Contour Trench cum Bund [印度]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Niranjan Sahu
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Samapatana nali o huda ( Oriya)
technologies_1480 - 印度
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
Patel Anita
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [印度]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- 编制者: Niranjan Sahu
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Contour trench cum bund is a bund laid out on contour along with trench either staggered or continuous to check the velocity of run off, conserve in situ moisture, increse ground water recharge and there by establish a sustainable land use system.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
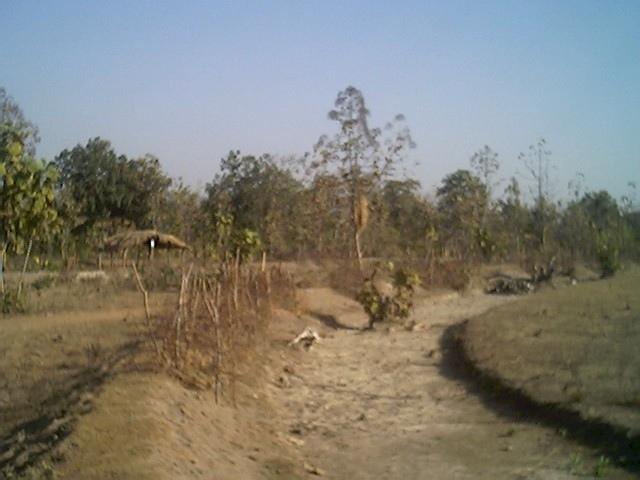
It is a structural measure. The bund is constructed taking the excavated earth from a trench of 1.5m X 0.3m cross section and leaving a berm of 0.3m and put along the contour. Loose boulder water way are constructed on the bund for safe disposal of excess run off.
Purpose: To break the slope of land. To reduce the velocity of runoff. To increase the in situ soil moisture and increase ground water table. To reduce down stream sand casting.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The process adopted for implementation of the intervention followed participatory planning through resource mapping, transect, well being ranking, problem identification, prioritisation and negotiation; thus benefit sharing, contribution and future maintenance of the stucture is ensured before establishment of the structure. The poor land and poor people get the opportunity first.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
印度
区域/州/省:
Orissa
有关地点的进一步说明:
Nangalbod-Tankamal Watershed,Mahanadi Basin
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
0.32
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.32 km2.
The technology area comprises of 0.3 2km2 within the watershed of 6 km2. The technology is an improvement of the age old practice of field bunding by the farmers.This has been promoted by the Soil Conservation department and watershed mission through watershed development programme.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Indegeneous but improved by Soil Conservation department, Watershed Mission, UNDP.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林牧业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 小米
- rice
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150 Longest growing period from month to month: Jun - Oct

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- cattle

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 选伐
产品和服务:
- 薪材
- 水果和坚果
- 放牧/啃牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The fertile top soil is gradually washed away.Productivity of the soil is also reduced. Thus, farmer is only taking minor millet in kharif.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of production. Soil is unable to retain moisture, so we suffer crop loss during long dry spell.Due to sand casting crop is also partially damaged in the down stream.
Nomadism: People allow the cattle to graze freely in the field after the crop is harvested
Selective felling of (semi-) natural forests: Yes
Problems / comments regarding forest use: People have started managing forest through VSS and Forest protection committee.
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: minor millets and up land paddy are the major crop under rain fed condition
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), education, access to knowledge and support services (Absence of institutional arrangements to disseminate the knowledge from lab to land and involve the users in implementation)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing (Subsistence economy, dependance on forests for fuelwood and fodder, livestock were low quality, free grazing type. And these were no regulatory mechanisms to share usufruct from forests with people.), poverty / wealth (Lack of capital at the grassroot to take the initiative by the farmers themselves)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
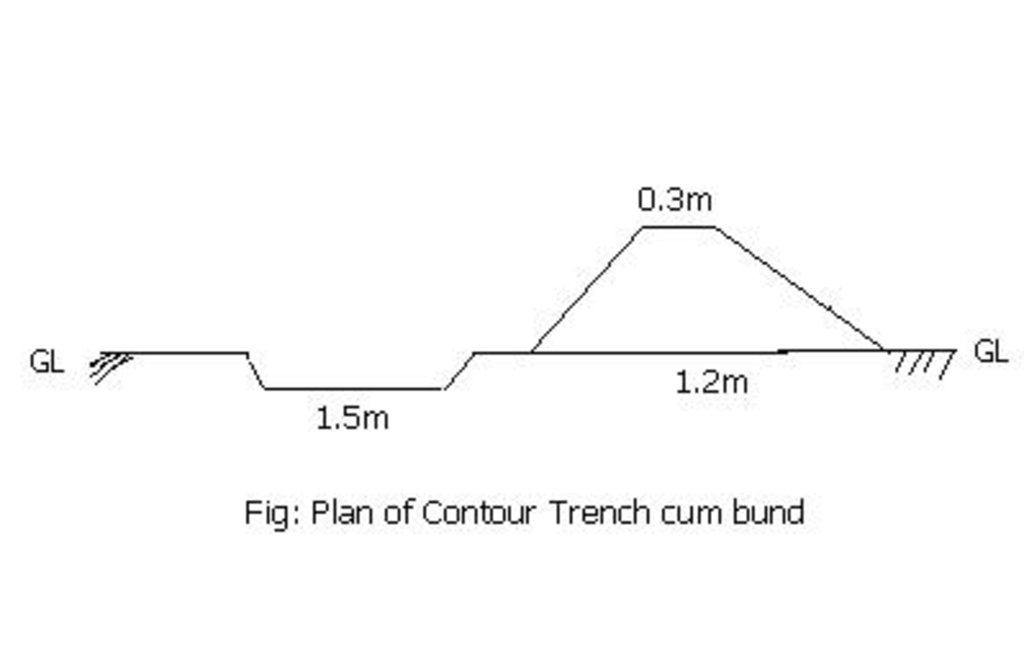
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: reduction of slope length
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard
Bund/ bank: semi-circular/V shaped trapezoidal
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.45
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 60
Construction material (earth): earth is dug from the trench in the up stream
Construction material (stone): picked up boulders available locally
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Indian Rupee
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
50.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Survey and alignment of trench, bund | dry season |
| 2. | Digging of trenches and construction of bunds | dry season |
| 3. | Construction of water way | dry season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 30.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Earth | ha | 1.0 | 98.0 | 98.0 | 30.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 200.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 4.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Grass turfing on bunds | during rainy season/annual |
| 2. | Maintaining shape and size of bund | after rainy season/annual |
| 3. | rearranging dispersed stone in water way | after rainy season/annual |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Cross-section and length of the structure per hectare
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1382.00
农业气候带
- 半干旱
80-100 days of rainfall occurs in most part of the state
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 101-500 m a.s.l. ( the technology area is located at 196m.a.s.l.)
Landforms: Hill slopes (ranked 1, the surrounding area is coverd with hillocks with forest) and footslopes (ranked 2, the technology area has undulating slopes with forest in betweem and mild slope)
Slopes on average: Also gentle (ranked 2) and flat (ranked 3)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Also moderately deep (ranked 2) and deep (ranked 3)
Soil texture: Also medium (ranked 2) and fine/havey (ranked 3)
Soil fertility: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
Topsoil organic matter: Also medium (ranked 2) and high (ranked 3)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (ranked 1) and medium (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Very low (ranked 1), low (ranked 2) and medium (ranked 3)
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 丰富
- 非常丰富
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 5% of the land.
20% of the land users are rich and own 15% of the land.
25% of the land users are average wealthy and own 20% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
5% of the land users are poor and own 25% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The livelihoods is less diversified. They also depends on NTFP marketing, off farm activities.
Level of mechanization: Animal traction (ranked ) and manual work (ranked 2)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology:
Cropland: 0.5-1ha (ranked 1, marginal farmers)
1-2 ha (ranked 2, small farmers)
2-5 ha (ranked 3, big farmers)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Due to construction of bund
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
Formal credit
Input constraints
注释/具体说明:
Timely availability of inputs
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
22 SHGs has been formed and strengthened
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
NRM volunteers has been developed
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
During identification of land ownership and location of waterways
生态影响
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
其它生态影响
Soil fertility
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
Water table in wells
Water availability in WHS
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
24
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
12 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: survey results
12 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: survey results
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The farmers have realised the benefits from farmers' group meeting and visiting to the technology area.The farmers have started maintaining the bunds. They have also started taking crops both on bunds and field.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Our crop can with stand dry spell How can they be sustained / enhanced? Planting of glaricidia and use of compost |
|
Value of land will increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? By maintaining bunds |
|
We can take crop in bunds How can they be sustained / enhanced? planting of bengal grams, tils, cow pea and sima |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Reduce runoff and velocity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Reduce sand casting in the down stream How can they be sustained / enhanced? Desilting from the trenches |
|
Crop diversification and promotion of improved agricultural practices How can they be sustained / enhanced? Through capacity building of volunteers and land users |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| loss of land | Productive use of trench and bunds |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Regular maintenance of the stone surplus | promote and strengthen user group |
| Open grazing | Promote community farming for collective actions |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Micro plan of Nangalbod-tankamal watershed. 12/30/2004.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
district Statistical hand book. 12/30/2004.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
Project Direcotr watershed, Nuapada
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach [印度]
Participatory Sustainable Rural Livelihood Approach adopts participatory tools for livelihood situational analysis of the five capitals(Physical, Financila,Social, Human and Natural) and prepare livelihood focussed micro plan with the commuity for sustai
- 编制者: Niranjan Sahu
模块
无模块