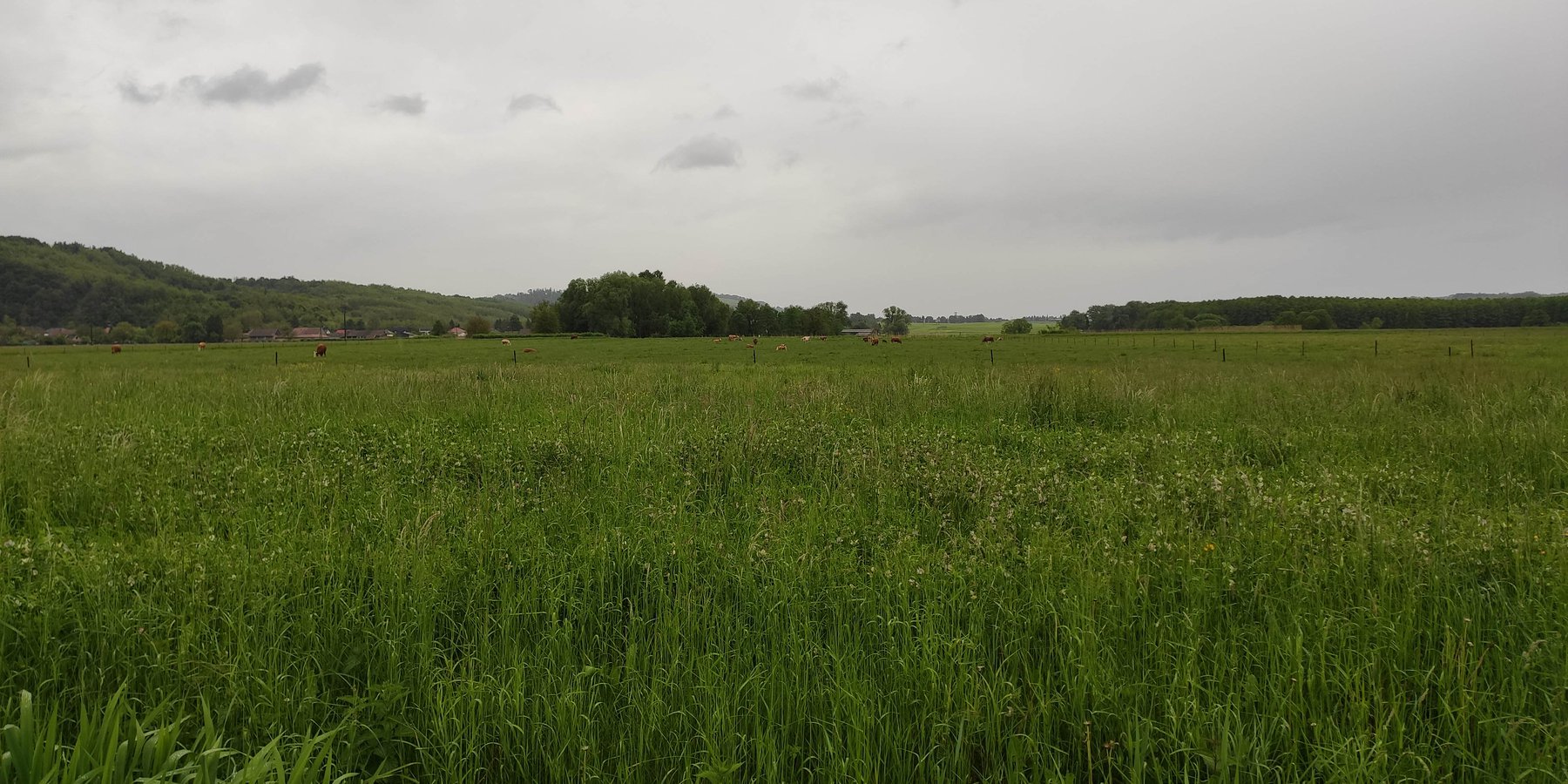
Meadows and pastures [Hungary]
- Creation:
- Update:
- Compiler: Brigitta Szabó
- Editors: Piroska Kassai, Zoltan Toth
- Reviewers: William Critchley, Rima Mekdaschi Studer
Rétek és legelők
technologies_6195 - Hungary
View sections
Expand all Collapse all1. General information
1.2 Contact details of resource persons and institutions involved in the assessment and documentation of the Technology
Name of project which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
OPtimal strategies to retAIN and re-use water and nutrients in small agricultural catchments across different soil-climatic regions in Europe (OPTAIN)Name of the institution(s) which facilitated the documentation/ evaluation of the Technology (if relevant)
Institute for Soil Sciences, Centre for Agricultural Research (ATK TAKI) - Hungary1.3 Conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT
The compiler and key resource person(s) accept the conditions regarding the use of data documented through WOCAT:
Yes
1.4 Declaration on sustainability of the described Technology
Is the Technology described here problematic with regard to land degradation, so that it cannot be declared a sustainable land management technology?
No
Comments:
Permanent grass is more suitable for conserving soil than arable cropping
1.5 Reference to Questionnaire(s) on SLM Approaches (documented using WOCAT)

Sustainable livestock and pasture management [Tajikistan]
Sustainable livestock and pasture management is implemented through creating Pasture Users Unions (PUU) which design and implement pasture and livestock management plans.
- Compiler: Kamolidin Abdulloev
2. Description of the SLM Technology
2.1 Short description of the Technology
Definition of the Technology:
Permanent meadows or pastures are more effective in controlling land degradation than arable cropping. They are especially appropriate in hilly regions on sloping land where the risk of water erosion is high.
2.2 Detailed description of the Technology
Description:
Permanent meadows and pastures are more effective in controlling land degradation than arable cropping. They are especially appropriate in hilly regions on sloping land where the risk of water erosion is high. This is a relevant technology also for valley floors where there is a regular inflow of water – resulting in sediment accumulation. Such grass cover has relevance also in plantations on sloping land.
There are some differences between pastures and meadows especially in their vegetation and land use. In general, meadows have a variety of natural growing plant species while pastures are often planted with specific types of grasses. Pastures are generally used for grazing animals while meadows are often mowed or harvested for hay (that is also often used for animal feed). Meadows may also be situated along streams or rivers on lowland areas, while pastures are typically situated on hilly regions.
Some of the most common grass species in Hungarian meadows are: meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis), smooth meadow-grass (Poa pratensis), and meadow foxtail (Alopecurus pratensis). Wildflowers (e.g Oxeye daisy, Field scabious) are also often growing on natural meadows in Hungary. On pastures the most common grass species are: ryegrass (Lolium perenne), tall fescue (Festuca arundinacea), and meadow fescue (Festuca pratensis). Hungarian pastures may also include legumes, such as red clover (Trifolium pratense) or white clover (Trifolium repens), which can help fix nitrogen in the soil and improve forage quality for grazing animals.
In the case of pastures farmers generally use a rotational grazing system, where the pasture is divided into sections and animals are periodically moved between them. Properly timed resting periods and regular rotation of pastures are essential for protecting the soil from erosion, promoting plant growth and nutrient uptake, and ensuring the long-term health and productivity of the pastures.
The main purpose of the technology (meadow and pasture land use) is to provide feed for livestock while reducing soil erosion and improving trafficability. The main conservation benefits are protection of the soil surface against transportation of particles by water or wind, thus avoiding soil loss and sedimentation. Due to lower velocity of surface runoff, more time is provided for infiltration of water into the soil, resulting in better water retention. In terms of production, meadows and pastures are predominantly used for providing hay or grazing land for ruminants. Different animals graze land differently, so the risk of soil degradation is lower in the case of cattle (which leave taller grass) and higher in case of sheep (which graze down to the soil surface), while in case of goats or pigs, the soil surface is easily damaged. In some special cases the main purpose of grass cover is simply soil conservation (very steep slopes, gully, etc.).
A significant proportion of grasslands (meadows and pastures) in Hungary are permanent, and they play an important role in agricultural production and the preservation of rural landscapes in the country. The common rules regarding the temporary or permanent use of agricultural land for this purposes (pasture or meadow) are contained in the Act CXXIX of 2007. The request for a land use change can be submitted at the local land offices. The most important requirement for land use change is that it must not result in a decrease in the total area of arable land below the minimum threshold set by the authorities and must not result in a decrease in the ecological value of the land. The conversion must be approved by the authorities and the appropriate land use permit must be obtained.
The application trend of this technology/solution is significantly depends on the situation of livestock production of a country. In Hungary, animal husbandry can be mentioned as the driving force of agriculture in the 1980s, with a share of 55-60% of its production value. However, by the end of the 1990s, this proportion had reversed and crop production had predominated. As there is no need for further pastures due to the decrease in livestock population, in recent times this type of land use change is not very common in Hungary.
2.3 Photos of the Technology
2.4 Videos of the Technology
Comments, short description:
video is not available
2.5 Country/ region/ locations where the Technology has been applied and which are covered by this assessment
Country:
Hungary
Region/ State/ Province:
Zala County
Further specification of location:
The case study area is situated within the Balaton Catchment Area in the western Hungary. The climate is moderately warm, moderately humid, the number of sunshine hours per year are high. Mean annual temperature of the region of the Lake Balaton is about 10 ˚C. The average amount of rainfall (600-700 mm / year) nationally means a medium rainfall zone. The Balaton Catchment area is 5765 km2. The main environmental purpose is to reduce pollutant (phosphorus and other plant nutrients) loads of Lake Balaton, where anthropogenic eutrophication is the main issue of environmental concern. Lake Balaton, with its nearly 600 sqkm area, is the largest shallow lake in Middle Europe. The lake as well as the surrounding area form very important natural (ecological, water and landscape) resources and are one of the major target areas of water related recreational tourism in Europe as a whole. 37% of the total catchment area is arable land which is much lower than the national average, 27% is forest, which exceeds the national average. 15% of the land suitable for grassland management, 5% is horticulture, 3% is pomiculture, 2% is viticulture, 1% is reed management and fish farming. The „Kis-Balaton” nature conservation area situated within the Balaton Catchment area. The „Kis-Balaton” wetland is under protection of the Ramsar Convention habitat.
Specify the spread of the Technology:
- applied at specific points/ concentrated on a small area
Is/are the technology site(s) located in a permanently protected area?
No
Map
×2.6 Date of implementation
If precise year is not known, indicate approximate date:
- 10-50 years ago
2.7 Introduction of the Technology
- Upon the initiative of the land user
3. Classification of the SLM Technology
3.1 Main purpose(s) of the Technology
- reduce, prevent, restore land degradation
- conserve ecosystem
- protect a watershed/ downstream areas – in combination with other Technologies
- reduce risk of disasters
- mitigate climate change and its impacts
3.2 Current land use type(s) where the Technology is applied
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
No

Cropland
- Annual cropping
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - barley
- cereals - maize
- cereals - wheat (winter)
- oilseed crops - sunflower, rapeseed, other
Number of growing seasons per year:
- 1
Is intercropping practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify which crops are intercropped:
cover crops are grown between cash crops
Is crop rotation practiced?
Yes
If yes, specify:
oilseed rape - winter weet - maize - spring barley
3.3 Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
Has land use changed due to the implementation of the Technology?
- Yes (Please fill out the questions below with regard to the land use before implementation of the Technology)
Land use mixed within the same land unit:
No

Grazing land
Extensive grazing:
- Ranching
Animal type:
- cattle - non-dairy beef
Is integrated crop-livestock management practiced?
No
Products and services:
- meat
Species:
cattle - non-dairy beef
3.4 Water supply
Water supply for the land on which the Technology is applied:
- rainfed
3.5 SLM group to which the Technology belongs
- pastoralism and grazing land management
3.6 SLM measures comprising the Technology

agronomic measures
- A1: Vegetation/ soil cover
3.7 Main types of land degradation addressed by the Technology

soil erosion by water
- Wt: loss of topsoil/ surface erosion
- Wg: gully erosion/ gullying
3.8 Prevention, reduction, or restoration of land degradation
Specify the goal of the Technology with regard to land degradation:
- prevent land degradation
- restore/ rehabilitate severely degraded land
4. Technical specifications, implementation activities, inputs, and costs
4.1 Technical drawing of the Technology
Technical specifications (related to technical drawing):
Establishment of grassland needs proper soil preparation before sowing. After arable land use weed control is very important on the stubble of the previous crop. Before primary tillage, fertilisation is needed mainly with fertilisers rich in elements that are not easily mobilised in the soil (eg. P and K), since after establishment of the grass cover, no inversion tillage can be carried out. Easily mobilised elements as N can be applied later as top dressing. After broadcasting fertilisers, deep primary tillage, secondary tillage and fine seedbed preparation, then sowing is needed. Sowing depth is shallow (1-2 cm), sowing can be carried out with a cereal grain seeder (12-15 cm inter row spacing), or grain can be evenly broadcasted after a ringed packer covered by a flat packer. Amount of seed: 50-60 kg/ha. For the germination of seeds good water supply is needed.
Author:
Zoltan Toth
Date:
27/10/2022
4.2 General information regarding the calculation of inputs and costs
Specify how costs and inputs were calculated:
- per Technology area
Indicate size and area unit:
ha
Specify currency used for cost calculations:
- USD
Indicate average wage cost of hired labour per day:
50
4.3 Establishment activities
| Activity | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | fertilization | before primary tillage |
| 2. | stubble tillage | |
| 3. | weed control | |
| 4. | primary tillage | |
| 5. | secoundary tillage | |
| 6. | seedbed preparation | |
| 7. | sowing |
4.4 Costs and inputs needed for establishment
| Specify input | Unit | Quantity | Costs per Unit | Total costs per input | % of costs borne by land users | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Equipment | stubble tillage | ha | 1.0 | 33.0 | 33.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | weed control | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | fertilization | ha | 1.0 | 15.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | primary tillage (ploughing 25-30 cm) | ha | 1.0 | 72.0 | 72.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | secoundary tillage (harrow+packer) | ha | 1.0 | 31.0 | 31.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | seedbed preparation | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| Equipment | sowing | ha | 1.0 | 24.0 | 24.0 | 100.0 |
| Plant material | seed (55 kg/ha) | ha | 1.0 | 262.0 | 262.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | fertilizers | ha | 1.0 | 380.0 | 380.0 | 100.0 |
| Fertilizers and biocides | herbicide | ha | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology | 892.0 | |||||
| Total costs for establishment of the Technology in USD | 892.0 | |||||
Comments:
Depending on the measures of the Common Agricultural Policy in the EU, subsidies for grass cover establishment may be claimed.
4.5 Maintenance/ recurrent activities
Comments:
Maintenance of meadow or pastures is the utilisation itself: hay production or grazing. In return there is an income.
4.6 Costs and inputs needed for maintenance/ recurrent activities (per year)
Comments:
Maintenance of meadows or pasture is the utilisation itself: hay production or grazing. In return there is an income.
4.7 Most important factors affecting the costs
Describe the most determinate factors affecting the costs:
prices of input materials (fertilizers, pesticides, fuel)
5. Natural and human environment
5.1 Climate
Annual rainfall
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1,000 mm
- 1,001-1,500 mm
- 1,501-2,000 mm
- 2,001-3,000 mm
- 3,001-4,000 mm
- > 4,000 mm
Agro-climatic zone
- sub-humid
distribution of rainfall is uneven
5.2 Topography
Slopes on average:
- flat (0-2%)
- gentle (3-5%)
- moderate (6-10%)
- rolling (11-15%)
- hilly (16-30%)
- steep (31-60%)
- very steep (>60%)
Landforms:
- plateau/plains
- ridges
- mountain slopes
- hill slopes
- footslopes
- valley floors
Altitudinal zone:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
Indicate if the Technology is specifically applied in:
- not relevant
5.3 Soils
Soil depth on average:
- very shallow (0-20 cm)
- shallow (21-50 cm)
- moderately deep (51-80 cm)
- deep (81-120 cm)
- very deep (> 120 cm)
Soil texture (topsoil):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Soil texture (> 20 cm below surface):
- medium (loamy, silty)
- fine/ heavy (clay)
Topsoil organic matter:
- medium (1-3%)
5.4 Water availability and quality
Ground water table:
5-50 m
Availability of surface water:
medium
Water quality (untreated):
poor drinking water (treatment required)
Water quality refers to:
surface water
Is water salinity a problem?
No
Is flooding of the area occurring?
No
Comments and further specifications on water quality and quantity:
Either drought or heavy rainfalls occur
5.5 Biodiversity
Species diversity:
- high
Habitat diversity:
- high
5.6 Characteristics of land users applying the Technology
Sedentary or nomadic:
- Sedentary
Market orientation of production system:
- commercial/ market
Off-farm income:
- less than 10% of all income
Relative level of wealth:
- rich
Individuals or groups:
- individual/ household
Level of mechanization:
- mechanized/ motorized
Gender:
- men
Age of land users:
- middle-aged
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 ha
- 0.5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1,000 ha
- 1,000-10,000 ha
- > 10,000 ha
Is this considered small-, medium- or large-scale (referring to local context)?
- large-scale
5.8 Land ownership, land use rights, and water use rights
Land ownership:
- individual, titled
Land use rights:
- leased
- individual
Water use rights:
- communal (organized)
Are land use rights based on a traditional legal system?
Yes
5.9 Access to services and infrastructure
health:
- poor
- moderate
- good
education:
- poor
- moderate
- good
technical assistance:
- poor
- moderate
- good
employment (e.g. off-farm):
- poor
- moderate
- good
markets:
- poor
- moderate
- good
energy:
- poor
- moderate
- good
roads and transport:
- poor
- moderate
- good
drinking water and sanitation:
- poor
- moderate
- good
financial services:
- poor
- moderate
- good
6. Impacts and concluding statements
6.1 On-site impacts the Technology has shown
Socio-economic impacts
Production
crop production
Comments/ specify:
Later it may still be possible to continue with crop production on the area.
fodder production
Comments/ specify:
Arable land use was turned into pasture
animal production
Comments/ specify:
In this example beef cattle production was started as a new business
Income and costs
diversity of income sources
Ecological impacts
Water cycle/ runoff
surface runoff
Comments/ specify:
As soil surface is covered permanently in a meadow or pasture, surface runoff decreases significantly.
excess water drainage
Soil
soil cover
Comments/ specify:
The most important benefit of meadows and pastures is that soil is covered permanently, that helps in the prevention of soil loss by erosion.
soil loss
soil crusting/ sealing
soil organic matter/ below ground C
Comments/ specify:
Using mowed grass as mulch can increase the carbon content of the soil.
Biodiversity: vegetation, animals
Vegetation cover
Comments/ specify:
There are more plant species present simultaneously in meadows and pastures than in cultivated fields, which is beneficial for soil health
animal diversity
Comments/ specify:
Especially naturally managed meadows attract wildlife and therefore increase biodiversity
habitat diversity
6.2 Off-site impacts the Technology has shown
buffering/ filtering capacity
Comments/ specify:
Water retention is better
wind transported sediments
Comments/ specify:
As the grass binds the soil particles, the wind cannot pick them up and carry them away even during dry periods.
6.3 Exposure and sensitivity of the Technology to gradual climate change and climate-related extremes/ disasters (as perceived by land users)
Gradual climate change
Gradual climate change
| Season | increase or decrease | How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| seasonal temperature | summer | increase | moderately |
| seasonal rainfall | summer | decrease | moderately |
Climate-related extremes (disasters)
Climatological disasters
| How does the Technology cope with it? | |
|---|---|
| drought | moderately |
6.4 Cost-benefit analysis
How do the benefits compare with the establishment costs (from land users’ perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly negative
Long-term returns:
positive
How do the benefits compare with the maintenance/ recurrent costs (from land users' perspective)?
Short-term returns:
slightly positive
Long-term returns:
positive
6.5 Adoption of the Technology
- 1-10%
Of all those who have adopted the Technology, how many did so spontaneously, i.e. without receiving any material incentives/ payments?
- 51-90%
6.6 Adaptation
Has the Technology been modified recently to adapt to changing conditions?
No
6.7 Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities of the Technology
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the land user’s view |
|---|
| Permanent soil cover |
| Continuous income |
| Strengths/ advantages/ opportunities in the compiler’s or other key resource person’s view |
|---|
| Provide better habitat conditions |
| Ecological advantages |
6.8 Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks of the Technology and ways of overcoming them
| Weaknesses/ disadvantages/ risks in the land user’s view | How can they be overcome? |
|---|---|
| Not enough hay/grass in drought seasons | locally grown fodder should be supplemented by external sources |
| Income is less than in crop production |
7. References and links
7.1 Methods/ sources of information
- field visits, field surveys
3
- interviews with land users
2
- interviews with SLM specialists/ experts
1
When were the data compiled (in the field)?
19/05/2022
7.2 References to available publications
Title, author, year, ISBN:
The grassland care handbook
Available from where? Costs?
Einböck (einboeck.eu), info@einboeck.at
Title, author, year, ISBN:
Verba&Kőszegi: The situation of livestock production, its prospects through the examples of a farm in Bács-Kiskun County. Gradus Vol 9, No 1 (2022) ISSN 2064-8014
Available from where? Costs?
https://gradus.kefo.hu/archive/2022-1/2022_1_AGR_003_Verba.pdf
7.3 Links to relevant online information
Title/ description:
How to manage a meadow for hay making and grazing pasture
URL:
http://www.magnificentmeadows.org.uk/assets/pdfs/Hay_meadow_and_pasture_management.pdf
Links and modules
Expand all Collapse allLinks

Sustainable livestock and pasture management [Tajikistan]
Sustainable livestock and pasture management is implemented through creating Pasture Users Unions (PUU) which design and implement pasture and livestock management plans.
- Compiler: Kamolidin Abdulloev
Modules
No modules