Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) [葡萄牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Celeste Coelho
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Deborah Niggli
Zona de Intervenção Florestal (Portuguese)
approaches_2588 - 葡萄牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与方法评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对方法进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)有助于对方法进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Aveiro (University of Aveiro) - 葡萄牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
10/02/2009
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 SLM技术问卷的参考
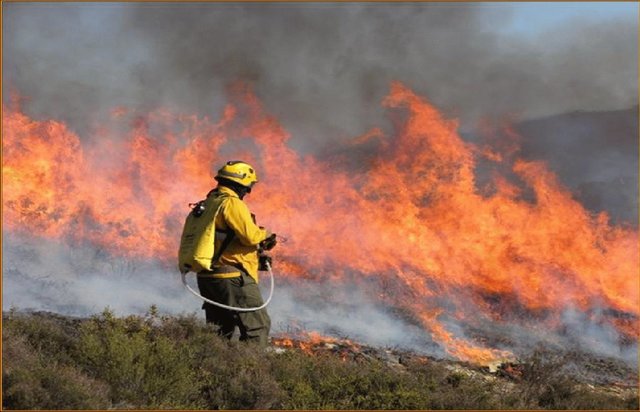

Prescribed fire [葡萄牙]
Use of prescribed fire (or ‘controlled burn’) to reduce the fuel load in the form of live and dead plant material and thus to prevent the likelihood of more damaging wildfire.
- 编制者: Manuela Carreiras
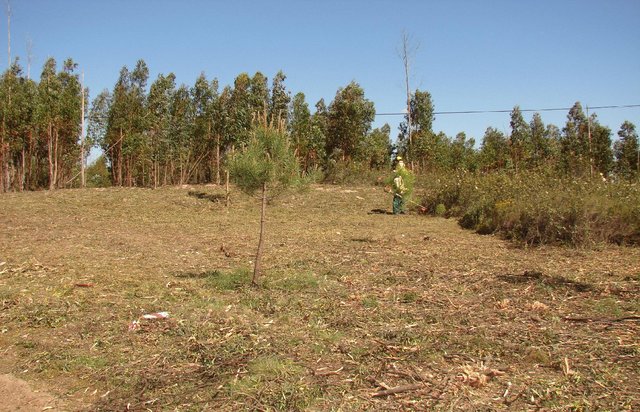

Primary strip network system for fuel management [葡萄牙]
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
- 编制者: Celeste Coelho
2. SLM方法的描述
2.1 该方法的简要说明
Forest Intervention Area (ZIF) is a territorial unit, where the main land use is forestry. This approach assembles and organizes small forest holders and defines a joint intervention for forest management and protection. Defined by law in 2005, and revised in 2009, each ZIF of private forest has to include at least a contiguous area of 750 ha, 50 landowners and 100 forest plots, and has to be managed by a single body, defined by ZIF members.
2.2 该方法的详细说明
该方法的详细说明:
Aims / objectives: The ZIF overall objective is to promote the efficient management of forest and to mitigate current constraints of forest intervention (e.g. land size and tenure). Other objectives are to develop structural measures for fire prevention, to integrate local and central administration actions and to implement the national and regional forest management policy at the local level. The final purpose of ZIF areas is to improve productivity in rural forest areas, contributing to rural development
Methods: The idea emerged after the catastrophic wildfires of 2003 and was developed and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, City Council, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries. The ZIF approach was legislated by Law 127/2005, and revised under Law 15/2009. Each ZIF assembles small properties, which will be jointly managed by a single entity, which can be a non-profit-making and voluntary organization or some other group of people approved by the forest owners. Each ZIF will have a Forest Management Plan (PGF), where the forestry operations and activities for ZIF area are defined accordingly to the guidelines of the Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning (PROF), and a Specific Plan to Forest Protection (PEIF), which includes actions to protect forest against biotic and abiotic risks. The management entity should have a team with qualifications and experience in forestry and with technical ability to design these plans.
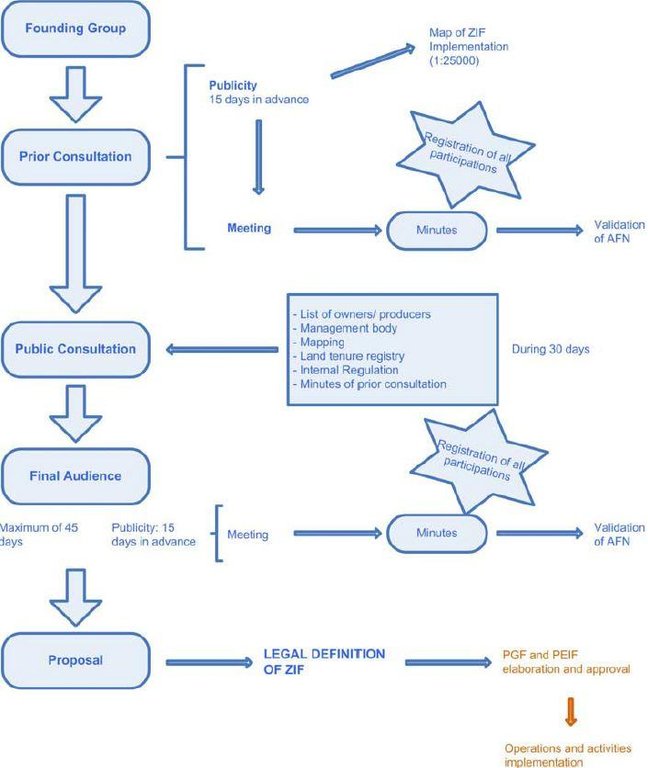
Stages of implementation: The legal constitution of ZIF includes six mandatory steps, namely the constitution of the founding group (group of landowners with at least 5% of a continuous area inside the ZIF), the prior consultation meeting, the public consultation, the final audience meeting, the proposal submission to the National Forest Authority (AFN) and legal publication of each ZIF (already done). After these procedures, the PGF and PEIF of each ZIF will be designed by the management entity and evaluated and approved by AFN. The implementation activities can then be implemented by the management entity or by individual landowners following the rules described on the plans. PEIF validity is five years and PGF validity is 25 years (still in preparation). [See figure below].
Role of stakeholders: The founding group is mainly composed of forest owners and producers and is the starting point for creating a ZIF. The management entity administers the ZIF in order to achieve their main purposes and the aims defined on the plans. AFN will support and monitor ZIF activities. ZIF non-supporting landowners are obliged to have a PGF for their land, as well as to accomplish the PEIF of the ZIF.
Other important information: The landowners inside the ZIF who are non-supporters do not have a clear role. Based on PROF - Plano Regional de Ordenamento Florestal (Regional Plan for Forestry Management and Planning), for ownerships of > 25 ha, the owners are obliged to have a PGF - Plano de Gestão Florestal (Plan for Forestry Management) for their property.
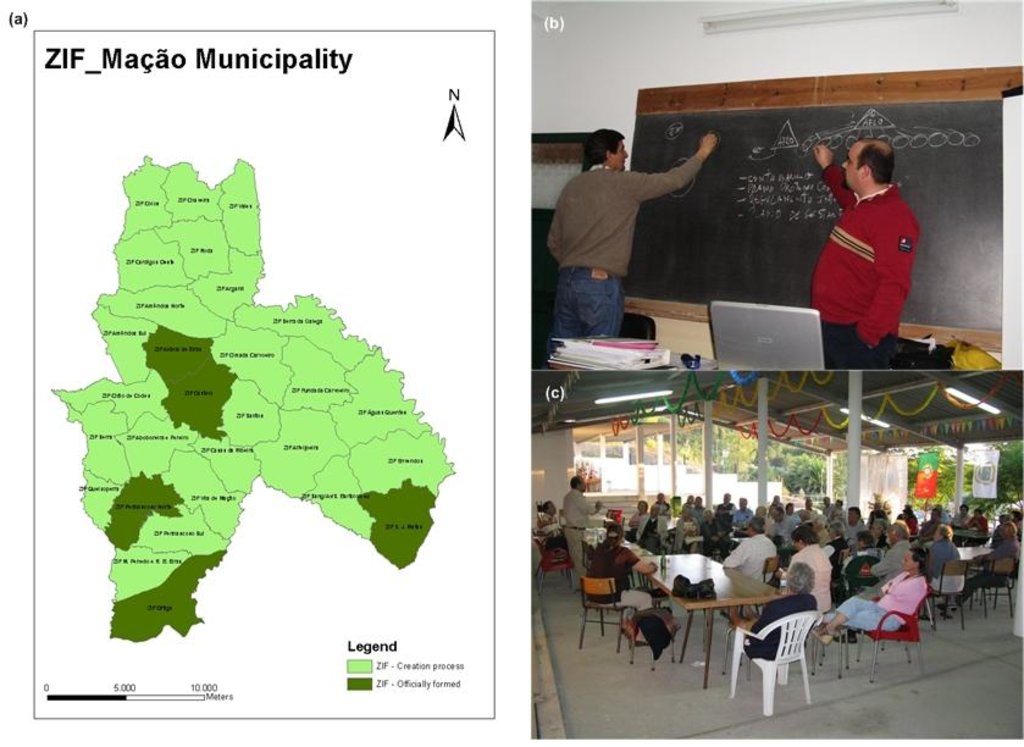
2.3 该方法的照片
2.5 采用该方法的国家/地区/地点
国家:
葡萄牙
区域/州/省:
Santarém
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mação
Map
×2.6 该方法的开始和终止日期
注明开始年份:
2003
2.7 方法的类型
- 基于项目/方案
2.8 该方法的主要目的/目标
The Approach focused mainly on other activities than SLM (The main objective is to increase land management and profitability)
- To promote the sustainable management of forest; - To coordinate the protection of forest and natural areas; - To reduce the conditions to fire ignition and spread; - To coordinate the recovery of forest and natural areas affected by forest fires; - To give territorial coherence and effectiveness to the action of local administration and others actors.
The SLM Approach addressed the following problems: - lack of forest planning and management, forest fires, land structure and tenure, land abandonment, rural depopulation and ageing.
2.9 推动或妨碍实施本办法所适用的技术的条件
社会/文化/宗教规范和价值观
- 阻碍
Social resistance to this approach. Landowners fear to lose tenure rights. Difficult to reach and find owners due to inheritance and out-migration. Rural depopulation occurred in the last decades.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Financial support, creation of new job opportunities in rural areas.
财务资源和服务的可用性/可得性
- 阻碍
High implementation cost.
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Governmental incentives
机构设置
- 阻碍
Scepticism about the practical effects of this approach. Very high costs for implementation and lack of private investment
Treatment through the SLM Approach: ZIF pilot areas will motivate implementation and investment into other ZIFs.
法律框架(土地使用权、土地和水使用权)
- 阻碍
Land structure and tenure (private holdings)
Treatment through the SLM Approach: Minimum area to constitute a ZIF is 750 ha
The existing land ownership, land use rights / water rights greatly hindered the approach implementation The ZIF join small properties and their management is undertaken as a single property, guide by a forest management plan. This entity can be a non-profit and voluntary organization or an other group of people approved by the forest owners and/or producers.
3. 相关利益相关者的参与和角色
3.1 该方法涉及的利益相关者及其职责
- 当地土地使用者/当地社区
Gender: mixed, Age: 50 years old
The majority of forest owners are usually pensioners, with low incomes
- SLM专家/农业顾问
AFLOMAÇÃO technicians
- 私营部门
Private organizations
- 地方政府
- 国家政府(规划者、决策者)
Municipality
如果涉及多个利益相关者,请注明领导机构:
Based on an initial idea from Mação local specialists; the national ZIF legislation emerged in 2005 and was revised in 2009
3.2 当地土地使用者/当地社区参与该方法的不同阶段
| 当地土地使用者/当地社区的参与 | 指定参与人员并描述活动 | |
|---|---|---|
| 启动/动机 | 互动 | Balance alternatives and take decision to test the agave forestry information sessions about ZIF approach; informal contacts, door-to-door approaches and formal agreement of the landowners to become ZIF members. |
| 计划 | 被动 | information sessions to present the ZIF plans (PGF and PEIF). |
| 实施 | 互动 | management activities can be made by the land owners or by the ZIF management entity. Regular meetings with ZIF members |
| 监测/评估 | 互动 | not defined yet |
| Research | 互动 | on-farm research, good practice demonstration and collaboration with research projects. |
3.3 流程图(如可用)
具体说明:
Legal process related with the ZIF constitution (blue)
Elaboration and approval of the ZIF plans (orange)
Implementation of the plans (orange)
3.4 有关SLM技术选择的决策
具体说明谁有权决定选择要实施的技术:
- 主要是SLM专家,咨询土地使用者之后
解释:
Users’ perceptions and expectations were also considered.
Decisions on the method of implementing the SLM Technology were made by by SLM specialists alone (top-down)
4. 技术支持、能力建设和知识管理
4.1 能力建设/培训
是否为土地使用者/其他利益相关者提供培训?:
是
- opinion leaders
涵盖的主题:
information sessions and individual contacts with opinion leaders
4.2 咨询服务
土地使用者有权使用咨询服务吗?:
是
说明/注释:
Name of method used for advisory service: Information sessions; Key elements: ZIF process, Explaining rational of ZIF for specific municipality and its conditions like depopulation, forest fires, etc, Elaboration of the ZIF plans; The extension system is well set up to ensure follow-up activities
Advisory service is very adequate to ensure the continuation of land conservation activities
4.3 机构强化(组织发展)
是否通过这种方法建立或加强了机构?:
- 是,非常
具体说明机构的强化或建立程度:
- 本地
提供进一步细节:
City council supports the forest association activities.
4.4 监测和评估
注释:
There were None changes in the Approach as a result of monitoring and evaluation: (* The monitoring procedures are not structured yet)
4.5 研究
研究是该方法的一部分吗?
是
明确话题:
- 社会学
- 经济/市场营销
- 生态学
- forestry, politics
提供进一步的细节,并指出是谁做的研究:
The approach includes technical and local knowledge. The idea was prepared and presented by a group of stakeholders (landowners, forest associations, among others) to the Ministry of Agriculture, Rural Development and Fisheries and legislated by the Law n. º 127/2005, 5 August.
Research was carried out both on station and on-farm
5. 融资和外部物质支持
5.1 该方法中SLM组成部分的年度预算
如果不知道准确的年度预算,请给出一个范围:
- > 1,000,000
注释(例如主要的资助来源/主要捐助者):
Approach costs were met by the following donors: government (Permanent Forest Fund): 100.0%; local community / land user(s) (ZIF implementation activities: National Strategic Reference Framework (60%), Land users (40%))
5.2 为土地使用者提供财政/物质支援
土地使用者是否获得实施该技术的财政/物质支持?:
是
5.3 对特定投入的补贴(包括劳动力)
- 设备
| 具体说明哪些投入得到了补贴 | 程度如何 | 对补贴做出具体说明 |
|---|---|---|
| Printer, toners, map production | 充分融资 | |
如果土地使用者的劳动力是一项重要的投入,那么是不是:
- 自愿
注释:
Landowners can work on their properties or can be substituted by the ZIF management entity. Some activities, such as the implementation of the Primary Strips Network System for Fuel Management can be supported by the municipality services.
1-technical, fully financed (FFP).2- preparation of PGF,partly financed. 3-implementation,partly financed.
6. 影响分析和结论性陈述
6.1 方法的影响
该方法是否帮助土地使用者实施和维护SLM技术?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Reduction of the number and likelihood of forest fires.
该方法是否有助于社会和经济弱势群体?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
It is expected that the increase in land productivity through the implemented technologies will help to improve the socio-economic situation of these rural groups.
该方法是否改善了阻碍SLM技术实施的土地使用权/用户权问题?:
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Did other land users / projects adopt the Approach?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
The initial social resistance to the approach will diminish through the existence of a successful ZIF.
Did the Approach lead to improved livelihoods / human well-being?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
Did the Approach help to alleviate poverty?
- 否
- 是,很少
- 是,中等
- 是,支持力度很大
It is expected that the implementation of this approach will contribute to the improvement of rural socio-economic conditions through productivity increase, creation of employment and promotion of local products.
6.2 土地使用者实施SLM的主要动机
- 规章制度(罚款)/执行
- 加入运动/项目/团体/网络
- aesthetic
- forest fires
6.3 方法活动的可持续性
土地使用者能否维持通过该方法实施的措施(无外部支持的情况下)?:
- 否
若否或不确定,请具体说明并予以注释:
The forest owners do not have the financial capacity to apply and support these activities by themselves.
6.4 该方法的长处/优点
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Social conscience (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: through awareness campaigns and information sessions provided at national and local level.) |
| Prevention of forest fires (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: the increase of forest management will contribute to the decrease of large forest fires. The implementation of integrated and global measures to fire prevention will be suitable within the ZIF approach.) |
| Restoration of burnt areas (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: The use of forest species to enable the protection and recovery of degraded soils or soils with high erosion risk has a very positive influence on the rehabilitation of burnt areas. However, many of these species are not economically attractive at short or medium term. The management of the land using ZIF model will allow the definition of the most affected areas for an urgent intervention.) |
| Increase productivity (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: present land tenure and structure of forest holdings constitute a bottleneck for forest productivity. The integrated management of the ZIF will allow a better management and use of the land, increasing the exploitation of timber and non-timber products and also increasing the resilience to wildfires.) |
| Improve forest management (How to sustain/ enhance this strength: promotion of the planting of more fire-resilient species which are better adapted to the local conditions. AFN should: (i) provide information about the guidelines; (ii) develop new policies and tools, which are more suitable to the local level; (iii) support and implement public awareness campaigns about forest values and services, and (iv) provide financial support to ZIF constitution and implementation activities.) |
6.5 该方法的弱点/缺点以及克服它们的方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Unattractive investment (low public support and lack of private support) | the need to review and reform the existing QREN or provide others means of support. Incentives to private initiative or donors should be found. |
| Highly bureaucratic nature of the ZIF approach | simplification of the bureaucratic process |
| Rather complex process: unclear role for the non-adherent landowners within the ZIF; ZIF has to follow many laws and plans; control and monitoring activities still not defined | clarification and simplification of the bureaucratic process of the ZIF |
| Costs related to the approach | major financial support from the government needs to be provided. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 方法/信息来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Decree- Law 127/2005, 5 August. Official Gazette n. 150 - I series A.: 4521-4527Decree-Law 15/2009, 14 January. Official Gazette n. 9 - I series: 254-267AFN (2011). Caracterização das Zonas de Intervenção Florestal. Lisboa, Autoridade Florestal Nacional: 54
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Prescribed fire [葡萄牙]
Use of prescribed fire (or ‘controlled burn’) to reduce the fuel load in the form of live and dead plant material and thus to prevent the likelihood of more damaging wildfire.
- 编制者: Manuela Carreiras

Primary strip network system for fuel management [葡萄牙]
Linear strips are strategically located in areas where total or partial removal of the forest biomass is possible. This technology contributes towards preventing the occurrence and spread of large forest fires and reducing their consequences for the environment, people, infrastructures, etc.
- 编制者: Celeste Coelho
模块
无模块