Pasture Management [土耳其]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mehmet Zengin
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2564 - 土耳其
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture (University of Selcuk, Faculty of Agriculture) - Türkiye1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
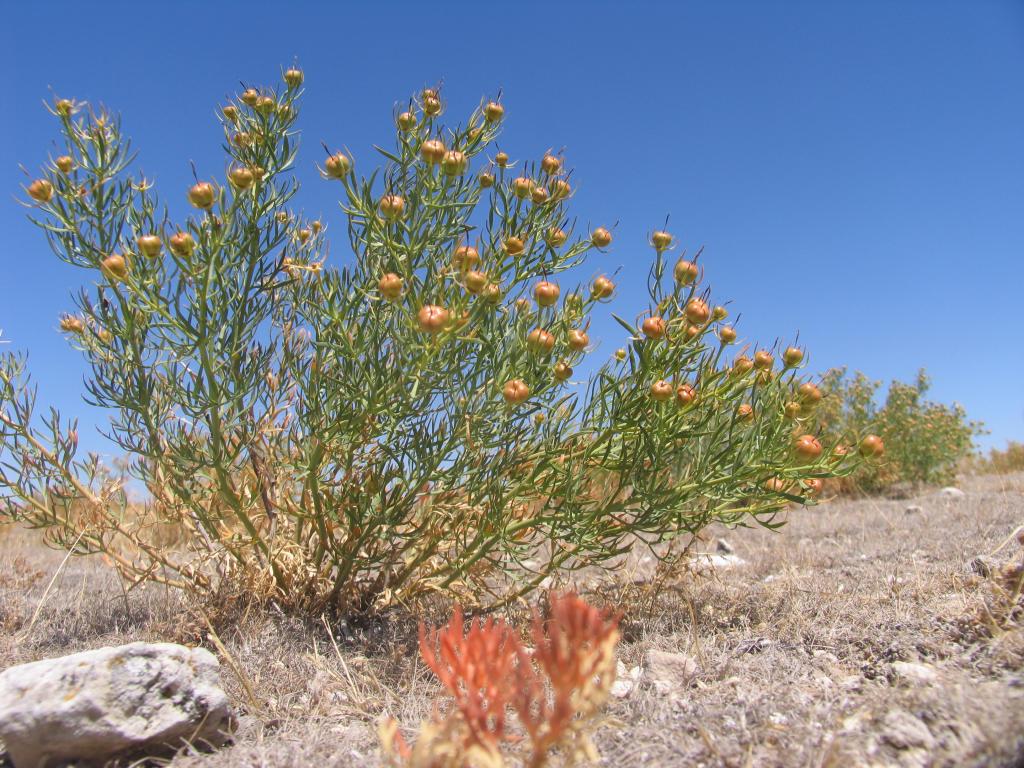
Farmers adopting the rotational grazing on pasturelands.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: Basic aim of the approach is to rest a certain part of pasture by rotational grazing helped with seeding, fertilizing and area closure to enable the new types and higher amount of herbacous plant cover.
Methods: SWC approach is applied in conjunction with the seeding and fertilizing of pastures in different periods of the year.
Stages of implementation: Teaching and training is achieved in winters, seeding and fertilising in early spring and grazing in winter.
Role of stakeholders: The trained stakeholders are expected to help with the seeding and fertilization activities. All farmes are responsible for the fulfillement of area closure rules.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
土耳其
区域/州/省:
Konya
有关地点的进一步说明:
Karapınar
Map
×2.7 方法的类型
- 传统/本土
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused on SLM only
To conserve pasture areas, to raise whealth of district people, to prevent the immigrant from rural areas to towns and cities.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Lack of money to conserve the naturel pastures, conflict over the use of already poor pastureland, lower income rates from animal feeding, low level of biodiversity (herbaceous plants) and lower biomass production.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 启动
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights moderately helped the approach implementation: Lands belong to state, so no problem arises among the farmers. Sheep owners graze in pastures rotationally and sharely.
- 阻碍
lack of legal regulation that orginise appropriate exploitation of pasturelands by farmers
Treatment through the SLM Approach: arising the counciseness of sustainable pasture management, increasing the quality and diversity of existing biomass.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Farmer unions such as irrigation union or specific crop production unions.
Males are culturally dominant in Turkish society. Rural affairs are generaly realised by men.
- NGO
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
SLM approach is raised by local specialists of national state governmental organisations and helped with land users.
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 外部支持 | local land users inspire and inform specialist and local decision makers for pastureland management |
| 计划 | 外部支持 | They are relatively active in the planning phase. |
| 实施 | 互动 | land users are particularly involved in the implementation phase. |
| 监测/评估 | 被动 | |
| Research | 无 |
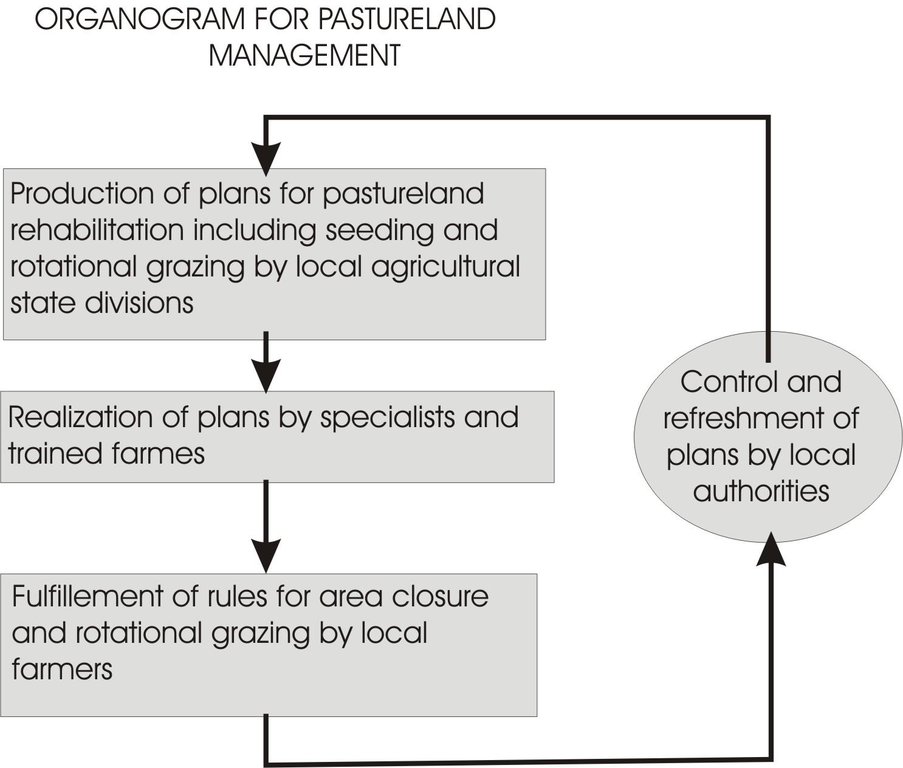
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
Organogram for pasturland management
作者:
Mehmet Zengin (Ziraat Fakültesi, Selçuk Üniversitesi, Konya)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 仅限SLM专家
解释:
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by SLM specialists alone (top-down)
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
如果相关,请说明性别、年龄、地位、种族等。:
Male and active farmers are mostly involved in training activities.
培训形式:
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
涵盖的主题:
Main types of herbacous plants in the region, feeding capacity of certain plant types, importance of area closure for rehabilitation of pastures etc.
4.4 监测和评估
监测和评估是该方法的一部分吗?:
是
注释:
bio-physical aspects were ad hoc monitored by project staff, government through observations; indicators: None
technical aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
socio-cultural aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
economic / production aspects were regular monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
area treated aspects were ad hoc monitored by government, land users through observations; indicators: None
no. of land users involved aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
management of Approach aspects were ad hoc monitored by government through observations; indicators: None
There were few changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: Monitoring and evaluation enable the understanding of rotation period for certain areas. The suitable herbaceous types are also safely determined after these works.
There were no changes in the Technology as a result of monitoring and evaluation: None
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 生态学
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- < 2,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: local community / land user(s) (Individual farmers and farmer unions): 15.0%; local government (district, county, municipality, village etc) (Local branches of agricultural state organizations): 80.0%; national non-government (NGO's such as TEMA): 5.0%
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Rotational grazing are adopted by more land users. Pastures improvement with the seeding and fertilizing is less applied.
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Local people around who adopted the approach improved their over-grazed pastures in the rate of 50 % by controlled grazing in their pasture lands.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加生产
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 减少工作量
- 规章制度(罚款)/执行
- 声望、社会压力/社会凝聚
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 否
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
Because they need financial support for seed and fertilizing costs to improve the pastures.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The approach and technology caused new opportunities and good economy. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Attention, money support and measurements.) |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Rotational grazing and improving for pasture management is consistent and useful. (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: Money support and training.) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Until enough improvement of the pasture farmers need fodder for their animal. | Growing fodder in their fields with the government support and teaching. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Especially pasture improving requires money support for soil tillage, fodder seeding and fertilizing. Sometimes there may be conflicts in the grazing of pasture improved. | Government supports and training. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块