Fodder Crop Production [土耳其]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Faruk Ocakoglu
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Yem Bitkileri Yetiştiriciliği (Turkish)
technologies_1015 - 土耳其
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
SLM专业人员:
Inci Tolay
Eskişehir Osmangazi University, Faculty of Agriculture
土耳其
Resident:
Caz Azmi
土耳其
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
DESIRE (EU-DES!RE)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Eskisehir Osmangazi University (Eskisehir Osmangazi University) - 土耳其1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
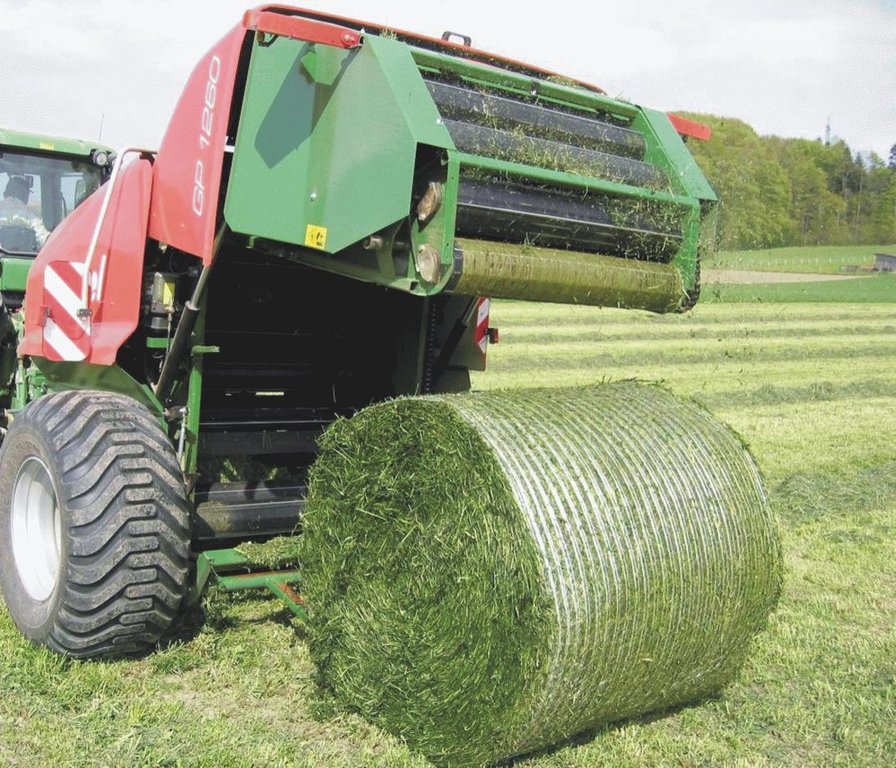
Production of fodder crops every year both for feeding livestock and increasing soil fertility.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
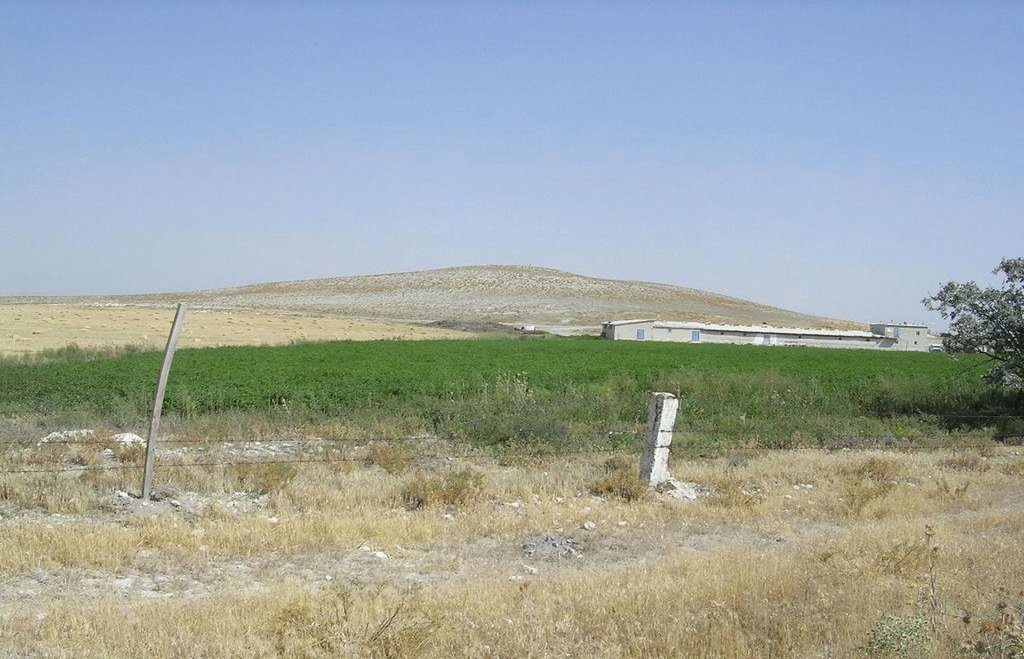
Fodder crops (maize, alfalfa, sainfoin, common vetch, triticale, oat, fodder beet, wheat and barley) are grown for hay production for livestock feeding. Growing fodder crops is a part of sustainable agriculture. The soil is protected in dry farming areas by covering the soil surface and leguminous fodder species (alfalfa, sainfoin, common vetch), which increases the soil fertility by nitrogen fixation. Applying the technology does not require extra inputs different from other agricultural crops. All that is needed is to identify a crop rotation plan including fodder production and regular agricultural crops.
Purpose of the Technology: Different fodder crops (legumineous and gramineous plants) are produced to feed the farmers’ own livestock. By enabling widespread and dense surface cover, It helps both in dry farming and irrigated areas to protect the soil from water and wind erosion.
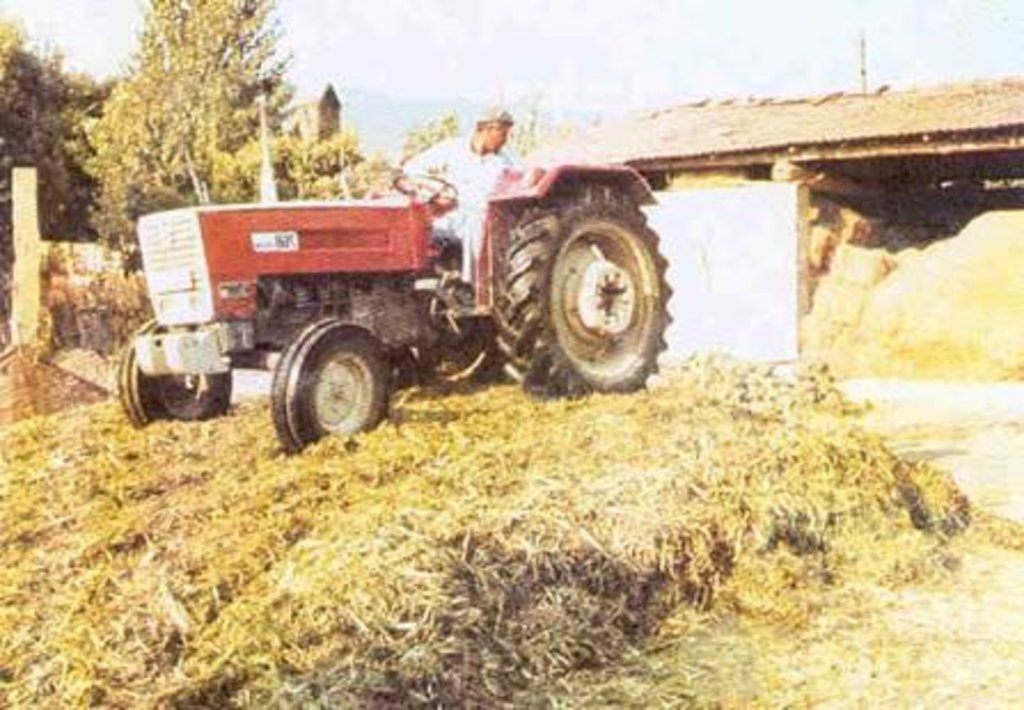
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Usually the soil is first ploughed. Soil cultivation machinery (tractor, disc plough, wide-sweep cultivator, disc harrow, fertilizer and seed drill) is used to prepare the soil for cultivation, to fertilize the soil and to sow the seeds. After seeding and growing of the crops, special machinery is used for harvesting.
Natural / human environment: Farmers who produce both livestock and field crops in particular can use this technology and get an improved benefit. They can increase income and at the same time protect their soil.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
土耳其
区域/州/省:
Eskişehir
有关地点的进一步说明:
Keskin Watershed
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 10-100 平方千米
注释:
Farmers think that the technology is helpful for livestock feeding and for increasing soil fertility
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 苜蓿
- 饲料作物 - 草
- 饲料作物 - 其他
- gramineous fodder species
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 180Longest growing period from month to month: Nov - Apr

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 经营牧场
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 绵羊
- cow
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): monoculture in dry farming areas, insufficient irrigation and rainfall, overgrazing, false cultivation techniques.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Insufficient technical help and interest to agriculture problems by government, urbanization pressure, land fragmentation, monoculture in dry farming areas, insufficient irrigation and rainfall, overgrazing, false cultivation techniques.
Ranching: cow, sheep,goat
Other grazingland: agropastoralism
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
Constraints of settlement / urban: some legal problems
Constraints of recreation: no problem
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
25-50 LU /km2
3.4 供水
注释:
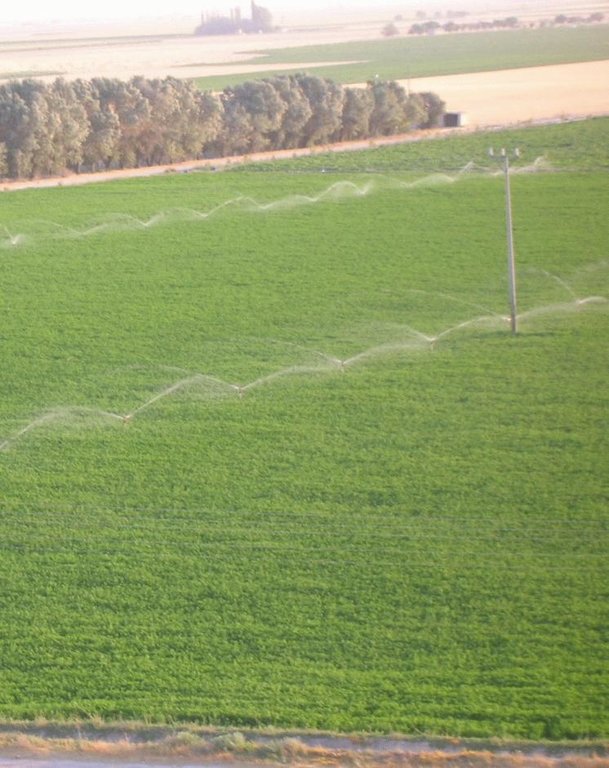
Water supply: mixed rainfed - irrigated, rainfed, mixed rainfed - irrigated, full irrigation
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A7:其它
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, relay cropping, cover cropping, retaining more vegetation cover, legume inter-planting, rotations / fallows
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation, Pk: sealing and crusting, Bl: loss of soil life, Bp: increase of pests / diseases, loss of predators
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Monocropping is dominant), land tenure, governance / institutional
Secondary causes of degradation: over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, overgrazing (Regular management in pasture is needed), urbanisation and infrastructure development (There are border and legislative problems), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Destroying of soil vegetation cover increase the evapotranspiration of soil water), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (In recent year low rainfall occurs), population pressure, education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
注释:
Main goals: prevention of land degradation
Secondary goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
A special harvesting machine used to bale fodder
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (state advisors are generally aquitained with enough agricultural information.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (need knowledge for alternative fodders, their mode of cultivation.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of biomass (quantity)
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Folder crops it depends on plant type
Relay cropping
Material/ species: Leguminious and gramineous plants are grovin intercroppingly
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Perennial legumes provide a cover on soil long time
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Legumunious fodders provide nitrogen fixation to soil
Legume inter-planting
Quantity/ density: 3t/ha
Rotations / fallows
Material/ species: Fallow is made in dry farming areas
作者:
http://turhaltarim.gov
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
YTL
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.3
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
20.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Buying a harvest machine |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 50.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 38.46 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
Life span of the harvest machine: 20 years
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Ploughing | before harvest/ annually |
| 2. | Provide seeds from agricultural agencies | |
| 3. | Fertilizing | |
| 4. | Irrigation |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Ploughing | ha | 1.0 | 175.0 | 175.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 300.0 | 300.0 | 75.0 |
| 植物材料 | Fertilizer | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Biocides | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Irrigation | ha | 1.0 | 280.0 | 280.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 1200.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 923.08 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Certified seed material and tillage costs (e.g. oil, machines) are the most determining factors affecting the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
3-4 months
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium
Soil drainage/infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table 5-50m (high in winter and spring; low in summer; medium in autumn)
Availability of surface water is medium (high in winter and spring; low in summer and autumn)
Water quality (untreated) is good drinking water ( Both ground and surface water)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: < 0.5%
2% of the land users are rich and own 29% of the land.
96% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
2% of the land users are poor and own 1% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: 1 % of land users have off farm income
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha, 0.5-1 ha (cropland), 50-100 ha (grazing land)
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,有命名
用水权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
20 % increase
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
75% increase
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
75% increase
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
20% increase
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Imncreased 40%
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
increased 30%
冲突缓解
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The improved livestock feeding increases income
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
SLM之前的数量:
50%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
水的回收/收集
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
SLM之前的数量:
25%
SLM之后的数量:
50%
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
SLM之前的数量:
10%
SLM之后的数量:
15%
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
下游淤积
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
| temperature below 10°C | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
100
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
95 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: financial support in cash
5% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
5 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Because of the high costs of the inputs land users do not want to apply the technology without external support
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Input prices are increasing and therefore farmers do not readily adopt the technology without some inducement.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It reduces the cost of fodder input How can they be sustained / enhanced? Subsidies should be continued |
|
It increases productivity of livestock How can they be sustained / enhanced? Technical knowledge should be given |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It improves the soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Technical and economic support is needed |
|
It improves the livestock health by means of mixed fodder How can they be sustained / enhanced? Technical and economic support is needed |
|
Increased protection of soil from water erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Trials in plots should be done to demonstrate the magnitude of this advantage, so that the farmers can easily accept this technology |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Technology increases water use | Drip irrigation in the suitable crops can be a partial solution |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land users awareness is low | They can be trained |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Ryder, M.H., Fares, A., 2008. Evaluating cover crops (sudex, sunn hemp, oats) for use as vegetative filters to control sediment and nutrient loading from agricultural runoff in a Hawaiian watershed. J. Am. Water Res. Assoc. 44, 640–653.
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
De Baets, S., Poesen, J., Meersmans, J., Serlet, L., 2011. Cover crops and their erosion-reducing effects during concentrated flow erosion. Catena, 85: 237–244.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块