Permeable rock dikes [布基纳法索]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Dieter Nill
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli
Diguettes filtrantes (French)
technologies_1619 - 布基纳法索
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Sani Mamadou Abdou
mamadou.sani@giz.de
Programme d’Appui à l’agriculture Productive (PROMAP), Niamey, Niger
尼日尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation - A contribution to adaptation and farmers ́ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel (GIZ)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Deutsche Gesellschaft für Internationale Zusammenarbeit (GIZ) - 德国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
01/07/2012
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Permeable rock dikes are erosion control structures to slow down runoff
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
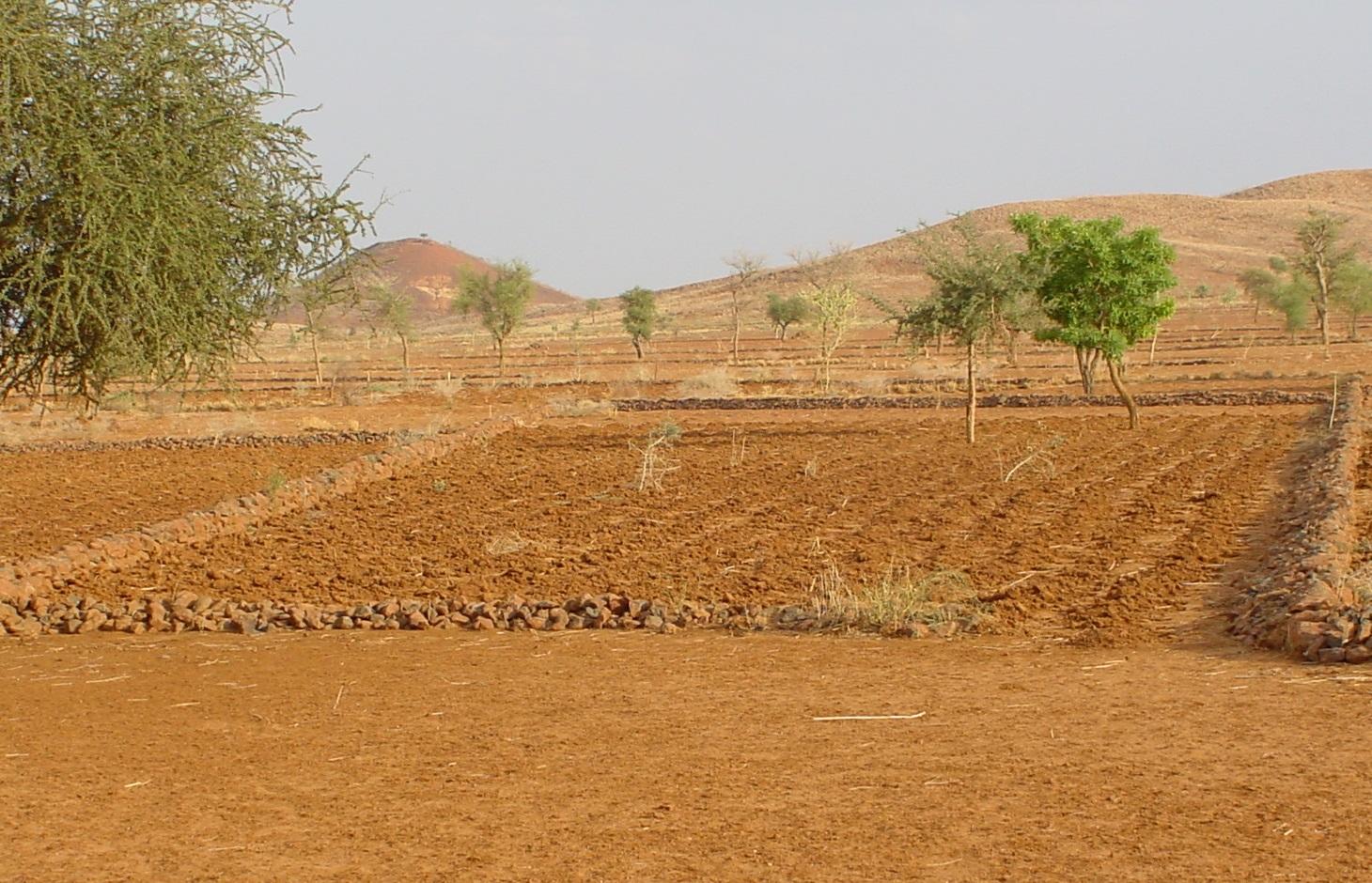
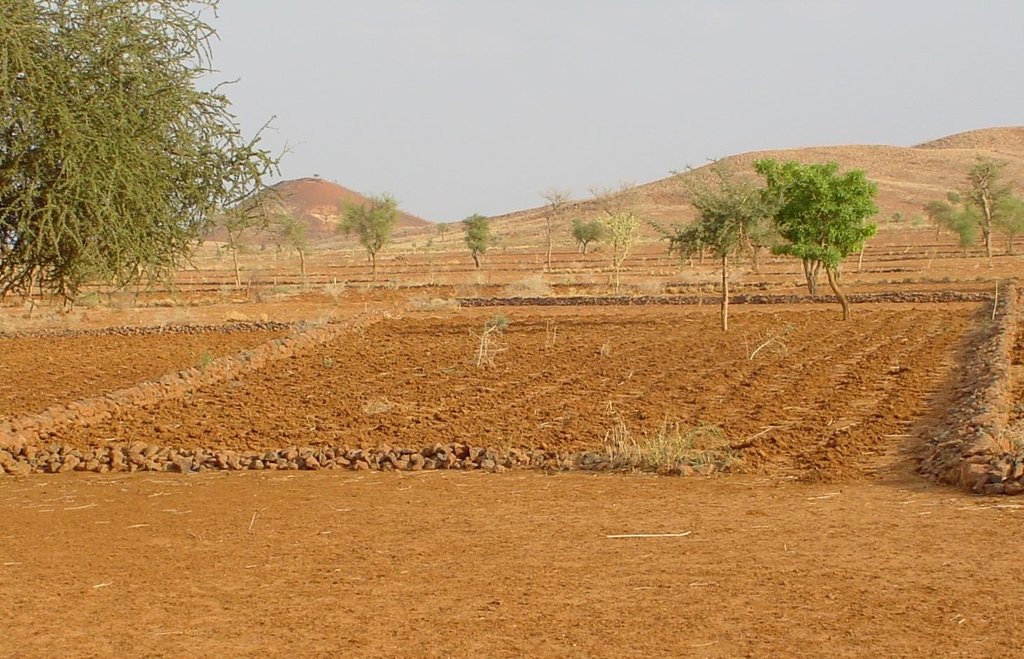
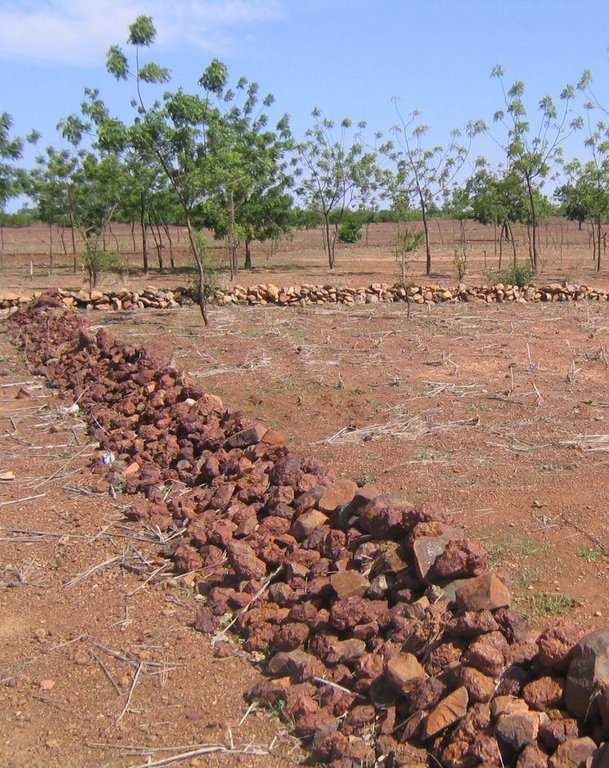
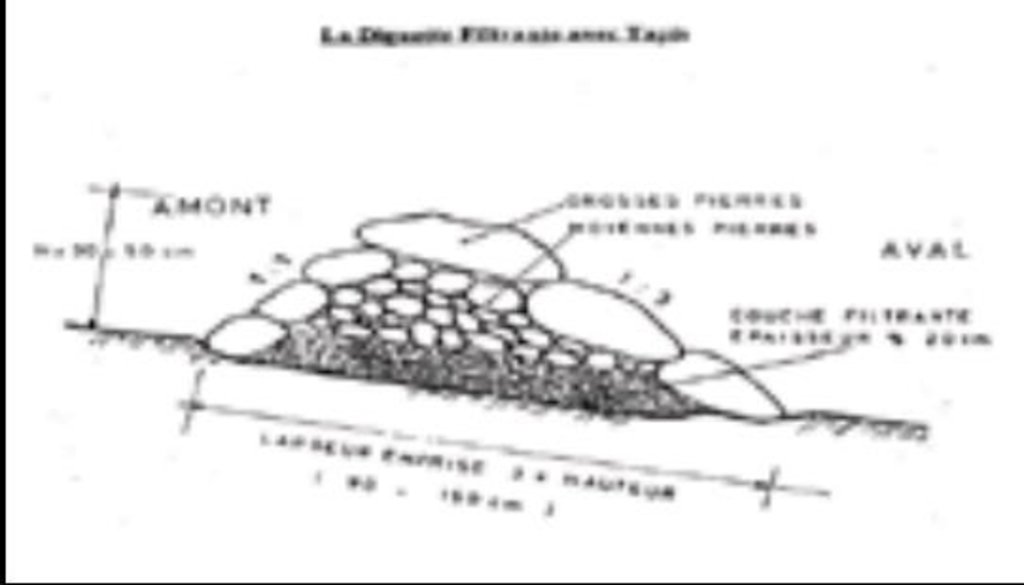
Permeable rock dikes are erosion control structures built along the natural contour of the land and designed to slow down runoff. They are built between 30 and 50 cm high and twice or three times as wide as they are high. They are made with different-sized stones and rocks, and the crest of the dike is horizontal. There are two main types of permeable rock dike: those without a filter layer, which are suitable for flat land with no gully erosion and those with a filter layer suited to land with heavy runoff.
Because of the way it is constructed, it dissipates the erosive force of the water. Sediment builds up behind it, resulting in the formation of terraces. It also increases the infiltration of surface water into the soil. The retention of water and fertile sediment by the dikes facilitates the development of natural vegetation along the structure. Grass and bush seeds are trapped by the dikes, favouring the spontaneous growth of natural vegetation, which contributes to restoring biodiversity and provides a habitat for wildlife. Good tree and grass cover developed along the dikes contributes to lowering soil temperature and reducing wind erosion along the entire length of the structure.
The reduction in runoff downstream of the dikes contributes to reducing alluvial deposits in the valleys further downstream. Watershed development with permeable rock dikes reduces siltation and gully erosion.
Permeable rock dikes are designed for use on cropland, but can also be used on forest/rangeland. They are recommended for ecological units with gravely and sandy-clayey soils and pediments. They can also be used to fill in small rills.
Studies conducted in the PATECORE area show that plots with permeable rock dikes averaged sorghum yields of 795 kg compared with 576 kg on control plots, which means that yields were 38% higher on improved plots. The production of straw for livestock increases in the same proportion as grain output.
With some upkeep, permeable rock dikes last at least 20 years. Before the rainy season starts, any stones dislodged by animals must be replaced. During the rainy season, the water can wear gaps in the dikes, which must be repaired immediately. The stability of the dikes can be reinforced by active revegetation (by sowing grass or planting trees). Without direct sowing, natural vegetation develops along the dikes after several years.
From the point of view of climate change adaptation, permeable rock dikes mitigate the effects of variations in rainfall. They are appropriate in wet period with heavy rain and violent downpours: permeable rock dikes constructed on the upper edge of the plot as a protective measure and a means of improving infiltration, protect land at risk from erosion. They are also appropriate during dry periods as they stop or slow down the flow of water. Permeable rock dikes improve infiltration and therefore increase and prolong the availability of water for crops. The permeable rock dike differs from the contour stone bund in that it is bigger in size, is constructed with various layers of stones and is designed to control stronger water flow. For this reason, such dikes are often constructed up-stream of stone bunds to dissipate the force of the water flowing from the plateaux and slopes.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
布基纳法索
区域/州/省:
Burkina Faso, Chad
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
developed, implemented and disseminated as part of projects and programmes undertaken from the 1980s onwards to combat desertification and improve natural resource management. Implemented by GIZ (German Federal Enterprise for International Cooperation), and PATECORE (project for land development and resource conservation in Plateau Central)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): surface runoff, soil erosion by water and wind, fertility decline
Constraints of common grazing land
Constraints of forested government-owned land or commons
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: August to October
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Unadapted landuse methods, reduced or abandoned fallow periods), floods, droughts, population pressure (rapidly growing population increasing pressure on land), land tenure (insecure access to land)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
Permeable rock dikes are built between 30 and 50 cm high and twice or three times as wide as they are high. They are made with different-sized stones and rocks, and the crest of the dike is horizontal. There are two main types of permeable rock dike: those without a filter layer, which are suitable for flat land with no gully erosion and those with a filter layer suited to land with heavy runoff.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, improvement of ground cover, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, water harvesting / increase water supply, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in organic matter, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, reduction in wind speed, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Bund/ bank: graded
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.3-0.5
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.5
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | levelling and marking out the contour line | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | collecting stones and loading them onto carts | 结构性的 | |
| 3. | transporting the stones by cart | 结构性的 | |
| 4. | building the dikes | 结构性的 | |
| 5. | applying manure | 结构性的 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Before the rainy season starts, any stones dislodged by animals must be replaced. | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | During the rainy season, the water can wear gaps in the dikes, which must be repaired immediately. | 结构性的 |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Machinery/ tools: pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level, etc.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The exact cost of constructing permeable rock dikes per hectare depends on the distance of the site from the quarry, the inclination of the terrain, which determines the spacing between the dikes, and the actual amount of stones transported in each lorryload or cartload. Supply of quarry rock/stones: 48 m3 for 200 m of dike.
Labour: 60 man-days per ha
• levelling and marking out the contour line: 1 man-day
• collecting stones and loading them onto carts:
20 man-days
• transporting the stones by cart: 20 man-days
• building the dikes: 19 man-days
• applying manure.
Transportation by cart:
• 20 cartloads of stones
• 20 cartloads of manure (if used).
Transportation by lorry:
• 11 lorryloads (skip loader – 4.5 m3 per load).
Other costs:
• equipment (pickaxes, shovels, wheelbarrows, water-tube level, etc.).
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
相对财富水平:
- 非常贫瘠
- 贫瘠
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 3% - 4% (mostly poor households below poverty line).
Off-farm income specification: men migrate temporarily or permanently to cities for off-farm income
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
traditional land use rights on fields, communal land on pasture and forest land
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
生产故障风险
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
冲突缓解
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Studies conducted in the PATECORE area show that plots with permeable rock dikes averaged sorghum yields of 795 kg compared with 576 kg on control plots, which means that yields were 38% higher on improved plots. The production of straw for livestock increases in the same proportion as grain output.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
生物多样性:植被、动物
植物多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The technique’s potential for replication depends on the type of terrain and the availability of a supply of stones within a reasonable distance. The technique is very effective as a flood control measure and is relatively easy to learn. Farmers are able to implement the technique themselves after two days’ training. This technique can only be implemented with highly motivated groups and villages, with strong working and mobilisation capacities.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The retention of water and fertile sediment by the dikes facilitates the development of natural vegetation along the structure. Grass and bush seeds are trapped by the dikes, favouring the spontaneous growth of natural vegetation, which contributes to restoring biodiversity and provides a habitat for wildlife. |
| Studies conducted in the PATECORE area show that plots with permeable rock dikes averaged sorghum yields of 795 kg compared with 576 kg on control plots, which means that yields were 38% higher on improved plots. The production of straw for livestock increases in the same proportion as grain output. |
| The reduction in runoff downstream of the dikes contributes to reducing alluvial deposits in the valleys further downstream. Watershed development with permeable rock dikes reduces siltation and gully erosion. |
| The technique is very effective as a flood control measure and is relatively easy to learn. Farmers are able to implement the technique themselves after two days’ training. |
| With some upkeep, permeable rock dikes last at least 20 years. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Permeable rock dikes are not as effective as contour stone bunds for the purpose of reforestation. This is because in the case of contour stone bunds, more linear metres are required per hectare than in the case of permeable rock dikes |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Good Practices in Soil and Water Conservation. A contribution to adaptation and farmers´ resilience towards climate change in the Sahel. Published by GIZ in 2012.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://agriwaterpedia.info/wiki/Main_Page
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块