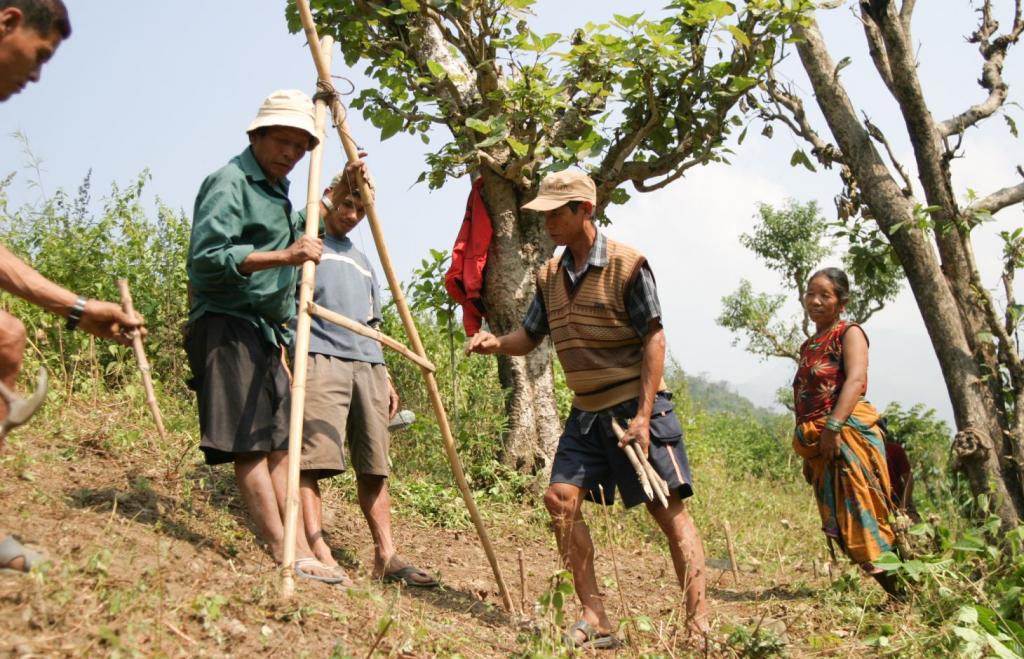
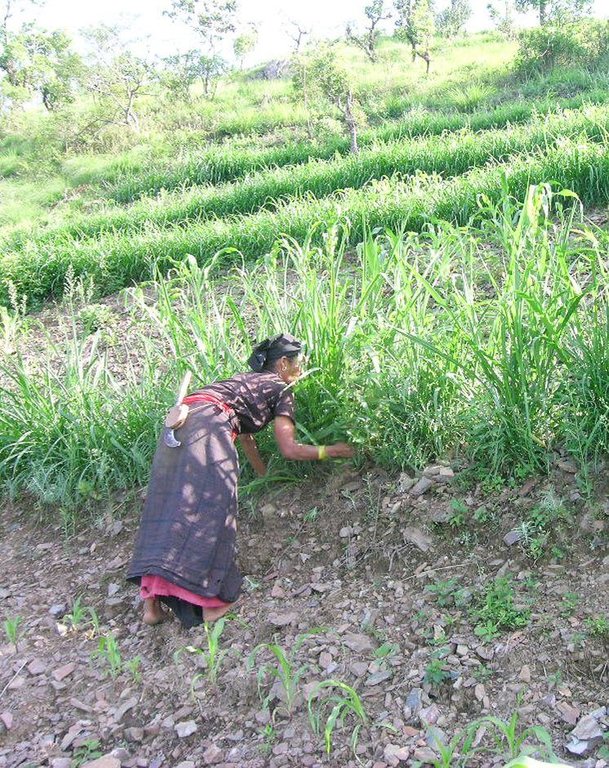
Participatory hedgerow management [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Sahabhagitamulak ghasehar bewasthapan (Main Contributor: Gyanbandhu Sharma, LI-BIRD)
approaches_2530 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Local Initiatives for Biodiversity, Research, and Development (LI-BIRD) - 尼泊尔有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/03/2013
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考

Hedgerow technology [尼泊尔]
A technology that uses hedgerows to help establish terraces on sloping land; farmers learn improved methods to manage a cultivation practice that stabilizes the soil, enhances food production, and adds to on-farm cash income.
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
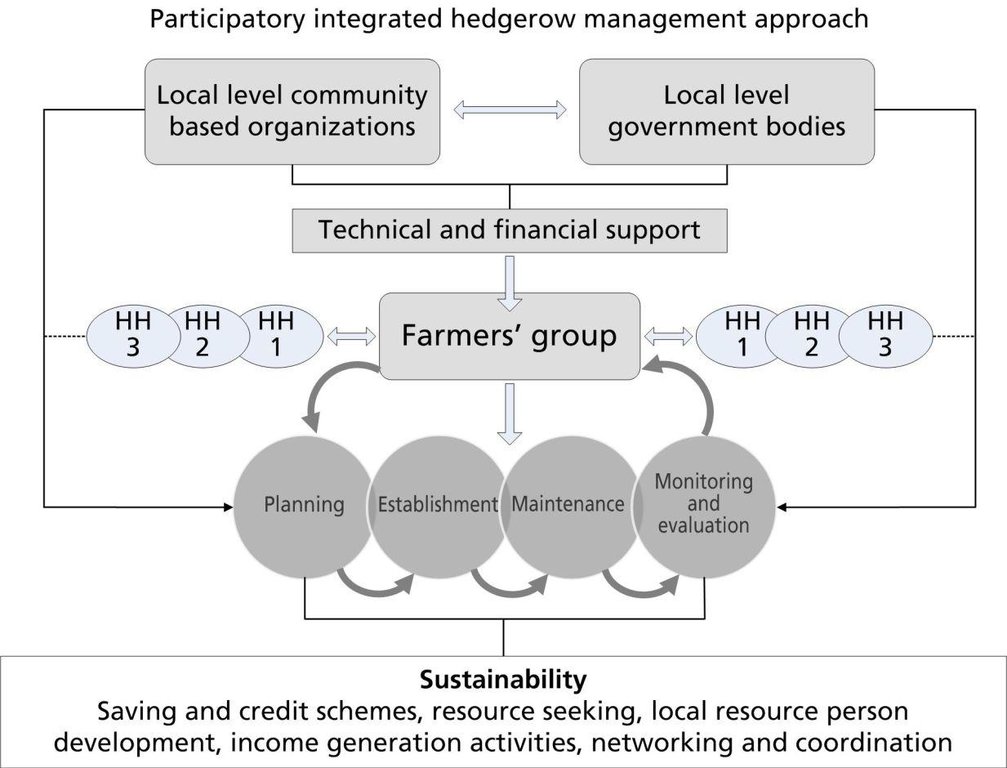
Hedgerow technology can be introduced through the joint participation of farmers, scientists, and related stakeholders. The whole community works together at all stages, including designing, planning, implementation, monitoring and evaluation, and scaling up.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Communities can establish better hedgerows by supplementing the traditional knowledge that they have employed for generations with scientific knowledge through a participatory process where both groups are involved in every step of planning, designing, and implementation. This approach recognizes the validity of the local knowledge that farmers have about their land and supplements it with scientific techniques to facilitate the implementation of methods which will yield better results sooner.
Methods: Hedgerow technology can be implemented by forming farmers' groups and using a participatory approach. This technology has the potential to be scaled up and applied on a broader scale. The steps for sharing labour and know-how to establish hedgerows can be summarized as follows:
• Capacity is strengthened through discussions with technical persons.
• Farmers, technical persons, and related stakeholders work together to come up with plans that make the best use of both the farmers’ indigenous knowledge on how to form hedgerows and their understanding of the landscape, and scientific knowledge, for designing and planning.
• The hedgerows are established by the farmers as per the consensual plan.
• Some farmers are designated to periodically inspect the hedgerows and to perform maintenance as needed.
• The technology is scaled up by farmers who disseminate the learning to other farmers through extension and knowledge sharing at different fora.
Stages of implementation: Farmers, technical persons, and related stakeholders were all involved at every stage. In addition, LI-BIRD, local community-based organizations, and other related stakeholders such as the district forest office and the district agriculture office were on hand to support the farmers' group by offering technical and financial resources. The farmers' groups had a vested interest in this approach and demonstrated their commitment by: generating funds from a savings and credit scheme and conducting income generating activities. They also worked to establish effective linkages and to coordinate with related stakeholders to obtain resources which would ensure that the group would be self-reliant in the long run. The involvement of a wide range of participants will ensure that the technology is not only effective but that it is also sustainable. Moreover, when neighbouring communities see how successful this approach can be, it is hoped that they also will adopt the technology.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Gorkha, Tanahu District
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (Income generation)
The objective of this approach was to introduce the technology through participatory planning, designing, and implementation by integrating farmers’ knowledge and experiences in the process.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: This approach addressed a few of the major problems in the area. The outstanding problems were:
• poor technical knowledge,
• lack of group efforts,
• lack of cash for investment,
• poor access to service providers,
• inadequate use made of farmers' traditional knowledge,
• inadequate knowledge resources, and
• poverty and poor social cohesiveness.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
Farmers had insufficient financial resources to implement the technology
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers learned how to apply for resources from different related stakeholders and they also learned how to generate cash from their own group using savings and credit schemes.
机构设置
- 阻碍
Farmers had no formal institutional mechanisms and also had no capacity to run their institutions
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers learned how to form a formal group and also improved their capacity to run their institutions
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 阻碍
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights hindered a little the approach implementation
了解SLM,获得技术支持
- 阻碍
Farmers had low technical knowledge
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Farmers shared their know-how and also learned from scientists, other farmers and related stakeholders
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
- SLM专家/农业顾问
- NGO
LI-BIRD
- 地方政府
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
Specialists and land users. During the design process, specialists organized on-farm visits and exposure visits. The plan was prepared jointly by the land users and the specialists who used each others' expertise.
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 被动 | At the beginning, the land users were mostly passive because they lacked information on sloping land management. |
| 计划 | 互动 | Land users were actively involved in the planning stage and they incorporated feedback from other stakeholders to finalize the action plan. During this phase they also prepared the land and the materials, and recruited the resource person needed to implement the technology |
| 实施 | 自我动员 | Land users were involved in the implementation phase mobilizing their group members and shared the new technical knowledge that they had acquired. |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | Land users and other stakeholders remained actively involved throughout the different stages of monitoring and evaluation. |
| Research | 外部支持 | Land users were actively involved in research work to test and validate the approach. |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是土地使用者,由SLM专家提供支持
解释:
Both farmers and specialist were involved in on-farm visits to assess the condition of the land; farmers attended seminars to acquire new knowledge and they also used this opportunity to share their own knowledge. Farmers and specialists together selected the technology.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by mainly by land users supported by SLM specialists
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
- Local Resource Person
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
涵盖的主题:
This approach provided training on hedgerow technology and group mobilization to enhance the capacity of land users, field staff, and local resource persons. Site visits to the demonstration areas were also organized for the land users.
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在固定中心
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Group Mobilization Method; Key elements: networking and coordination of farmers' groups with district level line agencies such as the district forest office, the district agriculture office, the district livestock office, and other relevant stakeholders for learning and sharing of information.
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,少许
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
具体说明支持类型:
- 能力建设/培训
提供进一步细节:
Trainings and sessions on capacity building were provided to the land users
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: The land users and project staff made regular observations of sediment deposition rates after the intervention.
technical aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: The land users and project staff made regular observations on the formation of terraces and control of erosion.
socio-cultural aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: The land users and project staff regularly observed sociocultural impacts
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: The land users and project staff regularly observed the extent to which the income of the land users changed.
area treated aspects were regular monitored by government, land users through measurements; indicators: The land users and government staff monitored the coverage of the technology.
no. of land users involved aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: Regular observations were made by the land users and project staff on how many land users were adopting the technology.
management of Approach aspects were regular monitored by project staff, land users through observations; indicators: The land users and project staff regularly observed how well the group functioned together and how well they linked with stakeholders
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Monitoring brought few changes; farmers used the information gathered during monitoring of on-farm demonstration to help them select the species they preferred but the technology remained the same.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 技术
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
On-farm technical research was a part of the approach applied by land users, specialists, and relevant stakeholders who were involved in hedgerow technology trials.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: national non-government: 20.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc): 10.0%; local community / land user(s): 70.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
如果是,请具体说明支持的类型、条件和提供者:
LI-BIRD provided some support.
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
否
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
This approach helped to stabilize the fragile hill slopes.
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The capacity of marginal ethnic groups increased; they learned how local institutions function and felt empowered to seek resources from their service providers.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
This approach was adopted by adjoining villagers and scaled up gradually in Dhading, Chitwan, Nawalparasi, and Makwanpur Districts. According to preliminary information, at least 450 households have now adopted this approach for sustainable land management.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
This approach helped to improve the livelihood status of the land users by helping to diversify their options for income generation and skills development.
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
After the implementation of this approach, land users could earn cash income and learned how to increase their capacity to implement income generating activities which would enhance their livelihoods.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 不确定
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
Individual land users were enthusiastic to implement the approach and to take it further. Land users who are shifting cultivators, and who typically have no land ownership, are slower to embrace the approach.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Sustained capacity building (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to build strong links and coordinate with government line agencies) |
| Improved access to services providers helped to enhance their capacity to cope with adverse conditions (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to build and maintain contact with government line agencies) |
| Local institutions were strengthened (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Established formal institutions and help to sustain them) |
| Land users actively participated and took ownership (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue capacity building and training. At present the government is initiating programmes with leasehold forest groups in Gorkha and Tanahu Districts that encourages the establishment hedgerows è Work to mainstream the approach within government programmes) |
| Collaboration helped land users to sustain their efforts (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Continue to build a sense of community between land users) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Difficult to develop common understanding | Organized regular learning and sharing to develop common understanding |
|
Farmers have only a limited understanding of the skills needed |
Continue to strengthen farmers' groups and continue to mobilize through sharing and learning |
| The approach is resource intensive. | Promote savings and credit schemes with farmers' groups. Mobilize farmers' groups so that they can petition other groups and line agencies for resources. |
| Time consuming | Work with land users to improve their time management and their ability to plan future activities and delegate responsibilities |
| Few farmers participated during the initial stages | Conduct awareness raising activities and promote activities that give some tangible benefits in the short term. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Building on partnership approaches in participatory identification of integrated agricultural technological packages suitable for sloping land areas (unpublished), Regmi, BR; Aryal, KP; Shrestha, PK; Tamang, BB (2003)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
LI-BIRD
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Hedgerow technology [尼泊尔]
A technology that uses hedgerows to help establish terraces on sloping land; farmers learn improved methods to manage a cultivation practice that stabilizes the soil, enhances food production, and adds to on-farm cash income.
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
模块
无模块