Establishment of educational ranger stations to involve youth in nature protection activity [Kazakhstan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Azhar Yeszhanova
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kazakhstan - Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM)
approaches_2459 - Kazakhstan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Approach
SLM specialist:
SLM specialist:
Zhumabayev Ermek
Director, FE 'Karagay-Shyrsha'
050060, Almaty, Al-Farabi, 75-a
Kazakhstan
SLM specialist:
Cheranev Vladimir
(7232) 24-12-16
Project Manager, GEF/UNDP Project
“Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biodiversity in the Kazakhstani Sector of the Altai-Sayan Ecoregion”, Office 409, 21 M. Gorky str., Ust-Kamenogorsk,
Kazakhstan
SLM specialist:
Yeskazyuly Renat
renat.eskazyuly@mail.ru
Specialist of the Department on Environmental Education and Tourism of Katon-Karagay National Park
Kazakhstan
SLM specialist:
Chugunkov Oleg
8 (7232) 24-15-38
oleg.chugunkov@undp.org
Expert in awareness raising, UNDP Kazakhstan
Office 409, 21 M. Gorky str., Ust-Kamenogorsk, 070019
Kazakhstan
SLM specialist:
Krykbayeva Raushan
8(72342)21761
katonoopt@mail.kz
Katon-Karagay State National Park
Kazakhstan, East-Kazakhstan Region, Katon-Karagay vil., 115 Bokeyev str.
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Central Asian Countries Initiative for Land Management (CACILM I)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Kazakh Institute of Soil Science and Agrochemistry - KazakhstanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
UNDP/GEF Project Uzbekistan (UNDP/GEF Uzbekistan) - UzbekistanName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Approach (if relevant)
Katon-Karagay National Park - Kazakhstan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
2. Description of the SLM Approach
2.1 Short description of the Approach
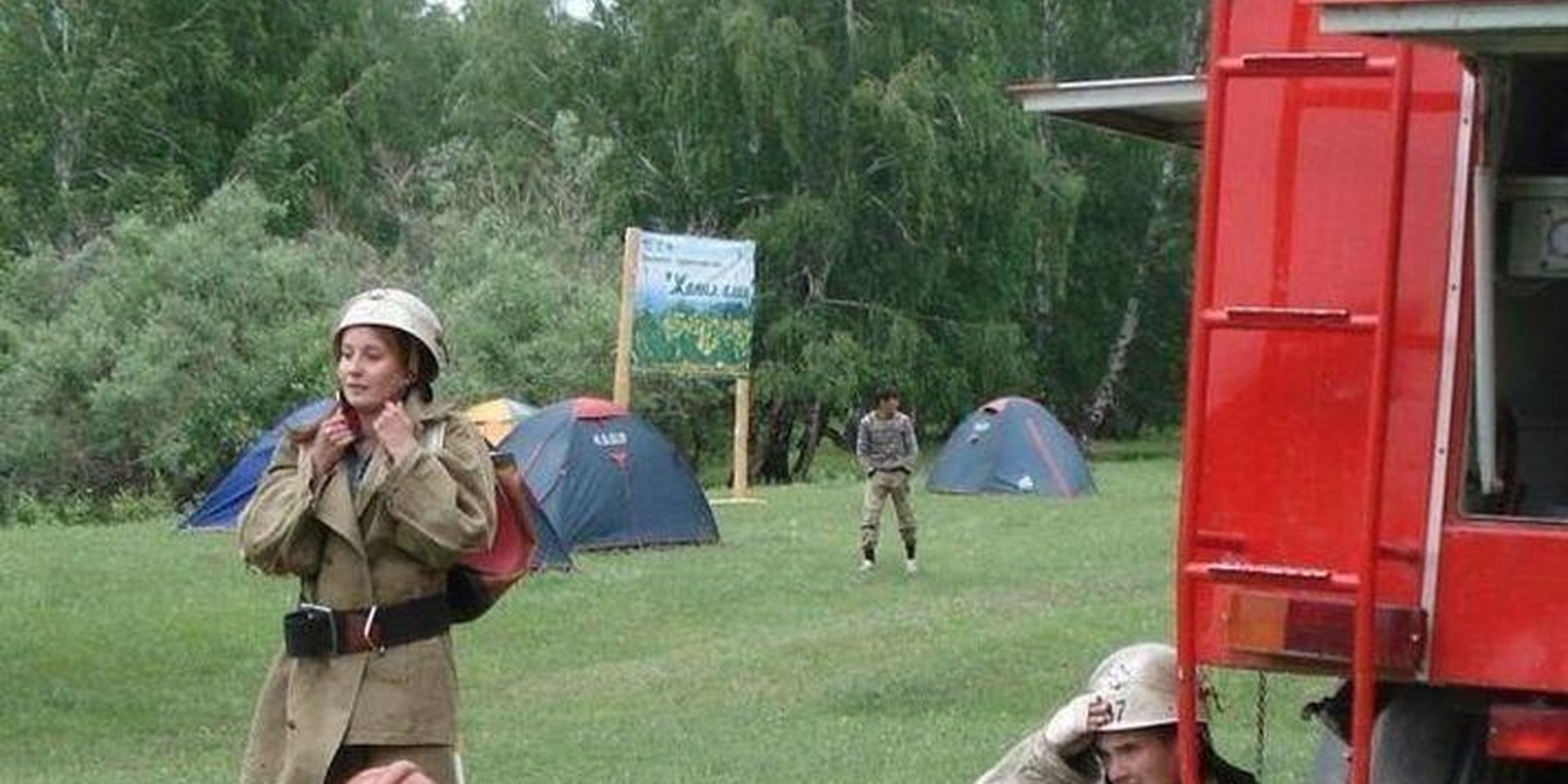
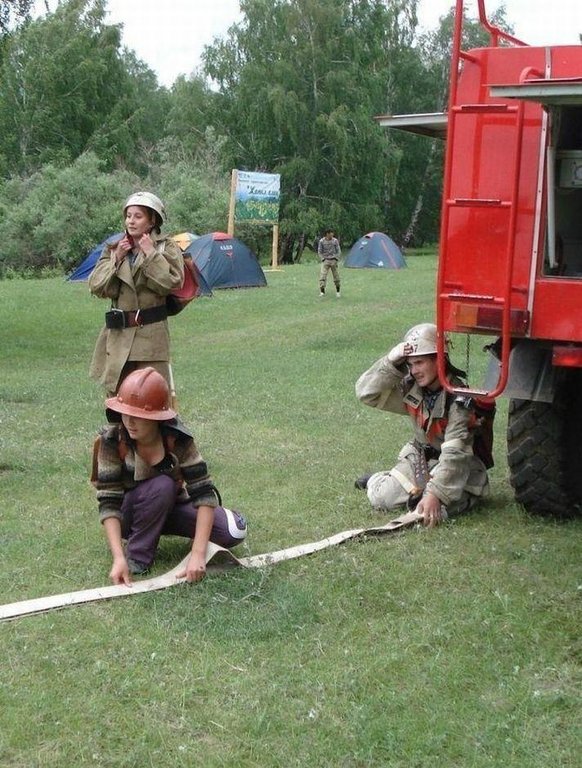
Establishment and activity of educational ranger stations on the basis of forestry units and secondary schools to involve youth in nature protection activity to conserve, restore and study unique natural features of the Kazakh Altai (in the frame of CACILM).
2.2 Detailed description of the Approach
Detailed description of the Approach:
Aims / objectives: Environmental education and involvement of coming generations in the conservation of forest ecosystems and reforestation of target areas through creation of nurseries and initial training of forestry specialists. Improved study of nature and deepened knowledge in Biology, Geography, Ecology
Methods: Forestry Schools are a tradition of the Soviet period. Relevant factors of negative impact on the fragile forest ecosystems in East Kazakhstan (fires, pests, illegal cutting) have necessitated the involvement of young people in forest protection activities. In the Katon-Karagay district 4 school ranger stations were created based on five secondary schools. The scholars are the members them. School ranger stations are self-governing organizations and the responsibilities are distributed among its members as it is distributed in any other establishments of forestry. One elected scholar-forester and a council which consists of 6-8 of the most active and experienced pupils, lead all activities. School teachers and foresters supervise their work but they are not members of School ranger stations. The most active school ranger station is the 'Cedar' in Uryl villlage. The main activity is to educate school children with the basics of forestry, monitoring, the practices of tree nurseries and protection of trees in the forests, the participation of school children in the state program 'Green Country’ and in national and international conferences and gatherings. The legal framework of land ownership ensures the sustainability of the approach on the state level and facilitates the implementation of this approach
Stages of implementation: 1.The initiative was taken by the administration of Berel Forestry Unit, the department on environmental awareness raising and education of Katon-Karagay national park and the director of the Uryl Secondary School. 2. Cooperation to discuss and agree on the role of the parties. 3. Agreement on Cooperation between the Office of the Katon-Karagay national park, Uryl secondary school and youth social organization 'Eco-tourism center'. 4. Training seminars for coaches and pupils of 'Cedar' school. 5. Distribution of approach and creation of 3 similiar schools in Katon-Karagay distric
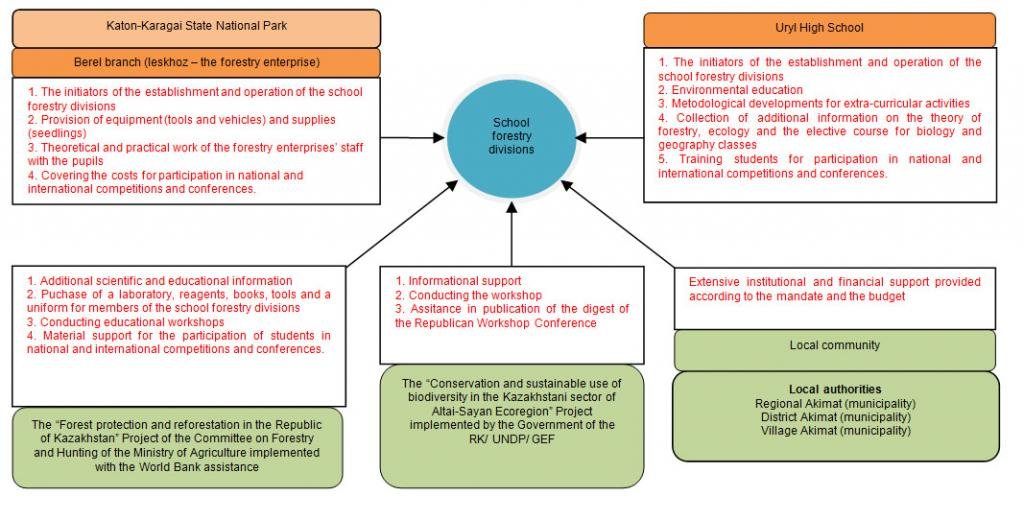
Role of stakeholders: Secondary school: environmental education, methodical gathering, information on Forestry and Earth sciences, preparing school children for national and international competitions and conferences. Katon-Karagay national park and forestry: tools, vehicles, plants, theoretical and practical work with school professionals, the cost of participation in competitions and conferences. Local authorities: institutional support. 'Forest Conservation and Reforestation' project: additional information, laboratory&reagents, tools, uniform for scholars, trainings. 'Conservation and Sustainable Use of Biodiversity of Kazakhstan part of Altai-Sayan Ecoregion'project: information support, seminars and assistance in the production of Conference Proceedings. Local community: all kinds of support
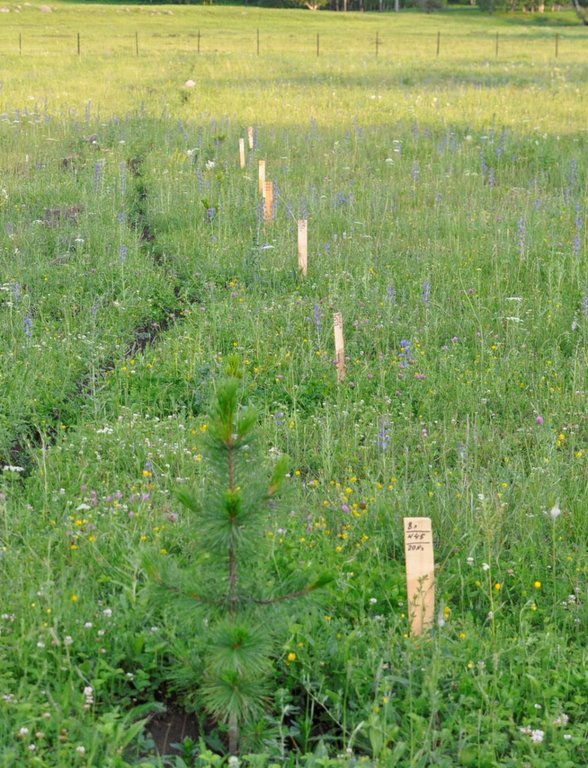
2.3 Photos of the Approach
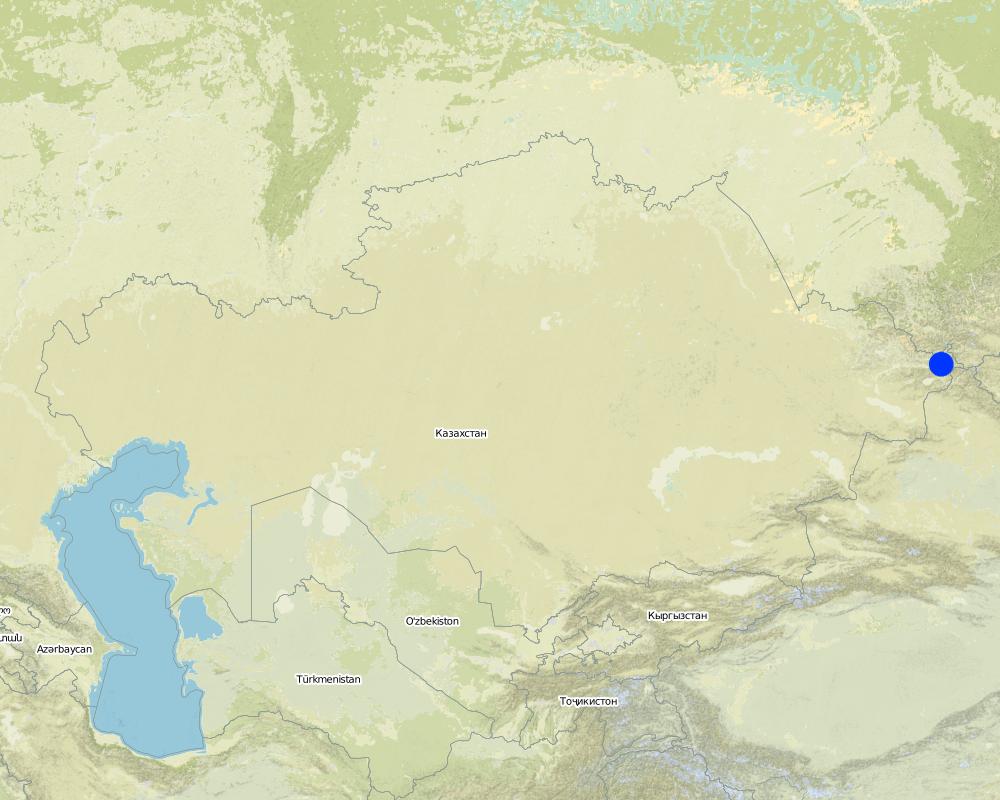
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Approach has been applied
Country:
Kazakhstan
Region/ State/ Province:
Kazakhstan/East-Kazakhstan
Further specification of location:
Katon-Karagay/Uryl village
Comments:
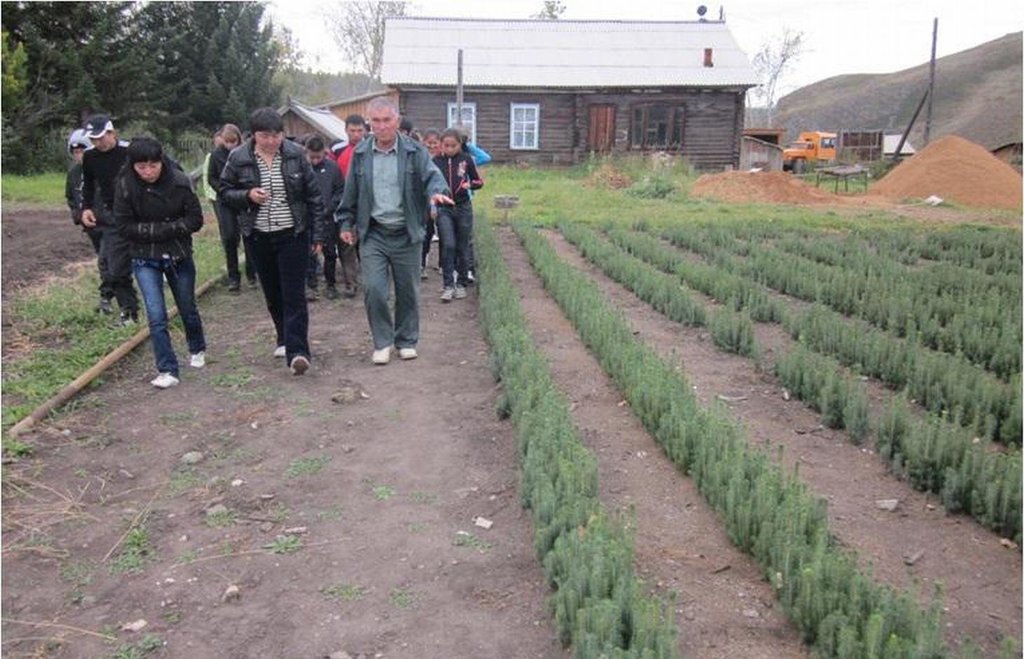
The approach is realized on the territory of Katon-Karagay State National Natural Park established according to the Resolution of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan #970 dated June 17, 2001. It is under the Forestry and Hunting Committee of the Ministry of Agriculture of the RK. The aim of the park’s creation is the conservation, study and restoration of unique natural features of South Altai, which has special ecological, scientific, cultural and recreational values. The total area occupies 643477 ha and the forest area of 1500 ha is monitored, assessed and protected with the participation of school children. Forest nursery occupying 0.5 ha is also part of the project and managed by the students, which is part of a national park.
Map
×2.6 Dates of initiation and termination of the Approach
Indicate year of initiation:
2004
Comments:
The approach is realized on the territory of Katon-Karagay State National Natural Park established according to the Resolution of the Government of the Republic of Kazakhstan #970 dated June 17, 2001. It is under the Forestry and Hunting Committee of the Ministry of Agriculture of the RK. The aim of the park’s creation is the conservation, study and restoration of unique natural features of South Altai, which has special ecological, scientific, cultural and recreational values. The total area occupies 643477 ha and the forest area of 1500 ha is monitored, assessed and protected with the participation of school children. Forest nursery occupying 0.5 ha is also part of the project and managed by the students, which is part of a national park.
2.7 Type of Approach
- успешное восстановление проSuccessful restoration of the program of the Soviet period
2.8 Main aims/ objectives of the Approach
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (training, monitoring and evaluation of the ecological state of forests, forest protection, environmental education)
Conservation of forest ecosystems, environmental education, training in basic forestry issues, professional orientation of youth in the field of forestry
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Increase in the number of wildfires; Diseases and pests of forest plants; Illegal wood cutting; Lack of theoretical and practical technical knowledge; Lack of young skilled specialists;
2.9 Conditions enabling or hindering implementation of the Technology/ Technologies applied under the Approach
availability/ access to financial resources and services
- hindering
Some delays in the provision of equipment and transport may occur
Treatment through the SLM Approach: According to the assessment, this issue is not an urgent one and currently is successfully being solved with the support of the administration of the national park and local authorities. Search of means from other sources is possible
legal framework (land tenure, land and water use rights)
- enabling
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly helped the approach implementation: The reliable legislative base concerning the right for owning land within the specially protected natural area of the republic - Katon-Karagay National Natural Park - allows for the securing of a stable approach on the state level and implementing this approach to a large extent.
workload, availability of manpower
- hindering
Lack of officially paid work hours for schoolteachers
Treatment through the SLM Approach: At present the issue has nоt been solved yet since there are no legal reasons for that. It is possible to solve this issue through official allocation of funds from the state budget, the local budget and improvement of legal base.
other
- hindering
Lack of a certificate or other document allowing active members of educational ranger stations to have priority in entering specialized educational institutions (for instance, in 'forestry' profession)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: There has been no such an official order yet, but efforts should be made to have permit from the Ministry of Education and Science to issue and include such a document in the list of achievements allowing preference when entering higher educational instit
3. Participation and roles of stakeholders involved
3.1 Stakeholders involved in the Approach and their roles
- SLM specialists/ agricultural advisers
Specialists of the Berel Forestry Unit
Schoolchildren of all social groups regardless of economic, gender, ethnic and religious relation are involved
- teachers/ school children/ students
Schoolchildren (12-16 years old), teachers of secondary school
- national government (planners, decision-makers)
Berel Forestry Unit and administration of Katon-Karagay National Park, secondary school of Uryl village
- Specialists of the “Forest Conservation and Expansion of Forest Area on the Territory of the Republic“ Project of the Forestry and Hunting Committee of MA RK with the support of the World Bank (Doctor of Biological Sciences Yermek Zhumabayev) and Government of RK/GEF/UNDP
3.2 Involvement of local land users/ local communities in the different phases of the Approach
| Involvement of local land users/ local communities | Specify who was involved and describe activities | |
|---|---|---|
| initiation/ motivation | interactive | Katon-Karagay National Park and forestry units – all kinds of support and introduction of the tradition of forest schools. Secondary schools teachers - motivation of scholars to participate actively in basic forestry issues and educational issues on the forests careful treatment and protection. |
| planning | interactive | Katon-Karagay National Park and forestry units - introducing of forest schools’ activity in the national park budgetary plan and workplan. Secondary schools teachers – inclusion of activities to be implemented jointly with forest school in the extracurricular workplan, methodical developments. |
| implementation | interactive | Technical and financial support, practical training of scholars in forest nurseries and on the territory of the national park; environmental education, training for participation in international and national conferences, workshops and additional literature on forestry and forest management. |
| monitoring/ evaluation | interactive | Katon-Karagay National Park and forestry units specialists, “Forest Conservation and Expansion of Forest Area on the Territory of the Republic“ Project of the Forestry and Hunting Committee of MA RK with the support of the World Bank, specialists of East-Kazakhstan University |
| Research | interactive | Workshops on selection of sowing material, methods in the accelerated growing of small coniferous standard seedlings, technologies and skills in the maintenance of the germaplasma viability of seeds, training and methodological literature on forestry and forest management. |
3.3 Flow chart (if available)
Description:
Organigram of the role of various parties in the creation and functioning of school forestries in the Katon-Karagai district of the East Kazakhstan region of Kazakhstan
Author:
Eszhanova Azhar (Kabanbai batyr-Pushkin, 67/99, Almaty, Kazakhstan)
3.4 Decision-making on the selection of SLM Technology/ Technologies
Specify who decided on the selection of the Technology/ Technologies to be implemented:
- mainly land users, supported by SLM specialists
Explain:
The administration of the Katon-Karagay National Park jointly with the Department on Primary and Secondary Education of the district and the region has made a decision to revive and support the successful tradition of the Soviet period for forest conservation, environmental education of schoolchildren and training of forestry specialists, the lack of which has become obvious in the last years.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. Organizational and methodical activity on environmental aspects were implemented by the director and teachers of the secondary school of Uryl village, the training of schoolchildren in technical issues was organized by specialists of the forestry economic unit
4. Technical support, capacity building, and knowledge management
4.1 Capacity building/ training
Was training provided to land users/ other stakeholders?
Yes
- The approach is applicable to involve schoolchildren in nature conservation activity and ecological education in various regions both with forest areas and for the protection of other ecosystems.
If relevant, specify gender, age, status, ethnicity, etc.
Schoolchildren (12-16 years old) are involved in extracurricular training (lectures, debates, workshops) in basic forestry issues and forest management, practical basic issues of forest monitoring and protection, as well as in the studies in nurseries and in the forest areas of Katon-Karagay SNNP, and in participation in the 'Zhasyl Yel' state program and in various national and international con
Form of training:
- on-the-job
- demonstration areas
4.2 Advisory service
Do land users have access to an advisory service?
Yes
- in schools
Describe/ comments:
Name of method used for advisory service: Support of the distribution of new approaches and technologies through studies related to forests; Key elements: 1.Training of Uryl ranger station members (schoolchildren, teachers and employees of the forestry economic unit) in the methods of the accelerated growing of standard seedlings of small coniferous trees (spruce, larch, pine and fir trees), 2.Delivery of new knowledge, transfer of technologies and practical skills to instructors on training Uryl educational ranger station and the Berel Branch of Katon-Karagay State National Natural Park on the maintenance of the germaplasma viability of seeds collected from forest genetic reserves; Name: Support of the distribution of new approaches and technologies through studies related to forests, through expansion of training to achieve forestry profitability, forest conservation and wood product market management
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; There is no state consultation service, but research and production facilities can provide consultation services. E.g. Kondratovskiy Research and Show Forest Nursery, Ltd. deals with the growing and realization of planting material of fruit and wood-shrubbery and coniferous tree sorts of high quality, seed collecting, testing of scientific studies and introducing into production.
4.3 Institution strengthening (organizational development)
Have institutions been established or strengthened through the Approach?
- yes, moderately
Specify the level(s) at which institutions have been strengthened or established:
- local
Specify type of support:
- capacity building/ training
- Seedlings
Give further details:
Training on the method of accelerated growing of standard seedlings of small coniferous trees, as well as knowledge, technologies and practical skills in the conservation of the germaplasma viability of seeds; support in the creation of areas for forest crops, cedar, fir and pine trees.
4.4 Monitoring and evaluation
Is monitoring and evaluation part of the Approach?
Yes
Comments:
Bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by land users, other through observations; indicators: The specialists of the forestry economic unit, the specialists of “Forest Conservation and Expansion
There were no changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 Research
Was research part of the Approach?
Yes
Specify topics:
- sociology
- ecology
- technology
Give further details and indicate who did the research:
Dr.Yermek Zhumabayev - training of teachers of Uryl forest school on accelerated growing of standard seedlings trees (spruce, larch, pine and fir trees); A.Dzhumagulova - pedagogical studies on environmental education; Renat Yeskazyuly - study of opportunities for tourism development and raising of awareness of environmental issues in the region.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. Financing and external material support
5.1 Annual budget for the SLM component of the Approach
If precise annual budget is not known, indicate range:
- < 2,000
Comments (e.g. main sources of funding/ major donors):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: other (“Forest Conservation and Expansion of Forest Area on the Territory of the Republic“ Project): 50.0%; government (Katon-Karagay National Natural Park of MA RK - tools, consumables (seedlings, fertilizers, stationаr): 50.0%
5.2 Financial/ material support provided to land users
Did land users receive financial/ material support for implementing the Technology/ Technologies?
No
5.3 Subsidies for specific inputs (including labour)
- equipment
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| tools | fully financed | |
- agricultural
| Specify which inputs were subsidised | To which extent | Specify subsidies |
|---|---|---|
| seeds | fully financed | |
| tree seedlings | fully financed | |
If labour by land users was a substantial input, was it:
- voluntary
Comments:
The activity is implemented in planned or free time beyond work and curricular activities.
5.4 Credit
Was credit provided under the Approach for SLM activities?
No
6. Impact analysis and concluding statements
6.1 Impacts of the Approach
Did the Approach help land users to implement and maintain SLM Technologies?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
Successful activity of educational ranger stations in the field of raising environmental awareness and education has drawn the attention of both state development programs and international projects that has led to the improvement of the material, technical, informational and research base allowing
Did the Approach empower socially and economically disadvantaged groups?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The approach has other specifics, though the administration of Katon-Karagay National Park initiated the support for children from low-income families.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The approach was shared through creation and involvement of 3 other forest schools in Katon-Karagay district - 'Or Altai', 'Ular' (since 2006 on the basis of the nursery of Medvedskiy forestry unit), 'Zheruyik' (since 2008 on the basis of Zhambyl secondary school). As a whole, more than 20 educational ranger stations have been created and are functioning in East-Kazakhstan region on the basis of: Katon-Karagay State National Park, 'Semey Ormany' West-Altai Nature Reserve.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The activity of forest schools is aimed at forest resources conservation, and so immediate and calculated economic impact in the form of well-being improvement is not expected
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- No
- Yes, little
- Yes, moderately
- Yes, greatly
The activity of educational ranger stations in not aimed at poverty reduction, but in theory, if sustainable development is maintained, it may lead to raising the population’s standard of living.
6.2 Main motivation of land users to implement SLM
- affiliation to movement/ project/ group/ networks
GRAN-PRI and the “Golden Cone” award at the international contest of schoolchildren from C.I.S.
- environmental consciousness
target group - schoolchildren
- Экологическое сознание, здоровье
целевая группа - школьники
6.3 Sustainability of Approach activities
Can the land users sustain what has been implemented through the Approach (without external support)?
- no
If no or uncertain, specify and comment:
At present, the whole training, monitoring and research activity is conducted solely on the basis and with the support of the state (Katon-Karagay National Park)
6.4 Strengths/ advantages of the Approach
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
1) Improving the knowledge and horizons of schoolchildren 2) Involving young people in useful work and preventing crime 3) Reducing the outflow of youth to cities 4) Training local staff for leshozes with in-depth knowledge of local natural features. (How to sustain / enhance this strength: 1) Attracting new knowledge, specialists, organizing conferences, trips, meetings 2) Informatization, propaganda, interest increase 3) Provision with housing, jobs 4) Comprehensive assistance in choosing a profession and entering universities) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
1) Support for environmental education and research 2) Relatively strong material and technical basis 3) Training forestry specialists for the future of sustainable forestry development and the protection of forests. (How to sustain / enhance this strength: 1) Attraction of environmental specialists, engineers, diversify information, conduct seminars, meetings, etc. 2) It is ensured and will continue to be provided by the state 3) To promote the possibility of entering higher and secondary special educational institutions in the specialty "Forestry" or "Plant protection" by issuing a confirmed document on active participation in the ranks of school forestry and practical experience in forest conservation activities . ) |
6.5 Weaknesses/ disadvantages of the Approach and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| 1. There is no material incentive for teachers 2. There is no official document confirming studies in the school forestry, helping with admission to universities 3. Legal insecurity (alleged use of child labor) | 1.Preview in the local budget or in the distribution of the workload in the school 2. Achieve the Ministry of Education and Science on the development of such an amendment to the legislative base 3. Amendments to the Labor Law of the Republic of Kazakhstan |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| 1. In the absence of material support, this initiative can be completed. 2. Not always schoolchildren after graduation can enter the universities of the appropriate profile 3. A not too large percentage of school forestry members go on an ecological profile. | 1. Constantly take care of allocating funds from the state budget 2. To seek allocation of special quotas for schoolchildren-activists of school forestries, to strengthen highly specialized training, to provide material support to children from low-income families (travel, accommodation in the city, etc.) 3. Strengthen the environmental And patriotic education, to guarantee the provision of work, housing |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
The materials of the national scientific and practical conference „Organization of the Work of Educational Ranger Stations as One of the Forms of Profession Orientation Activity to Train Specialists in Forestry“. October 4-5, 2010.
Available from where? Costs?
Katon-Karagay National Park, the Government of RK/GEF/UNDP Project “Conservation and Sustainable Use
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Administration of Katon-Karagay National Park reports
Available from where? Costs?
115 Bokeyev str, Katon-Karagay vil., East-Kazakhstan Region, Kazakhstan, 070908. Deputy Director
7.3 Links to relevant information which is available online
Title/ description:
Information of the implementation of “Forest Conservation and Expansion of Forest Area on the Territory of the Republic“ Project on the website of the Forestry and Hunting Committee of the Ministry of Agriculture of the Republic of Kazakhstan
URL:
http://www.fhc.kz/pkg/4712/
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules