Caldo Sulfocalcico [Nicaragua]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Fredys Paguaga
- Editor: –
- Reviewers: Johanna Jacobi, Alexandra Gavilano
Caldo Sulfocalcico
technologies_4584 - Nicaragua
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Para el mandato de backstopping para le programa gestion comunitaria de la cuenca de Rio Dipilto en Nicaragua (Gestion comunitaria - Nicaragua)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Ministerio del Ambiente y los Recursos Naturales - Nicaragua (MARENA) - NicaraguaName of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (DEZA / COSUDE / DDC / SDC) - Switzerland1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
El caldo sulfocalcico es una mezcla de azufre y cal, utilizado para prevenir las enfermedades causadas por hongos en las plantas. El caldo bordelés que contiene cobre y cal también previene las enfermedades en el cultivo de plantas frutales.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
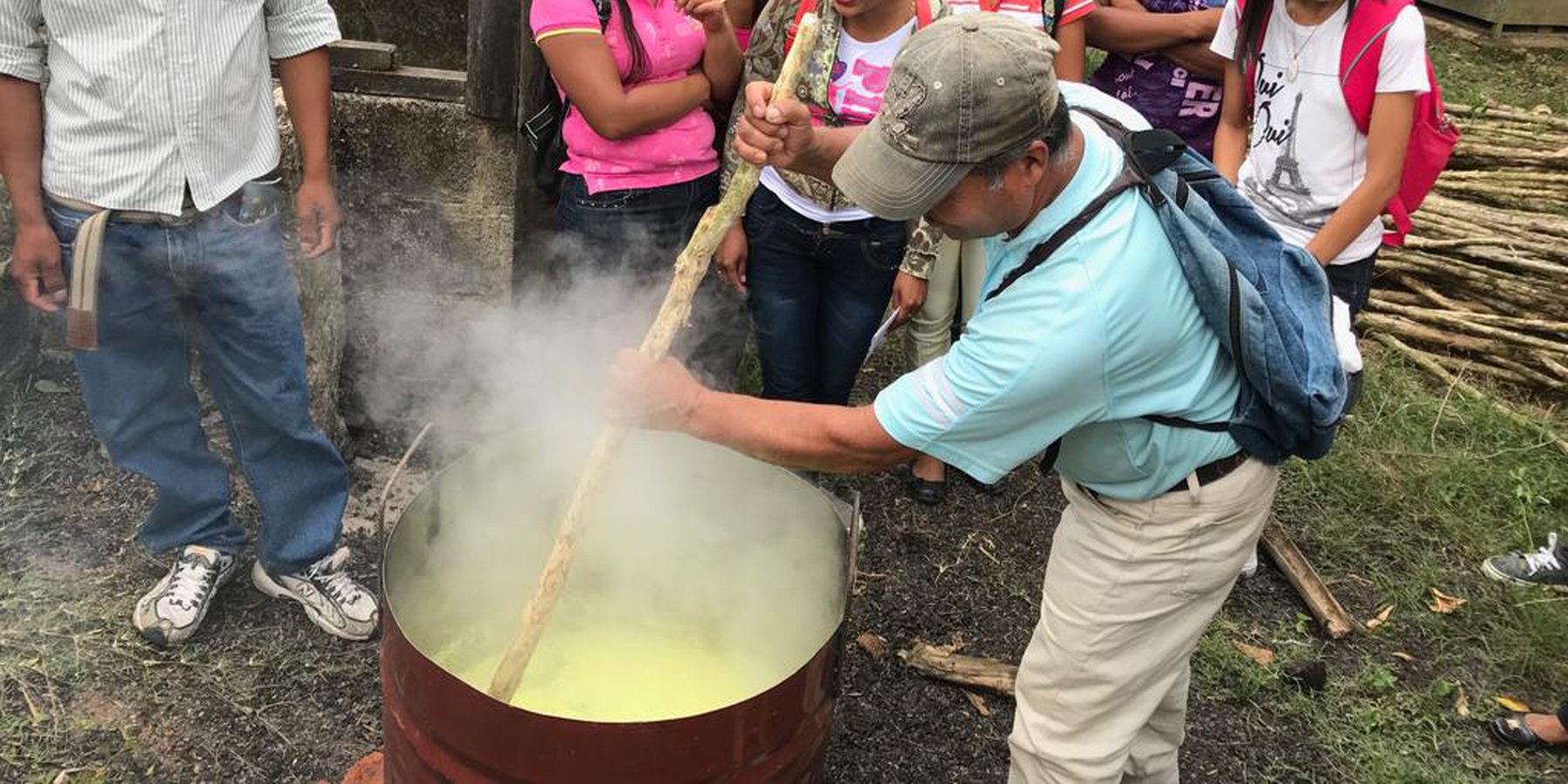
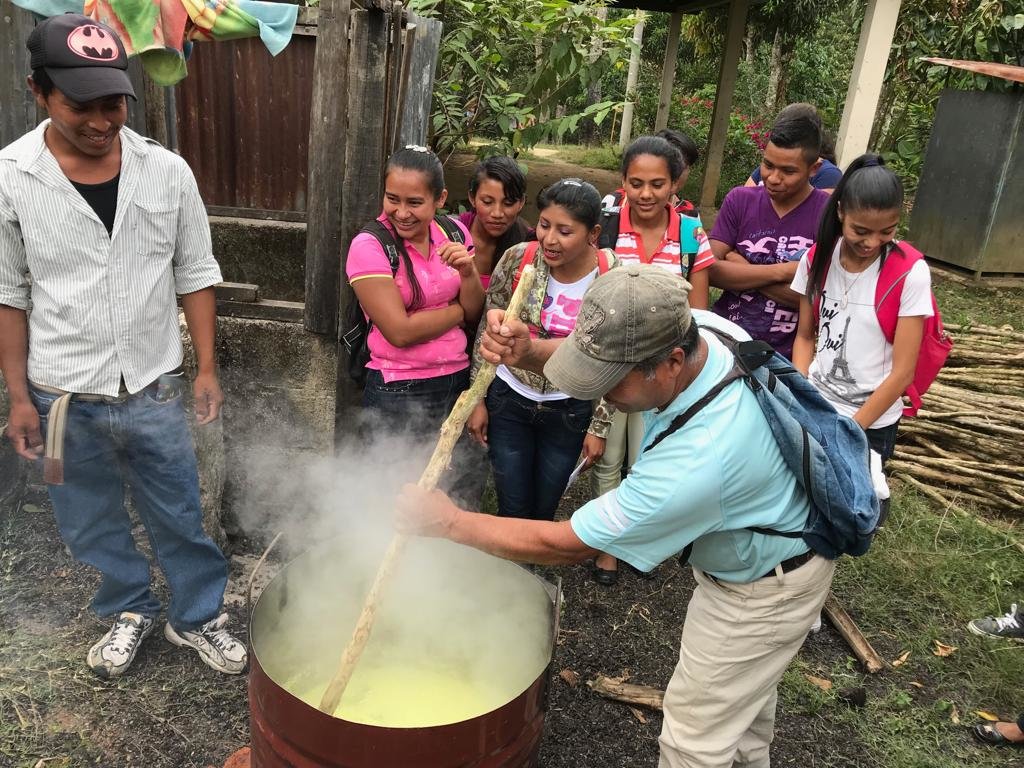
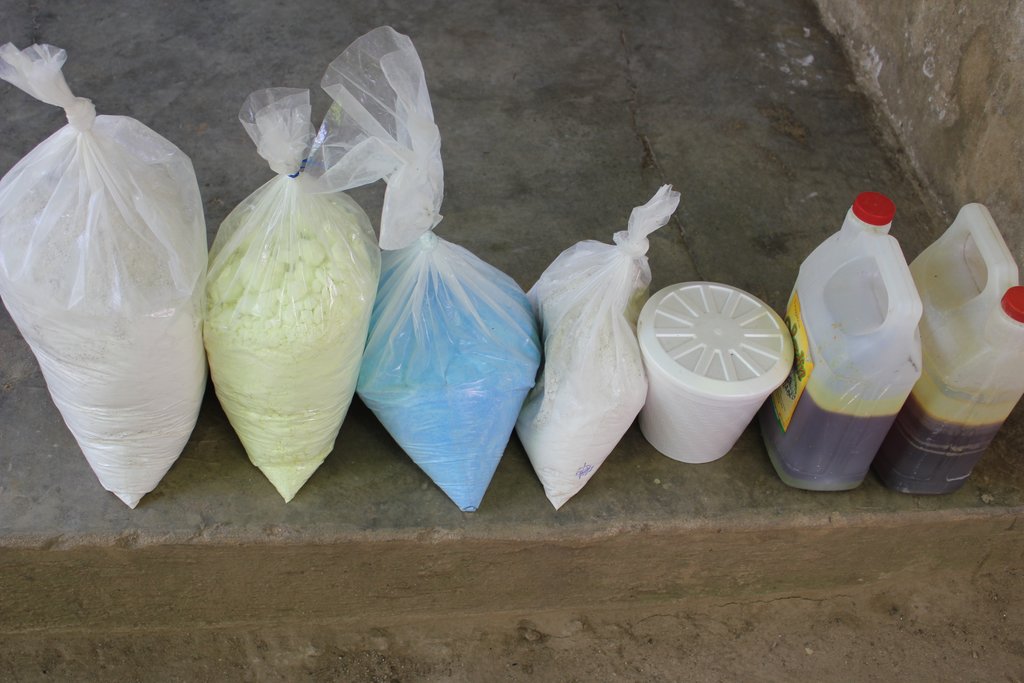
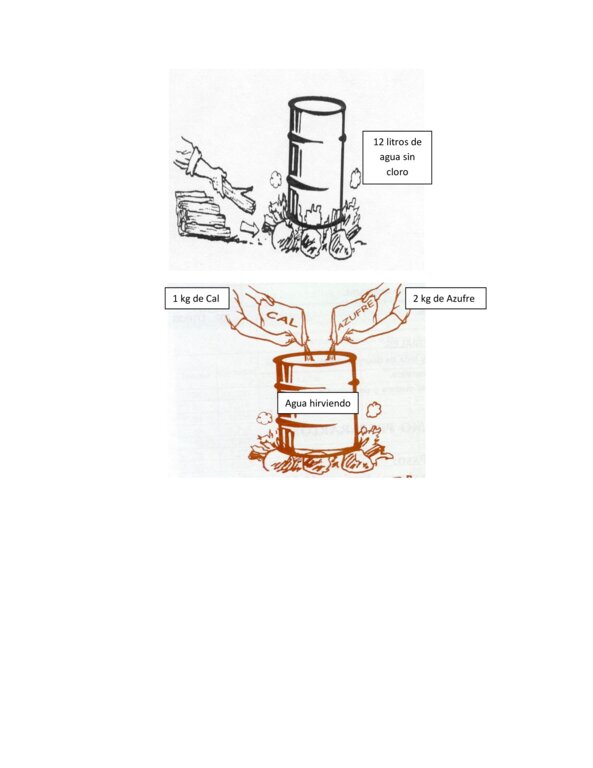
El caldo sulfocalcico se elabora en medio barril metálico con 2 kilogramo de azufre y 1 kilogramo de cal en 12 litros de agua, 5 rajas de leña para mantener encendido el fogón y de esta manera hacer hervir el agua, una ves que el agua este hirviendo depositar el azufre y la cal al mismo tiempo, esto se hace en agua herviendo ya que el azufre no es soluble en agua a temperatura ambiente, esta preparación se realiza removiendo constantemente hasta lograr diluir todo lo solido que se forma en el agua hirviendo y el punto es cuando toma un color rojizo, se deja enfriar y se guarda en botellas preferiblemente de color oscuro, no se debe guardar por mas de tres meses. El caldo sulfocalcico es un producto que ayuda en la prevención de las enfermedades causadas por hongos en los cultivos de: café, arboles frutales y hortalizas, así mismo permite la incorporación de nutrientes al suelo que ayudan a mejorar el proceso de floración y frutificación de las plantas. Se requiere para la elaboración del sulfocalcico azufre, cal, medio barril metálico, para hacer el cocimiento ademas de botellas plásticas de color oscuro para preservar y dar un adecuado almacenamiento.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
General remarks regarding photos:
Demostración practica de la elaboración de caldo sulfocalcico. Para guardar el caldo, se recomienda un recipiente de color oscuro. En la imagen se ve también el cobre para el caldo Bordelés (ver technologia aparte)
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Nicaragua
Region/ State/ Province:
Nueva Segovia
Further specification of location:
Dipilto
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
Yes
If yes, specify:
Cuenca del Río Dipilto, Área de Amortiguamiento del Área Protegida Serranías Dipilto y Jalapa
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
Indicate year of implementation:
2017
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
Specify how the Technology was introduced:
- through projects/ external interventions
Comments (type of project, etc.):
Programa de Gestion Comunitaria de la Cuenca Rio Dipilto
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- improve production
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- adapt to climate change/ extremes and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry

Cropland
- Annual cropping
- Perennial (non-woody) cropping
- Tree and shrub cropping
Perennial (non-woody) cropping - Specify crops:
- banana/plantain/abaca
Tree and shrub cropping - Specify crops:
- coffee, shade grown
- citrus
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Specify:
Algunos cultivos como las Musáceas se cosechan todo el año
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
Cultivo de Cafe asociado con musáceas, cultivo de cafe asociado con cítricos, cultivo de cafe asociado con arboles forestales de las especies guaba, bucaro y maderables como el cedro
Is crop rotation practiced?
No
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- No (Continue with question 3.4)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
Yes
Specify mixed land use (crops/ grazing/ trees):
- Agroforestry
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- agroforestry
- integrated pest and disease management (incl. organic agriculture)
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover

vegetative measures
- V1: Tree and shrub cover
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- not applicable
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Caldo sulfocalcico
Author:
Fredys Paguaga
Date:
21/03/2019
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology unit
Specify unit:
Cuenca Rio Dipilto
Specify dimensions of unit (if relevant):
97 Kilómetros cuadrados
If relevant, indicate exchange rate from USD to local currency (e.g. 1 USD = 79.9 Brazilian Real): 1 USD =:
32.6
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
C$ 150.00 ciento cincueta cordobas por dia de trabajo
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Caldo Sulfocalcico se pone a hervir 12 litros de agua en un fogon y cuando el agua esta hirviendo se le hecha el azufre y la cal y se remueve hasta lograr el color rojizo y se deja enfriar para guardarlo la dosis a utilizar es de 200 a 500 ml por bomba de 20 litros de agua | En un mismo día se prepara la mezcla |
| 2. | Caldo bordelés se hace en dos baldes plásticos con agua a temperatura ambiente y los baldes se llenan hasta la mitad y se le agraga le cobre en un balde y en el otro la cal se remueve y se hace la mezcla echando el cobre sobre la cal la dosis a utilizar es de 8 onzas por bomba de cobre y 8 onzas de cal y se puede aplicar el mismo día y si no fuera posible guardarlo por no mas de 12 horas | La aplicacion del producto se hace antes y despues de la floracion del cultivo y que es abortivo en periodo de floracion |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Labour | Azufre y cal | Kg | 1.0 | 2032.0 | 2032.0 | |
| Labour | Cobre y cal | Kg | 1.0 | 1197.0 | 1197.0 | |
| Equipment | Medio Barril metalico | |||||
| Equipment | Bomba de mochila | |||||
| Equipment | Baldes Plásticos | |||||
| Equipment | Bomba de mochila | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 3229.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 99.05 | |||||
If you are unable to break down the costs in the table above, give an estimation of the total costs of establishing the Technology:
3229.0
If land user bore less than 100% of costs, indicate who covered the remaining costs:
El Programa de Gestion Comunitaria de la Cuenca del Rio Dipilto
Comments:
El azufre no esta disponible en la localidad por la poca demanda
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
on surface
Availability of surface water:
good
Water quality (untreated):
good drinking water
Water quality refers to:
surface water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- medium
Habitat diversity:
- medium
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- mixed (subsistence/ commercial)
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- average
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- manual work
Gender:
- women
Age of land users:
- youth
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- small-scale
- medium-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Yes
Specify:
Escritura Publica y privada
Comments:
Derechos de uso de la tierra de manera Individual
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
slightly positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 11-50%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 0-10%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Es una tecnologia muy barata, de fácil aplicación, no contamina y previene enfermedades en los cultivos |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Mejora las propiedades físicas del suelo ya que se incorporan los minerales al mismo |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| La disponibilidad del producto en el mercado local sobre todo el azufre | |
| Requiere de mano de obra para la preparacion | |
| La dosificación incorrecta del producto, puede causar toxicidad en el suelo |
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Requiere de un plan de aplicación del producto, para obtener buenos resultados en los cultivos | |
| La falta de apropiación de la tecnología en los demás miembros de la familia y trabajadores responsables de las unidades de producción |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
3
- interviews with land users
4
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
21/03/2019
Comments:
Se realizo una entrevista directa a una mujer usuaria de la tierra
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
Agricultura orgánica Jairo Restrepo
URL:
wwwagriculturaorganica
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks
No links
Modules
No modules