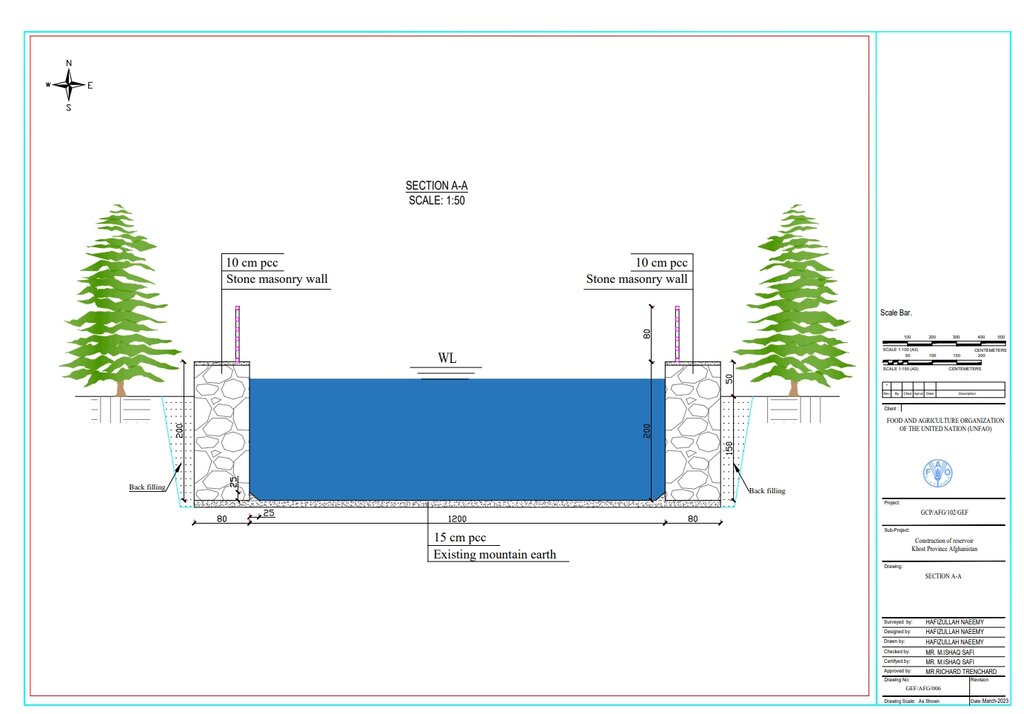
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Each of the three reservoirs measures 2m x 8m x 12m with a water depth of 2m, holding a total capacity of 192 cubic meters.
ผู้เขียน:
Hafizullah Naeemy
วันที่:
18/01/2023
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
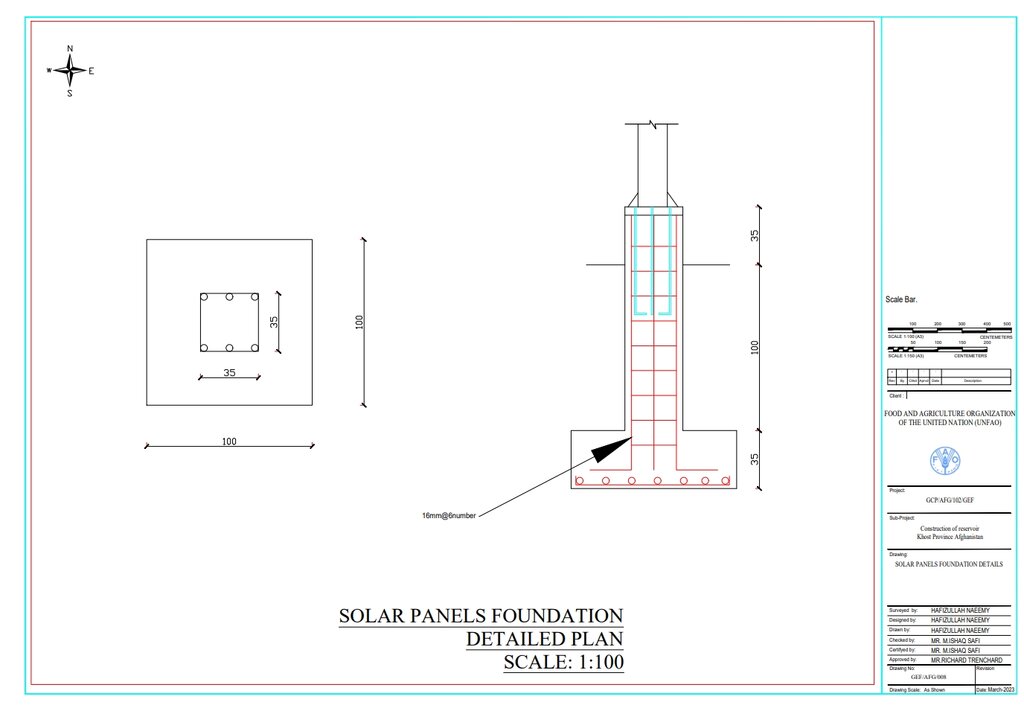
The solar panel stands, including their foundations, are 2 meters in height, with each panel measuring 1.2 meters high and 0.6 meters wide. The panels are installed at a 45° slope angle.
ผู้เขียน:
Hafizullah Naeemy
วันที่:
22/01/2023
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
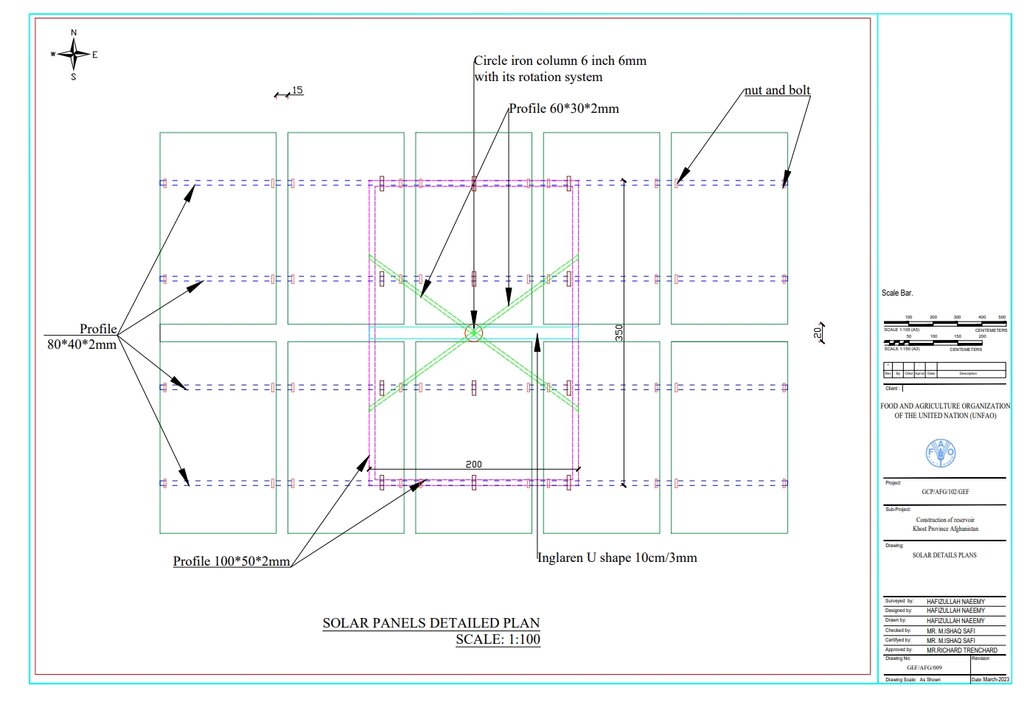
Detailed plan for solar panel installation: Three metal stands designed to support and rotate 26 solar panels, optimizing sunlight exposure throughout the day.
ผู้เขียน:
Hafizullah Naeemy
วันที่:
23/01/2023
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
20 Hectares
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
ระบุค่าเฉลี่ยของค่าจ้างในการจ้างแรงงานต่อวัน:
5 USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Conduction of survey, feasibility study, and site selection | 1st month |
| 2. | Finding of water source | 2nd month |
| 3. | Installation of solar power lifting system | 4rd month |
| 4. | Construction of reservoirs | 5th month |
| 5. | Installation of irrigation piping system | 12th-1st month of the year |
| 6. | Saplings delivered by supplier to the site from contracted nurseries | 1st-2th month |
| 7. | Planting of saplings | 2-3rdmonth |
| 8. | Preparation of two demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 9. | Planting of seeds for fodder and medicinal plants | 3rd month |
| 10. | Installation of barbed wire fencing for 20 hectares | 7-9th month |
| 11. | Ensurance of operation and maintenance of all systems | 24th month |
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Installation of solar system and pipe installation | Person/day | 100.0 | 6.0 | 600.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Digging pits, plantation and irrigation of Plants | Person/day | 453.0 | 6.0 | 2718.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Excavation of foundation | Person/day | 80.0 | 5.0 | 400.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Preparing demonstration plots for fodder and medicinal plants | Square meter | 25000.0 | 0.13 | 3250.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Stone Masonry | Person/day | 136.0 | 6.0 | 816.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Plastering | Person/day | 72.0 | 5.0 | 360.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Plain cement concrete | Person/day | 57.0 | 5.0 | 285.0 | |
| แรงงาน | Plain cement concrete PCC M20 | Person/day | 390.0 | 5.0 | 1950.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Entrance Gate | Number | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Solar panel 400W | Sheet | 26.0 | 140.0 | 3640.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Rotating PV panel mount | Number | 3.0 | 350.0 | 1050.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Submersible pump 2 inch (10PH-7500W) | Number | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | DC-AC current inverter 7.5-11kw | Number | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Distribution board | Number | 1.0 | 75.0 | 75.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sign board | Number | 3.0 | 3.0 | 9.0 | |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sign board | Number | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Walnut | Sapling | 2000.0 | 0.56 | 1120.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Almond | Sapling | 500.0 | 0.67 | 335.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Mulberry | Sapling | 100.0 | 0.44 | 44.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Pomegranate | Sapling | 500.0 | 0.51 | 255.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Alfalfa seed | Kg | 50.0 | 2.72 | 136.0 | |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Black Cumin seed | Kg | 15.0 | 6.72 | 100.8 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Tap | Number | 30.0 | 3.0 | 90.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Flexon 1 inch rubberized pipes | Meter | 1250.0 | 2.0 | 2500.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | DC current wire | Meter | 100.0 | 2.0 | 200.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | AC current wire | Meter | 150.0 | 2.0 | 300.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Polyethylene pipe 1.5 inch | Meter | 2000.0 | 2.0 | 4000.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Polyethylene pipe 2 inch | Meter | 780.0 | 3.0 | 2340.0 | |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Polyethylene pipe 3 inch | Meter | 300.0 | 5.0 | 1500.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Delivery to the site | Lump sum | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Galvanized iron pipe 2 inch for pillar | Meter | 125.0 | 5.0 | 625.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Galvanized iron pipe 1.5 inch for bracing | Number | 470.0 | 10.5 | 4935.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Fence | Meter | 15.0 | 25.0 | 375.0 | |
| อื่น ๆ | Double strand galvanized barbed wire for fencing | Meter | 4200.0 | 0.25 | 1050.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการจัดตั้งเทคโนโลยี | 36208.8 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 36208.8 | |||||
ถ้าผู้ใช้ที่ดินรับภาระน้อยกว่า 100% ของค่าใช้จ่าย ให้ระบุว่าใครเป็นผู้รับผิดชอบส่วนที่เหลือ:
FAO under GEF-7 project
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land users contributed primarily by digging pits for planting, preparing demonstration plots, and maintaining the system. Additionally, they hired guards to protect the area from disturbances. All other costs associated with the project were covered by the FAO GEF-7.
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Removal of sediment from reservoirs | Spring/annually |
| 2. | Safeguarding the site such as solar system, and on-site interventions | All seasons/regular |
| 3. | Repairing solar system & water pump and pipes | Regularly |
| 4. | Demonstration plots maintenance (pest-diseases control, mulching, weeding and Irrigation | Spring & Automn/annually |
| 5. | Replacing dead and dried plants | Feb/two times (1st & 2nd year) |
| 6. | Repairing fencing | Year around |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | Labour for cleaning the reservoir from sediment annually | Person/day | 15.0 | 5.0 | 75.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Hiring guards for safeguarding the site | Person/day | 12.0 | 100.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Fixing pump when needed | Lump sum | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Repairing pipes | Lump Sum | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Repairing solar panel when required | Lump sum | 1.0 | 1000.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Weed control | Person/day | 10.0 | 5.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Integrated Pest Management | Lump sum | 1.0 | 5.0 | 5.0 | 100.0 |
| แรงงาน | Irrigation | Person/day | 8.0 | 50.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Saplings | Number | 1500.0 | 0.56 | 840.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Local Seed | Kg | 15.0 | 26.0 | 390.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุสำหรับก่อสร้าง | Barbed wire | meter | 3000.0 | 0.14 | 420.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Replacing dead and dried plants | Lump sum | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 4830.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 4830.0 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Construction materials cost
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งแห้งแล้ง
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- บริเวณสันเขา (convex situations)
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องสภาพภูมิประเทศ:
The site is situated near a forest and rangeland, with a gentle slope of approximately 45 degrees and an elevation of 1,279.49 meters above sea level. Surrounding mountains are covered with wild olive forests.
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- ต่ำ (<1%)
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ดี
Water quality refers to:
both ground and surface water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ใช่
บ่อยครั้ง:
เป็นครั้งเป็นคราว
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
The water quality meets site requirements; however, seasonal fluctuations occur due to droughts. Floods in the lower gully, carry debris and sediments that can impact the source.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- ปานกลาง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
The site was rich in flora and fauna, but human and animal interference has led to significant degradation. Many indigenous plants have been uprooted, and wildlife has migrated due to the loss of habitat. In response, the community has begun to manage and restore the land through practices like rotational grazing and quarantine measures to combat illegal logging.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- < 10% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- จน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- กลุ่ม/ชุมชน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The land in question is communal and remains undivided, with no plans for future distribution. Most users have limited agricultural land downstream, typically no more than 0.5 hectares per household for crop cultivation. The learning site has been dedicated by the local community for future generations and educational purposes. Previously, this land was unused and primarily designated for grazing.
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- เป็นแบบชุมชนหรือหมู่บ้าน
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ใช่
ระบุ:
Land use rights in traditional legal systems are generally straightforward, with each family in a village having equal access to natural resources.
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Overall, this traditional approach emphasizes community and family roles in resource management, balancing individual rights with communal responsibilities
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Due to three to four decades of political conflict, people lack access to essential services and infrastructure. This situation has been largely overlooked, with insufficient attention given to providing these services. Additionally, there has been a lack of budget allocation and support from the government and NGOs. As a result, communities continue to suffer from inadequate resources and infrastructure development.
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The local community is adopting rotational grazing and quarantine measures on rangeland, while also exploring silage-making and hay production techniques. Additionally, they are identifying alternative winter feed options for their animals.
คุณภาพป่า /พื้นที่ทำไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The local community has successfully quarantined all forest areas, effectively controlling illegal logging and managing grazing. As a result, the forest has been revitalized and is undergoing natural regeneration
การผลิตของจากป่าทุกชนิดยกเว้นไม้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
The local community is utilizing Mazari palm for handcrafted products while also focusing on agroforestry. They have established fruit orchards and are collecting blackthorn, which they sell in the bazaar to support their livelihoods.
พื้นที่สำหรับการผลิต
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Previously, the community overgrazed the land and cut down trees for their livelihoods. However, after implementing quarantine measures and rotational grazing practices, the area is now showing signs of regeneration and has the potential to become a productive landscape in the future.
การจัดการที่ดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Following these practices, the local community has effectively managed more land under proper stewardship, including forest and rangeland quarantine and controlled grazing. They are now applying these methods in their vicinity, leading to the successful management of additional areas.
ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
การมีน้ำไว้ให้สำหรับการชลประทาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table and increasing availability for irrigation.
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งผลิตรายได้
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางด้านสันทนาการ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
FAO and Forest and Rangeland Management Association have successfully revitalized this area, transforming it into a lush and green landscape. Many of the previously destroyed species regenerated, creating a thriving ecosystem. This site is now a focal point, surrounded by majestic mountains and rich forests, with water flowing from the upper watershed. It has become a popular destination for picnics and visits, where people can enjoy the soothing sounds of birds and the vibrant greenery of the surroundings.
สถาบันของชุมชน
สถาบันแห่งชาติ
SLM หรือความรู้เรื่องความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
การเก็บเกี่ยวหรือการกักเก็บน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through applying quarantine, rotational grazing, control grazing the vegetation covered increased.
มวลชีวภาพ/เหนือดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Biomass above the ground is increased
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
most of the seed regenerating and all the cut trees and bushes revegetated.
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Various migratory animals and birds have returned to the area due to the protection measures in place and the prohibition of human activities.
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Most of the riverbanks have been successfully revegetated through effective control measures, including water filtration during rain and floods. Local communities have also learned to plant cuttings along the riverbanks and shorelines, contributing to the restoration of these vital ecosystems.
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
การปล่อยคาร์บอนและก๊าซเรือนกระจก
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Healthy ecosystems like forests and wetlands act as carbon sinks, absorbing more CO2 through photosynthesis. Improved soil health and vegetation cover also enhance carbon storage, while restoring habitats promotes biodiversity, creating a more resilient ecosystem that sequesters carbon effectively.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
น้ำที่ใช้ประโยชน์ได้
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Through revegetation and improved land cover, water seeps into the ground, recharging the water table.
การเกิดมลพิษในน้ำบาดาลหรือแม่น้ำ
ตะกอนที่ถูกพัดพามาโดยลม
ความเสียหายต่อโครงสร้างพื้นฐานของรัฐหรือของเอกชน
ผลกระทบของก๊าซเรือนกระจก
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | ลดลง | ไม่ดี | |
| ฝนประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ดี | |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ดี |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุหิมะประจำท้องถิ่น | ไม่ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ไม่ดี |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ดี |
ภัยพิบัติจากน้ำ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| น้ำท่วมฉับพลัน | ไม่ดี |
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Before the implementation of the project land users faced severe challenges, including drought, high temperatures, water scarcity for irrigation, reduced yields, and a lack of winter feed alternatives for livestock.
Following the introduction of sustainable rangeland management and biodiversity conservation, local communities adopted rotational grazing practices and protected forests from cutting, which had previously been their main source of income. As a result, vegetation cover improved, carbon stocks increased, and rainwater began to seep into the ground, recharging the water table, springs, canals, and Karezes. These efforts reulted in a more resilient and productive environment.
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านบวกเล็กน้อย
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวกอย่างมาก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The adoption of the technology in the specified area has primarily been spontaneous, significantly influenced by the support provided by the project. While a small percentage of land users may have received material incentives, the majority embraced the technology due to its demonstrated benefits and the project's educational efforts. This support helped to build trust and confidence among the land users, enabling them to implement the technology effectively in their practices. Overall, this highlights the importance of community engagement and capacity building in fostering sustainable land management practices.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| It is crucial for local communities to learn sustainable land and forest restoration techniques. These methods are not only accessible but also involve minimal operational costs. By empowering land users with this knowledge. |
| We can adopt sustainable land and forest management practices to revitalize our degraded land. This learning process is straightforward and easily applicable. |
| We have great opportunities and abundant resources to utilize. This area serves as a hub for scaling sustainable practices, allowing us to learn, observe, and implement solutions that will benefit future generations. |
| We can efficiently use surface water for irrigation instead of groundwater, helping to restore degraded land through these initiatives. |
| Reduce greenhouse gas emissions through effective carbon sequestration. |
| Learn regeneration techniques, rainwater harvesting, and grazing management methods like rotational grazing. Focus on producing fodder and medicinal plants, while understanding indigenous plants and shrubs for the future. |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| This site is highly accessible, surrounded by dense forests and extensive rangelands that can be utilized sustainably. |
| Local community members, university students, and stakeholders can easily visit this site. |
| This site is an excellent destination for tourists to visit, enjoy, and learn about the importance of natural resources and their management techniques. |
| The local community can easily adopt these simple techniques to learn sustainable land and forest restoration practices. |
| The local community has hired guards to maintain the site effectively. They are gaining knowledge and enhancing their capacity for future interventions, contributing positively to development initiatives. |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Insufficient maintenance and repair services for the technology. | Establishing strong linkages with service providers and maintenance support. This also facilitates nationwide technology transfer, enabling broader adoption and implementation of sustainable practices. |
| There is a lack of qualified professionals on-site to teach visitors the technical aspects of the technology. This gap hinders effective learning and limits the ability of visitors to fully understand and engage with the technology. | Hire on-farm officers to oversee and manage the learning site and provide information to visitors. |
| A check dam is required in the gully to store water for sustainability, especially during drought seasons when water availability decreases. | Construct a check dam in the lower section of the gully to store water for sustainability, allowing visitors to learn about water harvesting techniques. |
| There are currently no available resources for replacing the dead plants. | Establish nurseries for forest species to produce saplings that can replace dead and dried plants in the future. |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| There are concerns about windstorms and hail potentially damaging the solar panels. | The local community should establish a social fund to cover repairs for any damage to solar panels caused by windstorms or hail, as well as to fund the installation of fencing around the solar panel stands. |
| Concerns have arisen regarding land disputes as the local community acts on land distribution amidst a growing population. | All villagers should receive a formal guaranteed letter, signed by the district governor, ensuring that no future actions will be taken to redistribute this site among the villagers. |
| There is a lack of essential water structures, such as percolation tanks and detention ponds, for effective rainwater harvesting. | Construct percolation tanks and detention ponds to harvest rainwater, which can be used to water livestock. Additionally, this initiative will provide an opportunity to learn and implement dryland farming techniques. |
| Too much water is wasted through flexible pipe basin irrigation methods. Additionally, required live hedges for fencing and windbreaks. | Install a drip irrigation system with an efficient piping layout and plant pine, poplar, and other trees alongside barbed wire to create a windbreak and a natural barrier for site protection. This will also provide an opportunity to learn various agricultural techniques. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
20
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
11
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
5
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
3
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
10/10/2024
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The project was actively involved in all phases, from selection to implementation. Data was collected from local community volunteers, as well as SLM specialists and engineers.
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
N/A
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
N/A
7.4 General comments
The questionnaire is well-structured, but some sections, particularly 6.2 and 6.3, need simplification. Additionally, the database should provide outputs during data processing, highlighting both best practices and common mistakes related to the technology. This will help us generate a comprehensive report that showcases effective practices and identifies areas for improvement.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์

Stakeholder collaboration for building Learning Site for landscape … [อัฟกานิสถาน]
To raise awareness and ensure clear role delineation, a series of consultations were held with the local community, the Forest Management/Rangeland Management (FM/RM) association, and other key stakeholders. Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) that formally outlined the roles and responsibilities of each party was signed. Additionally, the FM/RM association issued a …
- ผู้รวบรวม: Mohammad Arif
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล