Planting Halophytes (Sporobolus verginicus, Dixie grass) for rehabilitation severely saline soil. [泰国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Kamontip Sasithorn
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
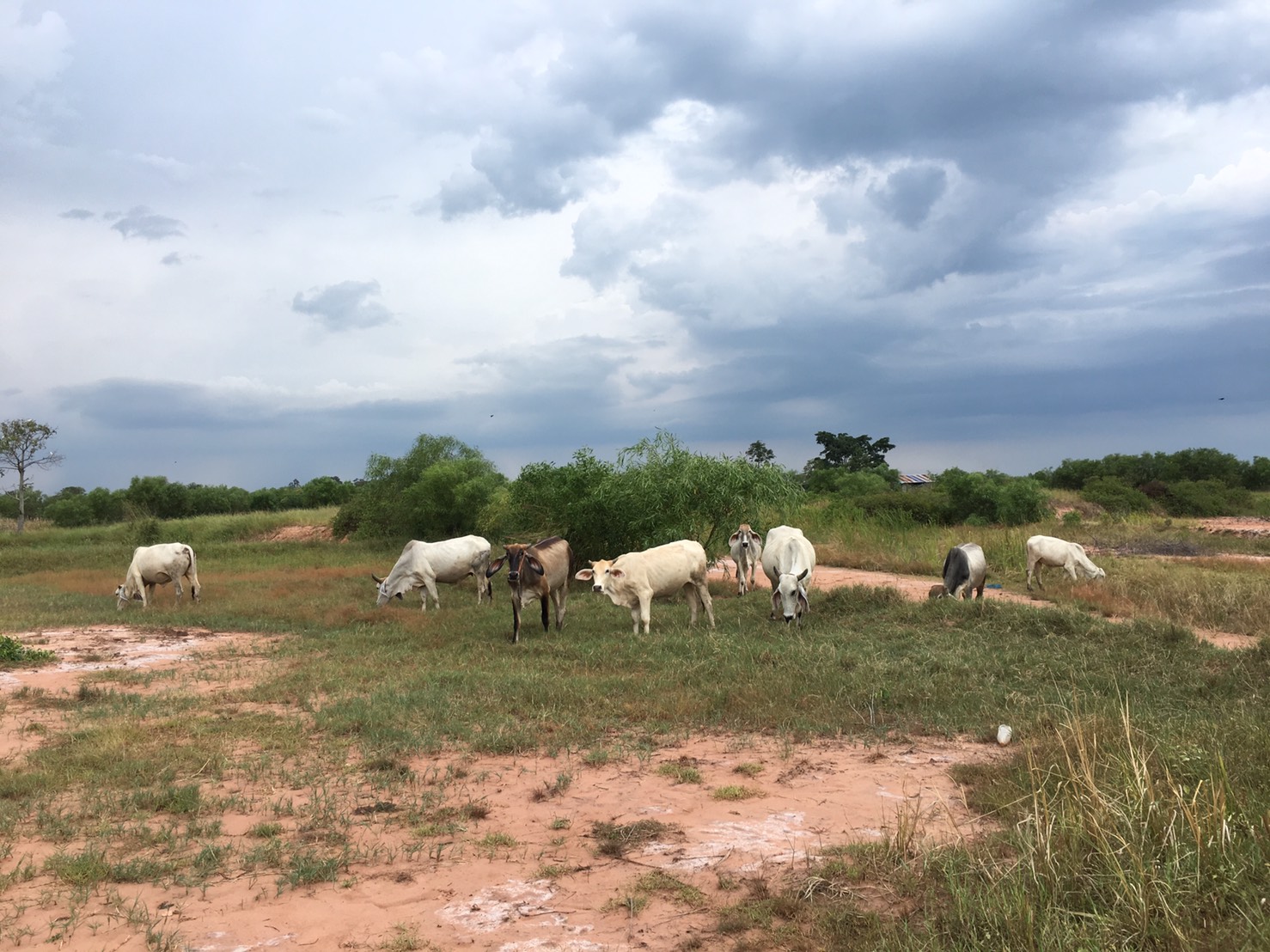
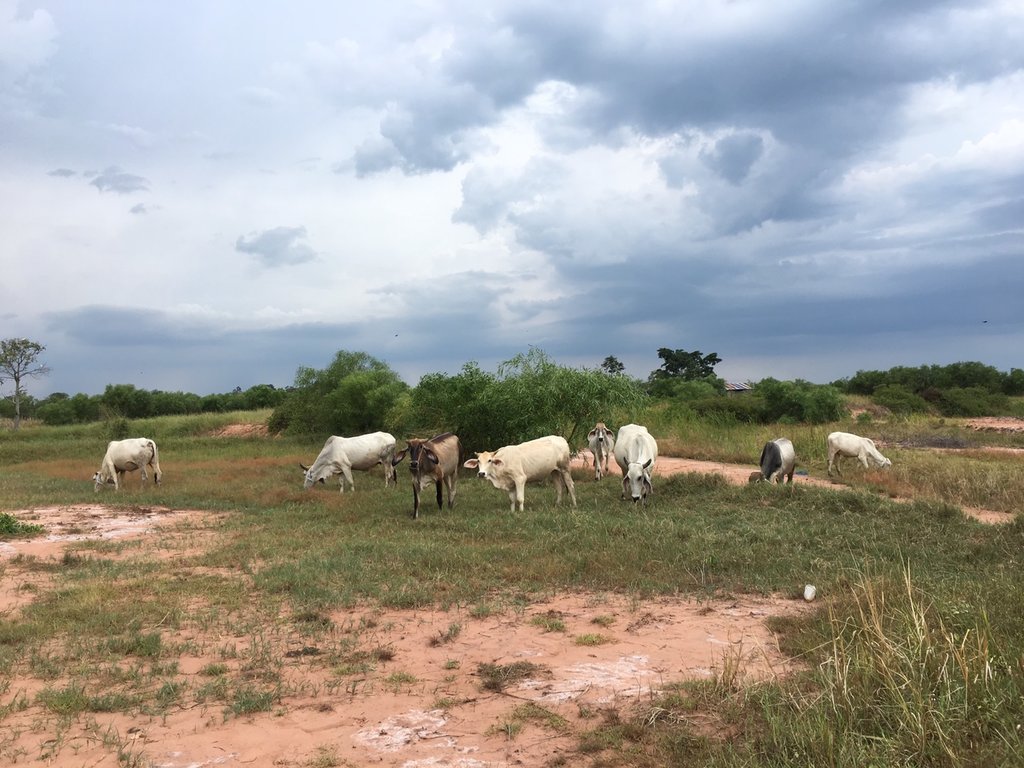
Planting Dixie grass in severely saline soil.
technologies_4158 - 泰国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Munkarn Charong
6 Bann Donpae Moo 8 Kut Chok Sub-district Bua Yai District Nakhon Ratchasima Province.
泰国
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
National Consultants:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Book project: where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide (where the land is greener)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Land Development Department LDD (Land Development Department LDD) - 泰国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
注释:
The technology is very well accepted by the land users.
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
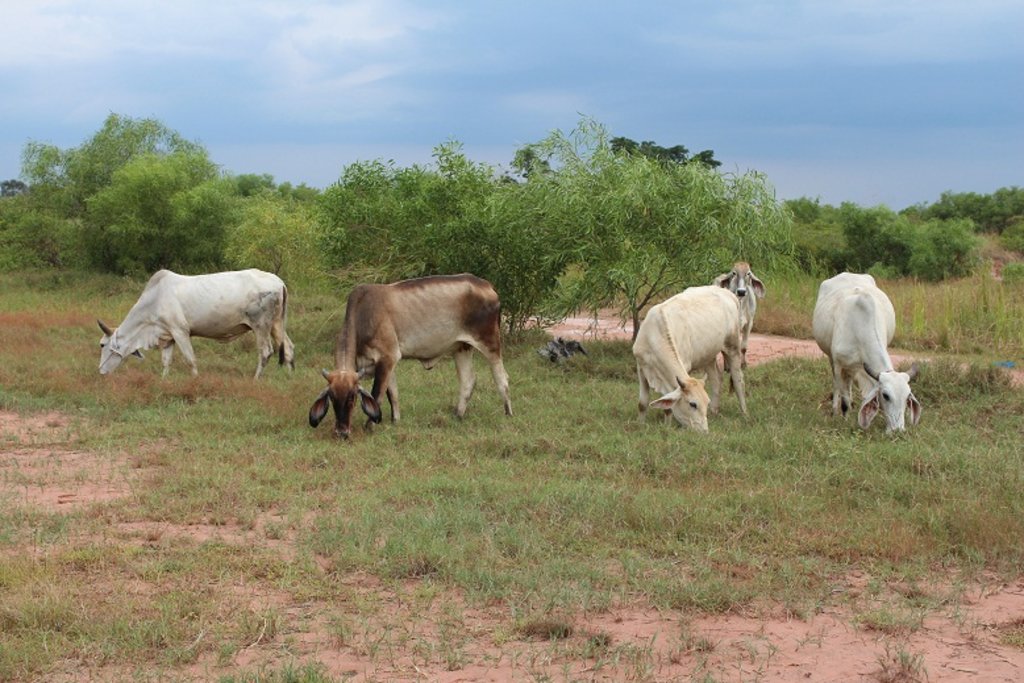
Planting Dixie grass (Sporobolus verginicus) which is halophytic plant aims to maximize land use for farmers and prevent extensive severely saline soil. The Dixie grass can be used as cattle feed. The LDD has put effort to disseminate the use of halophyte to cover more area of severely salt affected land.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Land Development Department (LDD) transfered technology of planting Halophytes (Sporobolus virginicus; Dixie grass) for rehabilitation severely saline soil on Mr.Charong Munkarn’s land. It located at 6 Moo 8 Kutchok sub-district, Buayai district, Nakhonratchasima province. The area is 0-2% slope and showing high soil electrical conductivity (ECe) of more than 16 dS/m, classified as severely saline soil which is mainly salt crusted and barren land. The weather is semi -arid, and the rainfall is 751-1,000 millimeters per year. The exotic halophytes, namely Sporobolus virginicus, coarse type (Dixie grass) could very well adapted to survive in severely salt- affected soil. The mechanisms of their tolerant ability include osmotic adjustment within the plant, salt exclusion, ion accumulation and sequestration excretion of salt via glands in plant leave or stem. The benefits of planting halophytes in severely saline soil are soil moisture conservation, salt accumulation prevention on the surface and utilization as feed for livestocks. The objectives of the technology are to 1) prevent distribution of severely saline soil. 2) maximize use of land for farmers. 3) to use halophyte grasses as cover crop and rehabilitation the ecosystem of severely salt-affected soil.
Halophytes plantation has been supported by Land Development Department under the project on Promotion of Integrated Saline Soil Management on sub-watershed area. The activity of rehabilitation severely salt-affected soil is planting salt tolerant tree and grass. The stakeholders are researchers of LDD who worked together with community volunteers on soil improvement, community leaders and farmers. Land Development Regional Office 3 (Nakhonratchasima) supported Dixie grass seedling, compost and chemical fertilizer. Dixie grass was planted at spacing of 20x20 centimeters on abandoned area and on ridges between rows of Acacia ampliceps. After 3 years of planting Dixie grass, it has been found that this barren land was covered by plants and much improved in biodiversity by the evidence of many varieties of wild grass, dragonflies, rats and birds. Farmers can grow rice and they use Dixie grass as feed for livestock. Moreover farmers are able to increased their incomes. The migration for job to big cities is reduced. From interviewing, farmers satisfied this technology of Sporobolus virginicus plantation for rehabilitation of severely saline soil. Besides lower in salination farmers get more rice yields and better environment and livelihoods. Although the planting halophytes is an improvement of severely saline soil, which is low input of vegetative measure however the recovery time of saline soil improvement is not as fast as that of engineering measure of high investment. Furthermore, the neighboring farmers often burn their rice straws after harvesting, that damages the Dixie grass and causes partially dead and thus lower the biomass.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
To interview Mr. Charong Munkarn on the use of Dixie grass for rehabilitation severely saline soil.
日期:
18/10/2018
位置:
6 Bann Donpae Moo 8 Kut Chok Sub-district Bua Yai District Nakhon Ratchasima Province.
摄影师的名字:
Kamonthip Sasithorn
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
泰国
区域/州/省:
6 Bann Donpae Moo 8 Kut Chok Sub-district Bua Yai District Nakhon Ratchasima Province.
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bann Donpae
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
技术现场是否位于永久保护区?:
否
注释:
The SLM technology site for planting Halophytes (Sporobolus virginicus; Dixie grass) to rehabilitate severely saline soil
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2015
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Soil management on sub-watershed area, activity of rehabilitation severely salt-affected soil by planting salt tolerant tree and grass.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

其它
具体说明:
Extremely salt affected areas
注释:
Extremely salt affected areas that can not used for agricultural land.
注释:
Saline soil areas should be rehabilitated using low investment technology by planting highly adapted salt tolerant species such as Dixie grass.
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 改良牧场
动物类型:
- 牲畜 - 其他小型动物
是否实行作物与牲畜的综合管理?:
否
产品和服务:
- 肉类
计数:
1
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Grass planting area of farmers outside the irrigation or rainfed area don't have enough water for cultivation.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物
- V5:其它
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Dixie is planted to prevent the spread of salt affect in the area.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
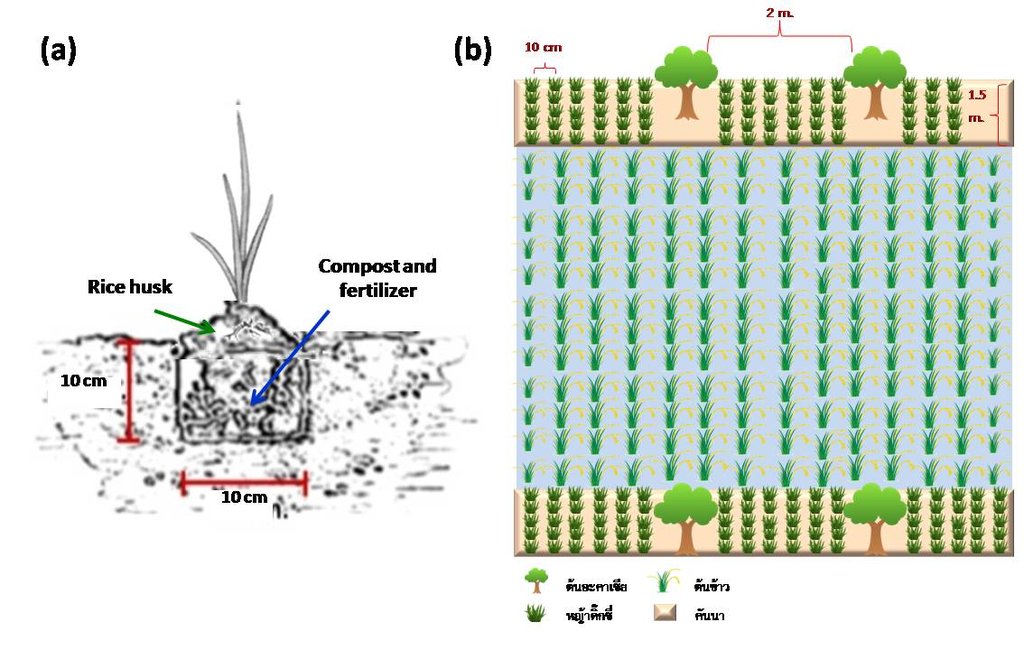
(a) Propagation of Dixie grass through shoot cutting of 2-3 inches long with
3 nodes is made and planted in bags filled with soil and compost. The seedling
is 1 month old before planting in the pit of 10x10x10 cubic cm. with 200 gm. of
compost and 6.25 gm of 15-15-15 chemical fertilizer then cover with rice husk
at 400 gm/pit, the spacing between pits is 30x30 square cm.
(b) A sketch of planting Dixie grasses on severely salt affected land with
Acacia ampliceps on the ridges. After 3 years of planting, Dixie grass
has been replaced by rice except those on the ridge.
作者:
Winai Chombut
日期:
18/10/2018
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Baht
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
32.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
300
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dixie grass nursery | May-July 2015 |
| 2. | Land preparation for planting | May-July 2015 |
| 3. | Fertilizer application | May-July 2015 |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labor cost for planting Eucalyptus (labor wage per day = 300 baht, 1 rai required to labor cost = 1200 baht) | Rai | 1.0 | 1200.0 | 1200.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Dixie seedling cost 1600 trees/rai, 1 baht for each seedling | seedling | 1600.0 | 0.5 | 800.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost cost 3.5 baht/kg, 0.2 kg/pit | kg | 320.0 | 3.5 | 1120.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Rice husk cost 4 baht/kg, 0.4 kg/pit | kg | 640.0 | 4.0 | 2560.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Chemical fertilizer 15-15-15 cost 20 baht/kg, 6.25 kg/pit | kg | 10.0 | 20.0 | 200.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 5880.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 183.75 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Land Development Department
注释:
Labor cost for land preparation, planting bored and seedling bored by LDD Chemical fertilizer 15-15-15, compost and rice husk are from farm products.
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | No maintenance activities because Dixies grasses can glow well and be multiplied extensively by themselves |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | No labor cost for maintenance | 0 |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The government policy on minimum labor wage is an important factor affected cost of the project.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1028.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Average annual rainfall from 1983-2012
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Meteorological Department
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Average temperature 21 - 36 degree Celsius, relative humidity is 75%
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
The geography is in the lower basin of Korat plateau in the Northeast Thailand
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Texture of top soil is fine loamy and more than 20 cm. below the surface is sandy loam or sandy clay loam, pH = 7 and increasing with depth up to 8.5, salinity is moderately to highly soil affected identified by percentage of the salt crust on the surface, very low P and K.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
水的盐度有问题吗?:
是
具体说明:
Slightly saline
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Shallow saline groundwater exists because of low lying discharge area and salt source beneath under the ground.
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
栖息地多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Before planting Dixie grass, species and habitat were low. After 3 years, field crab, field rat, dragonfly, earthworms, weasel, Snake, Local weeds and wildflowers used to be disappeared now are found.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Diligent farmer seeking more income by raising burn firewood from Acacia tree, catch field rat and bamboo shoot.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Farmers have been planting Dixie grass together with Acacia tree on rice bunds and burn firewood from Acacia tree
in order to get additional income.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
- Rainfed
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
作物质量
饲料生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
土地管理
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
灌溉用水的可用性
灌溉用水的质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
农业收入
收入来源的多样性
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
土地使用权/用水权
文化机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤堆积
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
酸度
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
外来入侵物种
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
滑坡/泥石流
干旱影响
飓风、暴雨的影响
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
微气候
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
温室气体的影响
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
| 森林火灾 | 适度 |
| 陆地火灾 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 山洪暴发 | 适度 |
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 昆虫/蠕虫侵扰 | 适度 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 延长生长期 | 不好 |
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
稍微积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 1-10%
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Farmers and land users acknowledge the benefit of the technology that decreasing salinity effect, planting Dixie grass mulching surface soil and grazing land for livestocks.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Dixie gases are very high salt tolerance and after planting the salinity obviously decreased. |
| The better environment that encourages the return of other plant species. |
| Secondly instead of leaving the land barren the land user can sell the Dixie shoots for propagation to Land Development Department. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Only halophytes especially Dixie can grow well on severely salt affected land. |
| After planting Dixie for few years, the soils are less saline that induces biodiversity of both fauna and flora such as birds butterflies, rats, earthworms and native flowers. |
| The farmers can use their land more extensively rather leave it barren. |
| Dixie grasses can be used as cattle feed that the land user can get higher income. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The land user lack of knowledge on halophytes and there is no other choice for better income than Dixie grass. | The SLM officers should visit them and provide better knowledge. |
| The neighboring farmers get used to the burning of rice straw after harvest causing death of Dixie grasses. | Public relation is needed to stop burning. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Not all the researchers and SLM workers understand the mechanism of halophyte and the importance of the Dixie grass to the project flow chart’s work plans. | They need to be well trained at various levels. |
| The farmers are not well approached and many of them know nothing about the project. | The officers should be trained and get better knowledge about the project. |
| The project follows up and evaluation is insufficient and ineffective. | The concerned project officers should pay more awareness on weakness and on obstacles of the success of the project. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
Visit 1 farmer/user's land.
- 与土地使用者的访谈
Interview with 1 farmer
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
The Land Development Department officers and planners (4)
- 根据报告和其他现有文档进行编译
Soil salinity research and development group of the Land Development Department's
reports (3)
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
18/10/2018
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Land Development Department
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.ldd.go.th/
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
where the land is greener - Case Studies and Analysis of Soil and Water Conservation Initiatives Worldwide
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/library/media/27/
标题/说明:
where people and their land are safer - A Compendium of Good Practices in Disaster Risk Reduction (DRR) (where people and their land are safer)
URL:
https://www.wocat.net/en/projects-and-countries/projects/drr
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块