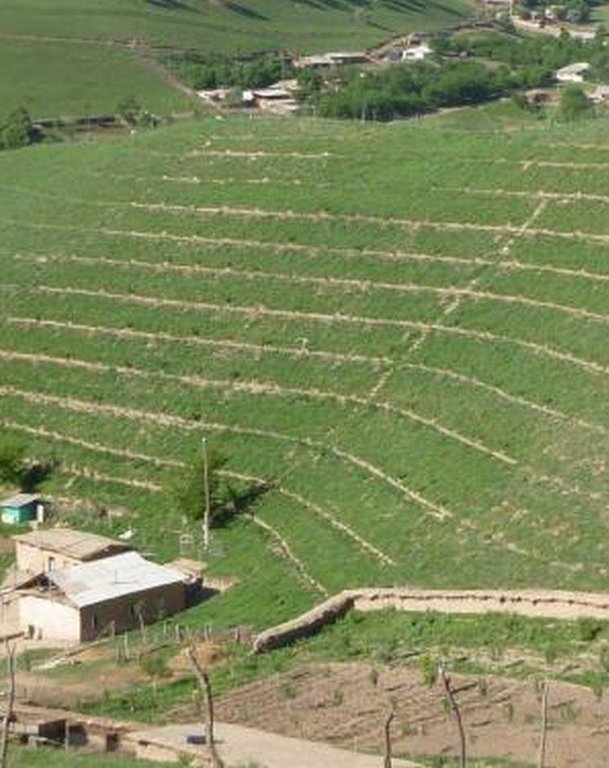
Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Manuchehr Rakhmatdzhonov
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Ташакули тадричии терассахо тавассути чуйборхои контури
technologies_1043 - 塔吉克斯坦
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: Aug. 20, 2019 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: July 22, 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: June 2, 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: May 31, 2017 (inactive)
- Gradual development of bench terraces from contour ditches: Dec. 27, 2016 (inactive)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
hafizova tahmina
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe, Tajikistan
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Welthungerhilfe e. V. (Welthungerhilfe) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/05/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
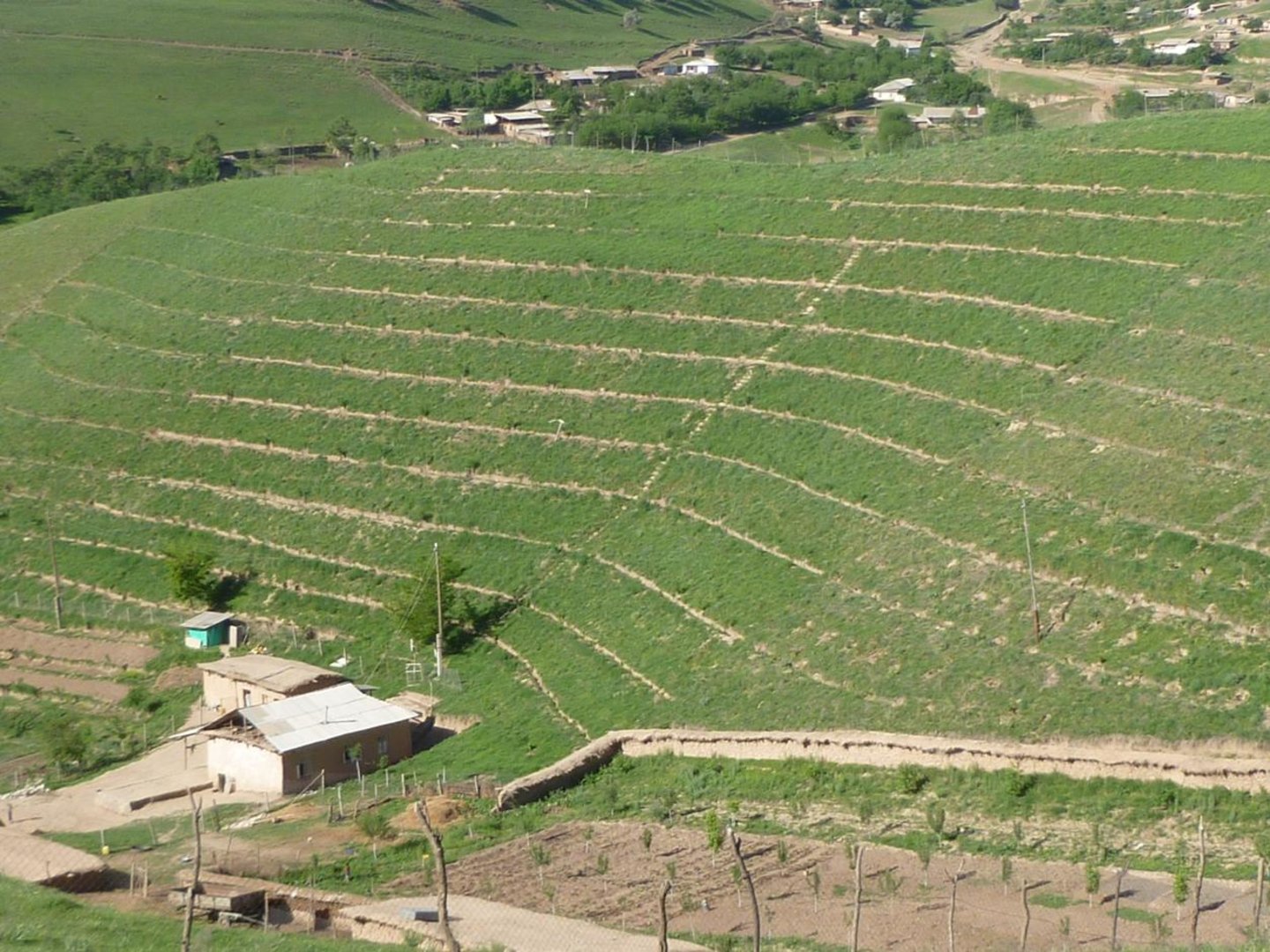
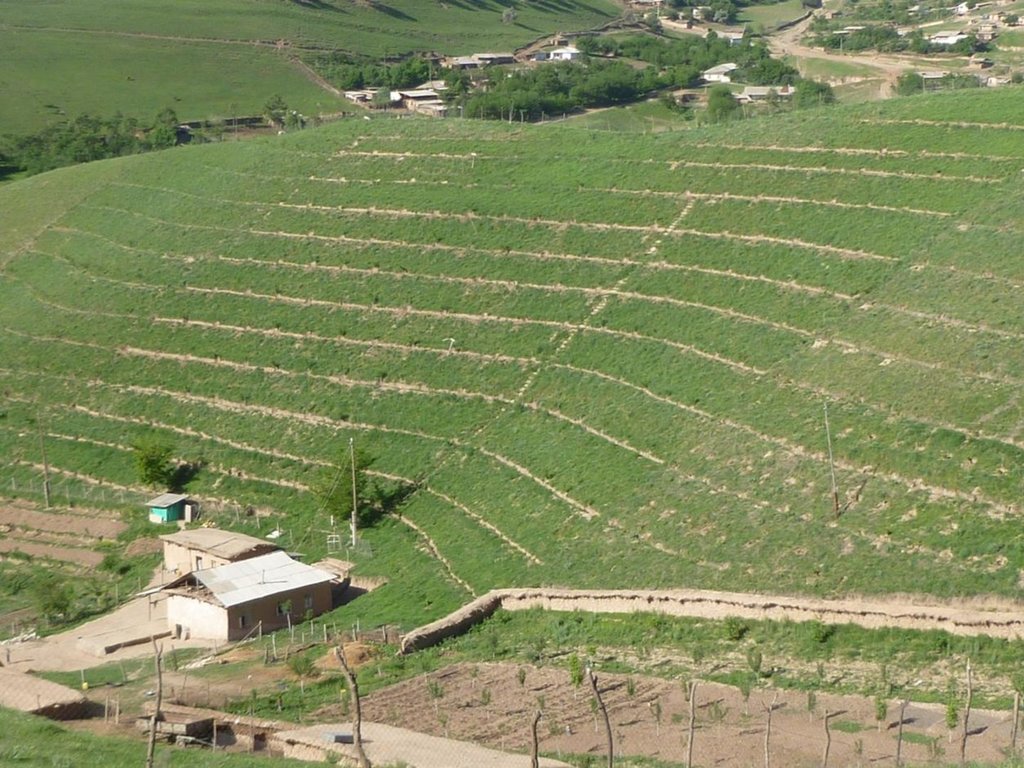
Use of the SLM technology facilitates the development of bench terraces from contour channels by gradually removing soil material up the slope for an estimated 5 years until the terraces on the slope reach a desired width of 1.2 m.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The SLM technology is thought to stop water run-off resulting in the prevention of damage to the top soil on steep slopes. This enables better distribution and infiltration of water into the soil. A complementing live fence, along with a metal net along the perimeter aim to stop livestock grazing. Contour ditches are planted in intervals with fruit trees, and the live fence is made of a combination of fire wood, trees and bushes. This combination makes possible the establishment of an agro forestry system on a slope in an area with limited irrigation using making use of the natural rainfall.
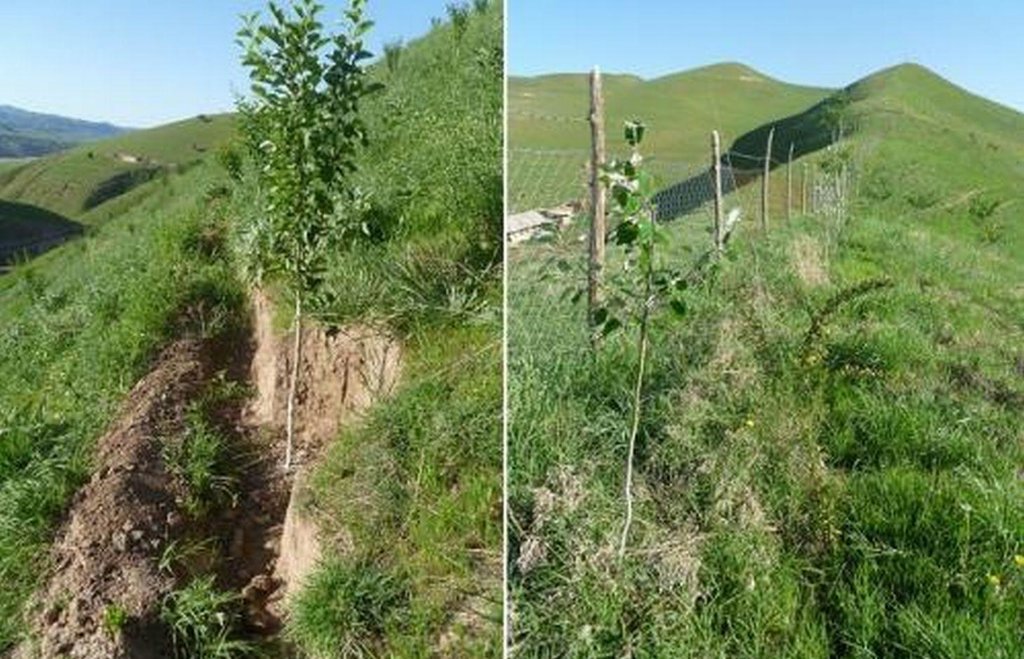
Details: 1. Ditches are dug out along the contour lines drawn by an "A" frame on the slope. 2. Seedlings are planted in 5 metre intervals, positioned right in the middle of the ditch. 3. The back wall behind each tree (upslope) has a half moon cutting to enable an even water/moisture supply. 4. The ditches are barriered with "septas" between two trees to trap water in the individual sections. 5. Horizontally across the ditches, the tree species vary, but vertically are homogeneous. 6. The strips between ditches are left free to enable natural grass to grow. 7. The residual soil material is mounted in front of the ditches in piles the width of a shovel. 8. The complementing perimeter live fence and metal net (1.5m height) is supported by wooden poles made of Acacia trees. (Assumed life span of poles is 25 years). 9. Improvised drip irrigation with 5 litre plastic bottles is used together with mulch coverage beneath the trees. 10. Species composition: apple, cherry, apricot, grape, walnut, pomegranate. In the garden; species of Acacia, Ailantus, dogroses and willow act as a live fence.
Purpose of the Technology: The aim of this system is to significantly reduce the water run-off that removes the top soil, and to subsequently prevent water erosion, and the formation/development of gullies. This can be achieved through the following methods; conserving the available resources and using them more efficiently, prevention overgrazing and improving the natural soil cover, as well as changing the type of land management towards a more sustainable and profitable one.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The plot was established on one side of a micro watershed. In mid February the contour lines were identified using an “A” frame. Digging of contour ditches then took until late February. The material was accumulated down the slope in deposits the width of a shovel to build a riser. At the beginning of March all the fruit tree seedlings were planted in the middle of the ditches. Perimeter fencing was constructed and live fence plants were planted up until late March. In May, the grass around the trees was cut and used for mulching beneath the trees. During June and July in the first year the plants needed watering 3 times a week which was done using a drip irrigation system with 5 litre plastic bottles. To help prevent the water heating and evaporating, the bottles were left under the mulch cover. Mulching and irrigation are repeated every dry and hot season. Every spring, the soil material is removed alongside the inner wall of the ditch just taking an amount that equals the width of a shovel, and accumulated down the slope to extend the riser. Materials required include: (1) Ditches: hand tools, stakes, rope, “A” frame, (2) Live fence: seedlings of Acacia, Ailantus, willow and dog rose, (3) Fencing: metal net, wooden poles, metal wire, (4) Cow dung, lime suspension, straw, mulch, plastic bottles.
Natural / human environment: The watershed can be characterised as follows: Hydrology - surface water is available only at times of rain and snow melt, this can be used for irrigation only. No sources of potable water exist. Soils are of loess type, as generally characteristic to the whole area. Flora - natural grasses prevail in the micro watershed, 9 species could be identified. Natural bushes and trees were completely removed due to high demand for fuelwood. Cultivation of rare tree varieties and household gardening was practiced in advance of the project. Fauna - Wild animals are often still seen such as turtles, lizards and snakes. Farm animals - mixed breeds of cattle, sheep and goats are very important. The households in this micro watershed area own almost 350 animals. The majority of these are kept for the summer season in adjacent pastures. The micro watershed was first inhabited in early 2000. Five households were established with a total of around 40 inhabitants. Family heads tend to be in their early 40s. Families have 7 to 9 members, including 5 to 7 children. All are of Tajik ethnicity, and Muslim, open to secular values. Of these 5 households, only 4 households have adopted the SLM technology. The fifth household only decided to join the project after witnessing their neighbour’s positive experiences. Both spouses tended to be involved in the activities. Both men and women took part in the training sessions and orientation meeting. However, it is likely that most decisions were made by the men, after the women had shared their ideas. Work load: providing the external inputs, construction and the heavy manual labour were done by the men. Maintenance work: watering, mulching and grass cutting was shared between men and women. Digging and fencing were performed in "hashars" - community labour groups. As women spend more time at home working within their households, they tend to perform more maintenance work on the plot compared to men. Other activities away from the farms are important to the family budget providing a means of extra income. This often includes men’s long term migration to Russia to find work.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Tajikistan, Khatlon
有关地点的进一步说明:
Baljuvon, Khirob
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: North - 38.284233°N 69.639420°E
South - 38.278485°N 69.639555°E
East - 38.281854°N 69.641276°E
South - 38.281250°N 69.638009°E
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 游牧
- 半游牧/游牧
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Implementation of land tenure rights at a local level was also a major barrier.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is a soil and water conservation project in place to manage water runoff, soil erosion and gully formation. Low land productivity only allows for wheat production with long fallow periods. Improper pasture management has led to overall overgrazing.
Nomadism: animals taken to summer pastures
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: animal graze around villages
Ranching: no practice
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: almost extinct
Improved pasture: no practice at all
Clear felling of (semi-)natural forests: No selection in times of electricity cuts in winter season.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, fruits and nuts, grazing / browsing, other forest products / uses (honey, medical, etc.), nature conservation / protection
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines): no irrigation network, heavy transports costs
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
注释:
Water supply: rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated, rainfed
Water supply: post-flooding
post-flooding
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: March - August
牲畜密度(如相关):
50-100 LU /km2
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.112 m2.
The application of the SLM technology is planned for the whole micro watershed which has a total area of 0.112 km2. Currently it has been impemented in 0.07km2 of this watershed.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S1:阶地

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: mixed cropping / intercropping, contour planting / strip cropping, mulching, legume inter-planting, manure / compost / residues, zero tillage / no-till, pits
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, aligned: -graded strips *<sup>3</sup>, aligned: -along boundary
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Tillage on steep slope >35%.), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Natural tree and shrubs removed completely.), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (Stocking rates do exceed the standards in multiple times), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Run-off is induced by maximum removal of vegetation cover.), land tenure (Unclear land right situation induces irresponsible attitudes.), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Very limited infrastructure development, vital infrastructure points are a long distance away.)
Secondary causes of degradation: Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Induces gully formation and mass movement.), droughts (If vegetation is dry then less soil cover is provided.), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (The gradient is over 30%.), population pressure (Large family sizes, and high growth rates causes increased need for food and living space in the area.), poverty / wealth (Very limited financial power to develop the land.), labour availability (Though cheap labour is available, it takes much effort to organise communities to work together for SLM activities.), education, access to knowledge and support services (Basic schooling of children, no state provided extension or training after school age.), war and conflicts (The after-effects of recent civil war still have some influence.), governance / institutional (Communist attitudes still persist, very slow institutional development.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
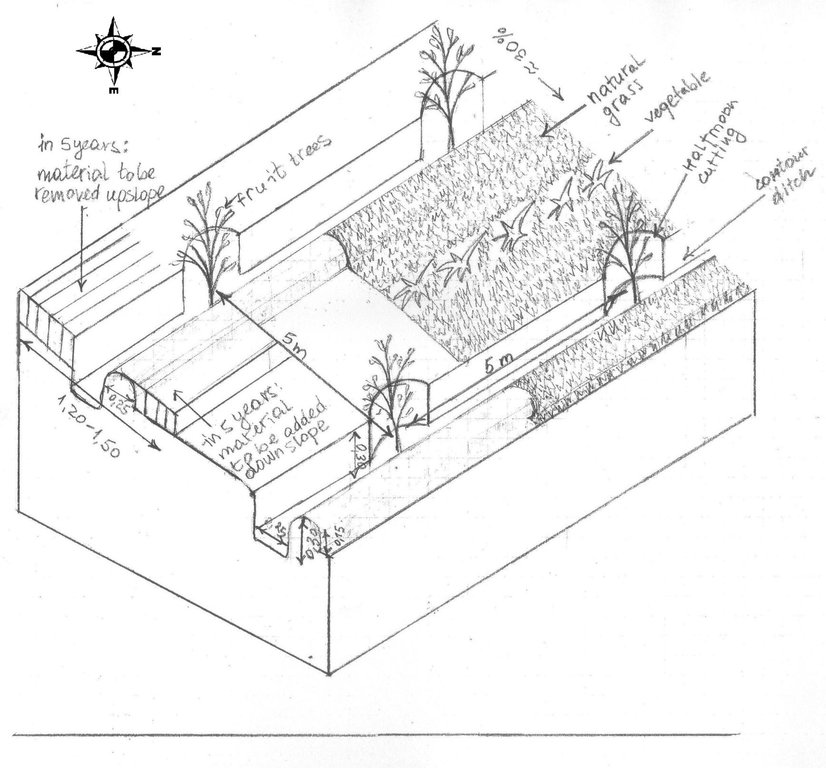
The drawing shows the contour ditches on a slope with a 25 - 30 % steepness. The gradient is 3-5%.
Vertically, the contour ditches are spaced at 5 m intervals. The upper left part of the drawing shows how the material on the slope will be removed in portions during the five years to create a levelled terrace. The ditches are planted with fruit trees, and strips of natural grass cover the space between the ditches. In the middle line of the strips in the bottom part of the plot the farmer has grown vegetables.
Location: Khirob village. Baljuvon/ Khatlon/ Tajikistan
Date: 06.05.2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Specific knowledge needed in the issues of integrated watershed management and technology.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Training needed in terms of technology, planning and implementation of activities.)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase of infiltration, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, increase of surface roughness, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Growing a few tomatoes and paprica on the bottom strips.
Quantity/ density: 4plants m2
Remarks: Down slope alongside the ditches.
Contour planting / strip cropping
Material/ species: Wild vegetation is left to grow.
Quantity/ density: very dense
Remarks: Over 9 species counted on the plot all palatable, cut for hay and mulch.
Mulching
Material/ species: Mulching from natural grass, over 9 species.
Remarks: Ditches and trees covered beneath.
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 2 raisers.
Remarks: As a test to cover raiser surface.
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Cattle dung suspended in water.
Quantity/ density: Once.
Remarks: Applied while planting the trees.
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: No tillage for intercropping completed.
Pits
Material/ species: Pits were dug to plant seedlings.
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 5
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): na
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Trees/ shrubs species: Ailantus, Acacia, dog rose, willow, poplar
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Apple, grape, pear, apricot, cherry, pomegranate, mulberry, walnut
Perennial crops species: little alfalfa and espercet
Grass species: 9 naturally growing species
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 30.00%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 25.00%
Retention/infiltration ditch/pit, sediment/sand trap
Vertical interval between structures (m): 5
Spacing between structures (m): 5
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.25
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.15
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Terrace: bench level
Vertical interval between structures (m): 3.50-3.80
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.25
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.20-1.50
Construction material (earth): the earth is removed upslope and added downslope to the front bank (raiser)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25-30%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 3-5%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: Communal pasture land was turned into an agroforestry system
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Self subsistance, market orientated agroforestry system
Layout change according to natural and human environment: Along the contour lines of the slope
Major change in timing of activities: Major seasonal activities in three seasons: spring agronomic and vegetative measures, summer and autumn yield harvesting, clearing the branches
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.00
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting seedlings in contour ditches | 植物性的 | February-March |
| 2. | Planting seedlings and bushes along the perimeter | 植物性的 | March |
| 3. | Cost of seedlings: frutiouse and firewood trees | 植物性的 | February -March |
| 4. | Gradual terracing by Broadening the ditch onslope and extending the raiser downslope | 结构性的 | every spring during 5 years |
| 5. | Membership fees | 管理 | |
| 6. | Attending the training | 管理 | |
| 7. | Management of staff | 管理 | |
| 8. | Taxes | 管理 | |
| 9. | Taxes | 管理 | |
| 10. | Membership fees | 管理 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | 80.0 | 355.0 | 28400.0 | 50.0 | |
| 植物材料 | mulching | 5.0 | 66.0 | 330.0 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | a wood frame | 5.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | tools | 15.0 | 4.5 | 67.5 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 28812.5 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Drip irrigation with plastic bottles | 农业学的 | first 3 years |
| 2. | Mulching | 农业学的 | once a year |
| 3. | Shaping the trees, cutting branches | 植物性的 | Autumn |
| 4. | Shaping the trees, cutting branches | 植物性的 | Autumn |
| 5. | Grafting | 植物性的 | March |
| 6. | Grafting | 植物性的 | March |
| 7. | Manuring | 植物性的 | March |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 植物材料 | mulching | person/day | 5.0 | 22.0 | 110.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | drip irrigation with plastic bottles | pers/day | 15.0 | 66.6 | 999.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1109.0 | |||||
注释:
Labour costs apply to the cultivation of the whole 7ha plot.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most affecting factors were the high cost inputs for construction material which usually has to be imported into the area: Fuel, metal nets for fencing, cement, etc.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Summer, >120 dry days
250-500 mm
Late summer, late autumn, rain prevails until the late autumn
500-750 mm
Late autumn mid spring, rain, snow.
750-1000 mm
avarage annual, usually up to 800mm
1000-1500 mm
not often, 1000mm heppen in single years
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. winters with possible extreme cold, warm summers, with hot spells in July August
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
hilly area, located on the foot of Vakhsh mountain range; micro watersheds feeding the bigger watershed of the Kyzylsu river
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Very few women are trusted to run a farm or make decisions about land use. Usually women have taken leading roles only if the men leave the family for long term migration, or have died. Only 8 women in the whole district are farm owners out of the total of 350 existing farms.
Women's involvement and level of freedom given to them are influenced by existing patriarchal values, and in many areas women often remain unaware of their rights.
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
3% of the land users are very rich and own 20% of the land.
5% of the land users are rich and own 10% of the land.
10% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
60% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
22% of the land users are poor and own 10% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Complemented by salary from state job, NGO activity, transport service and construction work in capital town and other regions, labour migration to Russia.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), mixed (subsistence/ commercial, mixed (subsistence/ commercial, commercial/ market
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha, 1-2 ha, 2-5 ha, 5-15 ha, 5-15 ha, 15-50 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
very little fodder could be collected
SLM之后的数量:
cut and carry fodder production
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
SLM之前的数量:
not possible
SLM之后的数量:
may cover 40 -50 percent of HH need only in 5 year
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
no
SLM之后的数量:
yes
产品多样性
SLM之后的数量:
yes
生产区域
SLM之前的数量:
no
SLM之后的数量:
yes
土地管理
SLM之后的数量:
yes
能源生产
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
no
SLM之后的数量:
yes
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
no
SLM之后的数量:
yes
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤压实
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Project subsidised only 50% of material inputs.
Comments on adoption trend: Metal for the net was costly- farmers had to convince the project to subsidise prior to adoption, otherwise would reject adopting (area has high risk of crop damage- high livestock density, grazing not controlled).
Year following implementation: 3 farmers in neighbourhood have adopted on own funds; much more are willing to adopt, but need external support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It helped to acquire more land user rights. |
| Land users feel they have an increased status in local society. |
|
It has good potential for replication in other areas. How can they be sustained / enhanced? It would be better if the more expensive parts of the input were subsidised. |
| Good long term perspectives for improvement of livelihoods. |
| It allows a positive long term change in household provision regarding food, employment and energy sources, allowing more spare time for cultural events and education. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It made possible the change to more sustainable land management techniques. |
| The technology is well suited to the sloping landscape and is easy to adopt. |
| The technology allows the use of locally available materials, and has low maintenance costs. |
|
It fits well to the local needs for land reclamation and conservation, and sits within the legislative frameworks. How can they be sustained / enhanced? There has been a recent state decree to encourage promotion of orchard development. |
|
It has a positive effect on the areas downstream. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Prior to implementation of the technology, areas downstream were often were damaged by floods. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It needed some immediate on-site adjustments when structuring the half moon cuttings in the contour ditches. | The farmer's opinion should be considered during the adoption of the technology, and to assist with any changes made. |
| It caused some disagreements between the farmers and the consultant over what part of the material input should be subsidised. | The consultant should try to ensure they understand the social and economic factors affecting the locals. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Needs more until the final structure is finished | This depends on the length and intensity of any precipitation/drought/dry spells etc. |
| It is a new technology in this area so will need some time to be proven effective. | |
| External knowledge is needed for the establishment and maintainance of the technology. | |
| Extra workers are needed for the complementary drip irrigation - child labour is often used for this. |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Scetch map of Khirob Microwatershed
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
DWHH Baljuvon Office
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Interim Narrative Report 01.05.2009-30.04.2010 Project TAJ 1068
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
DWHH Baljuvon Office
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Grant Application Form to EU Commision: "Individual incomes & Improving Living Standards in Khatlon and Sughd Regions", Tajikistan
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
DWHH Regional Office, Dushanbe mail to:
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块