Disability inclusive, flood resilient cluster village [孟加拉国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Subir Saha
- 编辑者: Subir Saha, Manuel Rothe
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
"Protibandhita Bandhob Bonna Sohisnu Gucca Gram"
technologies_2005 - 孟加拉国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Christoffel Blindenmission (CBM) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/11/2016
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
Not problematic with regard land degradation. It provides efficient and sustainable use of available land resources.
1.5 请参阅有关SLM方法的问卷

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [孟加拉国]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- 编制者: Subir Saha
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
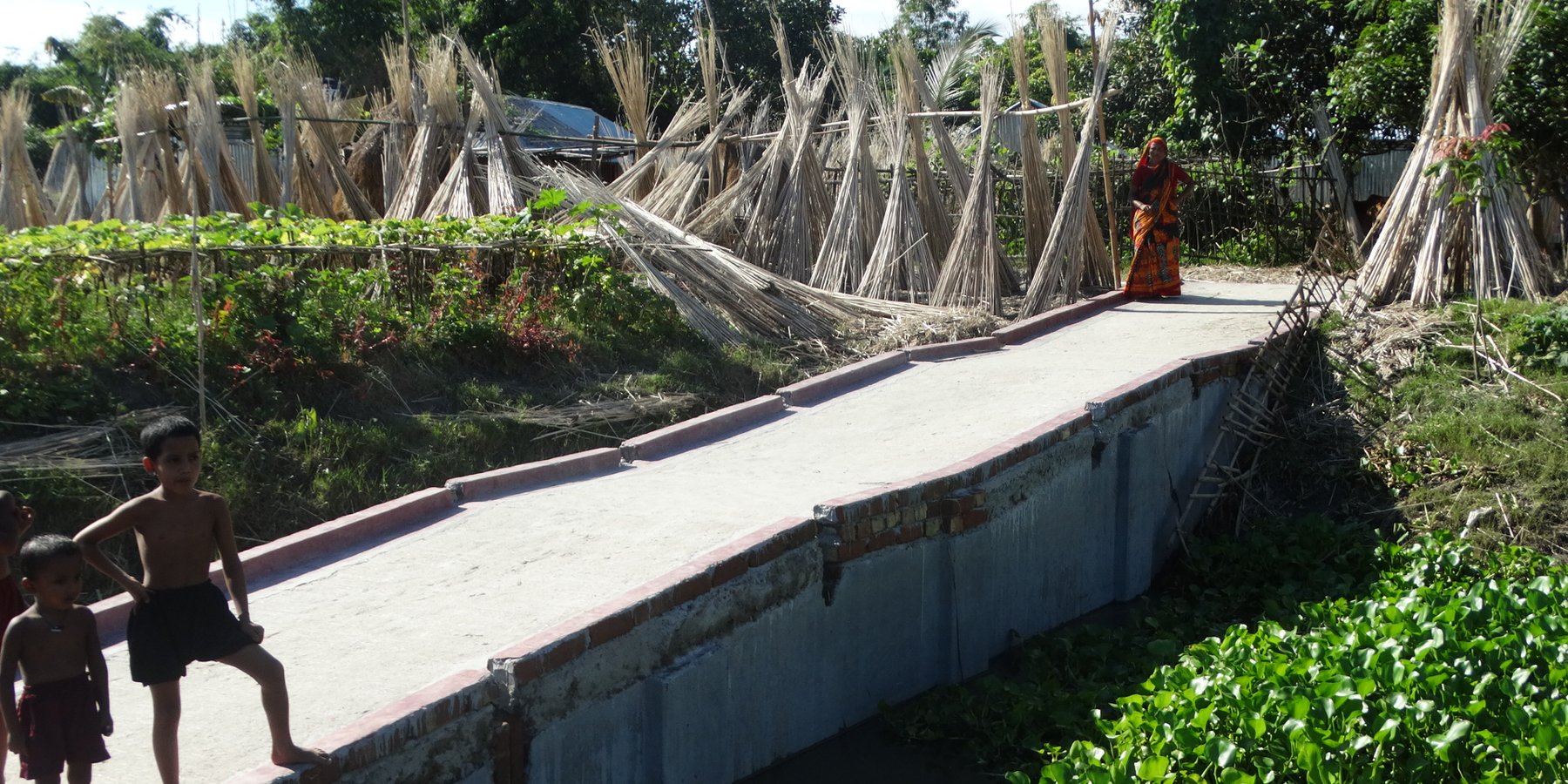
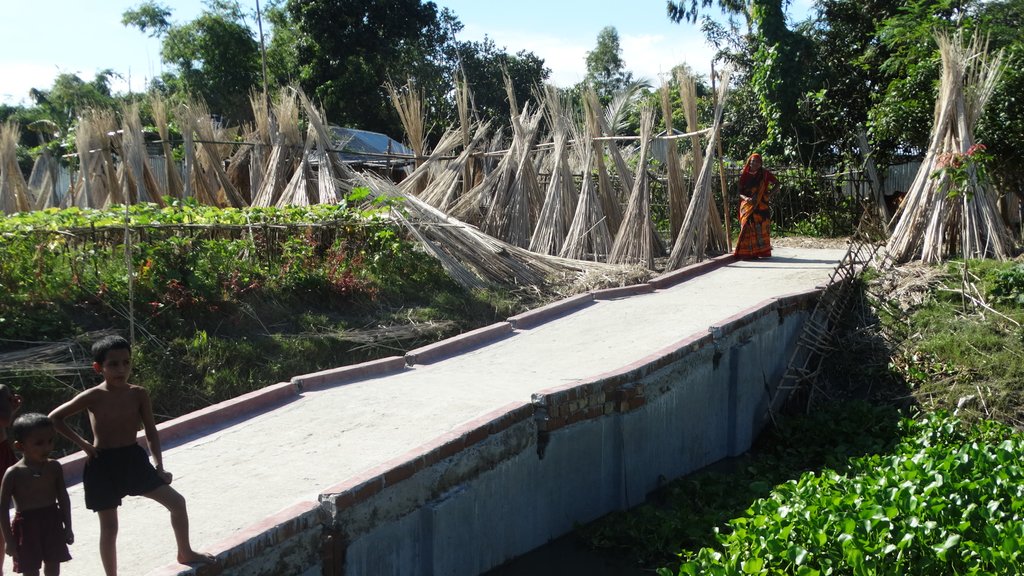
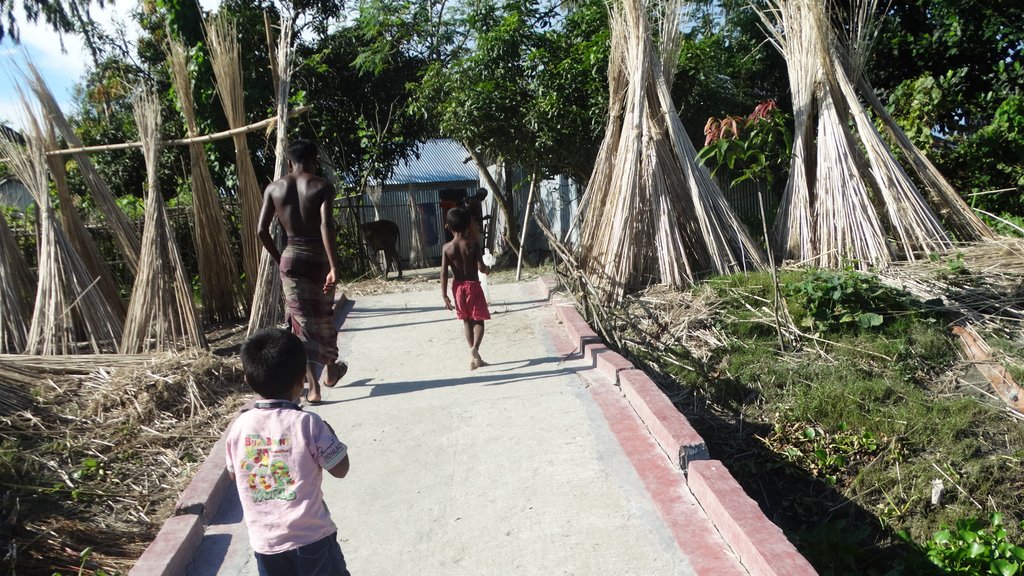
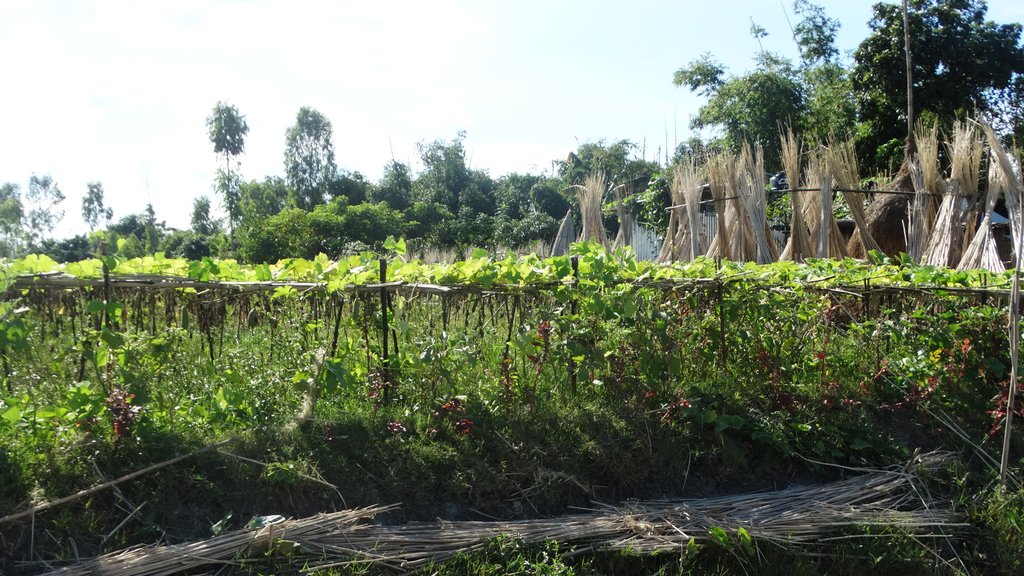
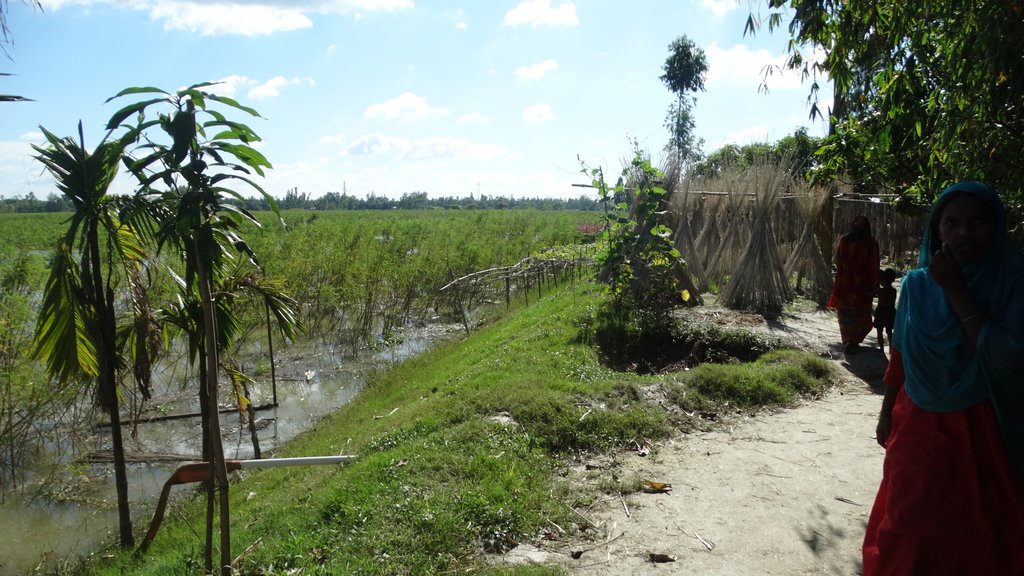
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village provides safe housing, food security and income generation for multiple families, including persons with disabilities, in a highly flood prone area of Gaibandha District in northern Bangladesh. The land was raised above flood level and is protected by deep rooted fruit trees to prevent soil erosion and provide income for the land users.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
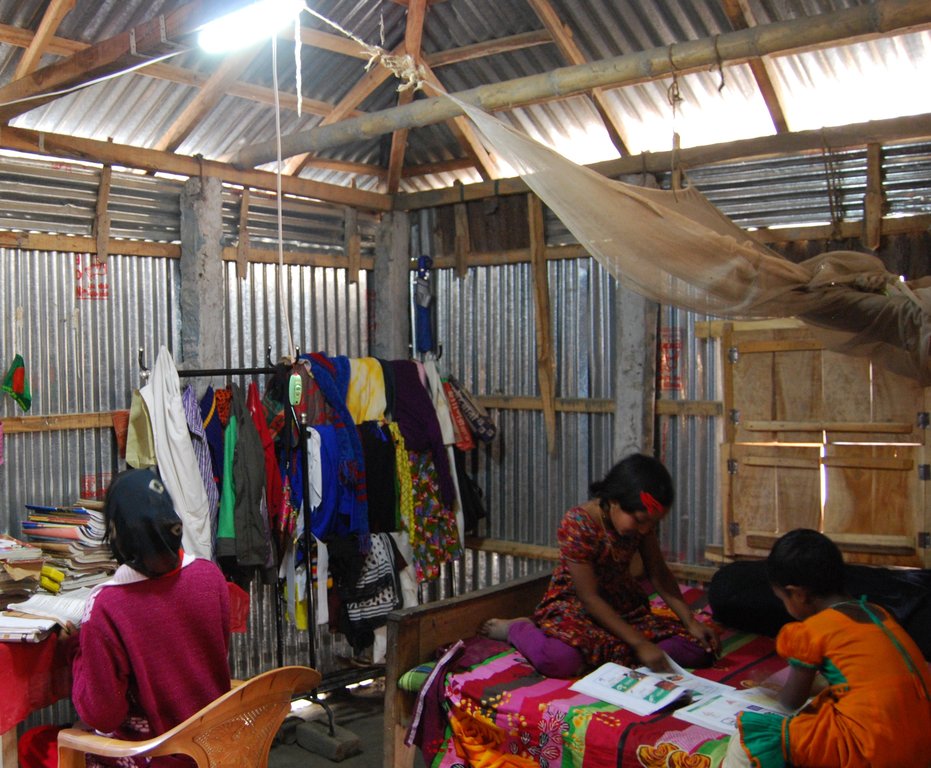
The inclusive, flood-resilient cluster village was introduced in a rural area with a high risk of recurring monsoon floods. The purpose of the technology is to provide safe housing, safe shelter for livestock, food security and income generation for ten families, including persons with disabilities.
The main components of the technology are:
1) The raising of a piece of land by seven feet (213cm), to three feet (91cm) above expected highest flood levels. Solid soil was banked up to encircle a 30'000 square feet (roughly 50x57m) piece of land and then the space within was filled up with sand collected from a nearby river bank. A one-foot layer of solid soil was added to cover the entire area.
2) The protection of the raised land from soil erosion during floods by planting a combination of deep-rooted fruit- and medicine trees around the border of the raised land. The trees include a number of different types of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees and one type of medicine tree, Azadirachta Indica, locally known as "Neem". In addition, the slope of the border area was covered by grass turf to protect the soil from being washed out by rain. Two types of deep-rooted and flood resistant grasses were used. A drainage system was installed to facilitate water runoff.
3) The planting of a 150 square feet (14m2) commonly used homestead vegetable garden at the center of the cluster village. The cultivated vegetables include red spinach, jute leaf, basella leaf, spinach, radish, cabbage, okra, bottle-guts, cucumber and beans, allowing for a summer and a winter harvest. Together with the fruit trees, the vegetable garden provides food security during prolonged flooding. They also provide improved nutrition and income generating opportunities through selling of a part of the harvest in the market.
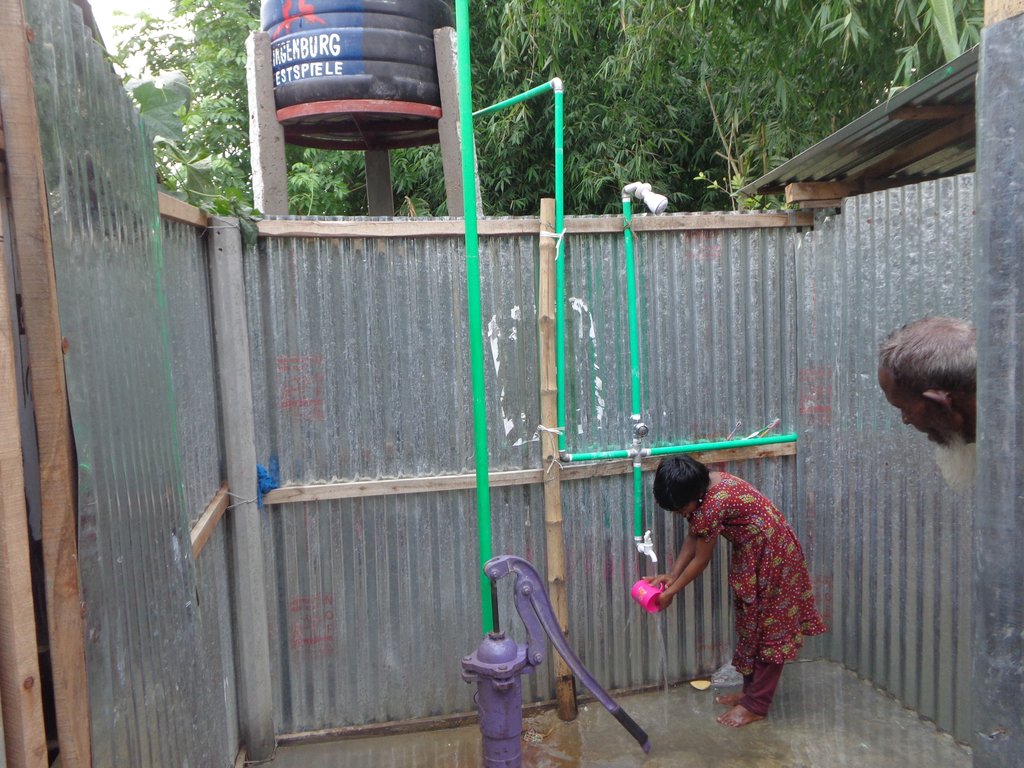
4) Making the village accessible for persons with disabilities through different accessibility measures, including the construction of a ramp, connecting the cluster village entrance with the road, and of accessible common Water-, Sanitation- and Hygiene (WASH) facilities, including a latrine, deep bore hole water source and water storage tank.
5) Installation of a solar panel to ensure uninterrupted, flood-resilient power supply. The level of power supply is sufficient to ensure coverage of electricity needs during flood season, when regular supply is around 15% below annual average.
The Cluster village was constructed as part of a disaster risk reduction project by CDD (Center for Disability in Development) from Bangladesh, with the support of CBM (Christoffel Blindenmission), an international development organization and funded by a donor from Germany. The main cost for inputs were provided to the land users by the project, including rent of construction machinery, paid labor, soil and construction material for the ramp and WASH facilities. The land users contributed labor and seedlings for the planning of the border trees and the homestead vegetable garden.
The main benefits of the technology from the perspective of land users are the protection it provides for houses and livestock, which would otherwise be in danger of loss during floods. The availability of food, water and electricity allows land users to remain in their homes during floods and avoid evacuation and the risk associated with it, including for example protection risks or the risk of theft. The flood protected vegetable gardens and fruit trees provide a year-round, sustainable source of food and income, providing food security and improved nutrition. The Neem tree provides medical and hygiene uses of the branches and leaves.
The cluster village is used as a safe space for the land users and other members of the community and their livestock during floods. Land users who are persons with disabilities or elderly benefit from the accessible infrastructure. With multiple families sharing land, the cluster villages provides optimal utilization of land resources. An additional benefit mentioned by land users is that the joint use by multiple families led to a more progressive social culture.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
孟加拉国
区域/州/省:
Gaibandha District
有关地点的进一步说明:
Horipur Union, Sundargonj Sub district,
注释:
Kani Charitabari, Horipur Union, Sundargonj sub district, Gaibandha District.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was introduced as part of a disaster risk reduction project, implemented the Center for Disability in Development (CDD) with the support of Christoffel Blindemission (CBM) and with participation and leadership of the local community. The project was financially supported a group of donors from Germany.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 降低灾害风险
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

定居点、基础设施
- 定居点、建筑物
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Summer and winter
牲畜密度(如相关):
Livestock are available in every household.
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
- 家庭花园
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
- S8:卫生/废水结构物
- S9:动植物庇护所
- S10:节能措施

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M6:废物管理(回收、再利用或减少)
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
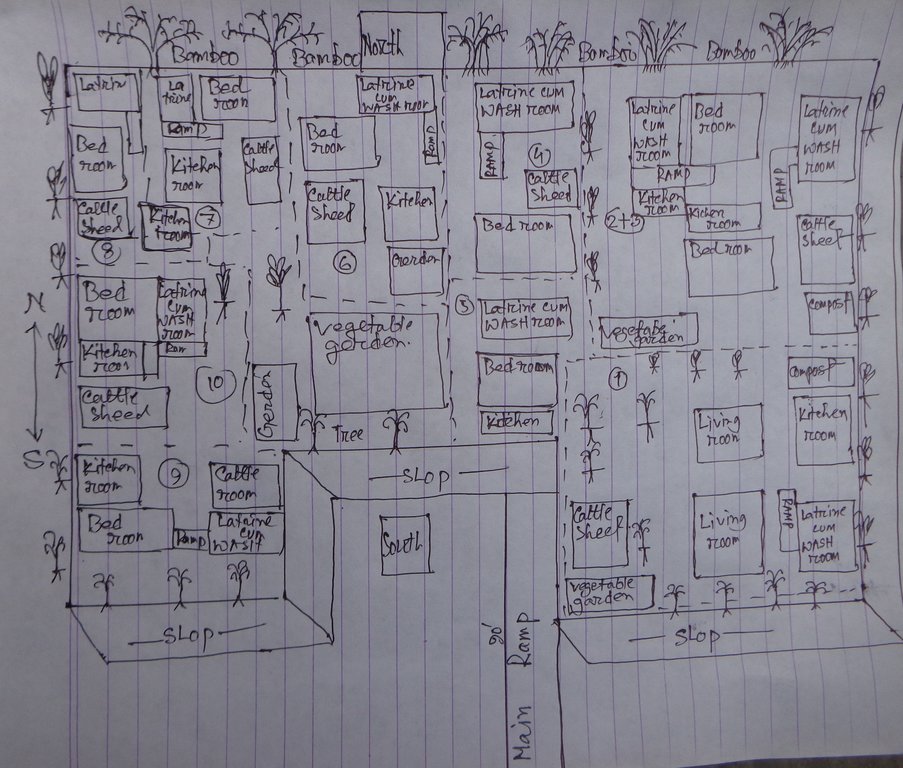
The drawing shows the layout of the disability inclusive, flood resilient Cluster village. The components of the technology are:
Raised land/plinth: 1) Purchase of land of a total area of 18'000 square feet (ca. 40x40m). Land ownership transferred to joint ownership of 10 families. 2) Collect 15'000 cubic feet (425m3) of solid soil from different pieces of land in the community. The soil was donated by members of the community, who were either related to the land users of the cluster village or donated in support of the construction of a safe space which can be used by the community during floods. 3) Banking up of 3 feet (91cm) of solid soil along the borders of the land. 4) Filling of area with 140'000 cubic feet (3965m3) of sand, extracted from a nearby riverbank with a rented sand extraction machine, raising the land to 6 feet (183cm). 5) Covering the entire area with one additional foot of solid soil, rasing the land to 7 feet (213cm), which means 3 feet (91cm) above the maximum expected flood levels.
Soil protected through deep-rooted trees: 1) Planting of deep-rooted and light-rooted fruit trees, surrounding the entire border of the raised land. The trees include deep rooted fruit trees like mango, black berry, jack-fruit, guava, coconut and areca nut, light-rooted fruit trees like banana and Papaya, a deep-rooted medicine tree, locally called "Neem" and the light-rooted Dhol Kalmi tree (pink morning glory). The number of deep-rooted threes was 100, with a spacing of around 5 feet in between each. They were planted to cover the entire perimeter of the raised land. In between the deep-rooted trees, 60 light-rooted trees were planted. In front of the deep-rooted trees, 60 bamboo bushes were planted to provide additional protection from wind and rain. 2) Turfing of the entire slope surrounding the cluster village with two flood resistant grasses: Durva (Cynodon dactylon) and Catkin grass. 3) Installation of a central drainage system with 15 plastic pipes ensuring water runoff from the wastewater pond.
Road access through ramp: The connecting ramp of the cluster village is 90 feet length, 6 feet width. There are five landing point of this ramp with smooth slopping. The construction material includes class one brick, brick stone, cement, sand, polythene and red oxide color for color contrast, which is appropriate for low vision and visually impaired persons. There is a 5 inch border on both sides of the ramp for safe movement of a wheel chair user.
Accessible household water and sanitation facilities: Latrine and wash-room are constructed for every house in the cluster village, following universal design standards. Latrines are connected to the wash room and the main house through ramps. There is a railing on both sides of the latrine and the entrance is wider for access of a wheel chair users. Water system for the latrine and wash room is provided from a water tank on three pillars behind the latrine, which is also connected to the main house for provision of drinking water. The tank is filled by hand pump ('magic pump') which functions with minimal hand pressure. The WASH facilities are accessible and usable by everyone including persons with disabilities, pregnant women or aged persons.
Home vegetable gardens: Every household has an individual homestead vegetable gardens where land users cultivate seasonal vegetables year-round. Gardens vary in size between averaging about 1.5 decimal (60m2) in size and are surrounded by bamboo fencing. The land owners are using organic fertilizer/compost for the vegetable production of their choice. By using cow's manure and wastage they are producing the compost in the behind of their houses in a ditch.
Solar system: A mini solar system is installed on the roof for each house by using a small panel with a 12-volt battery . Each system has the capacity of providing power for light for 8 hours. An introduction to system maintenance was given to the land users by the provider of the solar system.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
指定单位:
Cluster village
指定体积、长度等(如果相关):
18'000 square feet piece of land
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Bangladeshi Taka
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
80.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selecting the place for cluster village construction | 管理 | During rainy season in 2015 |
| 2. | Establish collaboration with 10 families who will become land users | 管理 | December 2015 |
| 3. | Land Raising & Ramp construction | 结构性的 | December 2015 to March 2016 |
| 4. | Reconstruction the existing houses of the land users on the raised land | 结构性的 | April 2016, before onset of rainy season 2016 |
| 5. | Planting of deep- and light-rooted fruits trees, bamboo bushes and grass turfing along the boundery | 农业学的 | February 2016 to March 2016 |
| 6. | Install accessible water & sanitation system | 结构性的 | April-June 2016 |
| 7. | Establish home garden in front of each house | 植物性的 | June-July 2016 |
| 8. | Install mini solar system for each house | 其它措施 | Aug-sep 2016 |
| 9. | Prepare livestock shed for each house | 结构性的 | October 2016 |
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
如果可能,按下表分列技术建立费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出建立该技术的总成本估算。:
1777380.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Land raising, tree planting and turfing on slope | person days | 290.0 | 300.0 | 87000.0 | 10.0 |
| 劳动力 | Ramp construction | person days | 115.0 | 350.0 | 40250.0 | 10.0 |
| 劳动力 | House reconstruction and WASH facilities | person days | 200.0 | 400.0 | 80000.0 | 10.0 |
| 劳动力 | Solar system installation | person days | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | WASH equipment (latrine, magic pump, water tank, pipes, switch, pillars and other) | pieces | 10.0 | 46658.0 | 466580.0 | |
| 设备 | Solar system | pieces | 10.0 | 6300.0 | 63000.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Deep rooted trees | pieces | 100.0 | 40.0 | 4000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seed for vegetable | KG | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Sapling purchase | pieces | 100.0 | 50.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Light rooted tree | pieces | 60.0 | 30.0 | 1800.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic fertilizer (compost) | KG | 600.0 | 10.0 | 6000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Rent for shallow machine for sand extraction | Daily rent | 10.0 | 28800.0 | 288000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Grass turfing | square feet | 15000.0 | 10.0 | 150000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Allowance for house reconstruction material | House | 10.0 | 2000.0 | 20000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Ramp construction | Piece | 1.0 | 125750.0 | 125750.0 | |
| 其它 | Project management (monitoring and support) | persons-days | 180.0 | 2400.0 | 432000.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1777380.0 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
The project, human resource supported by CBM, CDD and a funded by private donor.
注释:
Labor for tree plantation, home stead gardening & house reconstruction was contributed by the land users.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turfing: Repair leakages, replace grass etc. | 结构性的 | before onset of rains |
| 2. | Tree maintenance: Cutting branches, manure of roots etc. | 农业学的 | Rainy season |
| 3. | Vegetable gardening | 植物性的 | Summer & Winter season |
| 4. | Housing repairs | 结构性的 | After harvesting season/ once in a year |
| 5. | Water and Sanitation system servicing and repairs | 管理 | After harvesting season/once in a year |
| 6. | Solar system maintenance | 管理 | Winter season/once in ayear |
| 7. | Village group meeting for decision making and conflict resolution | 管理 | Once in a month |
| 8. | Organic composting/fertilizer production | 其它措施 | Continuous |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
如果可能,按下表分解技术维护费用,并列明各项投入和每项投入的费用。如果您无法分解成本,给出维护该技术的总成本估算。:
85000.0
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | House repairs | person days | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Ramp repairs | person days | 10.0 | 300.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Plingth raising and plantation | person days | 30.0 | 300.0 | 9000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Solar system servicing by technical experts | piece | 10.0 | 500.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seed for vegetable gardening | KG | 5.0 | 1000.0 | 5000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Soil for slope maintenance | square feet | 5000.0 | 10.0 | 50000.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Sand for slope maintenance | KG | 5000.0 | 2.0 | 10000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 85000.0 | |||||
注释:
Land users are agreed to contribute 100% maintenance cost
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Market fluctuation and scarcity of goods in the flood season.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Heavy rainfalls are one of the causes for flooding
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
是
规律性:
频繁
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
- 团体/社区
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Age of land users includes children, youth, middle-aged as well as elderly.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Land users jointly own the land of the cluster village. They do not own any additional agricultural land and work as daily laborers and sharecropers.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
Land users own the land of the cluster village jointly, including a proportional share of land- and water use rights.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Fruit and vegetable production increased after introduction of the cluster village. Because of decreased loss of home and property during floods, labor is freed for crop production which increased overall crop production in the wider area.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Fruit and vegetable quality is improved because of availability of Irrigation.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Livestock mortality rate is reduced because of safe space in Cluster village.
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Homestead vegetable garden and fruit tree plantation above flood level has a significantly reduced risk of production failure.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
The flood-protected homestead vegetable garden allows for higher product diversity.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Increased availabilty of flood protected land for vegetable gardening.
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
Energy supply was not available before installation of solar panel.
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
饮用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
家畜用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Installation of deep tube well water source.
家畜用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
Significantly higher water quality during flood, because of flood protected water source in cluster village.
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Irrigation available to land users after installation of deep tube well.
灌溉用水需求
注释/具体说明:
Demand for irrigation water increased because of vegetable garden.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Increase of farm income through selling of fruit and vegetables.
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
Additional income source through selling of fruit and vegetables.
经济差异
注释/具体说明:
Decreased income disparities between the land users of the cluster village due to fruit and vegetable production available to all land users, Decrease income disparities between land users of the cluster village and other members of the communty because of the reduction of loss from flood damage.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Somewhat increased workload for maintenance of technology but decreased because of avoidance of damaged from floods.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Increased food security through flood prodected homestead garden and tree plantation.
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Higher attendance of health workers because the cluster village offer suitable group meeting rooms and accomodation. Cluster village was constructed in vicinity of community clinic. Better hygiene through WASH facilities.
文化机会
注释/具体说明:
The cluster village is a suitable meeting point for the entire community, for social gatherings or festivals.
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
Cluster village offers common space for children and other land users for Joint recreational activities.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Much improved situation for persons with disabiltiies who are part of the land users. All persons with disabiltiies in the wider community use the cluster village as a safe space during floods. Improved situation for all land users who are from marginalized parts of society (daily laborers and share croppers).
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Soil erosion during floods decreased because of deep- and light-rooted border tree plantation.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Raised land as safe space above flood level.
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Drought impact in summer season decreased because of Irrigation.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
available shelter and safe space
注释/具体说明:
Cluster village provides additional safe space/shelter for the wider community.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 非常好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
Around 10-15% of households which equals roughly 70 households.
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
The technology is replicated by households who receive assistance from local government for families at risk of flood damage.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Peoples of cluster villages are selling vegetables and fruits in the local market and some of them are carrying the fruits in the distance market. They are becoming more interested to plant more fruit trees in the cluster village. If it is continue in future it would be a fruits and vegetable market in the cluster village. At the same time they started selling cows milk in the local market and its demand is increasing day to day.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Ownership of the land user's are there. Its a community driven initiative & disability inclusive in all respect. They are happy to give shelter to the other villagers during flood season. There is an opportunity to create an example of a model village in this area. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Its an innovative program. Peoples participation and their contribution is the main asset. Universal accessibility of the cluster village communicating benefit to other villagers during rainy as well as flood season. This pilot program can be replicated to other riverine areas in Bangladesh. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The intensity of floods is difficult to predict. With average flood levels rising, land users still have to live with the risk of flood levels going beyond the level of their rised land. | More research on changing weather/climatic patterns and scientific measurement of expected flood levels. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Government and Non government organizations extension services are not available in this area. Livelihood of the cluster village peoples depending on seasonal agriculture. | Income raising multiple activity need to be introduces. A small scale disability inclusive comprehensive project could be implemented here. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
7
- 与土地使用者的访谈
10
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
4
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Disability inclusive Disaster Risk Reduction [孟加拉国]
The disability inclusive approach is centered around the meaningful contribution and leadership of persons with disabilties during the entire project management cycle, from the planning stage to the evaluation of the impact of a project. It contributes to empowering them to overcome social exclusion and recognizes their needs and priorities …
- 编制者: Subir Saha
模块
无模块