Conservation Approach for Kouré Giraffes [尼日尔 ]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Soumaila Abdoulaye
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
approaches_2568 - 尼日尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Oumarou Ahmed
Ministry of Environment, Niger
尼日尔
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
GREAD (GREAD) - 尼日尔有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Environment and Sustainable Development of Niger (MINEDD) - 尼日尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
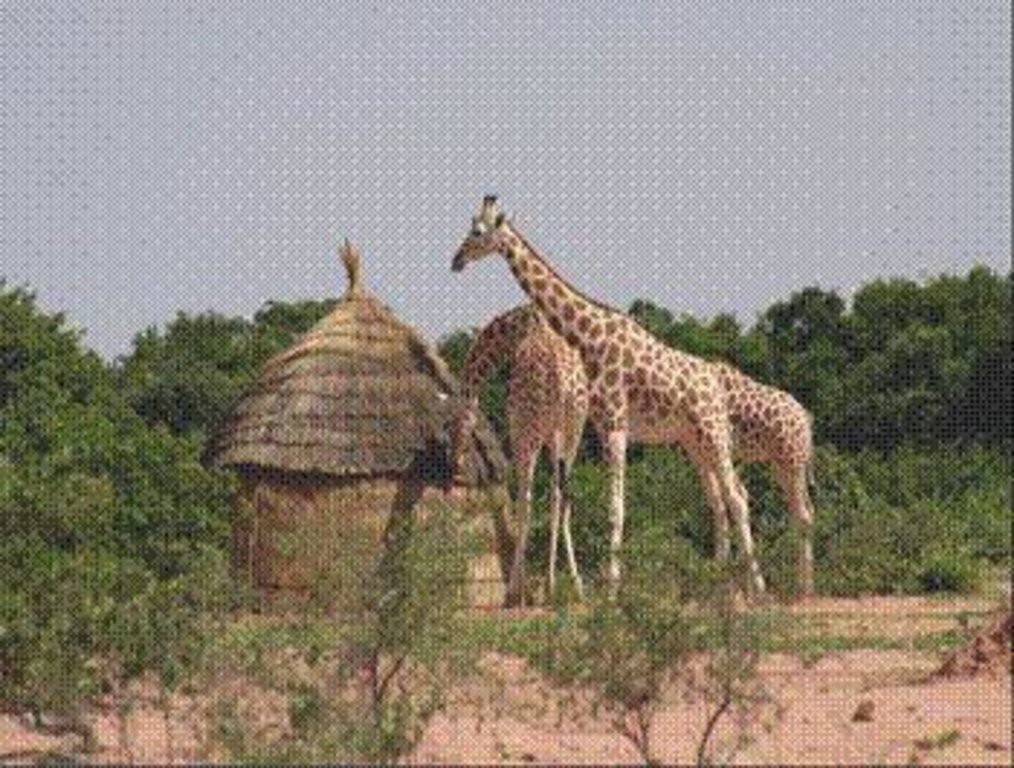
This participatory approach to protect the last population of white giraffes actively involves local people in conservation activities, while simultaneously strengthening local development and promoting ecotourism.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: The giraffe population in Kouré, Niger is unique because: (1) it includes the last representatives of white giraffes (Giraffa camelopardalis peralta) worldwide; (2) it thrives in an unprotected environment without any natural enemy (besides man); (3) it is in direct contact with rural communities and its livestock. The giraffe, reduced to only 49 individuals in 1996, was in danger of extinction due to a variety of reasons, the main one being the progressive deforestation in their habitat: the brousse tigré savannah vegetation. From 1996-2000, a government programme funded by international development agencies (SNV*, FFEM and the EU) has been carried out to sustainably protect the giraffes and their habitat. This program is based on a participatory approach which actively involves local people in conservation activities, while simultaneously strengthening local development and promoting ecotourism. Its revenues are redistributed to all local actors. A main pillar of the approach was the transfer of responsibilities in natural resources management to local organizations. User groups, a guides’ association, a project steering committee, etc. were formed and its members were trained.
Methods: Tourism and wildlife observation infrastructure was established – including a visitor’s centre, lodging, watch towers, etc – and tourism activities were organized: Guides are trained, registered and organized into an association. They receive a fixed salary and accompany tourists in turns. Furthermore they support project technicians and researchers in monitoring giraffes and collaborate with the network of government-employed foresters, which has been set up to control the conservation of the habitat. Tourists pay an entry fee for wildlife watching tours. The revenues and donations are partly used for management and conservation of the giraffe habitat and partly for socio-economic development of the villages (such as infrastructure projects). These revenues are managed directly by the ‘communes’ (municipalities).
Other important information: Thanks to the protection of the savannah vegetation through enclosures for regeneration, prohibition of cutting and closing down of rural wood markets the giraffe population has recovered considerably, comprising 200 individuals in 2008.
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼日尔
区域/州/省:
Tillabéri / Dosso
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kouré
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
1996
终止年份(若不再采用该方法):
2000
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on SLM with other activities (health, education, infrastructure, trade, micro-credit, river works, forest surveillance)
Durable and sustainable conservation of the giraffe population in the Kouré area and protection of their habitat; Building organizational and management capacity of the local population for protecting the giraffes; Fight against poverty by offering supplementary revenue to population through ecotourism (diversification of income).
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: Conflicts between giraffes and local population (damage to crops); Extinction of giraffes; Deforestation (giraffe habitat deterioration); Rural Poverty; Negative perception of fauna by the population; Absence of titled land ownership and of adapted forestry laws
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Women were also involved
- 地方政府
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
- 国际组织
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 无 | Ministries of planning, environment, tourism and artisan, EU, Association of French Volunteers for Progress (AFVP), SNV, beneficiaries. |
| 计划 | 互动 | Kouré Guides Association (AGK), groups of beneficiaries, project advisors and animators |
| 实施 | 互动 | Kouré Guides Association (AGK), groups of beneficiaries, project advisors and animators |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | AGK, groups of beneficiaries, project advisors and animators, department of Environmental Protection |
| Research | 无 | French Center for Agricultural Research for Development (CIRAD), University of Niamey, National Agricultural Research Institute of Niger (INRAN), International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) |
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 政治家和领袖
解释:
Initiation by the Ministries of planning, environment, tourism and artisan, EU, Association of French Volunteers for Progress (AFVP), SNV, beneficiaries
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
明确受训人员:
- 土地使用者
- 现场工作人员/顾问
如果相关,请说明性别、年龄、地位、种族等。:
members of community management committee, land users (women and men), professional guides, advisors
培训形式:
- 在职
- 农民对农民
- 示范区域
- 公开会议
- 课程
涵盖的主题:
Conservation technologies and SLM, ecotourism, professional guide skills, organization of associations, accountancy, agriculture
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
指明是否提供了咨询服务:
- 在土地使用者的土地上
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Dissemination of the approach was by rural animation tools (village planning, rapid PRA, etc.).; The Youth Association for Preservation of Natural Resources (AJPREN), U.S. Peace Corps, AFVP and local departments for Environmental Protection ensured a continuous programme of training, environmental education and awareness raising of guides and local people.
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 生态学
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
Research had been conducted on-farm in collaboration with local populations. Research topics treated were socio- economical, ecological, technical, giraffe habitat and genetics and agricultural.
Research was carried out on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- 100,000-1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: international (EU, SNV, FFEM): 100.0%
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 机械 | 充分融资 | |
| 工具 | 充分融资 | |
- 农业
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 种子 | 充分融资 | |
| 化肥 | 充分融资 | |
- 基建
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Tourism | 充分融资 | |
- 其它
| 其它(具体说明) | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Village development funds and Giraffe habitat management | 充分融资 |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
5.4 信用
是否根据SLM活动的方法给予信用值?:
是
对条件(利率、回报等)进行具体说明:
repayment conditions: Through village development fund; micro-credit was allocated without interest to women of women groups for agriculture or livestock production. Repayment occurred after six months. After termination of the project, ‘Care International’ continued giving credit however with interest..
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Improved sustainable land management: one director for the planning and management of the giraffe area was appointed.
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
financial support to women for agricultural production
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Adoption of Approach by other land users / projects: the ECOsystèmes Protégés en Afrique Sahélienne (ECOPAS) project adopted (2002) this approach which became the basis for national planning action for giraffes in Niger.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
3811 Euros/village had been distributed to the population of 20 villages through village development funds
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
creation of 13 permanent guide jobs; 900 woman developed agriculture production for marketing
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 增加利润(能力),提高成本效益比
- 支付/补贴
- well-being and livelihoods improvement
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 是
若是,请说明如何维持:
After the project was terminated, land users continued this approach without external support based on local development organizations, Association pour la Sauvegarde des Giraffes du Niger (ASGN) and Kouré Guides Association (AGK). Since 2002, the research component is being continued by ECOPAS / EU.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Populations organization and mobilization |
| Scientific research tools for decision making |
| Economic, financial and ecological impacts |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Absence of local and national financial contribution | provide regressive grants and promote endogenous funding of activities |
| Uncontrolled fast growth of giraffe population | transfer of giraffes to other protected habitats in West Africa. |
| Approach resulted from exterior initiatives | awareness raising and environmental education to develop ‘conservation behaviour’ in Niger |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Oumarou A. 2006. Elaboration d’une stratégie de conservation à long terme de la girafe au Niger, communication à l’atelier sur les girafes du Niger organisé du 22-24 novembre 2006 à Niamey (Niger) par le Ministère de l’environnement et de la lutte contre la désertification en partenariat avec ECOPAS/Union EuropéenneCompte rendu de l’atelier international sur la cogestion faune sauvage et bétail, organisé par Abdoulaye Sambo Soumaila et Marlis Lindecke, DED Niger et GTZ Eschborn, février 2001
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Compte rendu de l’atelier international sur la cogestion faune sauvage et bétail, organisé par Abdoulaye Sambo Soumaila et Marlis Lindecke, DED Niger et GTZ Eschborn, février 2001
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块