Sub-surface drainage on irrigated lands [南非]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Hans Edward King
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Ondergrondse dreinering, brakdreinering, natdreinering (Afrikaans)
technologies_1126 - 南非
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Richter Francois
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Wellington
南非
SLM专业人员:
Smit Jan
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Wellington
南非
SLM专业人员:
Steyn Francis
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, George
南非
SLM专业人员:
Oliver Gert
Department of Agriculture, Western Cape, Moorreesburg
南非
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Dept. of Agriculture, Western Cape (Dept. of Agriculture, Western Cape) - 南非1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Drainage of saturated and salinised soils by means of sub-soil drainage pipes
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
There is a lot of soil, wind and water erosion in this area. River erosion, not related to this SWC, is a problem over the whole area (on average 20 t/ha/y). Sheet and gully erosion occurs on commercial land. The whole area along the rivers varies up to 50 km.
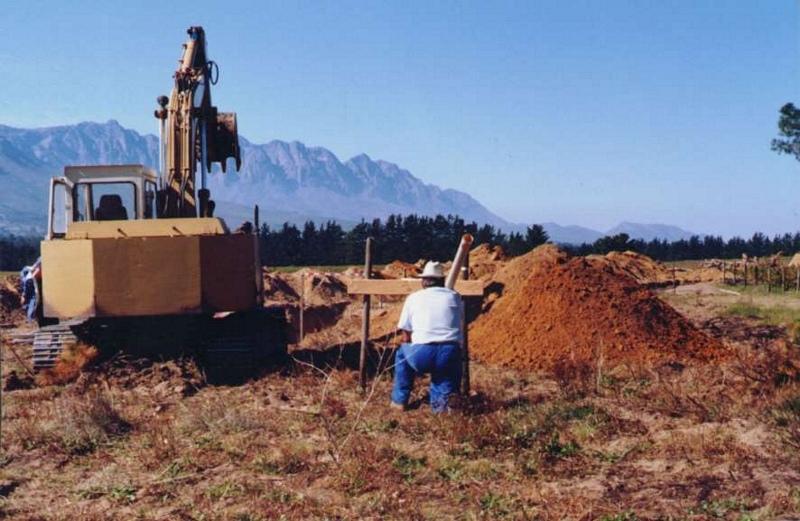
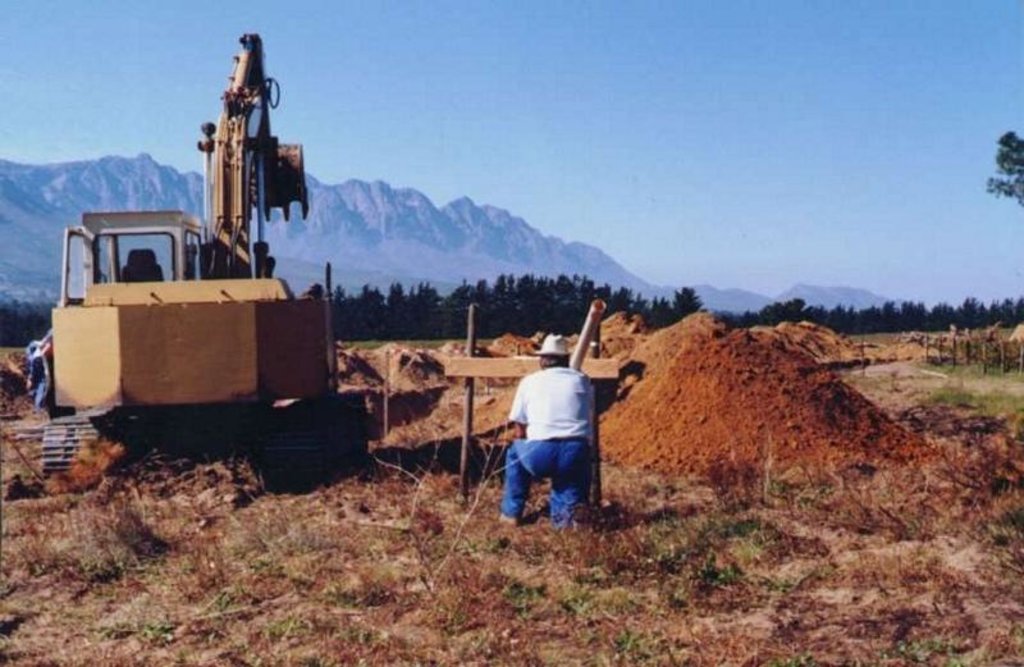
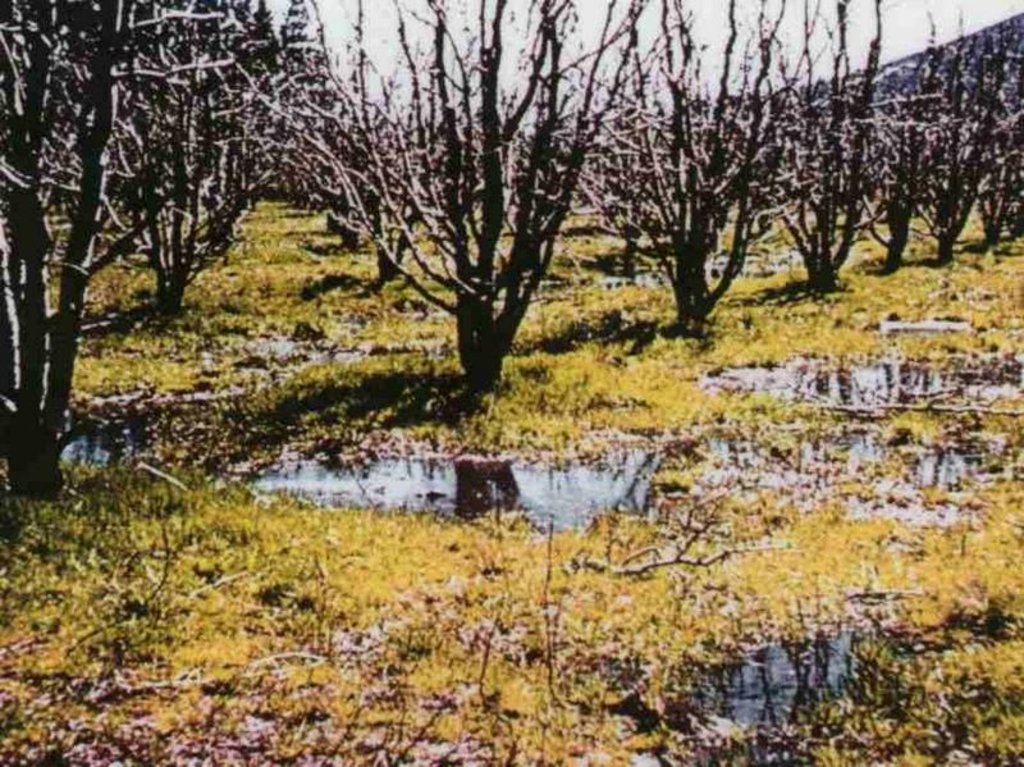
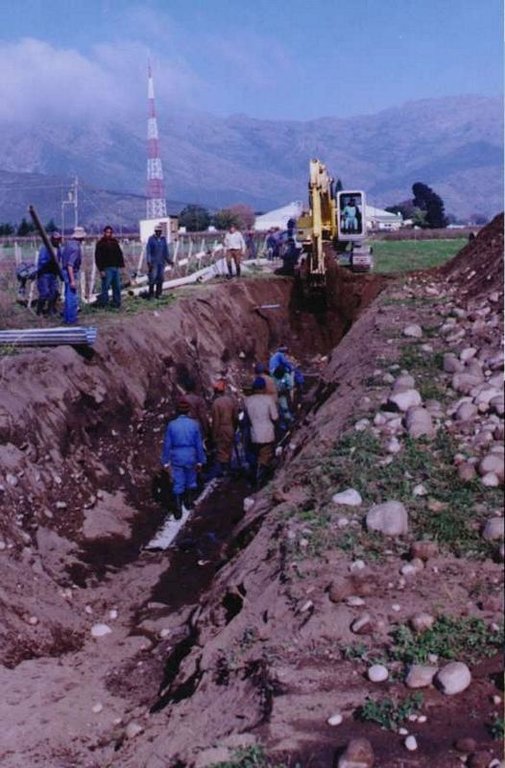
In some places drainage is inadequate and water-logging occurs. A system of sub-soil perforated pipes with surrounding filters was installed. Pipes laid at spacing determined according to the site conditions.
The overall purpose was to limit the level of the water table in the soil profile and remove salts, to provide an adequately aerated zone in the soil for a crops’ root system.
The system must be planned by a suitably trained person and constructed by an expert.
Drainage pipes must be flushed at least annually and roots removed whenever present.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
南非
区域/州/省:
Western Cape Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Southern Cape, Boland, Swartland
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
240.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 240 km2.
Technology also applied in other provinces. Boland 60% under agriculture and from this 20% under this technology. Swartland mainly wheat, 10% under irrigation and from this 20% is already drained. Southern Cape: 20% irrigated of which 20% is drained, 95% commercial farmers. Other parts in SA: KwaZulu/Natal (Pongola), Free state (Rietriver, Orange River), Northern Cape (Vaalharts, Douglas, Upington), Eastern Cape (Fish River, Sundays River, Langkloof)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Holland, USA - literature
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 柑橘属
- 葡萄
- 仁果类(苹果、梨子、柑橘等)
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Sep - Mar
注释:
major food crop: Deciduous fruit/citrus
other: Grapes
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Bad management (over irrigation). The washing of soil from one land to the other. High winter rainfall.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Loss of crop production due to saturation/salinisation of soil. Not putting money back what would be expect, because not enough growth, reduced crop roots deeper in soil and no growth in the area, slanted growth - salinised soils.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S7:集水/供水/灌溉设备
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cs:盐化/碱化

物理性土壤退化
- Pw:水浸
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Cs: salinisation / alkalinisation
Main causes of degradation: other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Rising water tables - As result of over irrigation, leaking dams and canals)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services (Lack of knowledge - Build dams & canals that leak, over irrigation)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: Removal of salts from soils, Decrease water table, Increase of soil aeration
Structural measure: subsurface drains
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 40-80
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.5
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 300
Construction material (other): Plastic perforated pipe with crushed stone filter
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 2%
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
15.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Dig trench | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 2. | Lay pipe | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 3. | Place filter material | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 4. | Build manholes | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
| 5. | Backfill trench | 150m/day, dry season Dec-Apr |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Install drainage system | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 15.0 | 150.0 | 75.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 450.0 | 450.0 | 75.0 |
| 施工材料 | Stone | ha | 1.0 | 100.0 | 100.0 | 75.0 |
| 施工材料 | Pipes | ha | 1.0 | 240.0 | 240.0 | 75.0 |
| 施工材料 | Manholes | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 75.0 |
| 其它 | Contractor overheads | ha | 1.0 | 200.0 | 200.0 | 75.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1390.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1390.0 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 12 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Flush pipes with water | All year/2 times a year |
| 2. | Cut roots in pipes | When required/ |
| 3. | Clean manholes | All year/2 times a year (was reduced) |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Maintenance | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 25.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 25.0 | |||||
注释:
Length of pipe (grid at 60 m spacing - i.e. pipe that average team lays in one day)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Suitability of soil for drainage (greater depth and permeability = lower costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
501-750 mm is closer to the mountain
农业气候带
- 半干旱
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium - low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
20% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of them are only farmers.
Level of mechanization: Tractors, trailer, plough, crop sprayers
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: Also 100-500 ha, but production capacity on all is really the same
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 团体
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
During rainy season (winter) tractor can drive on field without getting stuck in the mud, but construction process and maintenance of intercrops farming activities (negligble)
收入和成本
农业收入
其它社会经济效应
on farm employment
注释/具体说明:
due to higher workload
input constraints
注释/具体说明:
Construction must be financed
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Less bare soil
其它生态影响
soil fertility
restoration of original topsoil aeration
注释/具体说明:
Most of this soils have originally been saturated
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
downslope salinatation
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 11-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
50 percent of all households in this area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: estimates
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: estimates
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: More and more farmers are coming to do ditch drainage because there's more money available, if waiting period is more than 3 months the service from government is free of charge.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Greatly improved crop yield |
| Improved access for mechanisation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Greatly improved crop yield |
| Improved access for mechanisation |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital outlay | |
| Slight decreased in run-off water quality | |
| Insufficient information on soil properties |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Initial capital outlay | |
| Slight decreased in run-off water quality | |
| Insufficient information on soil properties |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Drainage Works for Western Cape (Afrikaans). July 1988.
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
HE King
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
National Drainage Manual (Afrikaans)
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
NDA - photostat costs
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块