Irrigated agro-biodiversity system in arid high mountain area [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Gulniso Nekushoeva
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1034 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - 塔吉克斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences (Tajik Academy of Agricultural Sciences) - 塔吉克斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
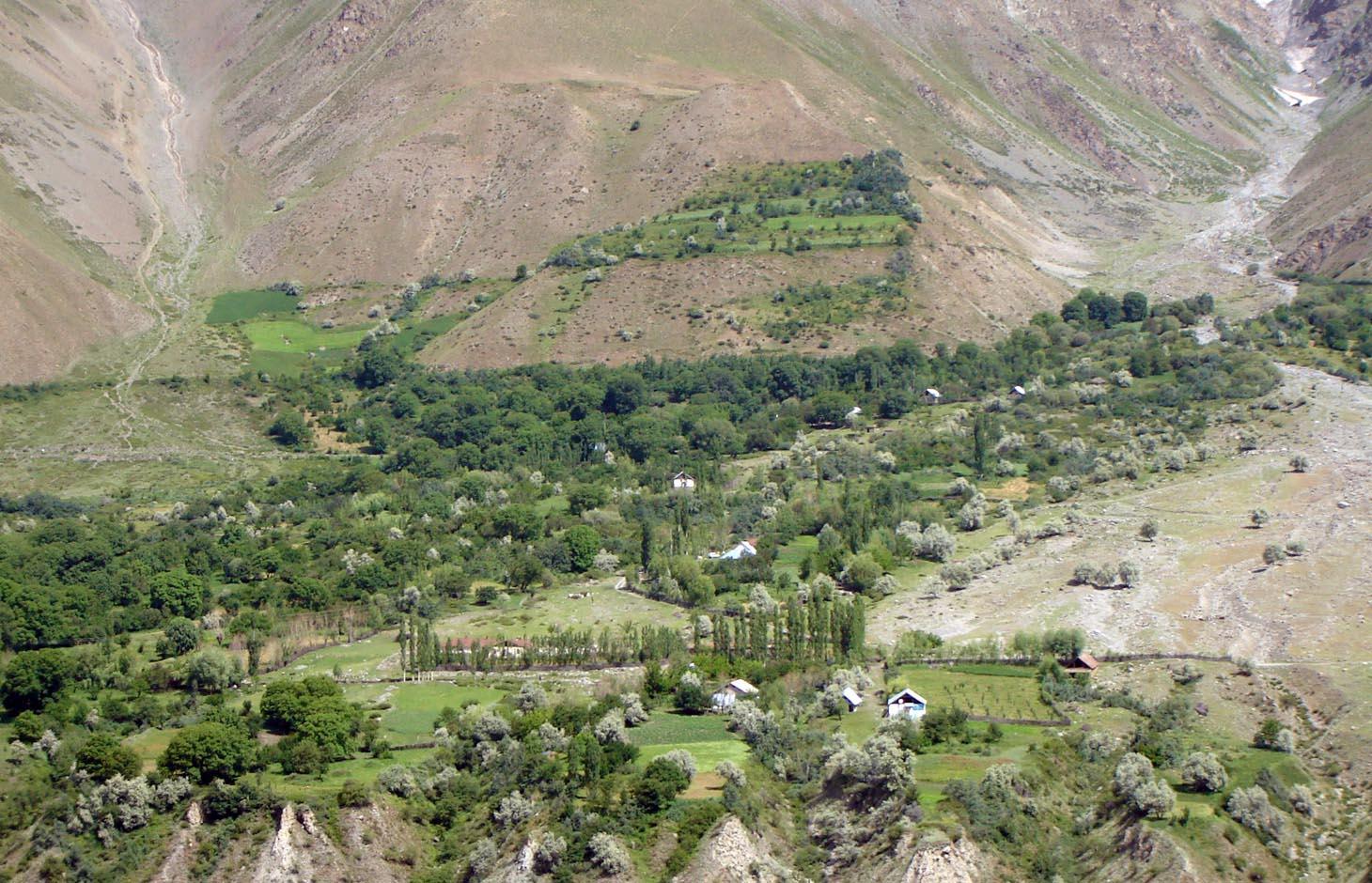
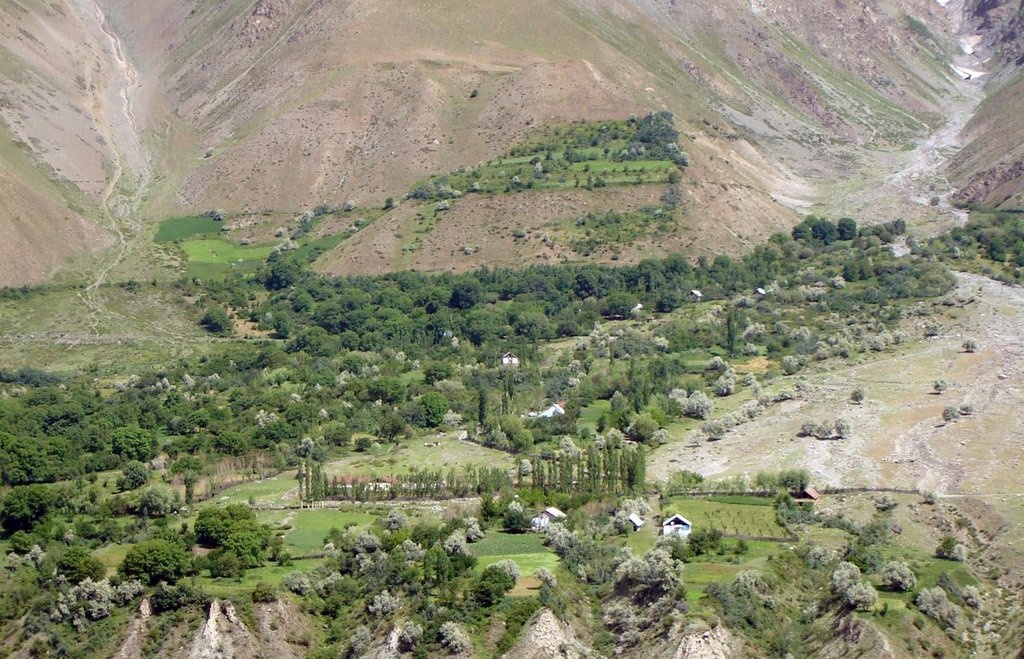
An individual farmer family, has changed an overgrazed pasture area on a steep slope in the upper part of the village into an irrigated agro-biodiversity system, by constructing an irrigation canal, by tilling and removing stones from the terraces for crop production and afforesting the surrounding area with fruit trees and bushes.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The site was established in 1989, with the construction of an irrigation canal. The canal brings water from a small watershed and the slowly melting snow fields within. In years with limited snowfall, the water is insufficient for irrigation throughout the summer months.It is a open, mud canal, 730 m long. When establishing new cropland, removal of stones from the plots is the most laborious part of the work. After an initial removal of stones, the land is tilled and appearing stones are again removed. This process is repeated several times.
Year round maintenance work is required to keep the canal functioning. Maintenance work on the cropland includes stone removal, manuring of potatoes fields, weeding and tilling.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
GBAO
有关地点的进一步说明:
Vanj / Udob / Trit
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
This technology can be found all along Vanj valley.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
注释(项目类型等):
A traditional agroforestry system is implemented on a steep slope above the village, as there is a lack of flatter cropland. This requires improved and carefully adapted land practices.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 饲料作物 - 苜蓿
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
- vegetables, sea-buckthorn
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
- 核果(桃、杏、樱桃、李子等)
- 树坚果(巴西坚果、开心果、核桃、杏仁等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150Longest growing period from month to month: May - September

森林/林地
- willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)"; withthorn, dog rose
产品和服务:
- 水果和坚果
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Water scarcity is the major factor limiting vegetation growth and agricultural production in this arid areas. The soils are stony and slopes are steep (20-30 degrees).
The area is irrigated from streams fed by snow and glacier melting, and therefore water availability is strongly depending on yearly snow precipitation. If due to climate change snowfalls are decreasing in the future, this is a threat for agriculture in the region.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): As the area is on steep slopes there is a high risk of small land slides triggered by irrigation. Fast snow melting in spring time may also cause land slides.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Mixed: Mf: Agroforestry
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: Old wallnut forests are used for agroforestry: there are potato, wheat, alfa-alfa and vegetable gardens below the nut trees.
Newly irrigated areas, are without wallnut trees and used for annual cropping and for perennial cropping.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

牧场
注释:
Extensive grazing land
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农业林学
- 横坡措施
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S1:阶地

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues, mineral (inorganic) fertilizers, breaking crust / sealed surface, breaking compacted topsoil, contour tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -contour, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wm:块体运动/滑坡

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wm: mass movements / landslides, Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Pc: compaction, Bh: loss of habitats, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, droughts (in years with droughts part of the perennial vegetation may dry up), land tenure (common grazing land), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (access to irrigation water, access to markets)
Secondary causes of degradation: poverty / wealth (early grazing, overgrazing), labour availability (mostly manual work and thus labour intensiv), governance / institutional (limited access to market, no water association)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Vast practical knowledge is required, through practical experiments, the practices were improved over time.)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), increase in organic matter, increase of biomass (quantity), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder), spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Agronomic measure: crop rotation on wheat fields
Material/ species: perennial fodder plants (alfa-alfa)
Remarks: high density of alfa-alfa plants
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: cow manure
Quantity/ density: 15
Remarks: for patatoe fields
Mineral (inorganic) fertilizers
Material/ species: "super phosphat" or "silitra"
Quantity/ density: 0.025
Remarks: for wheat fields
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Contour tillage
Material/ species: tilling using 2 ochs
Remarks: for wheat and patatoe fields
Aligned: -contour
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, F : fruit trees / shrubs, G : grass
Trees/ shrubs species: willow, "sangid", "Jachman bushes", "Kort (big bush)";
Fruit trees / shrubs species: sea-buckthorn, walnut, plum, appel, pear, apricot, mirabelle, whitethorn, cherry, dog rose
Grass species: graminoids and legumes
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 2500
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 750
Construction material (earth): The waterways are all dug into the ground, and are mostly fortified with bushes and trees.
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
Change of land use type: extensive grazing to agroforestry
Layout change according to natural and human environment: carefully designed layout taking advantage of flatter areas for cultivation of annual crops, and protecting steep slopes with perennial tree and bush cover
Control / change of species composition: mix of cultivated and wild plants (trees, bushes and grasses)
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tajik Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.4
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
30.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | spring |
| 2. | Construction of irrigation canal | autumn |
| 3. | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | spring |
| 4. | Alfa-alfa seeds (12kg/ha) | for 4 years, then can produce own seeds |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting of willows, cherry, pears | Persons/day | 1.0 | 100.0 | ||
| 劳动力 | Construction irrigation canal | Persons/day | 100.0 | 30.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Construction of on-farm water distribution network | Persons/day | 30.0 | 30.0 | 900.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Alfa-alfa seeds | kg/ha | 6.0 | 20.0 | 120.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 4020.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 913.64 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Wheat (barley) sowing | anually |
| 2. | Wheat (barley) sowing | |
| 3. | Tilling potato fields | 3 times per growing season |
| 4. | Irrigating wheat (barley, alfa-alfa) | times per growing season |
| 5. | Planting potato | during planting |
| 6. | Planting potato | |
| 7. | Applying fertilizer to wheat fields | 3 times per growing period |
| 8. | Maintenance of canal and on-farm water distribution network | spring and after rains |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Sowing wheat with ochses | Persons/day | 1.0 | 40.0 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Tilling with ochses | Persons/day | 6.0 | 40.0 | 240.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Irrigating wheat, barley alfalfa | Persons/day | 6.0 | 30.0 | 180.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Planting potatoe | Persons/day | 8.0 | 30.0 | 240.0 | |
| 设备 | Ochses for wheat sowing | Ochses/ha | 2.0 | 50.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Ochses for potatoe tilling | Ochses/ha | 6.0 | 30.0 | 180.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Donkey for carrying dung to the fields | loads | 120.0 | 0.66666 | 80.0 | |
| 设备 | Labour: Going with donkeys | Persons/day | 8.0 | 40.0 | 320.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Wheat seeds | kg | 200.0 | 1.2 | 240.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | tons | 12.0 | 50.0 | 600.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Poatoe seedling | kg | 800.0 | 1.0 | 800.0 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer for wheats | kg | 140.0 | 0.58571 | 82.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3102.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 705.0 | |||||
注释:
Costs were calculated fro an area of 5 ha. The length of the irrigation channel from the creek to the plot is 730 m.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
With regard to the establishment costs, the most determining factors are: the distance to the creek from where water is channeled away and the steepness of the slope and amount of stones when preparing the land for annual cropping. With regard to the maintenance costs it is the exposure of the water channel to rock fall and small land slides.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Most of the precipitation consits of snow, the main rainfall period is March / April
农业气候带
- 干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate. high mountain area
A2240 m asl
gricultural areas need irrigation, which is supplied by snow and glacier melt
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 2240 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
5% of the land users are very rich.
10% of the land users are rich.
70% of the land users are average wealthy.
15% of the land users are poor.
10% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The here described farmers family has very limited off-farm income. The farm provides sufficient fuel, fodder, fruits and potatoes for subsistence farming.
In general, seasonal migration to Russia is widespread in the area, which provides additional income in form of remittances. Only households with only young children, elderly and sick persons have no family member working in Russian.
Level of mechanization: One uses ochses for plowing, motorized is really rare.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
The land use right for the individual farmer is documented with an official land user certificate.
Water use right has been agreed on with the village council.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 Household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块