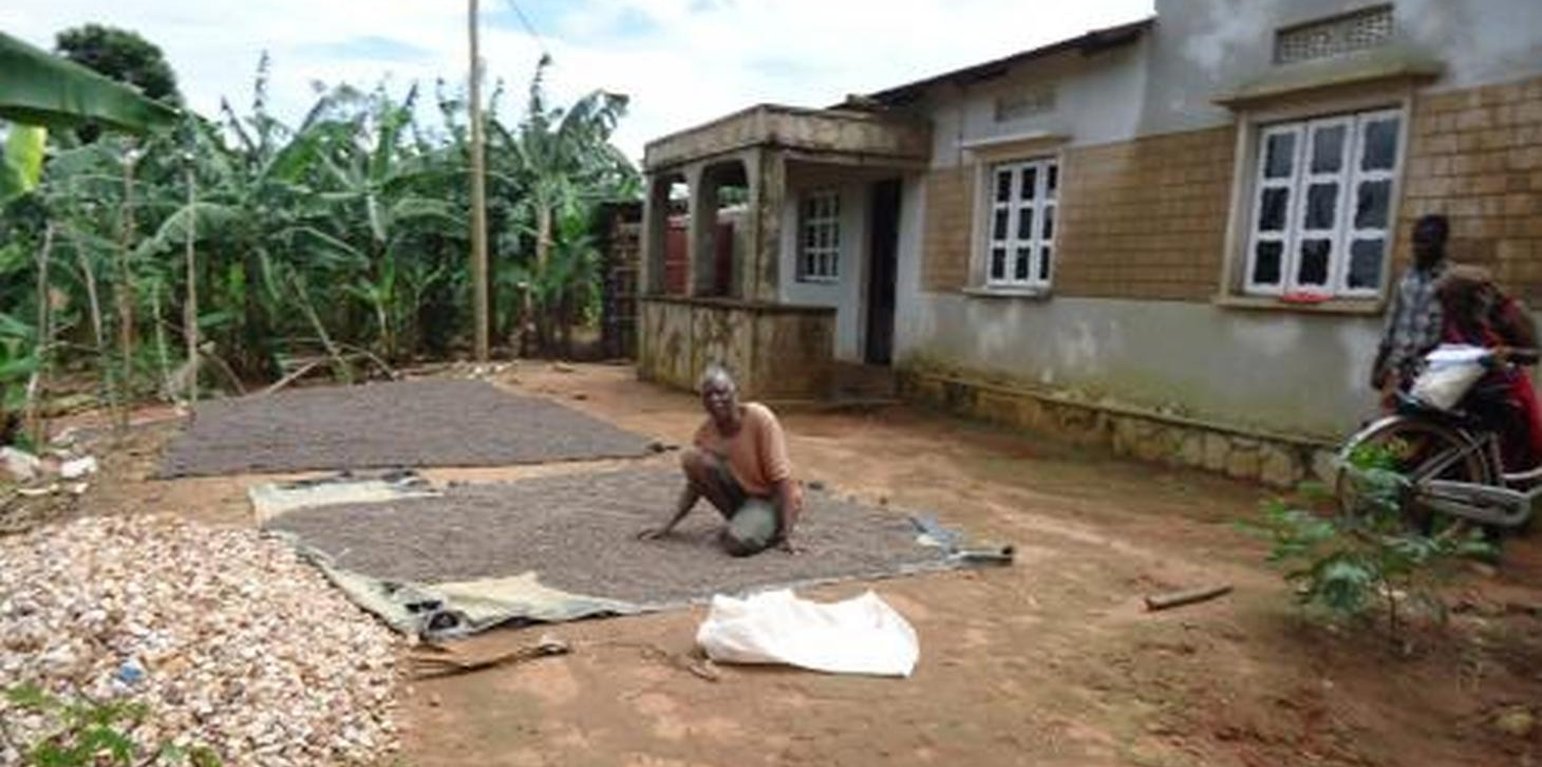




Buhaya agro forest system is a mix of annual and perennial crops together with trees and shrubs are densely planted on a restricted area usually 0.5 -2ha per household to increase crop yield, wood production and conserve soil and water. Buhaya agro forest system is applied on individual owned land specific at home steady. In this technology a plot of 1ha comprises of :
1.Perennial crops (coffee, banana, ) on average (10,000/36 coffee plants can be planted in one hector randomly in the alternating manner with banana, 10,000/25 banana stools) can be planted in 1ha randomly in the alternating manner with coffee.
2.Annual and biannual crops (eg. Maize, beans, cassava, sweet potatoes, yams etc) are planted in the between spaces. Maize and beans are planted twice in the short (Masika) and long rains (Vuli) where tubers are planted at any time throughout the year.
3.Trees and shrubs (eg. Makkhamia spps, Maesopsis and migorora). Trees are planted along the boundaries spaced at an average of 15m to act as wind break and timber production. Shrubs are planted at closed distance in between trees to act as live fence.
Buhaya agro forest system was practiced since early 1900. Application of farmyard manures and crop residue mulch are the supportive measures. The land owners keep small livestock/ few cattle under zero grazing to obtain manure for soil fertility improvem
Purpose of the Technology: The purposes for applying the technology is to control soil erosion and nutrient improvement.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The establishment of Buhaya agro forest system is done on a virgin land starting in the dry season July to September and it normally takes 2-5years by doing the following activities.
1.To prepare the land by cutting, removing/burning shrubs and grasses followed by land tillage. This is the difficult job and sometimes it can force the farmer to plant annual crops before planting perennial crops due to inadequate preparation time.
2.To dig holes of different size according to what crop is meant for in the alternating manner. This activity is done after harvesting annual crops in shot rainfalls (March to June).
3.To plant banana in July and August followed by coffee in September to November and March to May next year.
4.To plant trees along the boundaries followed by planting shrubs between the trees spacing to create a live fence.
5.To plant cassava, yams, pawpaw, avocados and mangoes. These are planted randomly and in a few quantity.
The maintenance of Buhaya agro forest system is the simple but tidies job requires all the year to be working in the garden. The required activities are
1.To weed the field as preparation for planting seasonal crops( i.e maize and beans) twice per year in dry seasons.
2.To remove unwanted banana suckers (desuckering) and harvested banana stems in order to maintain a required number of plants( mother, daughter and grand daughter) per stool. This requires a lot of time for assessing the plant health as well as spacing.
3.To plant and harvest maize and beans twice per year.
4.To prune coffee trees, harvest coffee cherry, dry, and market them once per year.
5.To replace harvested cassava and yams as required.
地点: Bukoba District (Kyema village), Tanzania, 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
分析的技术场所数量:
技术传播: 均匀地分布在一个区域 (approx. 1-10 平方千米)
在永久保护区?:
实施日期: 50多年前(传统)
介绍类型







| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Land preparation | persons/day/ha | 333.3 | 1.25 | 416.63 | 100.0 |
| Digging holes | persons/day/ha | 81.63 | 1.25 | 102.04 | 100.0 |
| Planting banana and coffee | persons/day/ha | 33.33 | 1.25 | 41.66 | 100.0 |
| Planting trees, shrubs and biannual crops | persons/day/ha | 158.6 | 1.25 | 198.25 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | |||||
| Axes | pieces/ha | 5.55 | 3.128 | 17.36 | 100.0 |
| Machete | pieces/ha | 5.55 | 1.877 | 10.42 | 100.0 |
| Hand hoes | pieces/ha | 5.55 | 3.128 | 17.36 | 100.0 |
| Spades | pieces/ha | 2.7 | 3.148 | 8.5 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Banana suckers | pieces/ha | 571.0 | 0.1875 | 107.06 | 100.0 |
| Coffee seedlings | pieces/ha | 357.0 | 0.3125 | 111.56 | 100.0 |
| Mysopsis | pieces/ha | 33.0 | 0.125 | 4.13 | 100.0 |
| Migorora | pieces/ha | 80.0 | 0.125 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| Avocado | pieces/ha | 11.0 | 3.167 | 34.84 | 100.0 |
| Mangoes | pieces/ha | 5.0 | 3.125 | 15.63 | 100.0 |
| Cassava | pieces/ha | 47.0 | 0.0317 | 1.49 | 100.0 |
| Yams | pieces/ha | 26.0 | 0.031 | 0.81 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1'097.74 | ||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1'097.74 | ||||
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 (美元) | 每项投入的总成本 (美元) | 土地使用者承担的成本% |
| 劳动力 | |||||
| Weeding | persons/day/ha | 200.0 | 1.25 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| Desuckering | persons/day/ha | 57.0 | 1.25 | 71.25 | 100.0 |
| Planting annual crops | persons/day/ha | 50.0 | 1.25 | 62.5 | 100.0 |
| Prunning, harvesting and drying coffee | persons/day/ha | 285.5 | 1.25 | 356.88 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | |||||
| Seeds | pieces/ha | 10.0 | 2.5 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| Seedlings | pieces/ha | 26.0 | 0.031 | 0.81 | 100.0 |
| Cassava | pieces/ha | 48.0 | 0.0317 | 1.52 | 100.0 |
| Beans | pieces/ha | 20.0 | 1.25 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | |||||
| Labour: Cassava and yams harvesting | persons/day/ha | 2.3 | 1.25 | 2.88 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 795.84 | ||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 795.84 | ||||
SLM之前的数量: 16kg
SLM之后的数量: 35kg
All crops are weeded at once
Individual had excess food for sale
Individual exposuers to expatriet and trading partners
No wind break events reported in the area
This technology supports high quality and quantity coffee and other crops production and as a results improves farmers income.