Contour Trench Bund [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff
Chuquorak Band Khaki (Dari)
technologies_1724 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Ershad Mustafa
mustafa.ershad@crs.org
Catholic Relief Services
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Catholic Relief Services/East Africa (Catholic Relief Services/East Africa) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
04/07/2011
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Community-Based Watershed Management [阿富汗]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
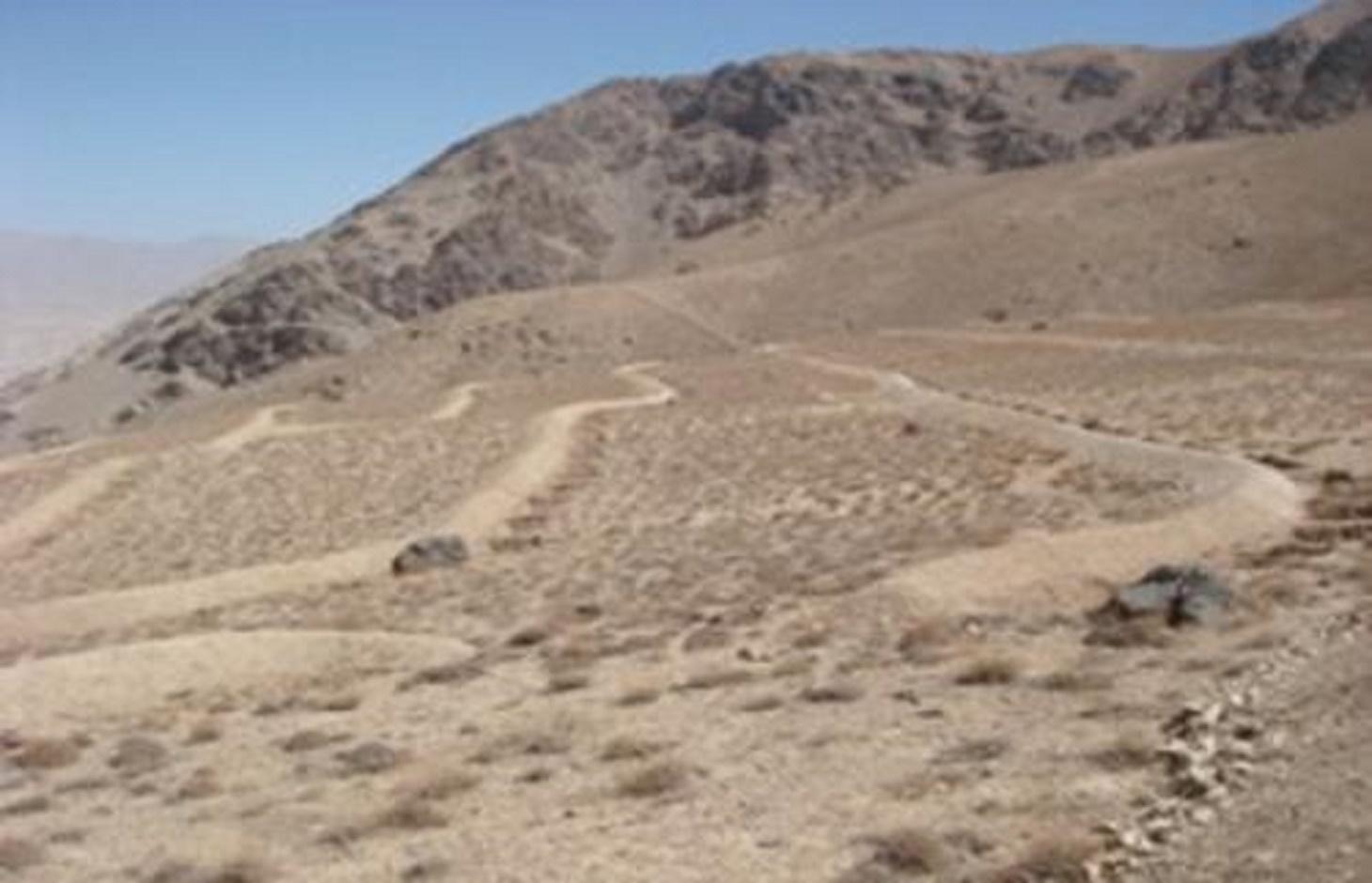
Contour trench bund applied on contour lines of moderate slope to trap run-off to improve infiltration and reduce flash floods.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The Contour Trench Bund technology is documented by Sustainable Land Management
Project/HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation with financial support of Swiss Agency for
Development and Cooperation(SDC) and close support and cooperation of the Catholic
Relief Service (CRS). The technology was applied in Sar-e Ahengaran watershed of Bamyan centre, an area of 0.08 km2 as part of a watershed project by the Catholic Relief Services (CRS). The total watershed area is 67 ha. The project started in October 2009 involving the community with funding support from USAID and CRS. The project came to an end in March 2013.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of the contour trench bund technology is to reduce excessive surface runoff and improve infiltration. It also contributes to increased vegetation cover.
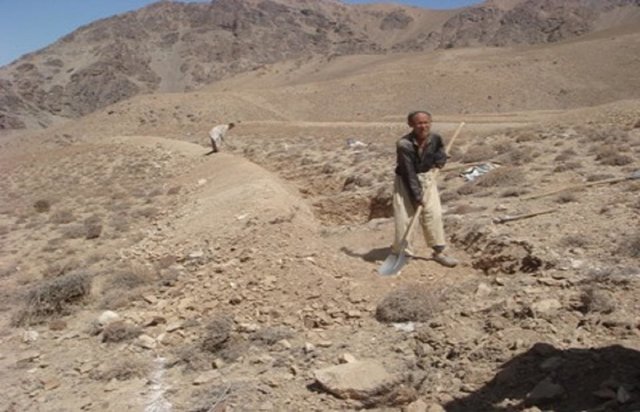
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The main activities for this SLM technology include: site selection and technical planning in October 2009; demarcation of contour lines using A-frame and lime; and digging trenches and construction of soil bunds. The technology was established over 10 months. The project used a “Cash for Work” approach; local people were employed for construction works. Cost-wise, approximately 7,536 USD were spent on this technology (approximately 942 USD/ha) with 90% contribution from the project and 10% from the participating community. There have been no maintenance costs so far for this technology.
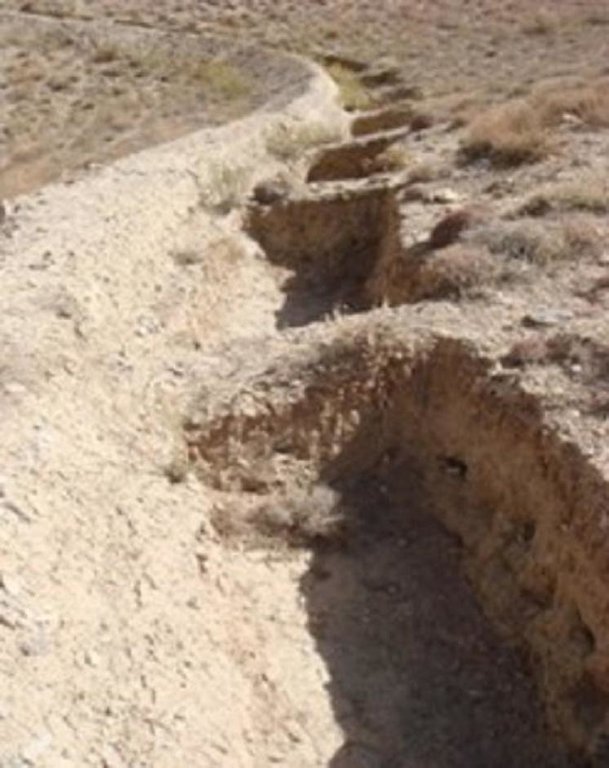
Dimensions of a trenches are: 0.7 m in depth, 1.2 m width, 3 m length and of the bunds: 0.45 m in height, 1.2 m in width, 100 m in length with 12 m spacing and 1.5 m vertical interval between two contour lines. Contour trenches were applied on hilly (16-30%) slopes at an altitude of 2500-3000 m. The technology is tolerant to temperature, seasonal rainfall, storms and droughts and sensitive to heavy rainfall events and floods. The soil in the watershed is sandy to loamy type, and infertile with a depth of 20-50 cm. The infiltration is medium.
The technology is part of the watershed management system. Other measures implemented included stone walls, cultivation of fodder grasses and ban on grazing and shrub cutting at the site. The land ownership (in the watershed) is communal with open access water rights. Medium scale land users, mainly men, applied the technology. Women and school children participated in meetings concerning awareness raising. There is also a watershed and pasture management committee for site management.
Natural / human environment: The annual rainfall in the area is 250-500 mm. The agro-climate is semi-arid and temperate type with the longest growing period of 180 days from April to October. The people in this area are mainly poor. 10-50 % of all income comes from off-farm activities. Access to health, market and financial services is low and education, roads, transport, drinking water and sanitation facilities are moderate. Agriculture is of mixed type, subsistence and commercial based.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Sar_e_Ahangaran, Bamyan center
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 结合其他技术保护流域/下游区域
- 降低灾害风险
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

牧场
粗放式放牧场:
- 半游牧/游牧
主要动物种类及产品:
Sheeps, goats and cattle
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Reduction of the vegetation cover causes flash floods and accelerated erosion. The water level goes down and there is no moisture in the soil.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Downstream flash flood and shortage of spring water due to overgrazing of the range-land.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Grazing land: Ge: Extensive grazing land
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180; Longest growing period from month to month: April to October
牲畜密度(如相关):
10-25 LU /km2
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.5 技术传播
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.08 km2.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S4:平沟、坑
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
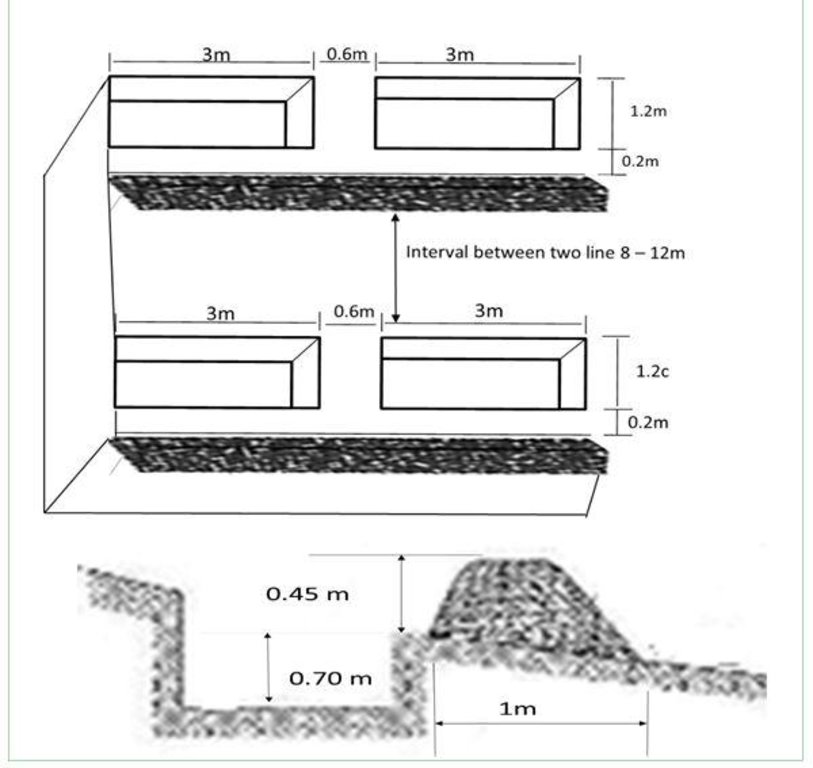
The technical drawing of the Contour trench bund showing the layout and dimensions/spacing of the structures.
Dimensions of the trench and bund are as following:
Trench specifications:
Depth: 0.7 m,
Width: 1.2 m, Length: 3 m
Soil bund specifications:
Height: 0.45 m
Width: 1.2 m
Length: 100 m
Spacing between contour lines:
About 8 -12 m (depend on slop)
Vertical interval:
1.5 m
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, increase of infiltration
Secondary technical functions: reduction of slope length, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Demarcation of the contour lines using A frame and Lime | 结构性的 | |
| 2. | Excavation of the trenches and construction of the soil bunds | 结构性的 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Demarcation of the contour lines | ha | 1.0 | 92.0 | 92.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Excavation of the trenches and construction of the soil bunds | persons/day/ha | 121.0 | 7.0 | 847.0 | 10.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 939.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 10 month(s)
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance costs so far for CRS. | 结构性的 |
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The establishment duration of the Contour Trench Bund was 10 months.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: Temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Workload does not give chance to women to work on the mountains.
Population density: < 10 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
50% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Busy with carpentry and migrate for work.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Due to better soil moisture
收入和成本
收入来源的多样性
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
社会经济弱势群体的情况
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Due to reduction in flash floods problem and increased access to drinking water, Seasonal job opportunities created through cash for work
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
注释/具体说明:
of surface run off
地下水位/含水层
土壤
土壤水分
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Due to more moisture
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
其它生态影响
disturbance of soil and vegetation during excavation works
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
And sedimentation
damage on agriculture fields
As the site is closed, grazing pressure shifts elsewhere
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| Extreme precipitation events especially if the technology is applied on steep slopes. | 不好 |
注释:
Increase size, stable bunds stabilized with vegetation
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The benefits will be more in the long term when trees, shrubs and fodder grasses are ready to harvest.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Appropriate information is not available.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Only soil bunds have been applied by a few farmers on their private lands.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology helps to create SLM based job opportunities for many people. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Needs external support/projects. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Demonstration of link between SLM measures and water source. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Conducting training and showing drawing. |
|
Technical knowledge of community enhanced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Share more aspects of the technology, where to apply and how. |
|
Flood reduction, greening of the area, increase the spring water. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Cultivate native plants, share experiences with more communities and SLM specialists. |
|
Good for land rehabilitation (extremely degraded lands). How can they be sustained / enhanced? Always combine with vegetative and management measures. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Farmers do not prefer to construct this technology because it requires soil excavation/disturbance. | One needs to show how such measures have been applied in other parts of the world for multiple benefits through action research. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Site selection | Apply technology at suitable site that has proper slope and is really degraded. Avoid places where there is already good vegetation cover. |
| Higher cost of establishment of the technology. | Encourage the community for more contribution or apply where absolutely necessary. |
| Technical design | The designer should research more about the site and discuss with the skilled people of the community before designing. |
| Few vegetative measures | plant fodder grasses and adapted trees between trenches. |
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community-Based Watershed Management [阿富汗]
Sustainable implementation of watershed management through appropriate SLM technologies, formation of organizational structures and capacity building of stakeholders
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
模块
无模块