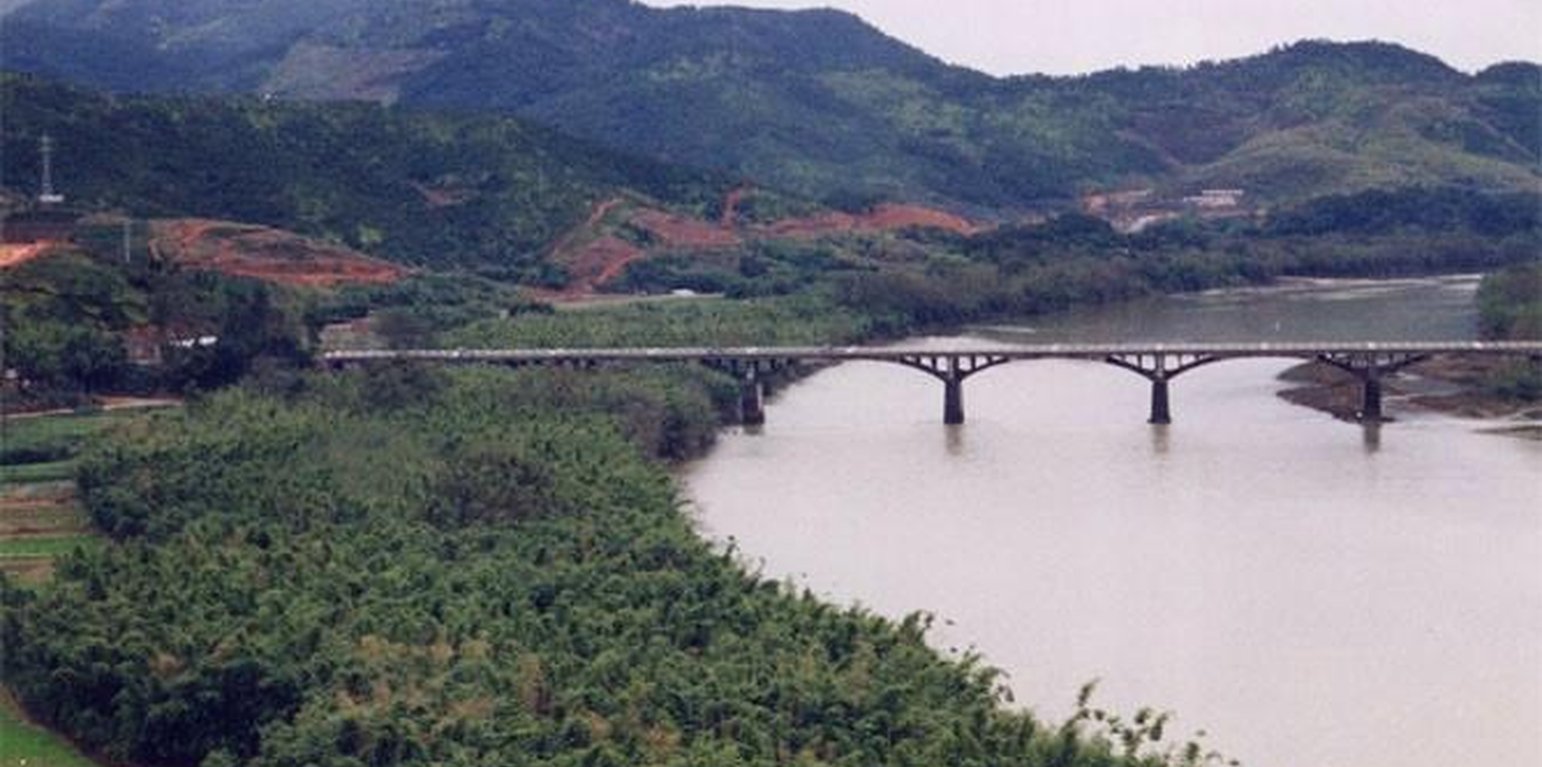
Comprehensive Development & Management of a Small Watershed
(中国)
Intergraded development of a small watershed
描述
The comprehensive measures including interplanting & intercropping are applied in the small watershed to control soil and water loss and improve integrated production.
Based on the national conditions and soil and water loss in the area, the corresponding SWC measures were adopted to pursue the targets including: 1. Closing the hilly and mountain area of 224ha for the timber forest and grass growing as well as preventing soil and water loss; 2. Adjusting the land use structure so as to strengthen the comprehensive development of the hilly land as well as crop land irrigation; 3. Changing the area of W & S loss to economic vegetation land; 4. Constructing reservoirs and roads.
地点
地点: Fujian Province, 中国
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (5.93 km²)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 不到10年前(最近)
介绍类型
-
通过土地使用者的创新
-
作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
-
在实验/研究期间
-
通过项目/外部干预
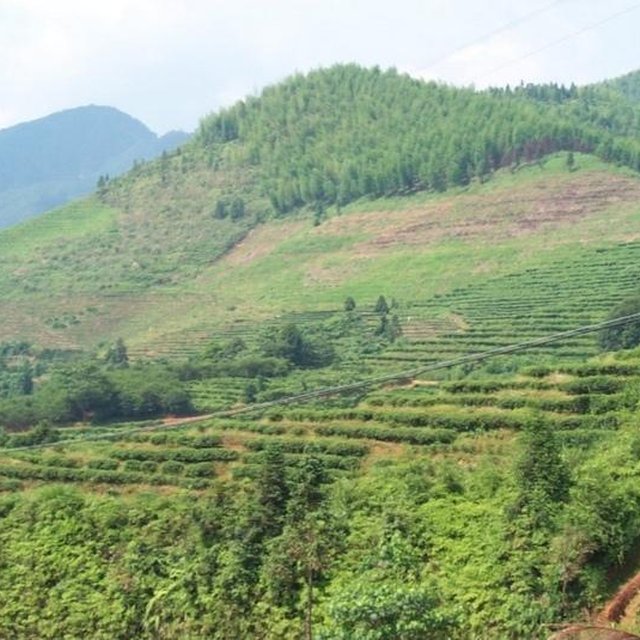

Comprehensive development & management of Xinxili small watershed (HUANG Xinquan (Fuzhou, China))
主要目的
-
改良生产
-
减少、预防、恢复土地退化
-
保护生态系统
-
结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
-
保持/提高生物多样性
-
降低灾害风险
-
适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
-
减缓气候变化及其影响
-
创造有益的经济影响
-
创造有益的社会影响
土地利用
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地: 是 - 农林牧业
-
农田
每年的生长季节数: 1
采用间作制度了吗?: 是
-
森林/林地Tree types: 冷杉属物种(杉木), 竹子, 松树属
产品和服务: 木材, 放牧/啃牧, 自然保持/保护
供水
土地退化相关的目的
-
防止土地退化
-
减少土地退化
-
修复/恢复严重退化的土地
-
适应土地退化
-
不适用
解决的退化问题
-
土壤水蚀 - Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀 , Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
-
化学性土壤退化 - Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
技术建立与维护:活动、投入和费用
投入和成本的计算
- 计算的成本为:
- 成本计算使用的货币:美元
- 汇率(换算为美元):1 美元 = 不适用
- 雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:1.44
影响成本的最重要因素
Because mechanic machines are not available, more labor forces are needed costing much. In addition, the expense for seeding, fertilizer, flagstone used in building dams take most of the total fees.
技术建立活动
-
closing mountain to afforest (时间/频率: 1990)
-
planting bamboo (时间/频率: 1990)
-
bamboo forest cultivated (时间/频率: 1990)
-
changing farmland to forest (时间/频率: 1990)
-
planting fruit trees (时间/频率: 1990)
-
Building sluice dams (时间/频率: 1990)
-
road constructing (时间/频率: 1990)
技术维护活动
-
fertilizing (时间/频率: 1990-1999 /3)
-
cleaning out ruderal (时间/频率: 1990-1999 /2)
-
Preventing and curing illness and insect pests (时间/频率: 1990-1999 /3)
-
Broadening road (时间/频率: 1995/timely)
-
highway maintenance (时间/频率: 1995/timely)
自然环境
年平均降雨量
-
< 250毫米
-
251-500毫米
-
501-750毫米
-
751-1,000毫米
-
1,001-1,500毫米
-
1,501-2,000毫米
-
2,001-3,000毫米
-
3,001-4,000毫米
-
> 4,000毫米
关于气候的规范
以毫米为单位计算的年平均降雨量:1609.0
斜坡
-
水平(0-2%)
-
缓降(3-5%)
-
平缓(6-10%)
-
滚坡(11-15%)
-
崎岖(16-30%)
-
陡峭(31-60%)
-
非常陡峭(>60%)
海拔
-
0-100 m a.s.l.
-
101-500 m a.s.l.
-
501-1,000 m a.s.l.
-
1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
-
1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
-
2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
-
2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
-
3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
-
> 4,000 m a.s.l.
土壤深度
-
非常浅(0-20厘米)
-
浅(21-50厘米)
-
中等深度(51-80厘米)
-
深(81-120厘米)
-
非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土)
-
粗粒/轻(砂质)
-
中粒(壤土、粉土)
-
细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下>20厘米)
-
粗粒/轻(砂质)
-
中粒(壤土、粉土)
-
细粒/重质(粘土)
水质(未处理)
-
良好饮用水
-
不良饮用水(需要处理)
-
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
-
不可用
应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入
-
低于全部收入的10%
-
收入的10-50%
-
> 收入的50%
个人或集体
-
个人/家庭
-
团体/社区
-
合作社
-
员工(公司、政府)
每户使用面积
-
< 0.5 公顷
-
0.5-1 公顷
-
1-2 公顷
-
2-5公顷
-
5-15公顷
-
15-50公顷
-
50-100公顷
-
100-500公顷
-
500-1,000公顷
-
1,000-10,000公顷
-
> 10,000公顷
土地所有权
-
州
-
公司
-
社区/村庄
-
团体
-
个人,未命名
-
个人,有命名
采用和适应
在所有采用这种技术的人当中,有多少人在没有获得物质奖励的情况下采用了这种技术?
-
0-10%
-
11-50%
-
51-90%
-
91-100%
户数和/或覆盖面积
510 households
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?
什么样的变化条件?
-
气候变化/极端气候
-
不断变化的市场
-
劳动力可用性(例如,由于迁移)
结论和吸取的教训
长处: 土地使用者的观点
长处: 编制者或其他关键资源人员的观点
弱点/缺点/风险: 土地使用者的观点如何克服
弱点/缺点/风险: 编制者或其他关键资源人员的观点如何克服
参考文献
审查者
-
David Streiff
-
Alexandra Gavilano
实施日期: Nov. 29, 2010
上次更新: March 14, 2019
文件编制者















