Participatory SLM Action Planning [不丹]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Karma Dorji
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2489 - 不丹
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Wangdi Tashi
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
不丹
SLM专业人员:
Dorji Tshering
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
不丹
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
National Soil Services Centre (National Soil Services Centre) - 不丹有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
MoA (MoA) - 不丹1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
14/03/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
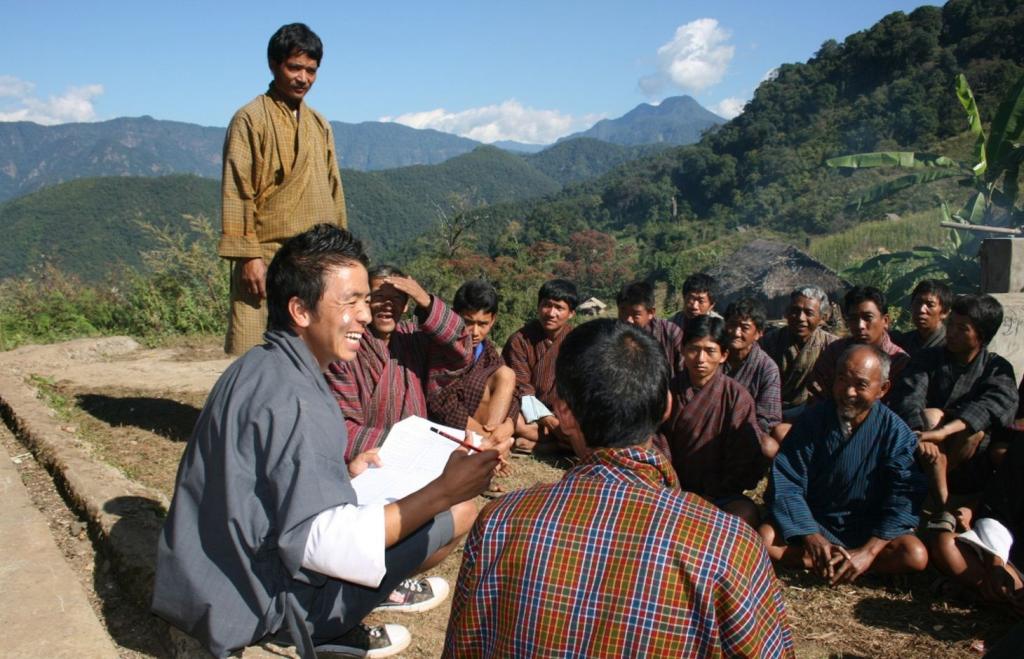
A methodology to identify in a participatory manner at village level land-based problems, its causal factors and mitigation measures to reduce land degradation and enhance rural livelihoods
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Participatory SLM Action Planning (SLM AP) is a methodology that aims at prioritiz-ing possible SLM interventions to mitigate the most critical land degradation issues. Priorities are based on the identification of land-based livelihoods and livelihood resources, the key area-based problems and their causes. SLM AP is carried out in the SLMP geogs (block) at chiog (village) level, including all community households. It involves elements of PRA/PLA such as problem census, cropping calendars, history lines, natural resource mapping and builds on the in-depth knowledge and understanding of farming households of their land, their problems and opportunities. The process is highly visual to include the illiterate and very interactive by giving the communities the lead in prioritizing their problems and deciding on SLM interventions.
Methods: The SLM AP is an iterative process, starting with building and training SLM planning teams (GSPTs) at geog level, comprising of extension staff and locally recruited geog SLM planners (GSPs) and geog administration staff. The GSPTs start awareness and mobilization activities in the first year at geog council level. This is followed by a 3 day SLM AP in each and every chiog of the geog to compile a chiog SLM action plan. The village SLM APs are combined into a geog SLM AP and discussed, amended and endorsed in a public meeting by the geog council. The necessary budget is allocated by SLMP project and implementation of the planned activities takes place at chiog level.
Stages of implementation: Implementation is preceded by intensive training and capacity building of the communities in SLM activities. In the second year a new SLM AP round is made, lasting only one day, with review of the previous SLM AP at chiog level. Potential new activities are identified, based on field experiences, to complete the new SLM AP for year 2. In the final year 3, a last SLM AP round is made in all chiogs to compile chiog and ultimately a geog SLM AP.
Role of stakeholders: SLM AP is an inclusive process and gender sensitive, with focus on vulnerable households. The approach includes participatory Natural Resource mapping at chiog level and participatory Monitoring & Evaluation to track implementation progress and impact and to get feedback of the communities.
Other important information: Environmental and social screening procedures are applied to exclude any negative impact on the land or on social groups. SLM AP was piloted in 3 geogs in 3 Dzongkhags since 2006 and has been rolled out to more than 130 chiogs in 9 geogs.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
不丹
区域/州/省:
Chhukha, Trashigang and Zhemgang Dzongkhags
有关地点的进一步说明:
9 separate geogs
2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2006
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2012
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (livelihoods, cash income, food security, capacity building, awareness raising)
- To build community capacity to assess land degradation and identify and prioritize mitigation measures
- Enhancement of rural livelihoods
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - Lack of awareness of land degradation processes, combined with limited technical knowledge to tackle its causes.
- Planning procedures are top-down and do not incorporate land-based issues adequately and fail to build local ownership and sustainability.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Large amount of cash to handle at municipality level
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training, monitoring and limitation of cash amounts
机构设置
- 阻碍
Delays in financial releases to decentralised level because of lengthy/complicated administrative chain
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training of key financial staff to shorten procedure and minimize frequency of budget releases
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights helped a little the approach implementation: Individual land titles of households favour greatly the planning and implementation of SLM activities
- 阻碍
Lack of efforts in implementing SLM technologies on land without ownership and living as tenants
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness on the importance of proper management to prevent decline in productivity and their own livelihoods through loss of soil fertility and or loss of land physically due to landslides and mass movements.
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Awaraness of communities and technical confidence of teams
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Training and capacity buidling
工作量、人力资源可用性
- 阻碍
Large volume of work, especially in growing season
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Make of use of lean winter season for labour-intensive SLM interventions
其他
- 阻碍
Small land holding sizes to spare a portion for SLM technologies
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Awareness on the advantages of SLM
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
communities of all chiogs
In all villages the most vulnerable community members were identified (wealth / well-being ranking), ranked and specific effort made to include them in most interventions, where possible.
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- 教师/学龄儿童/学生
- 地方政府
GSPT and Dzongkhag staff (Local government)
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
RGoB, MoAF, DoA
- 国际组织
GEF, World Bank
- monk body
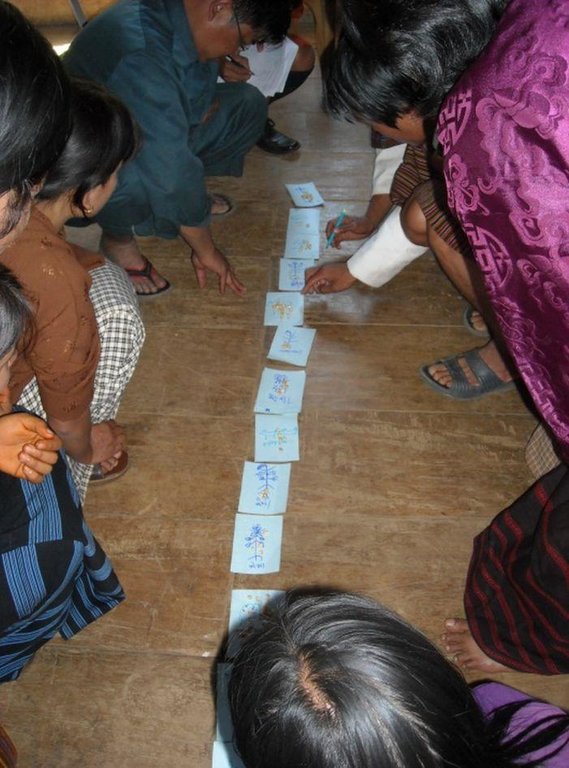
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | National level stakeholders in consultation with district and municipality staff developed the methodology through an iterative consultation process |
| 计划 | 互动 | Decentralised training and planning of SLM interventions at chiog level (130+ chiogs) in 9 geogs in 3 Dzongkhags |
| 实施 | 互动 | Range of SLM and livelihood activities at chiog level (130+ villages) during 6 year project period |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | Regular participatory M&E at chiog and geog level |
| Research | 被动 | Few focused SLM related research topics commissioned to governmental research institutions |
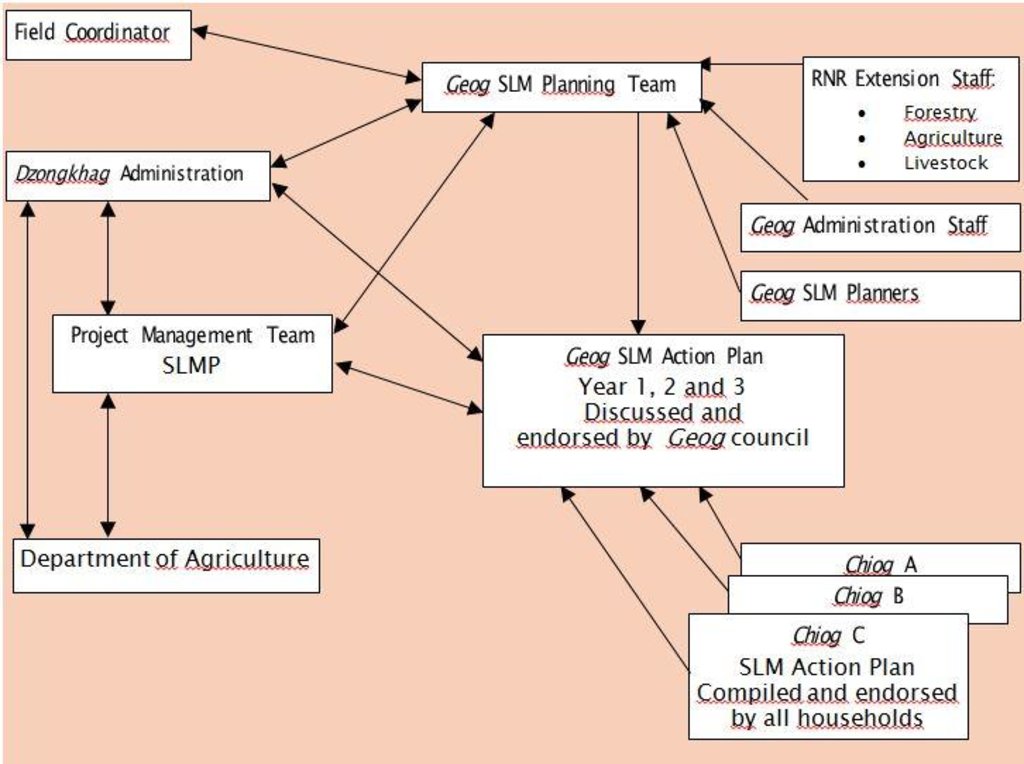
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
Overview of network of Stakeholders at chiog (village), geog and district level
作者:
Hans van Noord (Schoutenkamp 43 Heteren The Netherlands)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by SLM specialists with consultation of land users. The SLM planning was done in a very participatory manner with the land users as they best know the problems in their land i.e. where, how, when, etc. Planning done using participatory planning tools and field visits. Based on the problems at the site (site specific problems) then SLM Specialists make problem specific recommendations of SLM technologies. The main Monitoring and Evaluation was done after every six months when comprehensive information was collected with structured questionnaires along with site visits and meeting with the communities. M&E was also done as frequently as possible even while visiting the site for other purposes during the year without compulsory group meetings.
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
- Project management staff
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
Extensive training programmes for project management staff and field coordinators and the decentralised extension staff (forestry, livestock and agriculture) at geog level together with the geog administration staff and finally to all chiog communities (130+). Initial training was on SLM action planning and Natural Resource mapping; later on a range of technical intervention such as hedgerow establishment, check dam construction, bioengineering, afforestation, community forestry, fodder development, bamboo plantation, bench terracing etc.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: SLM planning knowledge transfer; Key elements: participatory planning, capacity and skills building of RNR extension staff; Whole range of extension advisory services by all extension teams related to SLM, cash generation and group formation
Advisory service is quite adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities; Capacity built, awareness raised, institutions supported. Adequate human and institutional capacities and awareness have been created during the GEF/World Bank SLM Project period and the effort is still being continued. The actual implementation of the SLM technologies in the field is constrained by inadequate fund support and small land holdings.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,少许
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
- 设备
- curriculum development support, seeds, seedlings
提供进一步细节:
Moderate support to monk body, schools, Non-Formal Education and geog administrations
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage of improved vulnerable land through SLM interventions; annual soil erosion plot measurements
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage of improved vulnerable land through SLM interventions; annual soil erosion plot measurements
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage and properties of specific areas of improved vulnerable land
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements and observations of acreage and properties of specific areas of improved vulnerable land
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations through participatory M&E meetings
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through observations; indicators: Regular observations and measurements by field extension staff (crop cut, animal production, volume of bamboo marketed; CBA study to establish economic viability
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff through measurements; indicators: Regular observations and measurements by field extension staff (crop cut, animal production, volume of bamboo marketed; CBA study to establish economic viability
area treated aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements of area treated: range of project indicators for vulnerable land improved
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, government through measurements; indicators: Regular measurements of households and farmers (male/female) participating
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by None through observations; indicators: WB, MTAC, Regular reviews with key stakeholders (Annual Review Workshops)
There were several changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Two-tier approach: combination of inclusion of all household combined with limited areal focus; vulnerable households focus; financial disbursement system; ch more cash-generating activities; more group/community focus; labour-saving machinery
There were few changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: change of type and variety of seeds and seedlings
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Little involvement, apart from some focused research on group formation at chiog level and studies on CBA, SLM-poverty linkage, rangeland management, rural-urban transition etc.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- > 1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (GEF-World Bank): 70.0%; government (RGoB): 20.0%; local community / land user(s): 10.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
Incentives for specific SLM interventions per area and through short-term input support (seeds and seedlings)
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 工具 | 部分融资 | |
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | 部分融资 | |
| Seedlings | 部分融资 | |
- 建筑
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| for fencing and dams | 部分融资 | |
- 基建
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| FYM sheds, irrigation channel renovation | 部分融资 | |
注释:
Mostly voluntary and some paid in cash (for labour-intensive SLM interventions) and limited other material support such as tools and seeds and seedlings
Not financed: roads, fertilizers, schools
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Considerable area of vulnerable land brought under SLM, reduction of loss of land, improved yields, improved income, improved animal production, improved fodder base
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Moderate improvement of vulnerable households (poorest and single-headed households) through targeted interventions and pro-active inclusion. The labour sharing approach in implementing SLM activities greatly benefited the resource (human and capital) constrained household.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The problem is unlikely to be overcome in the near future. Individual land titles of households favour greatly the planning and implementation of SLM activities
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Other government and donor-funded projects have adopted elements of the participatory SLM action planning methodology (DANIDA, REAP)
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
cash income, food self-sufficiency, community sense/bonding, reduced exposure to natural hazards related to land degradation/flooding
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Improvement of food self-sufficiency and cash generation opportunities
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 减少工作量
- 支付/补贴
- 声望、社会压力/社会凝聚
- 加入运动/项目/团体/网络
- 环境意识
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
Rural communities will need continued support by government staff through advice, finance and other support.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Decentralised, village level bottom-up planning and implementation ensures capacity building, ownership and empowerment of rural land users Participatory character gives a voice to farmers with in-depth knowledge of land-based issues and its causes and history Inclusiveness of approach, reaching to all households Helps to build community sense (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continued annual AP Continued annual AP; add with NR mapping and ITK studies and participatory M&E Continued annual AP; targeted focus on most vulnerable households Additional group formation and community group support ) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
|
Time-consuming and resource demanding Requires large workload of both extension staff and farmers Costly as the approach also covers actual implementation of all of planned SLM activities and reaches more than 130 villages for 3 year period |
Combine and align with Five Year Plan planning procedures; mainstreaming into governmental decentralised planning procedures Mainstreaming into regular planning and budgeting Spread over calendar year; labour-intensive SLM activities in lean winter season. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Working the Land - Documenting the Key Lessons of Sustainable Land Management on Steep to Very Steep Slopes in Bhutan 2011
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Indigenous Technical Knowledge (ITK) on Soil & Soil Fertility Management 2011
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Participatory Approaches in Sustainable Land Management – Planning, Implementation & Monitoring as Continuous Learning Processes 2011
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
National Action Plan to Combat Land Degradation 2010, 2014
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
BHUCAT, Best Practices and Guidelines from Bhutan for SLM on Steep to very Steep Slope
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Documentary of the achievements made in SLM through SLM Project
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Bhutan Land Cover Assessment 2010-Technical Report, NSSC, 2011
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Soil Erosion – Measurement and analysis of soil erosion plot data, NSSC, 2010, 2011
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Integrated Biodiversity Survey of the Lower Wangchhu Watershed, Bhutan 2010
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Rangeland Management in Bhutan 2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Study on Poverty Sustainable Land Management Linkages in Bhutan-A consultancy Report-2009 2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Participatory Action Planning Manual & Tool Kit 2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Sustainable Land Management Interventions: Cost Benefit Analysis Report 2009
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Rural Livelihoods and Peri-Urban Analysis 2008
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Review of Mainstreaming of sustainable Land Management in Government Policies and Plans in Bhutan 2008
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NSSC, DoA, MoAF, RGoB, A consultancy report
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块