Почво-охранные пруды для предотвращения овраго-образования [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Daler Domullojonov
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Farrukh Nazarmavloev, Alexandra Gavilano
Ҳавзҳои ҷамъоварии оби борон барои пешгирии селроҳаҳо
technologies_3418 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Key resource person(s)
SLM specialist:
1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Почвоохранный пруд - технология больбы с оврагообразованием
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
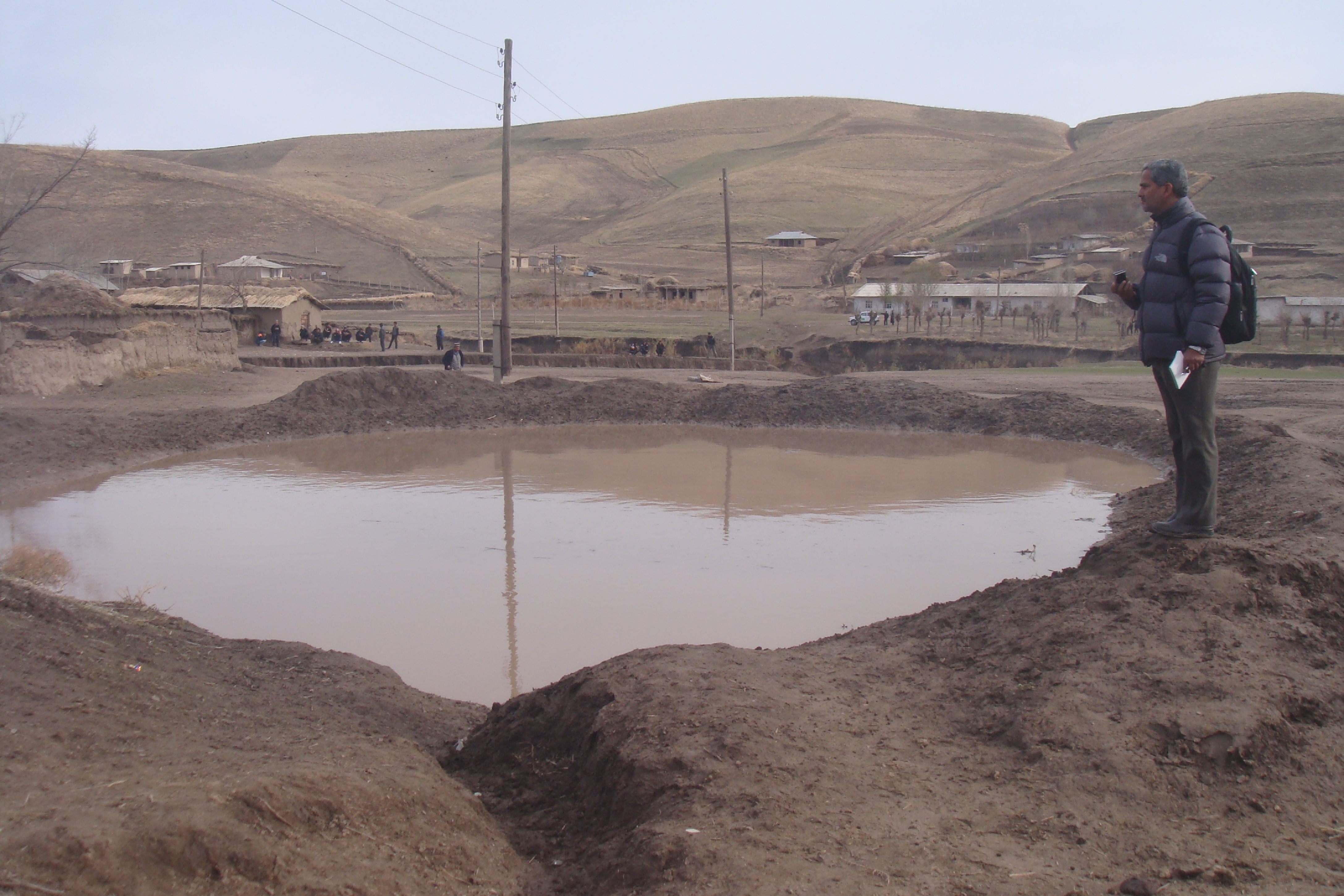
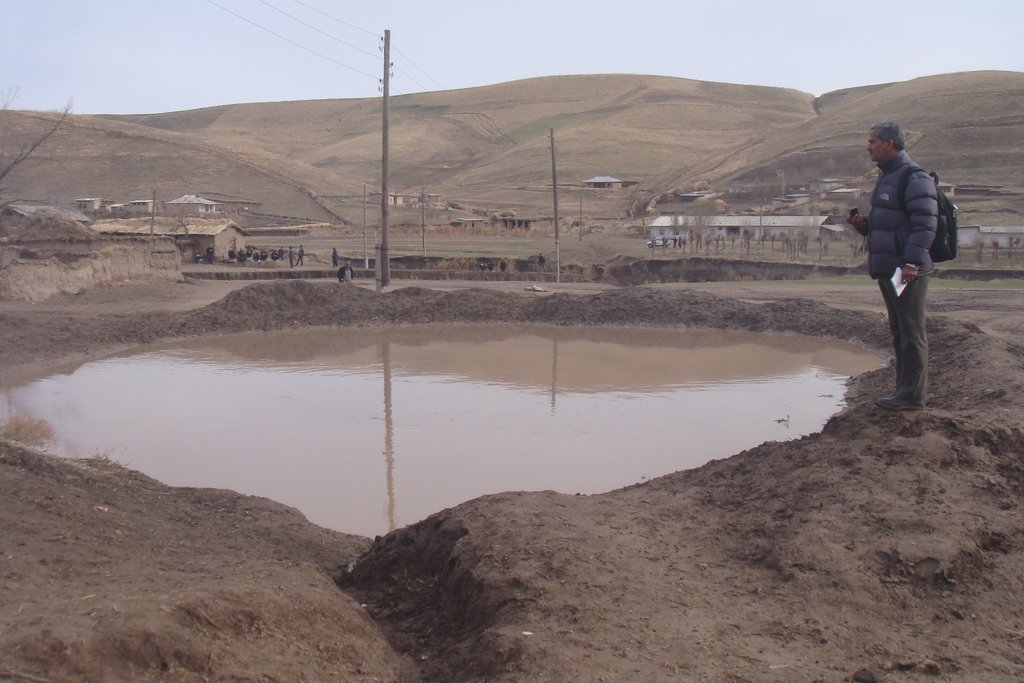
Почвоохранные пруды применялась в юго-восточной части Хатлонской области в частности в Темурмаликском, Балджуванском и Ховалингском районах, в адырно-низкогорном недостаточно увлажненном районе зимних пастбищ, полуобеспеченной богары и среднегорном увлажненном районе. Годовые осадки составляют в адырно-низкогорном районе 380 – 650 мм и в среднегорном увлажненном районе до 1000 мм. Около 80-90% атмосферных осадков в этих районах сосредоточены в осенне-весенний период. В сочетании с сложным рельефом местности, чрезмерным выпасом скота, вырубкой лесонасаждений и ведением хозяйствования на склоновых землях очень часто сосредоточенные талые или дождевые воды являются причиной появления оврагов. Которые смывают плодородный слой почвы и становятся причиной появления оползней.
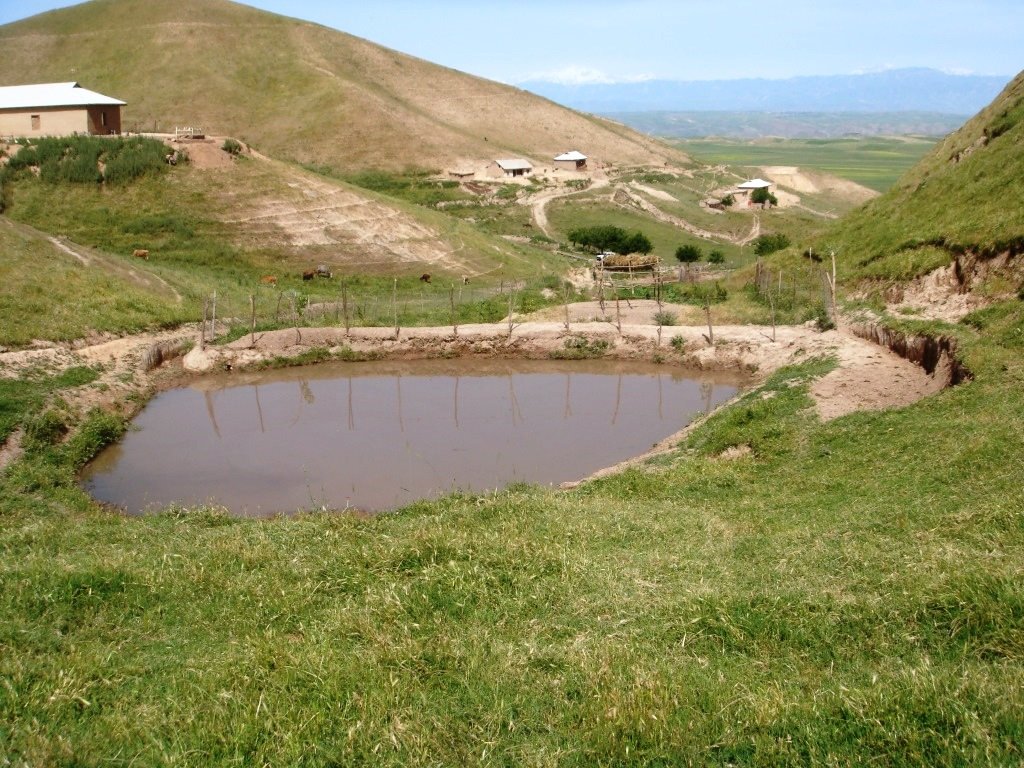
Почвоохранный пруд – это земляное сооружение выполнено в полвыемки и полнасыпи в форме полумесяца на безопасных участках вдоль оврагов. Эти пруды являются одним из разновидностей технологий биоинженерии и сооружаются с целью рассредоточения талых и дождевых вод, которые сосредоточенны в оврагах, предотвращения появления и расширения оврагов, сбора дождевой воды и последующего использования для скота или орошения. Для укрепления части полнасыпи сажаются различные лесонасаждения и обносятся ограждением для предотвращения от съедения животными. Пруды имеют входной канал и аварийный водозброс для предотвращения перелива через края и смыва. Пруды воздвигаются в ручную и с помощью бульдозеров с объемом до 1000 м3 в зависимости от метеорологических свойств местности и гидрогеологических свойств почв. Каскад почвоохранны прудов как правило сооружают в различных безопасных участках вдоль оврагов сверху вниз по течения.
Целью технологии является путем распределения сосредоточенных вод предотвратить появление / расширение оврагов и оползней на слоновых землях. Технология сравнительно недорогая, но требует очистки от наносов раз в года в зависимости от уровня заиления и покрытия почвенного покрова в верховьях. Технология фильтрует воду из прудов сверху вниз по течению в различных местах вдоль оврагов и благоприятствует увлажнению грунта, что способствует развития садоводства и виноградарства в предгорных районах.
Технология нравится пользователям из за простоты установки, способствует появлению дополнительного источника воды для животных на пастбищах и относительно невысокой стоимостью.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
районы Ховалинг, Балджувон и Темурмалик, Хатлонская область
Further specification of location:
23 села
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Comments:
Технология была распространена в 42 селах расположенных в предгорной зоне
Почвоохранные пруды были сооружают в различных безопасных участках вдоль оврагов сверху вниз по течения. Сосредоточенная вода в оврагах рассредоточивалась и фильтровалась, тем самым уменьшая риск стихийных бедствий
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2009
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- less than 10 years ago (recently)
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- during experiments/ research
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
В рамках проекта были завлечены группа местных и международных экспертов и на основании опыта других стран было разработана стратегия внедрения технологии.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- reduce risk of disasters
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Unproductive land
Specify:
Маргинальные склоновые земли и пастбища
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- cross-slope measure
- ecosystem-based disaster risk reduction
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

structural measures
- S5: Dams, pans, ponds
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
- Wm: mass movements/ landslides
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- reduce land degradation
Comments:
Почвоохранные пруды предотвращают появления и расширения оврагов
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
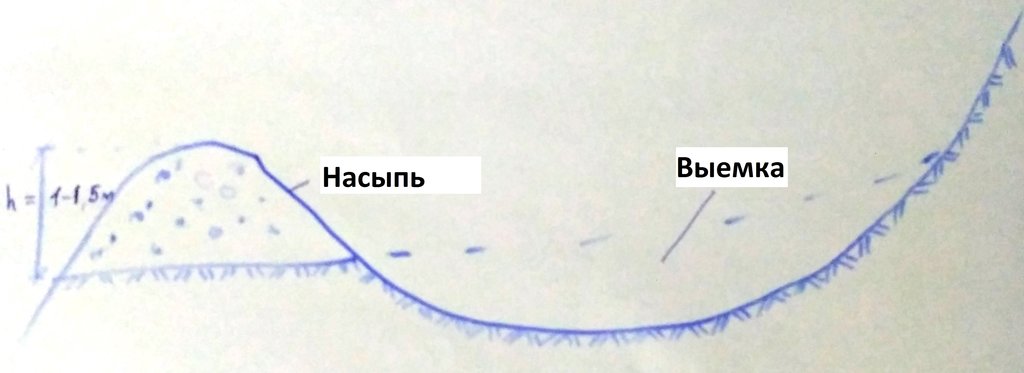
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Почвоохранный пруд выполняется в полвыемки и полнасыпи в форме полумесяца на безопасных участках вдоль оврагов. Высота насыпи может составлять максимум 1,5 м. Для придания устойчивости насыпная часть трамбуется, а для предотвращения смыва устанавливается аварийный сброс. В целях безопасности размер и уклон аварийного сброса устанавливают идентично или больше подводящего канала. Объем пруда может составлять до 1000 м3 в зависимости от характеристик почвы и мер безопасности. Количество прудов и их объем определяется путем определения максимального количества воды в водосборном бассейну, то есть общую площадь водозаборного бассейна умножают на максимальные осадки. Расстояние от одного пруда до следующего определяется по рельефу местности и нормам безопасности.
Author:
Домуллоджанов Далер
Date:
25/02/2018
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Почвоохранный пруд
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
объемом 300 м3
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
8.8
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
50
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Выемка грунта и трамбовка насыпи | 2 дня перед наступлением сезона дождей |
| 2. | Ручная выемка и разработка грунта | 2 дня |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Оплата труда тракториста | человека день | 2.0 | 200.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| Labour | Ручная выемка и разработка грунта | человека день | 20.0 | 50.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| Construction material | ГСМ | литр | 300.0 | 5.0 | 1500.0 | 30.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 2900.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 329.55 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
проект
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
| Activity | Timing/ frequency | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Очистка пруда | перед наступлением сезона дождей |
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Ручная очистка пруда | чел. день | 10.0 | 50.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology | 500.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 56.82 | |||||
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Инфляция и сезонность
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specify average annual rainfall (if known), in mm:
550.00
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
От 300-500 мм в год в Темурмалике, до 700 мм в Бальджуване и до 1100 мм в Ховалинге
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
п. Советский, Темурмаликский район и Ховалинг
Agro-climatic zone
- arid
аридная зона с резко континантальным климатом
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Почвоохранный пруд размещают на побочене для предотвращения подмывов
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- low
Habitat diversity:
- low
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- subsistence (self-supply)
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
- > 50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- poor
- average
Individuals or groups:
- groups/ community
Level of mechanization:
- animal traction
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- women
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- elderly
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- group
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- leased
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
- individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
harvesting/ collection of water
Quantity before SLM:
-2
Quantity after SLM:
3
Comments/ specify:
Почвоохранный пруды размещенные на притоках оврагов значительно уменьшают количество дождевой и талой воды в оврагах тем самым уменьшают смывающую силу потока воды
Soil
soil cover
Quantity before SLM:
-2
Quantity after SLM:
2
Comments/ specify:
Смыв почвенного покрова значительно уменьшилось. Часть смывающей плодородной почвы оседает в прудах
Climate and disaster risk reduction
landslides/ debris flows
Quantity before SLM:
-2
Quantity after SLM:
2
Comments/ specify:
Так как почвоохранный пруды размещенные на притоках оврагов и значительная часть воды собирается и фильтруется верхней части, то селевые потоки уменьшаются в нижней части
micro-climate
Quantity before SLM:
-3
Quantity after SLM:
1
Comments/ specify:
Почвоохранный пруды размещенные на притоках оврагов фильтруя воду верхней части и запасая влагу создают благоприятные условия для развития садоводства и хозяйствования в предгорной зоне и смягчают микроклимат
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
water availability
Quantity before SLM:
-3
Quantity after SLM:
2
Comments/ specify:
Местные жители вниз по течению используют воду из колодцев. Если раньше вода пересыхала в концу весны, то после использования технологии вода доступна и в засушливые годы.
damage on neighbours' fields
Quantity before SLM:
-2
Quantity after SLM:
2
Comments/ specify:
Почвоохранный пруды размещенные вверх по течению и на притоках оврагов значительно уменьшили смывание полей и нанесение ущерба прилегающим вниз по течению полям
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | very well |
| local hailstorm | well |
Hydrological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| flash flood | very well |
| landslide | not well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
very positive
Long-term returns:
very positive
Comments:
Установив пруды в начале, необходимо их очищать для поддержания технологии. Расходы по поддержанию являются незначительными.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
If available, quantify (no. of households and/ or area covered):
Технология использована в 23 селах и на примере этих сел дополнительно 2 села и 1 фермерское хозяйство переняли идею и установили пруды.
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
2 села и 1 фермерское хозяйство использовали эту технологию по своей инициативе и за свой счет
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Невысокая стоимость |
| Использование местных материалов |
| Многофункциональность (снижение риска стихийных бедствий, предотвращение оврагообразования, вода для ската и улучшение микроклимата) |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Простота в использовании |
| Невысокая стоимость ремонта |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Быстрое заполнение наносами | Более частая очистка |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| При недостаточной трамбовке есть риск смыва пруда | качественная трамбовка при строительстве и проведение регулярного мониторинга |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
опрошены около 10 землепользователей
- compilation from reports and other existing documentation
использованы технические и описательные отчеты
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules