Накопления осадков методом Барер ( бардюрования) на склоновых междуряди виноградников и садов в условиях богары [Tajikistan]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Rustam Kalandarov
- Editor: –
- Reviewer: Farrukh Nazarmavloev
Пешбанд кардани байни каторхои токзорхо ва дарахтони мевадеханда барои нигохдории самти об дар шароитхои заминхои лалми.
technologies_3657 - Tajikistan
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
SLM specialist:
Хусейнов Хасан
907 59 02 52
нет
Дехканская хозяйство "Хасан"
район Рудаки, дж. Руохати. кишлак Рохати.
Tajikistan
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Environmental Land Management and Rural Livelihoods (ELMAR)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Youth Ecological Centre Tajikistan (Youth Ecological Centre Tajikistan) - Tajikistan1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
06/03/2018
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
технология проблемы деградации не вызывает является природосберегающем.
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Влагоудержание путём бардюрования междурядий на склоновых участках при уклонах от З 0 до 10 % проводится для влагонакопления.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
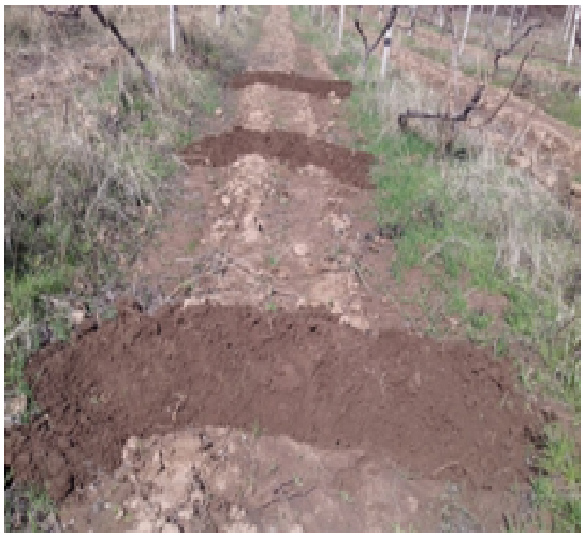
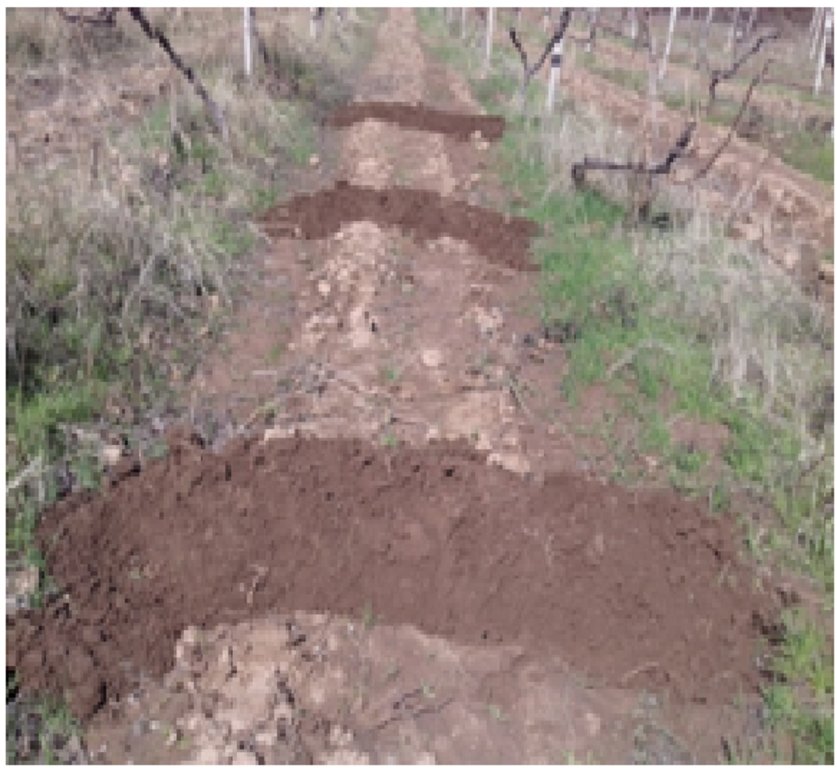
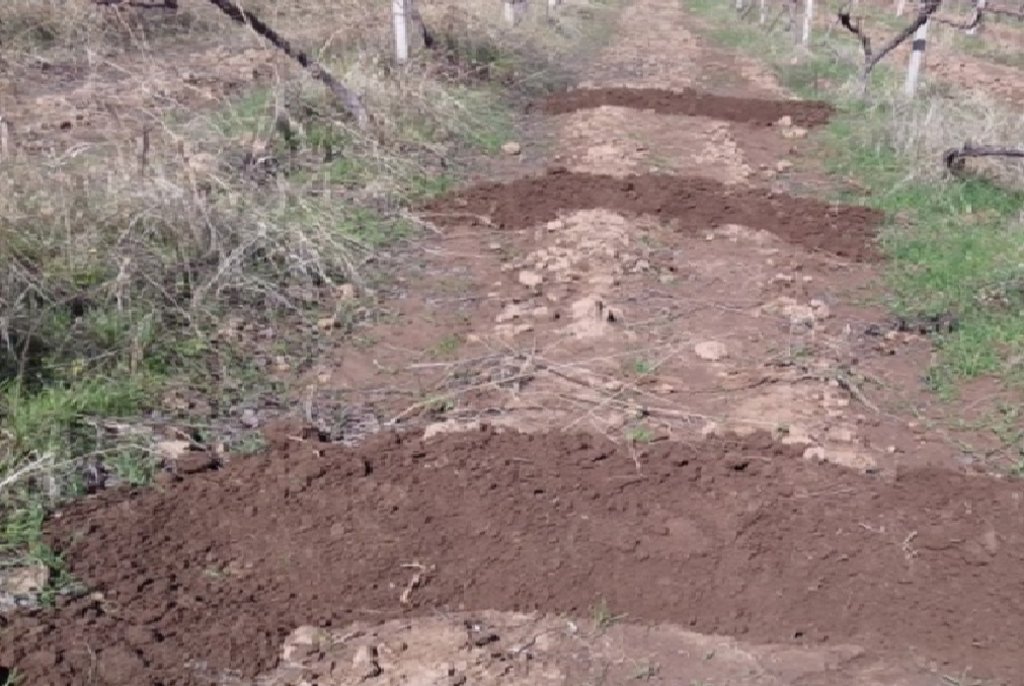
Тежнология применяется в условиях богарных виноградников и садов на склоновых землях джамоата Рохати, в селе Рохати, районе Рудаки в дехканских и других хозяйствах региона на богарных условиях. Технология применялась в основном на богарных землях, на высоте 1100 м. над уровнем моря. Сезонные осадки впадают осенью, зимой и весной, В последние годы осадков выпадает мало, около 500 мм. Богарные земли в Таджикистане расположены в горной и предгорной зоне. Богарные считаются земли расположенные на высотах от 950 до 1600 м над уровня моря где там где выпадают природные осадки в сумме от 500 до 750 мм, считается обеспеченной богарной. В Таджикистане в настоящее время около 16 тыс. бгарные земль и в дальнейшем их площадь будет возрастает. В последнее время на богарных землях осадков выпадает меньше за счет изменения климата. Применяется технология там, где деятельность землепользователи и в своих хозяйствах в основном занимаются садоводством,, виноградарством и скотоводством. Виноградники находятся в основном на пологах , склонах где осадков задерживается мало в основном они текают. Земле пользователи, у которых виноградники находятся на склонах, проводили совместно с учеными научные эксперименты бороздование междурядий, где были получены харошие результаты. На склонах с бороздованием в почве накапливалась влага, которая составляла в мае когда прекращались осадки 12- 14 % продуктивной влаги, которая сохранялось до созревания урожая, а на контроле без бардюрования продуктивная влага составлял 7 - 8%. После эксперимента земле пользователи использовали этод метод. Технология заключается в том, что бардюрование (бороздование) проводится в междурядах садов и виноградников ручным способом на склонах. Бардюрование проводилось через каждые 2 - 3 метра в зависимости от крутизны склона. Если склон от 6 до 8 С0 можно заложить бардюр через каждые 3 м. на склонах от 8 до 10С0 через каждые 2 м поднимают стену бордюра. Основная мероприятия проводятся осенью или рано весной, проводится бордюрование междурядий ручным способом, до начала выпадения осадков. . Бордюр поднимают высотой 50 - 60 см от земли, чтобы они задерживали осадки. После прикращения осадков в конце май месяцап все бардюры выравниваются для тракторам проводения ят молования трактором и сохранения влаги. Основная цель технологии путем бардюрования (бороздования) междурядий виноградников и садов задержание осадков (дождь, снег), что позволит предотвратить протекания воды и промывания почвы, предотвращает эрозию почв. Эта технодогия одновременно задерживает влагу зшишает почву от эрозии, смывания плодородный части почвы. Местным фермерам и дехканам это способ нравится, они регулярно проводят эти мероприятия. Преимущество в том что на склонных участках с бороздованием о накапливается больше влаги и можно получить хороший и качественный урожай. Обычны м методом молования или фрезерования после прекращения осадок только на равнинных местах накапливается влага, на склонах же она не задерживается, В связи с этим использование этой технологии на таких склонных участках будет очень приемлемым.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
на фотографии приведено рисунка как можно провести бардюр для задержание осадков и хранения на склоновых участок виноградников..
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Tajikistan
Region/ State/ Province:
Район Рудаки дж. Рохати, кишлк Рохати.
Further specification of location:
Район Рудаки, Дж.Рохати. кишлак Рохати.
Comments:
Участок находится на восточной части района Рудаки кишлак Рохати . Виноградные участки
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- as part of a traditional system (> 50 years)
- during experiments/ research
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Технология применяется уже несколько десяток лет даёт хорошие результаты по урожаюи по природохранение типа как эрозия почвы.
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied

Cropland
- Tree and shrub cropping
Main crops (cash and food crops):
Основным культурой является виноград.
Comments:
Культура винограда является многолетним доходлевый.
3.3 Further information about land use
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
Comments:
Данная технология выращивается на богарных условиях земледелия.
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
3.4 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- minimal soil disturbance
- cross-slope measure
- water harvesting
3.5 Spread of the Technology
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- evenly spread over an area
If the Technology is evenly spread over an area, indicate approximate area covered:
- < 0.1 km2 (10 ha)
Comments:
Технология применяется на склонных участок где повышает от 3 до 12 градусов уклона.
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A4: Subsurface treatment

structural measures
- S4: Level ditches, pits
Comments:
Мероприятия с использованием многолетних культур плодовые и виноград на богарных землях.
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion

water degradation
- Ha: aridification
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- reduce land degradation
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
4.2 Technical specifications/ explanations of technical drawing
На рисунке приведено схема размещения борозды междурядьях виноградного участки склоно от 6 до 9 градусов уклона. борозды размещены через 2 м и 3м по уклону где можно сохранить осадки.
4.3 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
от 5 до 10 га
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- US Dollars
Indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (if relevant): 1 USD =:
8.9
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
3 доллар США
4.4 Establishment activities
| Activity | Type of measure | Timing | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Проведения междурядовая вспашка на глубину почвы 40-45 см. | Agronomic | осень - весна |
| 2. | бардюрования (бороздования) междурядами на склонах ручным способом | Structural | Ранно весной. |
| 3. | конец весны проведения закрытие влаги молования почвы специальными плугам. | Agronomic | конец весны |
Comments:
Основным важным работой является во время проводить вспашку и делать борозды
4.5 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
If possible, break down the costs of establishment according to the following table, specifying inputs and costs per input. If you are unable to break down the costs, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
-1.0
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Наемные рабочие | чел | 3.0 | 3.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | Кетмень | шт | 3.0 | 3.5 | 10.5 | 100.0 |
| Other | Итог | 279.0 | 100.0 | |||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 19.5 | |||||
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
Землепользователем
Comments:
Все затраты производятся владельцем .
4.6 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
Comments:
Основная работа по сохранению влаги бороздования производится после осене - зимный вспашка земли под виноградниками и садов.
4.8 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
Человекский ручной труд
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Specifications/ comments on rainfall:
В зависимости от осенне зимне и весе ной осадками.
Indicate the name of the reference meteorological station considered:
Метеостансия ГМС Душанбе.
Agro-climatic zone
- semi-arid
Климат в основном зашушливая иногда зависит от годовой осадки.
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- concave situations
Comments and further specifications on topography:
Виноградники выращивается в разных пологах и закат и равнина крутые склоны богарных земель. Технология отмечено на высоте 1110 м. над ур. моря.
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
If available, attach full soil description or specify the available information, e.g. soil type, soil PH/ acidity, Cation Exchange Capacity, nitrogen, salinity etc.
Данных нет
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
> 50 m
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
Comments and further specifications on biodiversity:
По видовому разнообразию средняя растут кустарники полу кустарнички плодовые и ягодных культур.
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial
Off-farm income:
- 10-50% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
Indicate other relevant characteristics of the land users:
в основном землепользователем бывает среднего возраста и пожилые.
5.7 Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- medium-scale
Comments:
Хозяйство является среднего размера землепользования так как они является частными владельцами на небольших участках до 5 га земли.
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- company
Land use rights:
- communal (organized)
- leased
Water use rights:
- open access (unorganized)
Comments:
У многих землепользователей земля является частным и арендовано на несколько лет.
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
после применения технологии производства урожая улучшилось.
crop quality
Comments/ specify:
Когда на богарных землях обеспечено будед влагой урожай и качество улучшается на много раз так как технология к этому направлено.
Income and costs
farm income
Ecological impacts
Soil
soil moisture
Comments/ specify:
После применения почвенное влажность на склонах улучшилось
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
После применения технологии почвенный покров улучшилось.
soil crusting/ sealing
Comments/ specify:
образование корки на почве уменьшилось.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
Биоразнообразия после накопления влаги возрастало.
plant diversity
Comments/ specify:
растительность увеличился за счет накопления влаги.
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
damage on neighbours' fields
Comments/ specify:
Смыв почвы сократилось.
Comments regarding impact assessment:
Поскольку богарная земля только за счет осадков растет растительность . При этой технологии в основном сокращается смыв почвы эрозия. Накапливается где барер больше влаги.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | Type of climatic change/ extreme | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| annual temperature | increase | well | |
| seasonal temperature | winter | increase | well |
| annual rainfall | decrease | well | |
| seasonal rainfall | winter | decrease | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Meteorological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| local rainstorm | not well |
Other climate-related consequences
Other climate-related consequences
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| reduced growing period | well |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
Comments:
Получаемые результаты и расходы по подержанию технологии краткосрочного и долгосрочного является позитивным.
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 10-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many have did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
Comments:
Любой лиц может принимат технологию без никаких ограничения.
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Основан только для накопления влаги и сохранения растительности эрозию почвы от смыва осадки. |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Основан только для накопления влаги и сохранения растительность и эрозию почвы от смыва осадков. |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Каждый год проводится бардюрования. |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Каждый год проводится бардюрования. |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
Число опрощенных 4 землепользователя.
- interviews with land users
одного землепользователья.
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
"Возделования винограда на богарных землях Таджикистана". Савченко А.Д. Бродниковский М.И. Каландаров Р.Ю. 1989г.
Available from where? Costs?
0.2 цент доллар США
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules