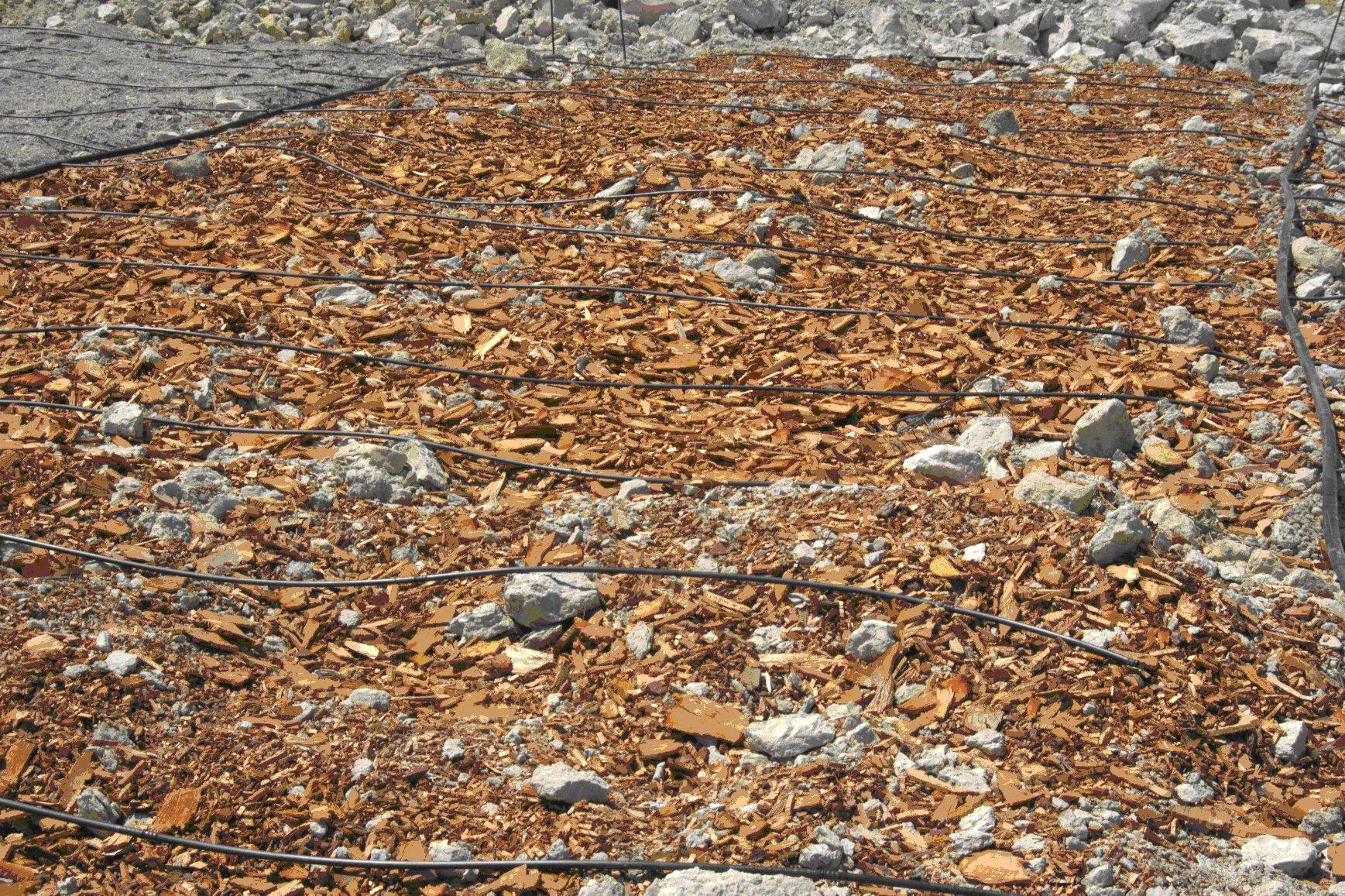
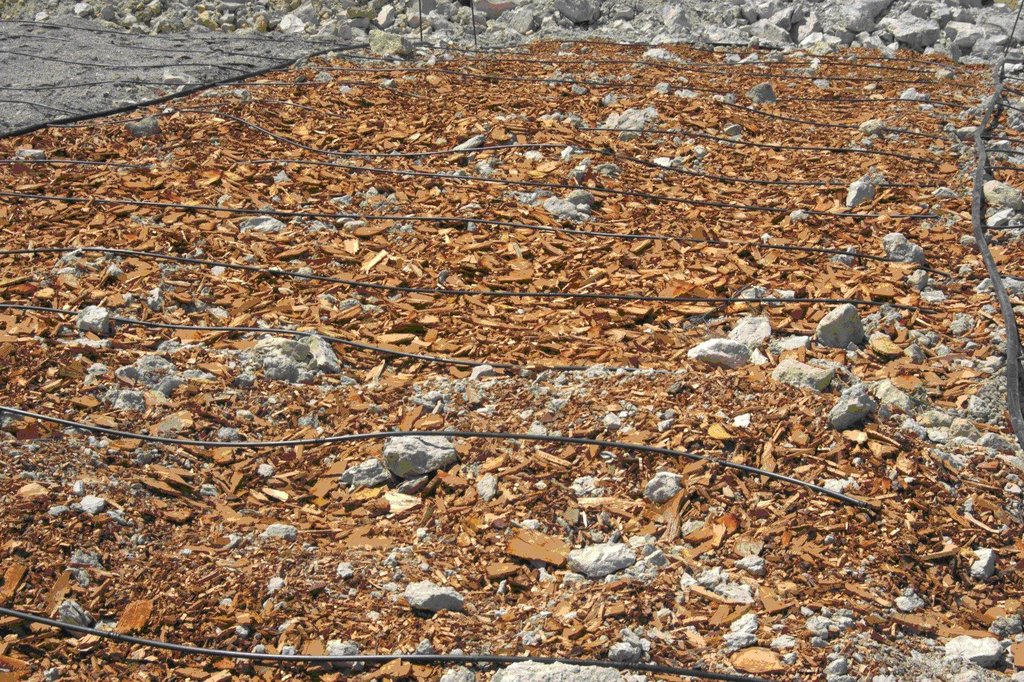
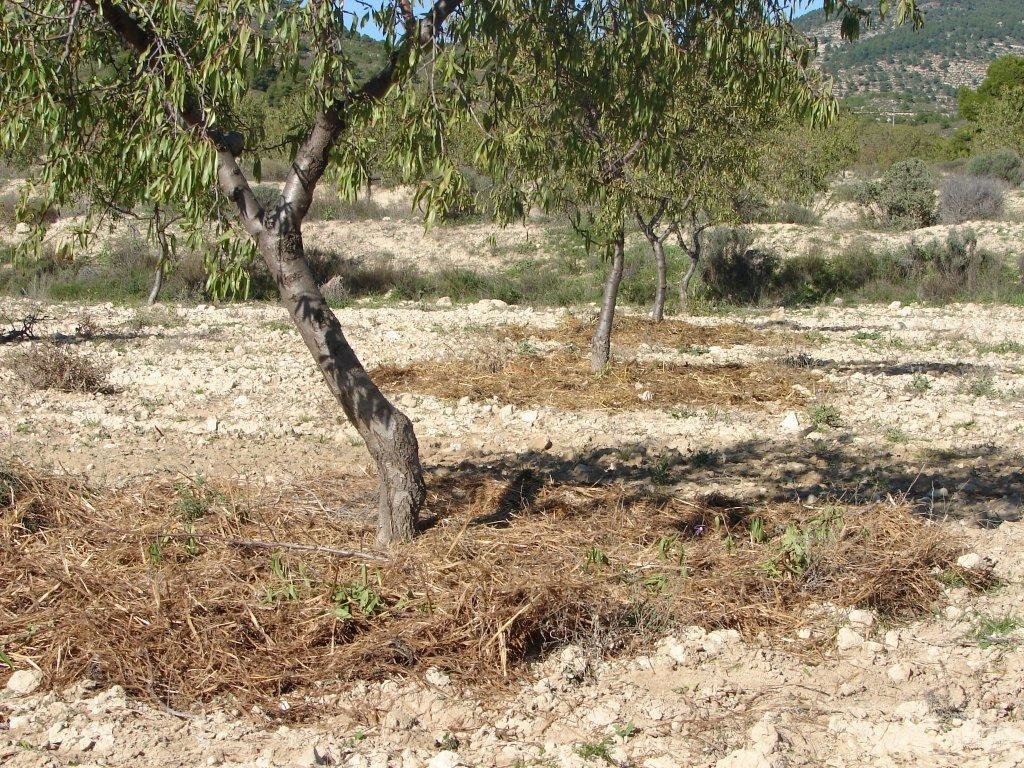
Organic mulch under almond trees [Spain]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Joris De Vente
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Alexandra Gavilano, Fabian Ottiger
Acolchados orgánicos en campos de almendro (ES)
technologies_1109 - Spain
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
Ibáñez Torres Ascensión
Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
EEZA-CSIC (EEZA-CSIC) - Spain1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Regional rural development programme [Spain]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Compiler: Joris De Vente
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Organic mulching to protect against rain-splash, sheet wash and rill formation, reduce evaporation losses and weed growth.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Organic mulch is applied in Almond fields to provide a permanent surface cover that protects the soil against soil erosion, reduces evaporation and limits the growth of weeds. This makes that less ploughing is needed under Almond trees that are normally ploughed 3-5 times per year if no mulch cover is present. The material used for mulching can be diverse. Most feasible are straw or bark and wood chips from pruning residues from almonds and forest species (mostly pines). Alternatively, alpha-grass can be used as mulch. Mulch can best be applied late spring or early summer in order to maintain soil humidity of spring rainfall. Mulch should come mixed and homogenised. It is spread around trees by a mechanical spade or by the arm of a caterpillar. A layer of maximum 3-5 cm of mulch should be applied for economical reasons.
Purpose of the Technology: The ultimate goal of organic mulching under almond trees is to maintain soil water through a reduced evaporation and reduce soil loss by erosion. A mulch covers reduces soil erosion by 1) reducing raindrop impact, 2) increasing water infiltration, 3) increasing surface storage, 4) decreasing runoff velocity, 5) improving soil structure and porosity, and 6) improving the biological activity in the soil. Mulching prevents off-site effects of erosion like flooding, damage to infrastructure and siltation of water reservoirs, while maintaining or slightly increasing crop productivity. The mulch results in a higher soil roughness, a better infiltration of water into the soil, and so also in a reduced runoff. The mulch also has a favorable effect on soil quality since the organic material of the mulch will slowly decompose and provide nutrients to the soil. The decomposing part of the organic mulch will increase aggregation and soil structure through the production of organic compounds (e.g. humic acids). The reduced necessity for ploughing of the Almond fields will result in less fuel use and labour as well as reduced emission of CO2. In addition, the mulch cover prevents weeds to grow and so less competition from weeds will occur and less herbicides are needed.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of mulching depends on the material used for mulching. Given its availability, the easiest is the use of pruning residue from Almond trees. Almonds are pruned in autumn, and residue can be chopped and applied directly or stored in the field until early spring. Residues are chopped and spread around the tree stem and if enough material is available between tree stems. Alternatively, and depending on availability, pruning residue of pine trees or alpha-grass can be used. Pine tree residue should come from nearby forest stands and need to be chopped just like the almond pruning residue in spring. Litter from the forest floor should not be used as this will cause damage to the forest. Alpha-grass is very common in the region and should be harvested in winter in the fields surrounding the cultivated area without destroying the plant allowing it to regenerate. The alpha-grass does not need to be chopped and can be put around the tree stem of the almond trees.
Natural / human environment: The technology is feasible for soils of shallow to medium depth (between 20-60 cm), and with gentle to moderate slope gradients (2 - 8%). The climate is semi-arid with a mean annual rainfall around 300 mm. Droughts, centred in summer commonly last for more than 4-5 months. Annual potential evapotranspiration rates larger than 1000 mm are common. The production system is highly mechanised and market oriented but depends strongly on agricultural subsidies. All cropland is privately owned.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Spain
Region/ State/ Province:
Murcia
Further specification of location:
Guadalentin catchment
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Mulching is a well-known technique. However, until now not widely applied under semi-arid conditions without irrigation. With irrigation, plastic mulch is widely applied.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- tree nuts (brazil nuts, pistachio, walnuts, almonds, etc.)

Grazing land

Forest/ woodlands
Type of tree:
- Pinus species (pine)
Comments:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): A lack of water availability seriously limits the production potential of the soil and results in a low vegetation/crop cover. The relatively high soil erosion rates cause various off-site related problems (i.e. flooding, reservoir siltation) and on-site problems (i.e. gully formation and loss of soil depth).
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Lack of water for irrigation of crops limiting the crop types that can be planted as well as the crop yield of dryland farming.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 Water supply
other (e.g. post-flooding):
- all three
Comments:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
Comments:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wo: offsite degradation effects

physical soil deterioration
- Pk: slaking and crusting

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
Comments:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pk: sealing and crusting, Ha: aridification
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Almond fields often have a very low surface cover by vegetation during long periods of the year, due to frequent ploughing, leaving the soil unprotected against raindrop impact and rill or gully forma), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Reduced infiltration capacity causing runoff and soil erosion), poverty / wealth (Alternative and more profitable labour sources are a permanent risk of land abandonment that can lead to degradation.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (High intensity erosive rainfall is common), droughts (Dry periods and dry years require higher water availability)
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Photo of how the mulch should be divided under the tree stems. If enough material is available, a continuous cover without bare surfaces between trees is recommended.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Knowledge on the type of material used for mulch is essential)
Technical knowledge required for land users: low (The application in the field is simple)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase in organic matter
Mulching
Material/ species: organic material (almond pruning, pine chips, alpha-grass)
Quantity/ density: max 3-5 cm
Author:
Joris de Vente
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of per (to cut pruning residue) |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Per (to cut pruning residue) | piece | 1.0 | 4761.0 | 4761.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 4761.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 4761.0 | |||||
Comments:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
Life span of the per: 10 years. Number of parties sharing: 2
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cut alpha-grass (optional) | winter |
| 2. | apply mulch of alpha-grass, almond and pine tree pruning residue | early spring or autumn after almond pruning |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Cut alpha-grass (optional) | person/days | 4.0 | 95.25 | 381.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | apply mulch of alpha-grass, almond and pine tree pruning residue | person/days | 4.0 | 10.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Machine use | person/days | 0.5 | 88.0 | 44.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | Mulch | tons/ha | 15.0 | 55.53333 | 833.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 1298.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 1298.0 | |||||
Comments:
Machinery/ tools: Tractor and chopper to chop the almond pruning residue.
The original price of the chopper is estimated at $4761. In calculations it is assumed that the chopper is shared between at least two farmers, and with an average farm size of 10 ha, which gives a price of $238/ha establishment costs. Calculations include the cutting of alpha-grass to apply this as mulch in addition to the chopped almond and pine tree residue. Excluding the alpha-grass as a mulch reduces the total maintenance cost to 650. Leaving out also the chopped pine tree residue and using only the chopped almond pruning residue reduces maintenance costs to $44. The costs were indicated assuming a distance of 7 meter between almond trees and a mulch cover around each tree of 3*3 meters. Prices are for spring 2008.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Labour for cutting alpha grass, and the price of the mulch are most determining factors of the costs. Almond prunings are free of charge (except for costs to chop them), but will not provide enough mulch. Chopped Pine pruning or straw mulch are relatively expensive.
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Thermal climate class: subtropics
Thermal climate class: temperate. The higher parts are generally somewhat colder
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Traditionally most agriculture is done by men in this region.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
15% of the land users are rich and own 20% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 75% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 5% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is no difference in the ones who apply the technology and those who don’t. Most farmers do have an off-farm income for example from hunting, work in a factory, or office.
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
Comments:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha, 100-500 ha
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- state
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
Comments:
Most land is privately owned. Some shrubland or forest is state property. Water use is organised by permits to water extraction from aquifers on individual basis. Water rights are provided and controlled by the Water authority of the Segura river basin (CHS).
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Water availability and quality
demand for irrigation water
Income and costs
expenses on agricultural inputs
farm income
Socio-cultural impacts
SLM/ land degradation knowledge
conflict mitigation
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quality
surface runoff
excess water drainage
evaporation
Soil
soil moisture
soil cover
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
animal diversity
beneficial species
Climate and disaster risk reduction
emission of carbon and greenhouse gases
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
downstream flooding
downstream siltation
groundwater/ river pollution
buffering/ filtering capacity
wind transported sediments
damage on neighbours' fields
damage on public/ private infrastructure
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
Comments:
Mulch is relatively expensive and so implies an additional cost.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
Comments:
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: There is not so much awareness, and most farmers are afraid of possible costs of mulching and don’t count on increased crop yield.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
|
A good surface cover throughout the year provides good protection against erosion and helps reducing number of tillage operations and expenses How can they be sustained / enhanced? no suggestions |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
|
The main advantage is that a good surface cover is obtained below almonds that traditionally are characterised by a very poor surface cover during the whole year. The mulch will reduce evaporation and prevent erosion to take place. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cheapest type of mulch should be identified (alpha grass, chopped pruning residues, …). |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The price of the mulch | Look for alternative low cost materials |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| The price of the mulch and/or the price of carrying it to the field | Look for alternative low cost materials, the nearest to the plots as possible. |
| Once the mulch in situ, any tillage operation would incorporate it to the soil, reducing part of its initial benefit; if the mulch is green (alpha grass) it would depress soil N levels upon decomposition, though it would increase SOM in the medium-long term | Avoid tillage in mulched areas |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Smets, T., Poesen, J. and Knapen, A., 2008. Spatial scale effects on the effectiveness of organic mulches in reducing soil erosion by water. Earth-Science Reviews, 89(1-2): 1-12.
Available from where? Costs?
Internet
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Verdu and Mas 2007. Mulching as an alternative technique for weed management in mandarin orchard tree rows. AGRONOMY FOR SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT. 27(4): 367-375
Available from where? Costs?
Internet
Title, author, year, ISBN:
http://www.isahispana.com/
Available from where? Costs?
Internet
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Mellouli, H.J., van Wesemael, B., Poesen, J. and Hartmann, R., 2000. Evaporation losses from bare soils as influenced by cultivation techniques in semi-arid regions. Agricultural Water Management, 42(3): 355-369.
Available from where? Costs?
Internet
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Regional rural development programme [Spain]
Regional development programme to protect natural resources and stimulate rural economies.
- Compiler: Joris De Vente
Modules
No modules