Taungya systems for forest management [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Philip Ileta
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kilimo cha miti na mazao ya msimu (Swahili), Intercropping trees with annual crops
technologies_1156 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Mugishagwe Wilson
Ngara District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
SLM专业人员:
Waluce Michael
Ngara District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
SLM专业人员:
Sangatati Joesephat
Ngara District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
SLM专业人员:
Waziri Zawadi
Ngara District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ngara District Council (Ngara District Council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
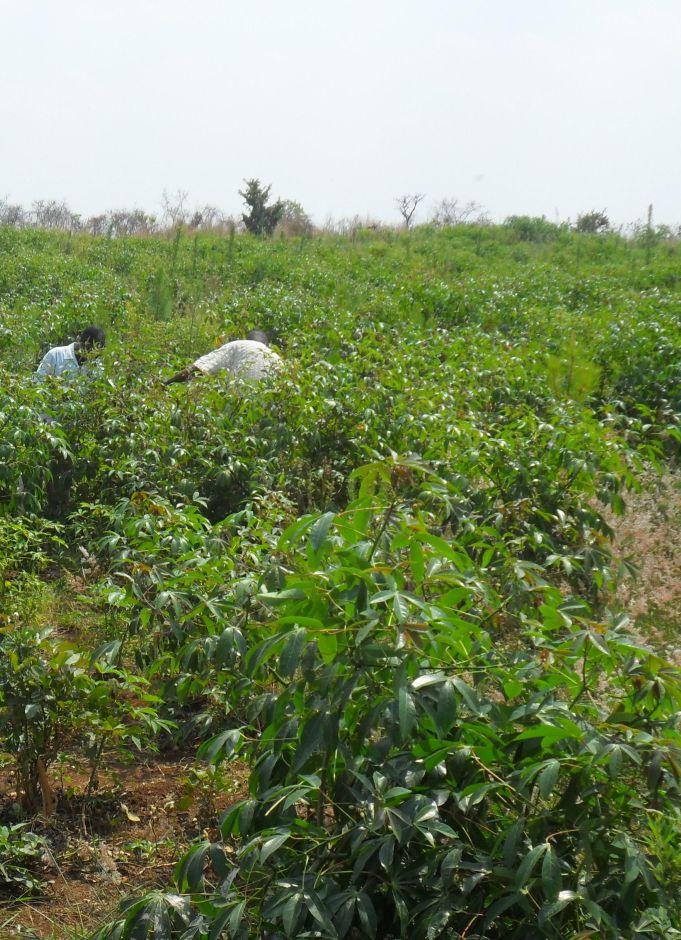
A forest management system whereby trees are inter-cropped with annual crops until when the crops below can no longer flourish due to the dense canopy of trees.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The overall purpose is to establish and manage forest in a sustainable manner. Land preparation is done during the dry season. Prepared seedling is planted at the beginning of the rainy season at recommended spacing. The area between trees is intercropped with selected annual crops. The crops can continue to be grown until the tree canopy covers the ground (3 to 4 years period). At this stage the system does not support intercropping and the trees are left to grow on their own. The Taungya technology is applied on degraded forest or a new established forest. Recomended supportive technologies are contours for erosion control and manure application for soil quality improvement.
Purpose of the Technology: A well established and managed forest/woodlot ensured in the degraded forest by:
-Intercropping with selected annual crops to improve soil cover, water infiltration, soil organic matter, reduce soil erosion and water evaporation.
-To conduct multiple tending operations for the tree plots and crops (weeding,firebreaks,pruning and thinning)thus minimizing the costs and maximizing returns
-Increased productivity and production through diversification strategies.
-Enhance food security and income.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: -Land preparation during dry season (June to Sept).
-(Allignment,marking and pitting for tree seedlings (Oct-Nov)
-Planting of trees(Nov-Dec)
-Planting of crops (Oct-Nov)
-Weeding
-Harvesting crops
Natural / human environment: Fire threats during dry season, Termite attacks to trees, High costs for labour to perform tending activities in large forest plots
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Kagera
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ngara
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 0.1-1 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is <0.1 km2.
The plantation is planted mainly with Pinus caribaea and few compartments Maesopsis eminii of 3 years and intercropped with cassava,gnuts and beans,well weeded and firebreaks established. The plantation covers 32 hectares.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Various projects of afforestation have been active in the area before and during the Refugee influx from Rwanda and Burundi 1994-2007
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 根/块茎作物 - 木薯
- gnuts
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: Oct to Dec; Second longest growing period in days: 90; Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

森林/林地
- 植树造林
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
- timber trees
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 放牧/啃牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): High fire incidences during dry seasons, Red clay loam soils harden and dry easily during dry spells, Forest are usually long term investments,thus high costs of inputs before harvests
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): High fire incidences during dry seasons, High costs for weeding and slashing
Problems / comments regarding forest use: Softwood plantation
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 农业林学
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A3:土壤表面处理

植物措施
- V3:植被的清理

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pk:熟化和结壳
- Pi:覆土
注释:
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), change in temperature (Fires become more aggresive in hot dry season)
Secondary causes of degradation: soil management (To enhance infiltration of water to hard subsoil), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Acute shortage of fuelwood in the area)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
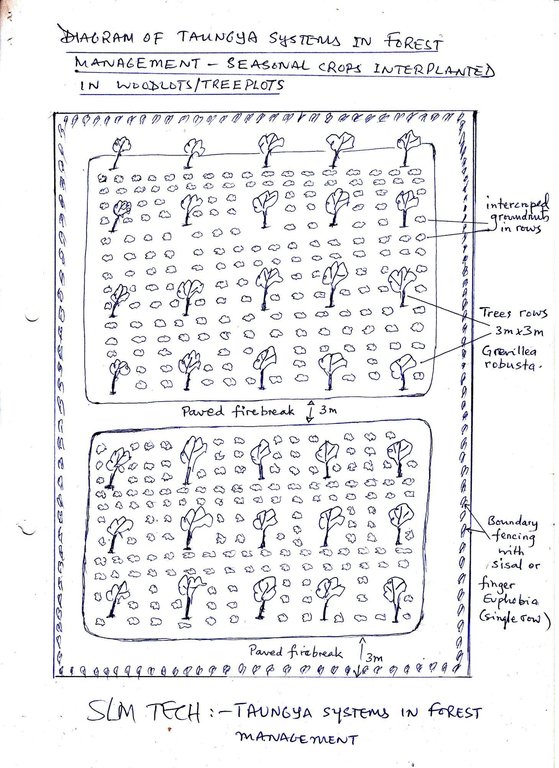
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Diagram of Taungya system in forest management -seasonal crop inter planted in woodlots/tree plots.
Location: Rusumo village. Ngara District Council/Kagera/ Tanzania
Date: 15 May 2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Experience in agroforestry extension is usually enough to assist farmers)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (A number of manuals provide guidance on afforestation projects)
Main technical functions: reduction of dry material (fuel for wildfires)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), control of fires
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: cassava cuttings
Quantity/ density: 500/ha
Remarks: between tree rows
Cover cropping
Material/ species: beans
Remarks: between tree rows
Retaining more vegetation cover
Material/ species: Plant tree seedlings
Quantity/ density: 1700/ha
Remarks: Line planting 2.5mx2.5m
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: crop residues in repeated seasond
Remarks: remain to decay in tree plots
Breaking crust / sealed surface
Material/ species: thorough land cultivation using hand hoes
Remarks: during initial land preparation
Breaking compacted topsoil
Material/ species: continuous cultivation and weeding -hoes
Remarks: enhance water infiltration
Aligned: -linear
Number of plants per (ha): 1700
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2.5
Trees/ shrubs species: Pinus caribaea
Perennial crops species: cassava
Gradient along the rows / strips: 8%
Change of land use type: convertion of rweya(uncultivated grassland) to woodlot/forest plantation
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Perform agronomy practices for crops,sivicultural practices for trees
Layout change according to natural and human environment: increseased soil cover due to many planted trees and agricultural crops
Major change in timing of activities: plant trees at the start of long rains to maximise survival rates
Control / change of species composition: indigineous trees highly deforested, replaced with planted forest of high cormecial value
Other type of management: Establishing firelines/roads each year enables easy prevention/controll of wild fires.
作者:
Ileta Philip, P.O BOX 30 Ngara
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tanzania shilling
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.25
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Allign and screef 3m wide roads around tree plot and between compartments | before dry season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Allign and screef 3m wide roads around tree plot | persons/day/ha | 200.0 | 2000.0 | 400000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes, machetes and axes | pieces | 10.0 | 6000.0 | 60000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Tree seedlings | pieces | 1700.0 | 200.0 | 340000.0 | 50.0 |
| 植物材料 | Cassava cuttings | pieces | 5000.0 | 20.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Beans | kg | 25.0 | 500.0 | 12500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 912500.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 570.31 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | routine twice sesonally |
| 2. | Slashing and screefing firebreaks | once yearly |
| 3. | Prunning excess tree branches | every 3 yrs |
| 4. | Slashing short grass and screef firebreak roads | once yearly |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Weeding | persons/day/ha | 100.0 | 2000.0 | 200000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Slashing and screefing firebreaks | persons/day/ha | 50.0 | 2000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Prunning excess tree branches | persons/day/ha | 5.0 | 4000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Slashing short grass and screef firebreak roads | persons/day/ha | 10.0 | 2000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 340000.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 212.5 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: hoes, matchets, axes, slashers, handsaws, per hectare year (2012)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
high labour especially during establishment and repeated tending of crops and trees
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is medium - high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: The plot is on top of the plateau/ridge
Availability of surface water: Is good when further away, because the permanent rivers Kagera and Ruvuvu are 2km below the plateau.
Water quality (untreated): Good because a gravity scheme supplies water to nearby areas 2kms, but for agriculture only because seasonal agriculture in the dry season in wetlands along the rivers.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: labour works performed well by both men and women
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
10% of the land users are rich and own 30% of the land.
20% of the land users are average wealthy and own 40% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: The land user is a businessman and have good number of cattle,however there are many other tree plots in the village owned by other farmers
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
注释:
0.5-1 ha: Farmers in the village have many eucalyptus tree plots for firewood and poles,but now opening new land for planting pines Agroforestry practices widespread in banana cropping system in the village
15-50 ha for cropland
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
注释:
water free for agricultural use,minimum payments for domestic use
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Harvesting of crops
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
At rotation age 15-20 yrs
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Multiple tending operations (crops and trees)
其它社会经济效应
liv
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Increased income from agriculture crop sales improve food security availability of forest products decreased workload mainly for women-branches of trees and thinnings for firewood
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤结壳/密封
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
As windbreaks
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
注释:
The control of fires can be improved by boundary planting of fire tolerant plant species e.g sisal(Agaves sisalana),euphobia spp etc
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Benefits from timber harvest from18 yrs and above,but can harvest for pulp at 8yrs,short term benefits from trees include thinnings for firewood short term from crop sales, decreased input costs due to multiple tending
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
24 households covering 100 percent of stated area
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 51-90%
注释:
4 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
20 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The planting of pine and intercropping with cassava,gnuts and beans has been adopted by many farmers due to the anticipation of carbon trading in future and expansion of cormecial forestry
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Large ares of land in Rusumo are still uncultivated/no settlements and many farmers have opted to establish woodlots of pines-as highly paying project in future with posibilities for accessing bank loans
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increased incomes |
| Diversified food crops |
| Fire outbreak prevention/control |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Production of timber and firewood |
| Enhanced food security |
| Prevention of fire to damage trees/crops |
| Reduce soil erosion-improved soil cover |
| Improved carbon sequestration |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High labour costs | grow food crops for 3-4 yrs |
| Shading increases and can no longer support crops | seek advise from agriculture/forestry depts prunnings, thinning on time |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High labour costs | in places with shortage of lands renting farm plots |
| Difficult to use machines in tending,weeding etc | Timely prunning and thinning regimes |
| Shading increses and can no longer support crops | Keep dogs and seek support from Game control department |
| Can be hiding place for vermin |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/12/2011
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块