Organic amendment located in dripper point in organic citrus production [西班牙]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Alicia Morugán-Coronado
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Ursula Gaemperli, Gudrun Schwilch
Aplicación de estiércol de oveja en puntos de riego por goteo en la producción de cítricos orgánicos
technologies_2010 - 西班牙
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Interactive Soil Quality assessment in Europe and China for Agricultural productivity and Environmental Resilience (EU-iSQAPER)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Agrochesmistry and Environment Department, University Miguel Hernandez (UMH) - 西班牙1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
23/03/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
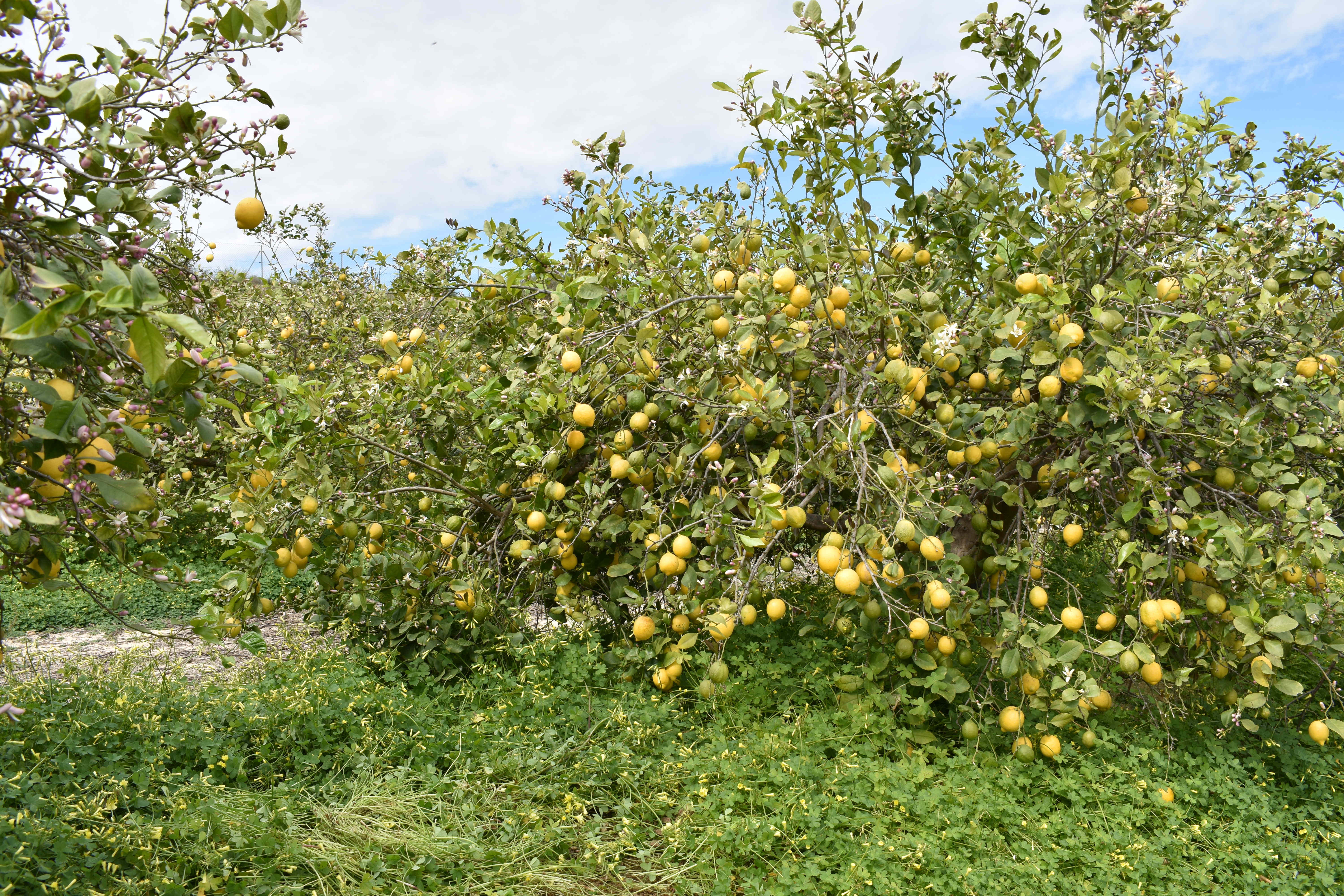
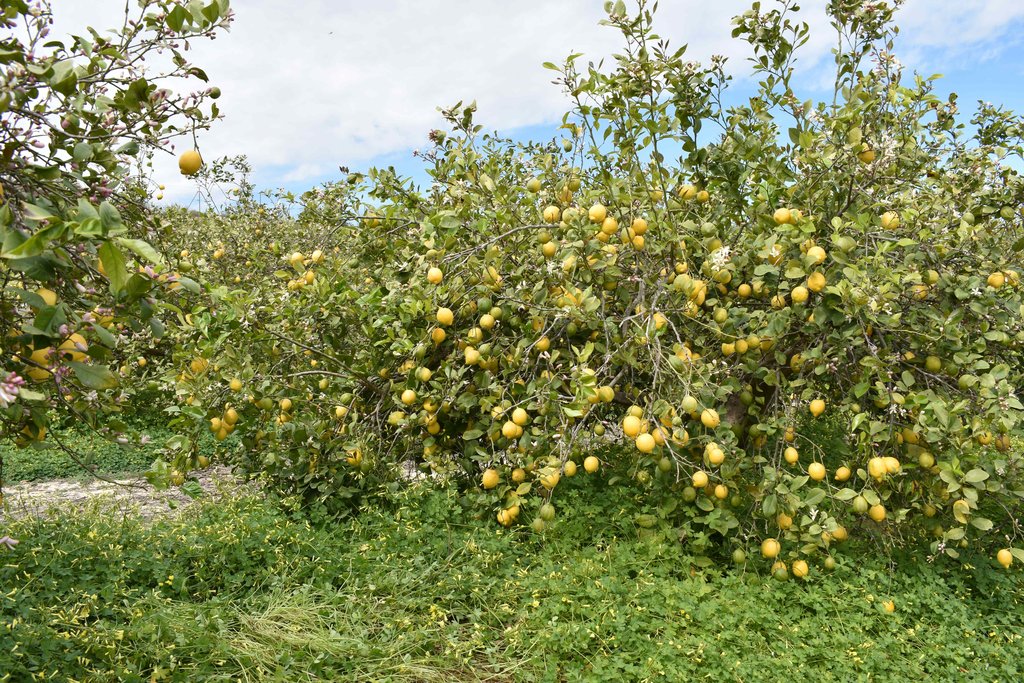
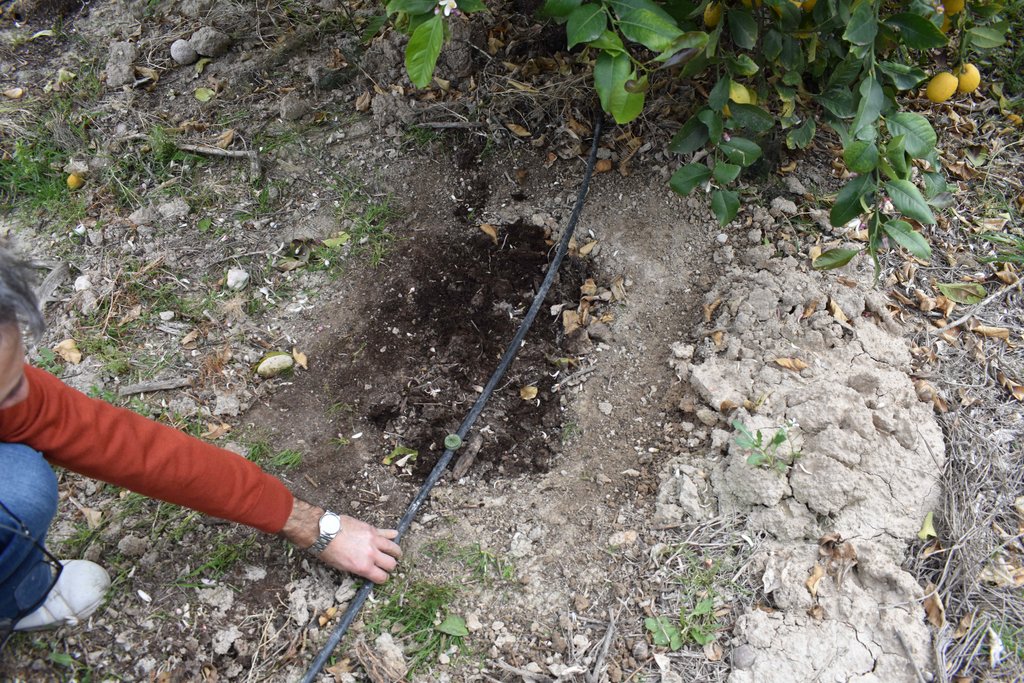
The land user applies organic amendment located in a dripper point. Sheep manure is applied every year in holes under the foot of every lemon tree. The holes are dug with a shovel.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Natural / human environment: This SLM technology was established in land under sustainable agricultural in the region of the Vega Baja del Segura (Spain). The region under study is the most southerly county within the Valencian Community (Comunidad Valenciana). Our study site focuses on the province of Alicante. The county is Vega Baja del Segura, which has a total area of 957.73 km2. The county of Vega Baja de Segura covers the region from Orihuela to the mouth of the Segura, where it meets the Mediterranean Sea in Guardamar del Segura (Alicante). Agricultural production in this county is of a very high quality and is intensely competitive. Despite this, the region’s traditional agriculture industry is nonetheless being overtaken by other sectors, with the scarcity of water emerging as a key factor in this shift. Currently, 67% of the arable area relies on irrigation systems. In this area, small holdings yield the majority of the agricultural production: 76% of agricultural estates cover less than five hectares. The main cultivation, in terms of area, is in trees (22,900 ha). Citrus trees (lemon, orange, and mandarin) are the main trees grown in the area (INE, 2009).
Purpose of the Technology: Initially, the main objective of the land user applying the technology was to improve the soils and crop production in his fields by promoting sustainable agricultural management in the Vega Baja region. The previous use of land was conventional with inorganic fertilization and intensive ploughing. The land user had to convert the conventional lemon tree orchard to organic farming with more sustainable practices. The initial investment was very high and he needed nearly 7 years to get certified in Eco-certification and labelling by the Comité de Agricultura Ecológica de la Comunidad Valenciana.
The land user makes all kind of innovative practices to improve soil fertility and crop production; the most pioneering initiative was to apply organic amendment located in dripper points. Organic certified sheep manure is applied every year in September in holes under the foot of every lemon tree. The following year, the position of the hole is moved around the tree. The holes are dug with a shovel; each hole is 0.4 m wide and 0.2 m deep. The eco-certificate sheep manure is bought from sheep holders. The sheep manure is composed of NPK (2.9; 1.8; 2.4%) with a C/N ratio of 8.8. The organic matter content is 44.5% and the moisture value is 53.8%. The irrigation is by drippers and it includes fertilizers in it. The land user is controlling the fertirrigation dose, changing the amount depending on the nutritional state of the orchard and climatological conditions. As part of the organic agriculture, the weed is not removed anymore. Pest control is done by biological methods: fly adhesive traps, pheromones moths traps, Bacillus thuringiensis solution sprayed, paraffin oil and copper sulphate applied by drip irrigation. The pruning remains are kept on the soil surface as a mulching.
The major benefit is an enhancement of the soil organic content in the long term. There is also an improvement of the orchard productivity. The lemon trees become less prone to diseases and pests. The major disadvantage is the high costs at the beginning to change from conventional to organic and to get the Eco-certificate.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
The organic amendment application is located in dripper points. Sheep manure was applied in holes near to the lemon trees. This technology was established in sustainable agricultural soil in the region of the Vega Baja del Segura.
日期:
23/03/2017
位置:
Orihuela (Spain)
摄影师的名字:
Alicia MC
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
西班牙
区域/州/省:
Vega Baja/Alicante
有关地点的进一步说明:
Orihuela
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2014
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
The lemon is harvested between February and March
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
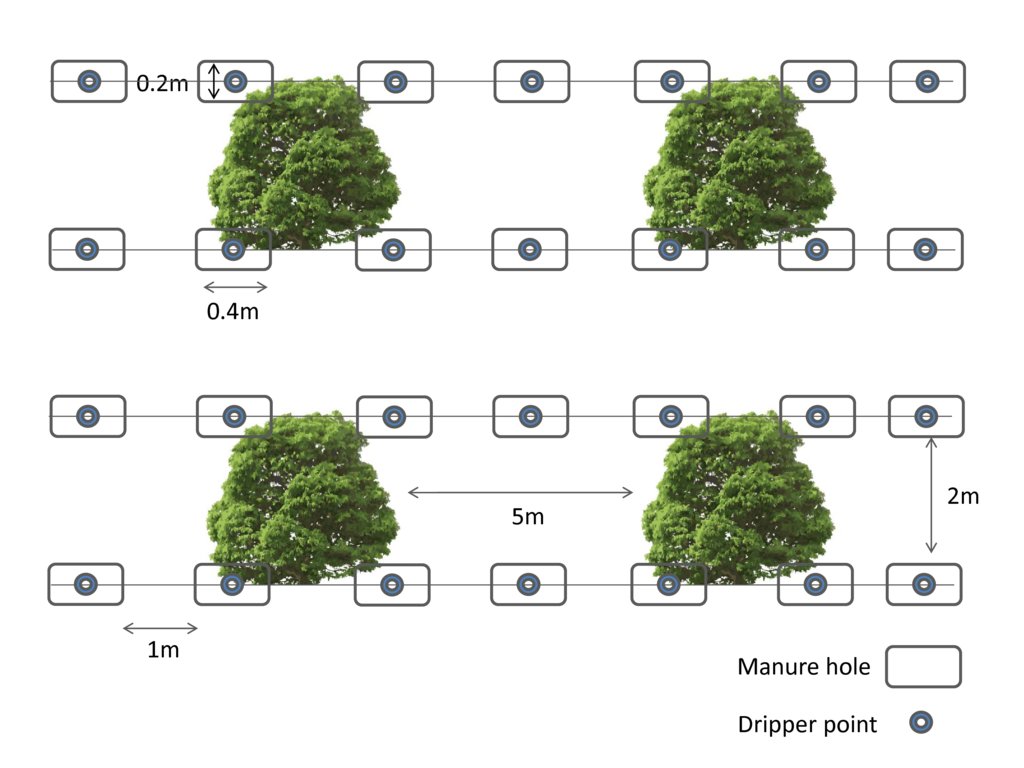
Species used: Lemon tree (Citrus verna)
Lemon tree root depth: 0.5-0.6m
Spacing between plants: 5m
Spacing between manure holes: 1m
Vertical intervals between drip irrigation rows: 2m
Width holes: 0.2m
Lengths holes: 0.4m
Depths holes: 0.2m
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
7.7 ha
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Euro
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
0.944508
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
60
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Digging hole | 农业学的 | September |
| 2. | Organic amendment | 农业学的 | September |
| 3. | Irrigation | 农业学的 | all year |
| 4. | Biological control | 农业学的 | all year |
| 5. | Fertirrigation | 农业学的 | All year, except autumn and winter |
| 6. | Pruning material left on soil surface | 农业学的 | May, July and August |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Organic amendment | person/hour | 5.0 | 6.0 | 30.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pruning | person/hour | 100.0 | 6.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Fertirrigation | person/hour | 100.0 | 6.0 | 600.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Biological control | person/hour | 30.0 | 10.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tractor with trailer (hire per day) | piece | 2.0 | 30.0 | 60.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Organic amendment | kg | 1200.0 | 30.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertirrigation | Litres | 1400.0 | 8.0 | 11200.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Bacillus thuringiensis | Kg | 60.0 | 20.0 | 1200.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Copper sulphate solution | Kg | 5.0 | 30.0 | 150.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Paraffin oil | Litres | 10.0 | 30.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Adhesive trap | piece | 100.0 | 10.0 | 1000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pheromone trap | piece | 10.0 | 40.0 | 400.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 51840.0 | |||||
注释:
The price of sheep manure is so high because he has to buy it from eco-certified sheep holders.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The pests, and the loss of product caused by unexpected weather.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
250.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 机械化/电动
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
The land user observe that the crop production increased two times with the organic agriculture management.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
The lemon fruit with the organic farming management is bigger than before with conventional management.
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
Changing the irrigation to drip irrigation the land user can save water.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Less use of fertilizer, less tillage, no herbicides/pesticides.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
The price of eco-certified lemon in the market is 3 times higher than conventional and the expenses on agricultural inputs are lower.
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Only work for digging the hole, maintaining fertirrigation, harvesting and pruning, but no work for applying pesticides, tillage and weeding.
社会文化影响
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Improved health due to non-application of herbicides/pesticides.
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
The farmer can buy more land due to this income.
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Due to this eco-management, the farmer became well-known and recognized in the region. He appears in television and teaches other farmers and became the president of the regional farmer association.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
The farmer learned a lot about the soil and enhanced his continued education.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Less water is used through drip irrigation.
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Better infiltration due to better soil structure due to the manure application, thus less runoff.
土壤
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Less soil compaction due to better soil structure due to the manure application.
养分循环/补给
注释/具体说明:
Adding sheep manure increases nutrients.
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Adding sheep manure increases organic matter.
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
The organic farming enforces the lemon trees against pests and diseases.
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
The organic farming enforces the lemon trees against pests and diseases.
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
注释/具体说明:
Flood impacts is less due to better soil structure.
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
Land movements decrease due to better soil structure.
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Drought impacts decrease due to more soil moisture.
碳和温室气体的排放
注释/具体说明:
Increase the carbon in the soil due to organic farming and the manure application.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
No pollution by herbicides/pesticides.
温室气体的影响
注释/具体说明:
Increase the carbon in the soil due to organic farming and the manure application.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 夏季 | 增加 | 好 |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 好 |
| 滑坡 | 非常好 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The land user had problems to cope with the money input to establish the SLM technology at the beginning of the process, but he believes that in 10 years the perspective will be better and he will recover the money spent at the beginning.
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 气候变化/极端气候
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
The dose of manure application was modified regarding the climatological conditions.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Reduction of soil degradation |
| Enhacement of soil fertility |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Improvement in crop production |
| Contribution towards a better social acknowledgment of the sustainable farming |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The high dependency on climatological conditions | Pay special attention in soil structure |
| Strict control of organic amendment input with exhaustive verifications and monitoring of the sheep manure | Improve verification process. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Short response time to the weather risk or plagues | Daily monitoring of crop and soil response. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1: land user
- 与土地使用者的访谈
2
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1: Biological control advisor
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
no
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Citrisol S.Coop (farmers association)
URL:
http://citrisol.es/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块