Solar Cooker [博茨瓦纳]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Julius Atlhopheng
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger
Setofo sa marang a letsatsi
technologies_1385 - 博茨瓦纳
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
University of Botswana (University of Botswana) - 博茨瓦纳1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/02/2009
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
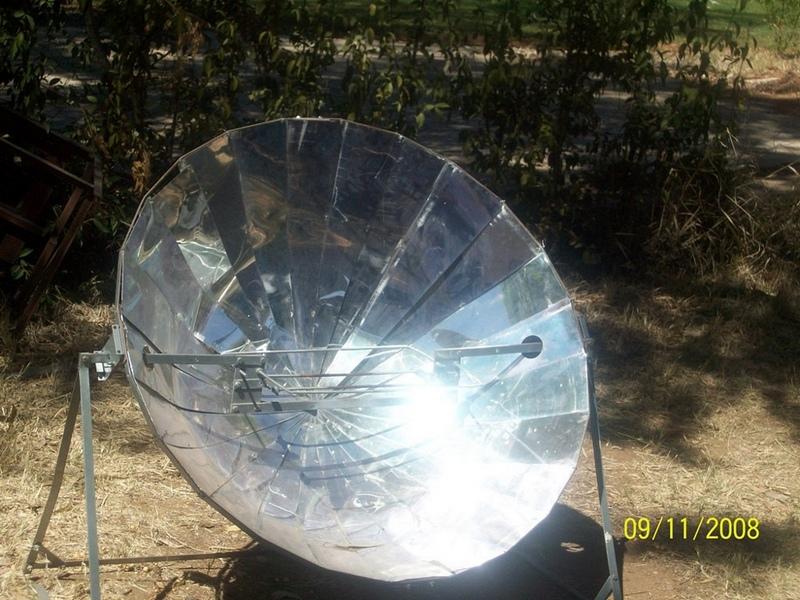
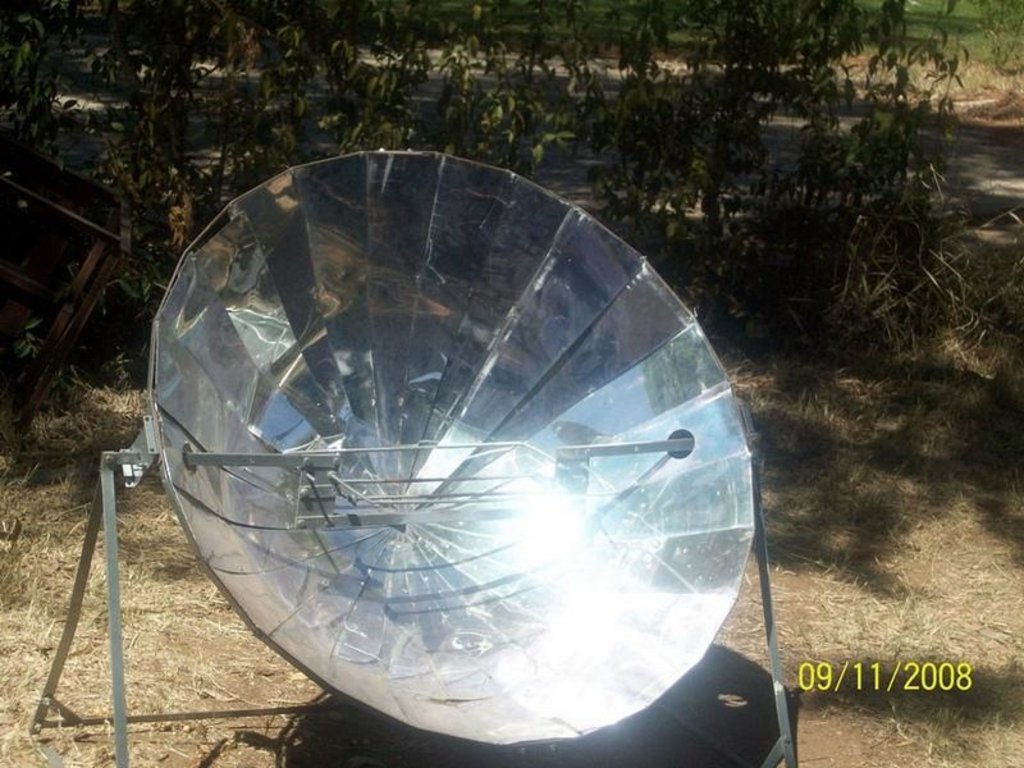
技术定义:
Harnessing solar energy through solar cookers
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The basic principle of all solar cookers is to concentrate sunlight using a mirror or some type of reflective metal. It is used to concentrate light and heat from the sun into a small cooking area making the energy more concentrated and therefore more potent. Parabolic shaped solar cookers - when a three dimensional parabolic is aimed at the sun, all the light that falls upon its mirrored surface is reflected to a point known as the focus.
The technology is supplied by the Rural Industries Innovation Centre (RIIC) in Botswana. The solar cooker is maintained by cleaning the reflector mirrors with soft cloth soaked in soap and rinse with clean water. Turn reflector anti-clockwise until it hits the stand leg to lock it in place when it not in use. The solar cooker requires frequent adjustment and supervision for safe operation.
The solar cooker is best used in an open atmosphere with direct sunlight. A solar cooker needs an outdoor spot that is sunny for several hours and protected from strong winds and where food will be safe. Solar cookers do not work at night or on cloudy days
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
博茨瓦纳
区域/州/省:
Botswana
有关地点的进一步说明:
Southern District
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

混合(作物/放牧/树木),包括农林
- 农牧业
主要产品/服务:
Main products semi-nomadism/pastoralism: Beef cattle/goats,chicken/sheep,donkeys
Main products ranching: Beef cattle
Major cash crop seasonal cropping: Sorghum
Major food crop seasonal cropping: Maize
Major other crop seasonal cropping: Beans,Melons

定居点、基础设施
- Solar cooker
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Overgrazing the commons, droughts, saline water and overharvesting of fuelwood for heating and cooking purposes leading to deforestation and land degradation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Same as above
Grazingland comments: Technology not applied in Boteti at the moment
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fn: Natural
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Mixed cropping is the traditional practice but government extension advice promotes monocropping which majority find expensive and risky.
Constraints of settlement / urban: No constraint
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - Mar
牲畜密度(如相关):
1-10 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 节能技术
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
SLM is point specific
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Et: loss of topsoil
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Most rural households use fuelwood for cooking, heating and lighting and sometimes cut live trees)
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (The study area is prone to drought), droughts, land tenure (The study area is communal grazing land), poverty / wealth (There are few employment opportunities in the study area and poor agric production hence most residents do not have adequate income to buy alternative sources of energy.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation, rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, increase of biomass (quantity), control of fires
Construction material (other): Metal + reflective mirrors or shiny alluminium sheets
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Pula
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
6.6
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 0.3 month(s)
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Material + Labour -these are current date costs
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Material followed by labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Seasonal summer rains in 6 months dry (LGP=75-179 days)
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics. Subtropical thermal climate. Semi-arid with dry winters (LGP=75-179 days)
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 501-1000 m a.s.l. (part of the Makgadikgadi Basin)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table; >50m (ranked 1, for boreholes) and 5-50 m (ranked 2, wells in Boteti River bed)
Availabilty of surface: Poor/none (unreliable river flows and rainfalls)
Water quality (untreated): poor drinking water (treatment required, unusable, sometimes too salty even for animal/livestock consumption) and poor drinking water (treatement required, salty waters in most areas ) Both ranked 1.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Biodiversity: Low (ranked 1, a grazing zone with some arable agriculture.However, the area is sandwiched between Central Kalahari and Makgadikgadi game reserves) and high (ranked 2, several national parks/game reserves nearby)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 非常丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: N/A
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
(Rich cattle barons (0.1 and 0.5%)).
(Most inhabitants (0.6 and 0.3%)).
(Subsistence farmers (0.3 and 0.2%)).
Off-farm income specification: Save labour time to fetch firewood and helps consrve forests.Limited off-farm income opportunities for everyone,including non-adopters of the technology.
Market orientation of production system: subsistence (self-supply), subsistence (self-supply), commercial/ market
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 2-5 ha
Grazing land: 1,000-10,000 ha (ranked 1, ranches and cattle posts) and 5-15 ha (ranked 2, subsistence farming)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
注释:
The SLM technology can be used by anybody, it is not group specific.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
能源生产
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
With respect to firewood collection
社会文化影响
娱乐机会
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Less demand on the time and labour of women and the girl child who are the main collectors of firewood
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It provides cheaper alternative sources of energy.Reduced workload for firewood collectors(women and girl child)
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 不好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| Cloudy weather | 不好 |
注释:
N/A
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
1% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Helps conserve trees,otherwise cut for fuelwood-saves 1 ton of wood per year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Disseminate the technology to rural household |
|
Reduces labour time for gathering fuelwood How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve incomes of rural household so that they could afford the technology |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
1) Helps conserve trees,otherwise cut for fuelwood-saves 1 ton of wood per year How can they be sustained / enhanced? Disseminate the technology to rural household |
|
2Reduces labour time for gathering fuelwood How can they be sustained / enhanced? Improve income of rural households so that they could afford the technology |
| Solar energy is renewable and entirely non-polluting |
| Smoke free cooking |
| Solar energy is free |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Strong winds can upset cookers and pots on them if not sheltered | Build unroofed shelter around cooking area |
| Open cooking exposes food to dust |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| 1)Only cook when it is sunny | Safe storage facility |
| 2)Parabolic cookers need frequent adjustment | Build unroofed shelter around cooking area |
| Need to stole cooker during rainy season | |
| Strong winds can upset cookers and pots on them if not sheltered | |
| Open cooking exposes food to dust |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块