Crimson clover as an overwintering cover crop for nitrogen supply [สโลวีเนีย]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Tamara Korošec
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: Gregor Kramberger
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Inkarnatka kot prezimni dosevek za oskrbo z dušikom
technologies_7507 - สโลวีเนีย
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ชื่อของโครงการซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Integration of cover crops into field crop rotation - Slovenia (EIP-AGRI)ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Chamber of Agriculture and Forestry of Slovenia – Institute of Agriculture and Forestry Maribor (KGZS) - สโลวีเนีย1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
Crimson clover, overwintered as a cover crop, forms a symbiotic relationship with nitrogen-fixing bacteria, capturing nitrogen and thus enriching the soil. This helps reduce the need for synthetic fertilizers and aids in soil erosion control, weed suppression, and improved soil structure.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
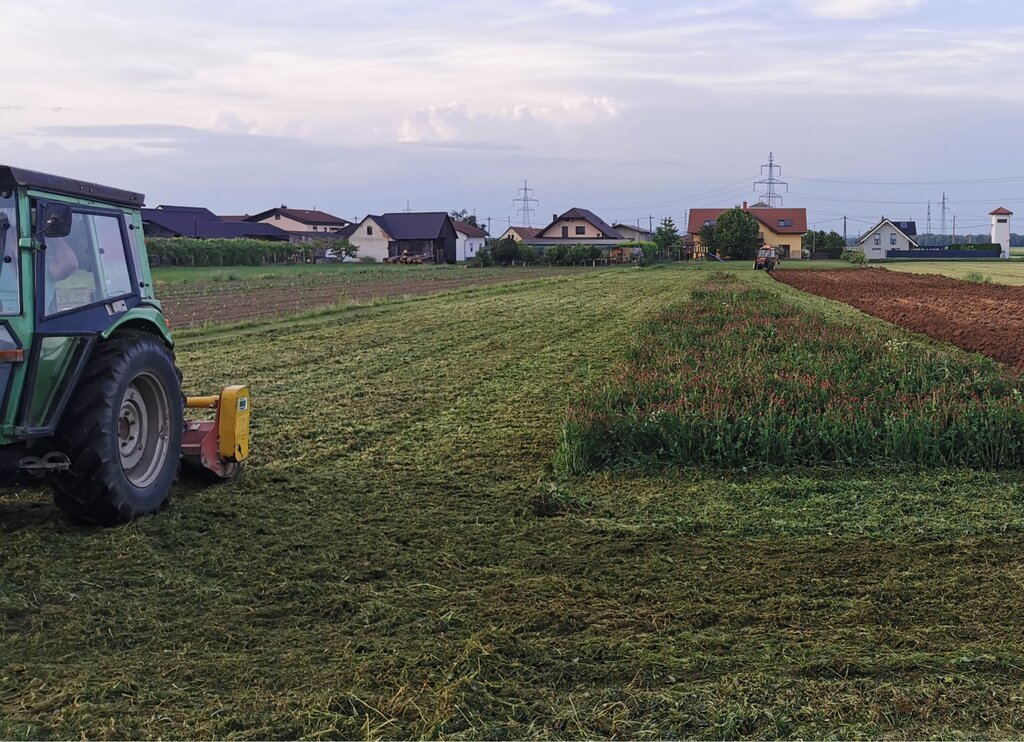
Crimson clover (Trifolium incarnatum) is a winter annual legume used as a cover crop for nitrogen fixation, erosion control, and soil improvement. It is well suited to mild winter climates and can be integrated into various farming systems. It can be sown alone or in mixtures after the main crop is harvested. It covers the soil from late summer until spring and can be used as fodder or for green manure.
Its key function is nitrogen fixation through the help of nitrogen-fixing bacteria (Rhizobium). Through the winter it protects the soil from erosion, prevents nutrient leaching, and helps suppress weeds. The deep root system improves soil aeration and drainage. When terminated, it adds organic matter and nutrients to the soil, and its nectar-rich flowers attract pollinators and provide a habitat for beneficial predatory insects.
Crimson clover is often included in multi-year crop rotations. Activities include light tillage or no-till. Sowing usually takes place in late August to early September - or at least 6 to 8 weeks before the first frost. Fertilization with mineral nitrogen is not required, but phosphorus and potassium can help in establishment. Minimal maintenance is needed as these plants suppress weeds and reduce pests, but some fungal diseases may occur in wet conditions. Termination involves mowing or rolling at 50% bloom and then herbicides, or it can be incorporated as green manure.
Farmers value crimson clover for its multiple benefits including cost savings from reduced fertilizer use. Livestock farmers use it for forage. Some challenges may arise in colder climates, and when the soil is wet or compacted.
Under trials, the use of crimson clover as a cover crop to supply nitrogen was compared with a ryegrass cover crop and with fallow land, where no cover crops were used. The seeds were sown during two periods—early (August) and late (September)—and the cover crops were not further fertilized. The cover crops were terminated before sowing maize. The fallow area and the ryegrass area were fertilized according to the requirements of maize (215 kg N/ha) and soil analysis (for P and K). Half of the crimson clover area received no N fertilization, and the other half received only half of the required N. The maize crop was monitored by measuring soil, maize growth, grain yield, whole plant weight, and root weight. Crimson clover contributed between 61.6 and 78.6 kg of symbiotically fixed N ha⁻¹. The total soil amount of N accumulated by crimson clover was 100.7 kg N ha⁻¹, twice as much as under Italian ryegrass. The maize grain yields were significantly the lowest (10.9 t DM grain ha⁻¹) where crimson clover was sown early and the maize received no additional N. When crimson clover was used and maize was fertilized with half the N rate, grain yields were equivalent to those obtained on plots that received the full N rate (Italian ryegrass 13.5 t DM ha⁻¹, and the bare fallow control 13.4 t DM ha⁻¹).
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
สโลวีเนีย
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Podravje
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Selnica ob Dravi, Cirkovce, Pragersko
ระบุการกระจายตัวของเทคโนโลยี:
- กระจายไปอย่างสม่ำเสมอในพื้นที่
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 ตร.กม.(10 เฮกตาร์)
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
ไม่ใช่
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The technology is spread throughout arable land in Slovenia. The trial was conducted only on six farms in Podravje region .
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ระบุปีที่ใช้:
2024
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- ด้วยการริเริ่มของผู้ใช้ที่ดินเอง
- ในช่วงการทดลองหรือการทำวิจัย
- ทางโครงการหรือจากภายนอก
ความคิดเห็น (ประเภทของโครงการ เป็นต้น) :
The European Innovation Partnership (EIP) projects for agricultural productivity and sustainability (EIP-AGRI) enable exchange of knowledge for agriculture, forestry, and rural areas. The technology was introduced on these farms through the EIP project: "Integration of Cover Crops in Crop Rotation – Possibilities for Replacing Nitrogen from Mineral Fertilizers in Fertilization of the Next Crop"
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- ปรับปรุงการผลิตให้ดีขึ้น
- ลด ป้องกัน ฟื้นฟู การเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
- รักษาสภาพหรือปรับปรุงความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
- ปรับตัวเข้ากับการเปลี่ยนแปลงภูมิอากาศของโลก สภาพภูมิอากาศที่รุนแรงและผลกระทบ
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
ไม่ใช่

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
Annual cropping system:
Maize/sorghum/millet legume
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
ไม่ใช่
Is crop rotation practiced?
ใช่
ถ้าใช่ ระบุ:
5 year crop rotation: 3 different main crops in 5 years, plus cover crops after spring crops
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- จากน้ำฝน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การปรับปรุงดิน / พืชคลุมดิน
- การจัดการความอุดมสมบรูณ์ของดินแบบผสมผสาน
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการจัดการพืช
- A1: พืช/สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
- A2: อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ความอุดมสมบูรณ์ในดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยน้ำ
- Wt (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบนหรือการกัดกร่อนที่ผิวดิน

การกัดกร่อนของดินโดยลม
- Et (Loss of topsoil): การสูญเสียดินชั้นบน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Although primary cause of technology is natural nitrogen supply, the technology indirectly addressed also the soul erosion.
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
The technology of using crimson clover as a cover crop (variety 'Bolsena') to supply nitrogen was compared with the ryegrass cover crop (variety 'Turtetra') and fallow land, where no cover crops were used. Each plot covered area of 0.75 ha. The seeds were sown during two testing periods—early (August) and late (September)—and the cover crops were not further fertilized. The cover crops were terminated through mulching or ploughing before sowing the main crop, which was maize. The fallow area and the ryegrass area were fertilized according to the maize's requirements (215 kg N/ha) and soil analysis (phosphorus, P; potassium, K). Half of the area with crimson clover received no nitrogen fertilization, and the other half received only half of the required nitrogen (107 kg N/ha). The maize crop was monitored throughout the growing season by measuring soil nitrogen and assessing maize growth.
ผู้เขียน:
Tamara Korošec
วันที่:
03/03/2025
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
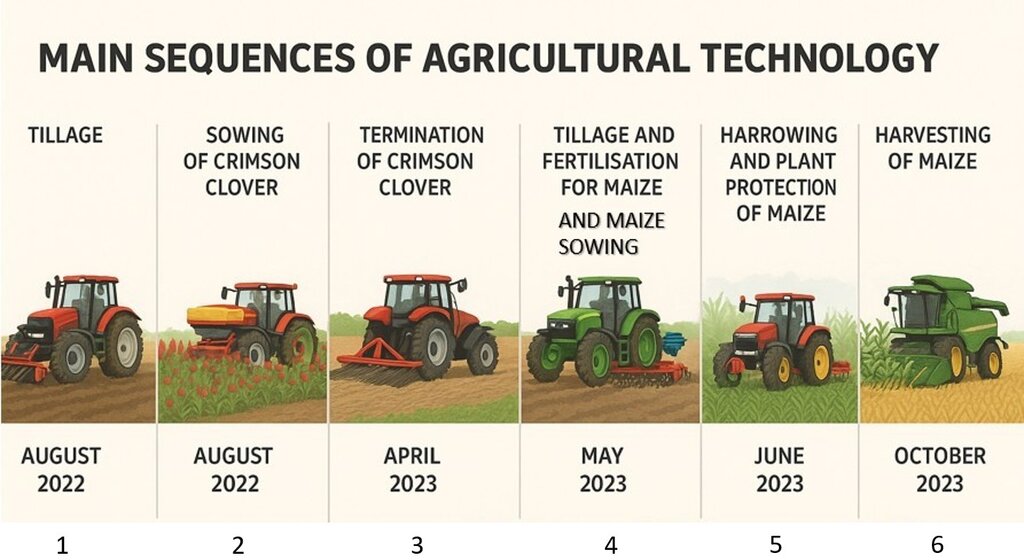
Main sequences of the technology: 1. tillage and seed bed preparation (disc cultivator or similar) for sowing cover crop (crimson clover) after the winter cereals harvest (August 2022); 2. sowing of crimson clover is usually combined with tillage, or done separately (August 2022); 3. mechanical termination of crimson clover (April 2023), 4. tillage, fertilisation, seed bed preparation and sowing of maize (may 2023), 5. harrowing and plant protection (herbicide) of maize (June 2023), 6. harvesting of maize (October 2023).
ผู้เขียน:
Tamara Korošec (made with Chat GPT)
วันที่:
30/09/2025
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ให้ระบุว่าค่าใช้จ่ายและปัจจัยนำเข้าได้รับการคำนวณอย่างไร:
- ต่อพื้นที่ที่ใช้เทคโนโลยี
ระบุขนาดและหน่วยพื้นที่:
ha
อื่นๆ หรือสกุลเงินประจำชาติ (ระบุ):
EUR
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
0.85
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
None
4.4 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าที่จำเป็นสำหรับการจัดตั้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
None
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Stubble preparation (tillage) for crimson clover + sowing (stages 1 and 2 in diagram) | August (or September) |
| 2. | Mechanical cover crop termination and soil preparation before maize sowing (stage 3 in diagram) | end of April |
| 3. | Sowing of maize (stage 4 in diagram) | May |
| 4. | Fertilisation (part of stage 4 in diagram) | May, June |
| 5. | Hoeing and weed control (herbicide) (stage 5 in diagram) | May, June |
| 6. | Harvest (maize) (stage 6 in diagram) | October |
| 7. | Drying (maize) (part of stage 6 in diagram) | October |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| แรงงาน | All labour costs | hour | 6.0 | 15.0 | 90.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Stubble preparation for crimson clover (tillage) | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Sowing of crimson clover | ha | 1.0 | 46.3 | 46.3 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Mechanical termination of the crimson clover | ha | 1.0 | 37.5 | 37.5 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Tillage and seed bed preparation for maize | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Maize sowing | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Maize hoeing and weed control | ha | 1.0 | 60.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| อุปกรณ์ | Maize harvesting | ha | 1.0 | 140.0 | 140.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Crimson clover seed | ha | 28.0 | 3.5 | 98.0 | 100.0 |
| วัสดุด้านพืช | Maize seed | ha | 1.0 | 290.0 | 290.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 150.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| ปุ๋ยและสารฆ่า/ยับยั้งการเจริญเติบโตของสิ่งมีชีวิต (ไบโอไซด์) | Herbicide | ha | 1.0 | 80.0 | 80.0 | 100.0 |
| อื่น ๆ | Drying of maize grain | all harvest | 1.0 | 428.0 | 428.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 1589.8 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1870.35 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of maintaining the Technology:
1561.8
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The above calculation is for combination of crimson clover cover crop and half the amount of nitrogen fertilizer (107 kg/ha) for maize production. This technology had similar grain production (13.7 t/ha) as full application of mineral nitrogen (215 kg/ha) with combination of fallow land or ryegrass as cover crop. The revenue for this technology from selling the grain was 2877 €/ha (0.21 €/kg). Crimson clover with no additional mineral fertilisation for maize had significantly lower yields (10.9 t/ha) and thus lower revenue per hectare (2289 €/ha; 0.21 €/kg of grain). For crops which need less nitrogen than corn, the additional mineral N fertilisation would not be necessary and so costs would be lower. Farmers get 180 € of basic subsidies per ha and further 148 € per ha for greening through the winter (EU CAP).
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
Most important factors affecting the costs are the price of seeds and machinery hours.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.1 ภูมิอากาศ
ฝนประจำปี
- < 250 ม.ม.
- 251-500 ม.ม.
- 501-750 ม.ม.
- 751-1,000 ม.ม.
- 1,001-1,500 ม.ม.
- 1,501-2,000 ม.ม.
- 2,001-3,000 ม.ม.
- 3,001-4,000 ม.ม.
- > 4,000 ม.ม.
ระบุชื่อของสถานีตรวดวัดอากาศที่ใช้อ้างอิงคือ:
ARSO - Environmental Agency of Republic of Slovenia, archive data (last 10 years) for main station in Podravje region - Letališče Edvarda Rusjana Maribor
เขตภูมิอากาศเกษตร
- กึ่งชุ่มชื้น
Continental Climate (Central and Northeastern Slovenia). Meteo station Letališče Edvarada Rusjana Maribor:
Cold winters and hot summers. The average yearly temperature (last 10 years) is 11.5 degrees C.
Large temperature fluctuations between seasons. Average maximal temperature 16.7 degrees C. , the average minimal temperature is 6.4 degrees C. Absolute max. temperature (ave 10 years) was 34 degrees C, and the average absolute minimal temperature approximately -10 degrees.
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
ให้ระบุถ้าเทคโนโลยีได้ถูกนำไปใช้:
- ไม่เกี่ยวข้อง
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
เนื้อดินล่าง (> 20 ซ.ม.ต่ำจากผิวดิน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
The test fields were on different soil types:
- Eutric alluvial soils pH 6,6-7,2
- Dystric brown soils on non calcareous sandy gravel sediments, pH4,6-5,5
- Eutric brown soils on alluvial-colluvial sediments and deluvium, pH 5,6-6,5
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
5-50 เมตร
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
ดี
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
เป็นน้ำเพื่อการดื่มที่ไม่ดี (จำเป็นต้องได้รับการบำบัด)
Water quality refers to:
ground water
ความเค็มของน้ำเป็นปัญหาหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
กำลังเกิดน้ำท่วมในพื้นที่หรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
In Slovenia all drinking water is treated by chlorine. If we compare it to the rest of the world, we have good drinking water, but we never use it untreated.
5.5 ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ
ความหลากหลายทางชนิดพันธุ์:
- สูง
ความหลากหลายของแหล่งที่อยู่:
- ปานกลาง
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพ:
Under the cover crop area soil biodiversity is high. Regarding overall habitat, the test areas are in intensive agricultural areas, that is why the habitat biodiversity which is otherwise high in Slovenia, is rated as moderate.
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
อยู่กับที่หรือเร่ร่อน:
- อยู่กับที่
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
รายได้ที่มาจากนอกฟาร์ม:
- 10-50% ของรายได้ทั้งหมด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- การใช้เครื่องจักรหรือเครื่องยนต์
เพศ:
- ชาย
อายุของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
- วัยกลางคน
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดกลาง
5.8 กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดินและสิทธิในการใช้น้ำ
กรรมสิทธิ์ในที่ดิน:
- รัฐ
- รายบุคคล ได้รับสิทธิครอบครอง
สิทธิในการใช้ที่ดิน:
- เช่า
- รายบุคคล
สิทธิในการใช้น้ำ:
- เกี่ยวกับชุมชน (ถูกจัดระเบียบ)
- เช่า
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
ไม่ใช่
ระบุ:
Land use rights in Slovenia are primarily based on modern statutory law, not traditional or customary law. The main frameworks are the Constitution of the Republic of Slovenia, the Law of Property Code (Stvarnopravni zakonik, SPZ), the Agricultural Land Act (Zakon o kmetijskih zemljiščih, ZKZ), and the Spatial Planning and Building Acts (Zakon o urejanju prostora, Gradbeni zakon, etc.).
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ตลาด:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
พลังงาน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ถนนและการขนส่ง:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
215 kg/ha mineral nitrogen for 13.4 t of maize grain
หลังจาก SLM:
107 kg/ha mineral nitrogen for 13.7 t of maize grain
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased maize grain yields with less use of nitrogen fertiliser (positive impact)
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
ค่าใช่จ่ายของปัจจัยการผลิตทางการเกษตร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
201 €
หลังจาก SLM:
101 €
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
reduced expenses on mineral fertiliser for 100 kg of N per ha (positive impact)
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
ปริมาณน้ำ
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
improved water retention, filtration, drainage (positive impact)
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
water retention capacity improved (positive impact)
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
late summer to spring soil cover
การเกิดแผ่นแข็งที่ผิวดิน /การเกิดชั้นดาน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
lowered soil crusting, which is a positive impact
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
จำนวนก่อน SLM:
0
หลังจาก SLM:
61-150 kg/ha
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
symbiotic nitrogen fixation with crimson clover 61 - 150 kg/ha N fixation (depending on the weather and soil conditions)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
green manure from cover crops increases soil organic matter
ความหลากหลายทางชีวภาพของพืชและสัตว์
การปกคลุมด้วยพืช
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
diversified vegetation cover
ความหลากหลายของสัตว์
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
increased soil microbial community, diversified crop rotation, benefits for pollinators
ลดความเสี่ยงของภัยพิบัติ
ผลกระทบจากน้ำท่วม
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
better drainage
ผลกระทบจากภัยแล้ง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
Lowered evaporation from soil, water retention capacity
ผลกระทบของพายุไซโคลน พายุฝน
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
protection against erosion due to heavy rain storms
Specify assessment of on-site impacts (measurements):
On-site impacts included direct field measurements and expert judgements/ predictions on the basis of data from this and previous experiments.
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความสามารถต้านทานการเปลี่ยนแปลง / ความสามารถในการคัดกรอง
แสดงความคิดเห็น/ระบุ:
green cover filters the nutrients that go to the groundwater
Specify assessment of off-site impacts (measurements):
Off-site impacts are predicted by expert judgements/ predictions on the basis of data from this and previous experiments.
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูร้อน | เพิ่มขึ้น | ปานกลาง |
| อุณหภูมิตามฤดูกาล | ฤดูหนาว | เพิ่มขึ้น | ดี |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูร้อน | ลดลง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| ฝนตามฤดู | ฤดูหนาว | ลดลง | ปานกลาง |
สภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ (ภัยพิบัติ)
ภัยพิบัติทางอุตุนิยมวิทยา
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| พายุลูกเห็บประจำท้องถิ่น | ปานกลาง |
ภัยพิบัติจากสภาพภูมิอากาศ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| คลื่นความร้อน | ไม่ค่อยดี |
| ภัยจากฝนแล้ง | ไม่ค่อยดี |
ภัยพิบัติทางชีวภาพ
| เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|
| การบุกรุกของแมลง / หนอน | ดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
ด้านบวก
6.5 การปรับตัวของเทคโนโลยี
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
They are mostly motivated by subsidies, so spontaneous adoption is a small percentage.
6.6 การปรับตัว
เทคโนโลยีได้รับการปรับเปลี่ยนเมื่อเร็วๆนี้ เพื่อให้ปรับตัวเข้ากับสภาพที่กำลังเปลี่ยนแปลงหรือไม่:
ไม่ใช่
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Lower costs for mineral fertilizers, subsidies for seeds |
| Good for soil health |
| Good for water absorption |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Climate change adaptation |
| Soil improvement - increase in organic matter, soil biodiversity, water capacity |
| Fixation of nitrogen form air, less mineral fertilisers |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Drought during the seeding of catch crop | earlier or later sowing - however it has an impact anyway |
| Additional work (compared to bare fallow) | combined machinery (soil preparation + sowing combined) |
| Risk of frost if the crimson clover is too big going into winter | sowing and mulching at right time |
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| Not applicable for all main crops - early spring crops do not get the same benefits as late spring/summer crops | for early spring crops other nitrogen fixings plants can be used. |
| Nitrogen runoff if no main crop follows after crimson clover destruction | always plant main crop right away |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
regular field visits and monitoring on 4 farms / fileds
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
4 farmers
- การสัมภาษณ์ผู้เชี่ยวชาญด้าน SLM หรือผู้ชำนาญ
consultation with colleagues from the Life science faculty (2)
- การเก็บรวบรวมมาจากรายงานและเอกสารที่มีอยู่
previously prepared reports form the EIP project
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
The project was carried out for 2 years. The data were compiled during the whole time - regular monitoring, interviews, sampling...
7.2 การอ้างอิงถึงสิ่งตีพิมพ์
หัวข้อ, ผู้เขียน, ปี, หมายเลข ISBN:
GSELMAN, Anastazija, LISEC, Urška, KOROŠEC, Tamara, PODVRŠNIK, Miran. S prezimnimi metuljnicami do nadomeščanja dušika iz mineralnih gnojil = Winter legumes as a substitute for nitrogen from mineral fertilisers. V: ČEH, Tatjana (ur.), KAPUN, Stanko (ur.). 32. mednarodno znanstveno posvetovanje o prehrani domačih živali [tudi] Zadravčevi-Erjavčevi dnevi 2024 = 32nd International Scientific Symposium on Nutrition of Farm Animals [being] Zadravec-Erjavec Days 2024 : zbornik predavanj = proceedings : Murska Sobota, 14. in 15. november 2024, 14th and 15th November 2024. Murska Sobota: Kmetijsko gozdarska zbornica Slovenije, Kmetijsko gozdarski zavod, 2024. Str. 61-66, graf. prikazi. ISBN 978-961-96187-7-6. [COBISS.SI-ID 215866371]
ชื่อเรื่อง ผู้เขียน ปี ISBN:
in various Slovenian libraries - in Slovene
7.3 Links to relevant online information
ชื่อเรื่องหรือคำอธิบาย:
Website
URL:
https://dosevki.um.si/
7.4 General comments
Just a remark on question formulation: the instructions in section 6.1 appear a bit ambiguous when the response scale for some specific questions appears "reversed" in relation to the guideline parameter - such as "soil crusting" where a negative value is in fact a positive outcome.
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล