Microtranque para la recolección de agua lluvia [Chile]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Meliza González Cáceres
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1689 - Chile
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
SLM specialist:
Gallardo Rojas Alexis
Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María
Chile
SLM specialist:
Gallardo Aravena Iván
Universidad Técnica Federico Santa María
Chile
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Construcción de un microtranque para la cosecha de aguas y su utilización en el riego de los cultivos.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
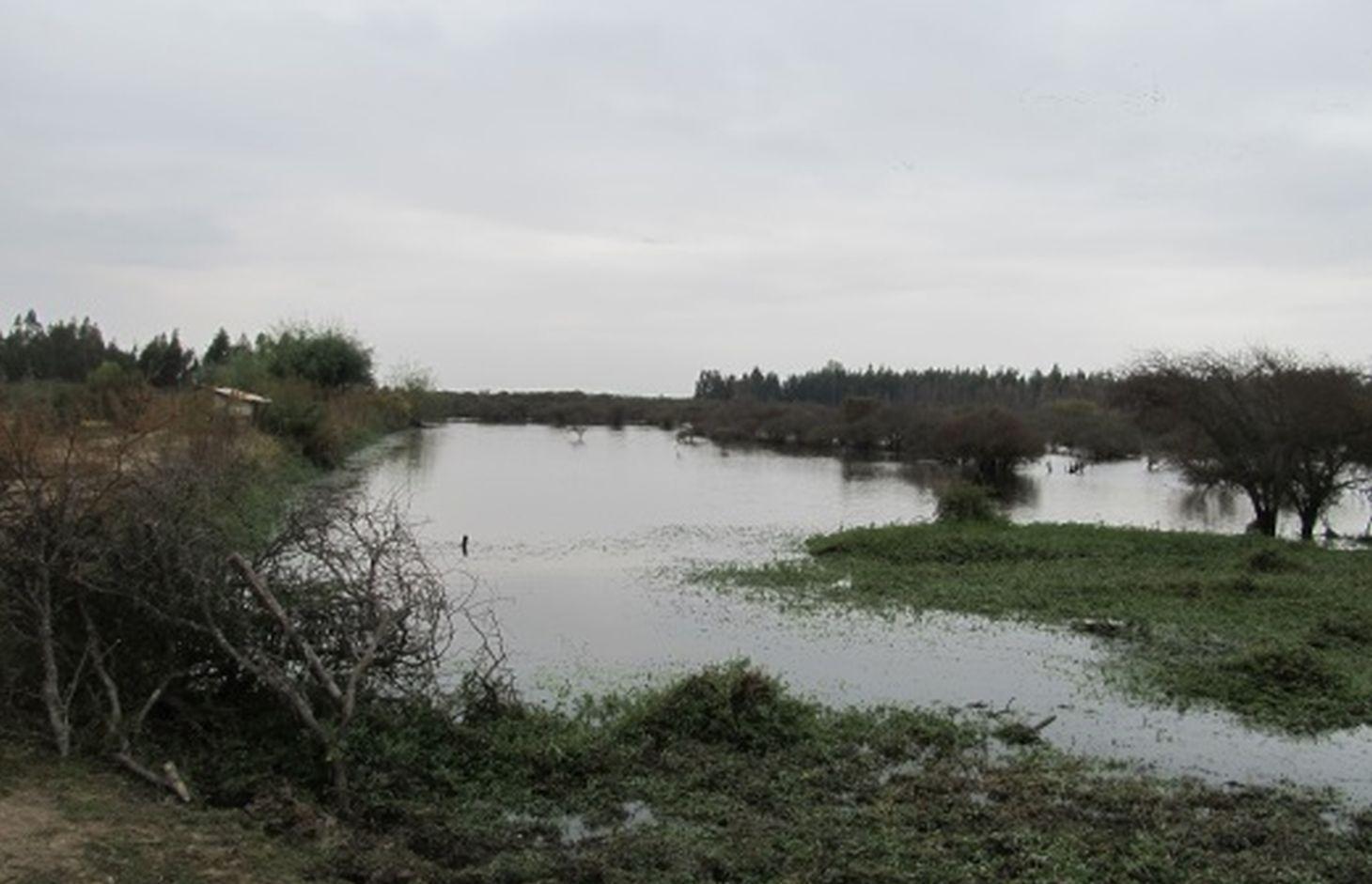
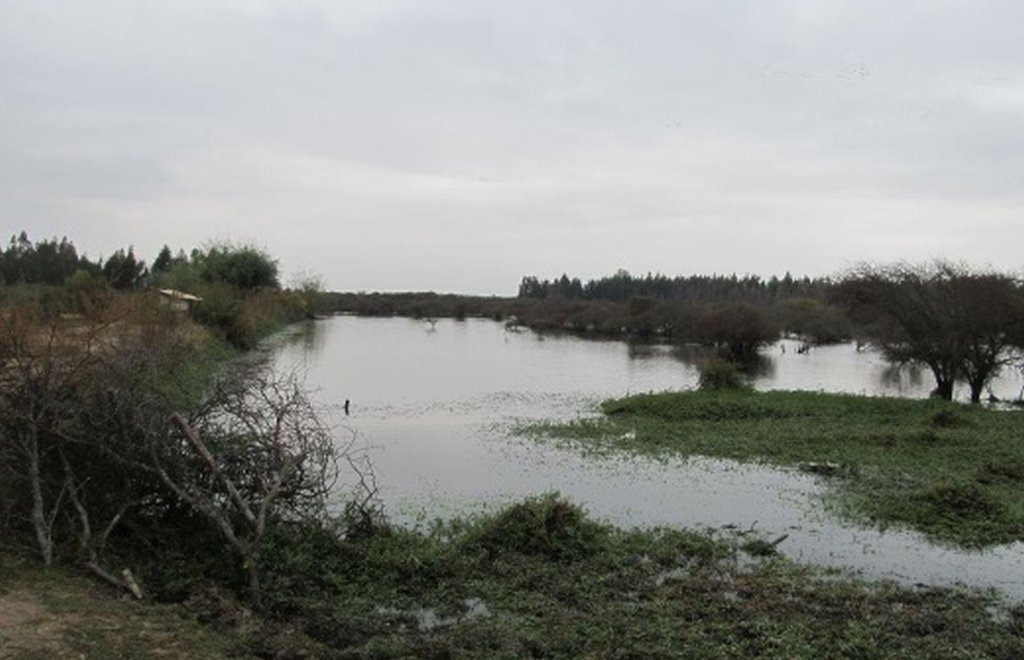
Construcción de un muro de tierra compactado para acumular agua lluvias y aguas provenientes de derrames de un predio ubicado aguas arriba. La topografía del terreno es perfectamente adecuada para la construcción de este tipo de obra. Inicialmente, se levantó un muro de mediana dimensión y el canal de riego, buscando seguir la pendiente necesaria para trasladar el agua desde el tranque hasta el cultivo. La siguiente etapa consistió en la ampliación del tranque, levantando el muro de tierra en la parte más profunda, a seis metros, utilizando maquinaria.
Se planea, a futuro, expandir el largo del muro para aumentar la capacidad de captación y almacenamiento del tranque.
Se debe cuidar que el agua no rebase los muros, debido a que la obra se destruiría, por lo que existe un rebalse especial que permite evacuar el agua hacia zonas de poca importancia en caso de que sea necesario, pudiendo requerirse el uso de maquinaria menor. Al contrario, si el nivel del agua disminuye, puede ser necesario usar motobombas para extraer el agua del fondo del estanque y llevarlo hacia los cultivos.
Propósito de la tecnología: El objetivo es cosechar aguas lluvias y aguas proveniente de derrames de predios agua arriba para poder utilizarla en el riego del cultivo de arroz, ante un escenario de creciente escasez de agua.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Chile
Region/ State/ Province:
VII Región del Maule / Retiro
Further specification of location:
Bureo
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If precise area is not known, indicate approximate area covered:
- 0.1-1 km2
Comments:
0.6 - 1 km2
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through land users' innovation
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- fodder crops - other
- trigo, arroz
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- berries
- espárragos
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1

Waterways, waterbodies, wetlands
- Ponds, dams
Comments:
Problemas principales del uso de tierra: Cambio de los caudales de las aguas subterráneas
Los cultivos agrícolas principales annuales son arroz, trigo, espárragos, frambuesas, berries y pastizales en menor medida.
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- mixed rainfed-irrigated
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- water harvesting
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S5: Dams, pans, ponds
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

water degradation
- Hg: change in groundwater/aquifer level
Comments:
Causas principales de degradación: sequías
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Microtranque de productor individual. Las fotos muestran, de izquierda a derecha, la zona de inundación de mayor profundidad y la salida del agua hacia canales de riego, la ubicación de la motobomba usado para extraer agua de bajo nivel, la zona de rebalse y finalmente el muro de contención de aguas lluvias.
Lugar: Bureo. Retiro
Fecha: 2013-05-04
Conocimientos técnicos necesarios para el personal / asesores de campo: medio (conocimiento sobre maquinaria adecuada y momentos críticos donde se necesite evacuar el estanque para prevenir el derrumbe del muro de tierra.)
Conocimientos técnicos necesarios para los usuarios de la tierra: medio (Se requiere conocimiento para operar maquinaria, eventualmente, y para identificar escenarios en que se requiera evacuar caudal del estanque para prevenir el derrumbe del muro de contención.)
Principales funciones técnicas: captura de agua / incremento en el abastecimiento de agua
Presa / charco / estanque
Profundidad de zanjas / pozos / presas (m): 6
Ancho de zanjas / hoyos / presas (m): 100
Longitud de zanjas / pozos / presas (m): 100
Especificación de presas / cacerolas / estanques: Capacity 60000m3
Author:
Alexis Gallardo, Ivan Gallardo
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
other/ national currency (specify):
CLP
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
476.2
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Estudio topográfico | Inicio |
| 2. | Obra gruesa | Inicio |
| 3. | Construcción canal de riego | Inicio |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Mano de obra | 1.0 | 1050.0 | 1050.0 | 5.0 | |
| Equipment | Uso de máquina | 1.0 | 2730.0 | 2730.0 | 5.0 | |
| Other | Subcontrat. estud. topográfico | 1.0 | 420.0 | 420.0 | 5.0 | |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 4200.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 8.82 | |||||
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
temperado
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- low (<1%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
poor/ none
Water quality (untreated):
for agricultural use only (irrigation)
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- animal traction
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
Densidad de población: 10-50 personas/km2
Crecimiento anual de población: negative
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, not titled
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- individual
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
product diversity
production area
Socio-cultural impacts
Contribución al bienestar humano
Comments/ specify:
Mejora de la cantidad y calidad del agua disponible.
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
water quantity
harvesting/ collection of water
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | well |
| local windstorm | well |
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | not well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| general (river) flood | not well |
Comments:
Sí, fue modicada para ser más tolerante al cambio climático en los últimos 10 años. Inicialmente, se construyó una pared sin estudios previos, siguiendo la forma de la cuenca, con el fin de atrapar aguas de lluvia. Dado el resultado de éste, se decide invertir en una obra de mayor envergadura que comprende 50 ha de inundación para lograr mantener cultivos productivos en la zona, favoreciendo, a su vez, la diversidad animal existente, como la presencia de patos silvestres y ganado. Esto fue logrado con financiamiento público (95% de INDAP, correspondiente a USD 2992.44) puesto que se requirió principalmente de horas/máquina.
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Mejor disponibilidad de agua en cantidad y calidad. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Mejora el manejo de los caudales. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Diseños deficitarios. | Mayor dedicación y experiencia por parte de los programas de financiamiento para el riego. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
- interviews with land users
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
18/08/2014
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
FAO (2014). Sistematización de Prácticas de Conservación de Suelos y Aguas para la Adaptación al Cambio Climático. Metodología basada en WOCAT para América Latina y el Caribe.
Available from where? Costs?
http://www.fao.org/3/a-i3741s/index.html
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules