Enhanced mulching in banana and coffee plantation [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Iwona Piechowiak
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Okwalila ebinyasi omukibanja
technologies_1184 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
Government:
Government:
Mashauri Babylus
Bukoba District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
Government:
Rutatinisibwa Dominick
Bukoba District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
Government:
Rwezahura Raphael
Bukoba District Council
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
SLM专业人员:
Kaihura Fidelis
K-TAMP
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Indigenous knowledge transfer [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- 编制者: Godfrey Baraba
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Application of Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass mulch in banana and coffee plantation to reduce soil erosion, improve soil fertility and moisture and ensure high productivity
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
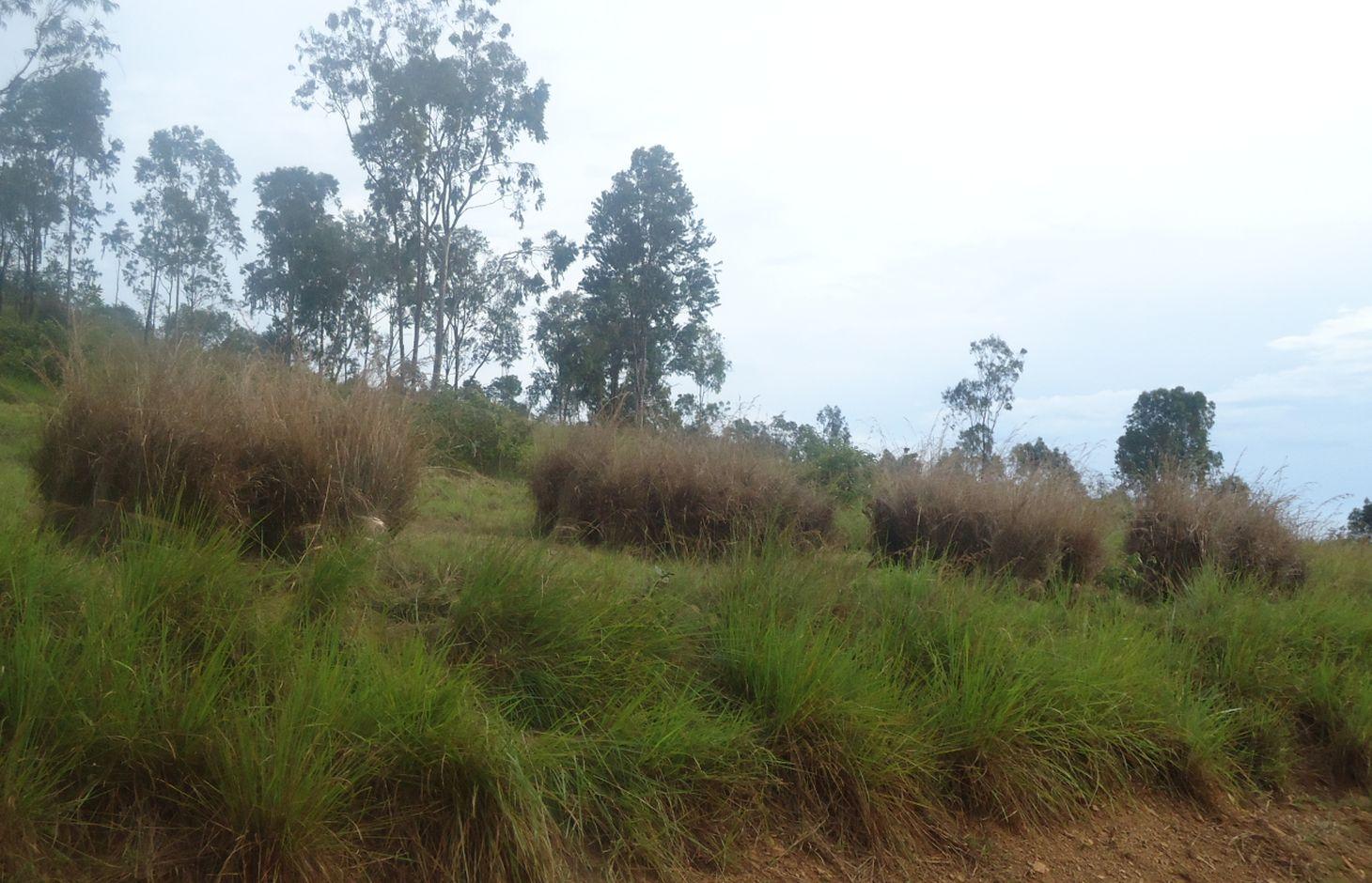
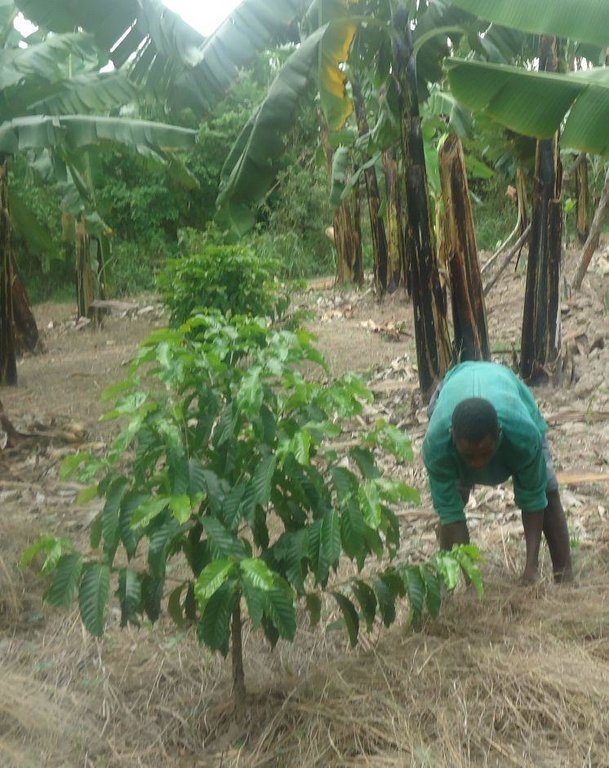
The technology is applied in coffee and banana fields in the sub humid climate. The technology objective is prevention of land degradation specifically nutrient improvement, erosion control, soil moisture and soil health (soil's living organisms) improvement. The materials applied are very variable perennial grass from 60-240 cm high. Panicle loose and narrow up to 50 cm long, with slightly spreading or contiguous racemes with shortly hairy or nearly glabrous spikelets 3.5-5 mm long. The materials are spreaded to 15cm thickness, manually across the slpoe, once per year, at the beginig of short rains.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose of the technology is to retain moisture content in soil by promoting water infiltration during and after the rains, promoting water holding capacity through decay and formation of organic matter. Grass mulch control soil erosion by intercepting raindrops (splash erosion) that detach soil particles. Grass mulch technology improves soil nutrient through grass decomposition.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: There is no establishment activities for the technology only maintenance activities (operational activities) are required once a year.
Maintenance activities include collection of mulching grasses -The grass is cut and collected by household or hired labor. The quantity of grass required per hectar is 1,500 cubic metre equivalent to 375 bundles.
To spread/apply mulching grasses -Grass is spread manually across the slope preferably to 15cm thickness. Dry grasses are spread across the slope with thickness of maximum 15cm. It is recommended to apply mulch grass around 15cm from the banana trunks.This is done once annually before the onset of short rains (during Augost and September)
Natural / human environment: The technology is applied on coffee/banaana fields. The Rainfall is 1000-1500mm, the subhumid climate (temp 26 -30 degree centigrade) and two growing seasons. The technology is meant for soil water evaporation contol and is tolerant in dry spell season while sensitive to excessive rains.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Tanzania
有关地点的进一步说明:
Bukoba District (Karong village)
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
注释:
Only one farmstead considered
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 根/块茎作物 - 红薯、山药、芋头/椰子,其他
- 根/块茎作物 - 木薯
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 咖啡,露天种植
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- Maesopsis
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120; Longest growing period from month to month: September (mid)- January (mid); Second longest growing period in days: 65; Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, excessive soil water evaporation, fertility decline and reduced organic matter content
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Excessive weed invasions and reduced productivity
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A7:其它
注释:
Specification of other agronomic measures: Grass mulching
Type of agronomic measures: mulching
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bl:土壤寿命损失

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Cultivation along the slope), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), land tenure (few farmers own grassland), poverty / wealth (Peasants are not able to purchase grass mulch)
Secondary causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Poor soil cover), droughts (There is soil water evaporation)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
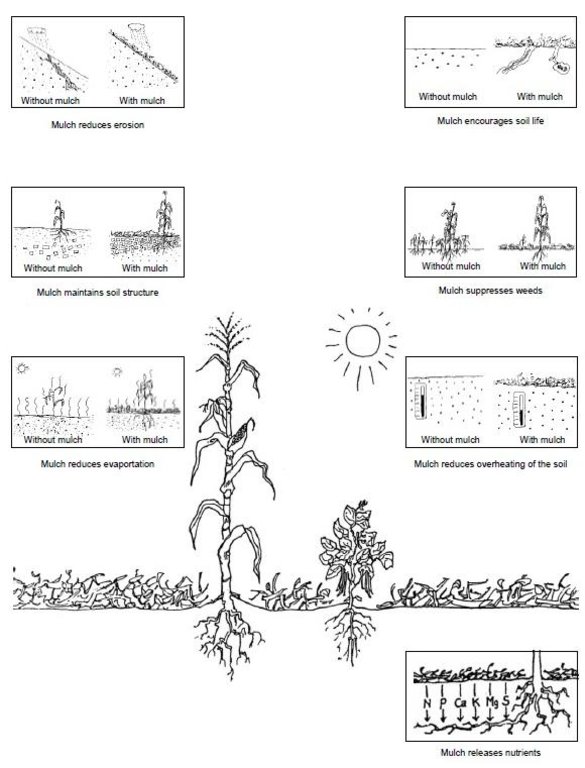
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
What is the use of mulching?; Source: Müller-Sämann and Kotschi (1994)
Location: Karonge Village. Bukoba District Council
Date: 26 Feb 2014
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Mulching
Material/ species: Dried grasses (Thatch and Hyperrhenia Rufa grass )
Quantity/ density: 1500m3/ha
Remarks: Spreading across the slope
作者:
Godfrey Baraba, DED Bukoba District Council, Box 491, Bukoa.
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.25
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Collection of mulching materials | May-June |
| 2. | Application of mulching materials (spreading) | June-August |
| 3. | Weeding | July and January |
| 4. | De trashing | February and September |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Collection and Apllication of mulching materials | persons/day/ha | 16.0 | 1.5625 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Mulch | ha | 1.0 | 117.0 | 117.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 142.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 142.0 | |||||
注释:
per hectar of land protected; cost of purchasing 375 bundles of grass and their spread to be $0.3 per bundle and 20 mandays at $ 1.2
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Cost of purchasing mulch grass is the most determinate factor. Mostly due to long distance to fetch the grass and the scatered nature due to degradation and encroachment by tree planting.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Short rains Sept-November, long rains March-May,length of dry period 180 days
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: 6.25%
Altitudinal zone: 1194 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low - medium
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: De trashing commonly done by men, collection and application of mulch commonly done by women
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
20% of the land users are rich and own 40% of the land.
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 60% of the land.
Market orientation of production system: Coffee is purely for commercial while banana is for both subsistance and commercial
Level of mechanization: Cultivation is done at establishment phase, another farming systems limits mechanization
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
The technology is highly adopted by well to do farmers, either having off farm source of income or old farmer after achieving reasonable savings. This is because the communal range land has encroached by protected forest.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
Church:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Hyperrhamia rufa is un palatable, hence its dominance implies reduced fodder quality.
畜牧生产
注释/具体说明:
Unpalatability of Hyperrhamia rufa implies reduced nutrient intake, hence animal production is reduced.
生产故障风险
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
0
SLM之后的数量:
135
注释/具体说明:
Purchase of mulch grass, without transport and labor for spreading mulch.
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Increased banana productivity, labores earn income for purchasing food
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Practiced farmers respected as inovators as well as progressive farmers
社会经济弱势群体的情况
SLM之前的数量:
0 mandays
SLM之后的数量:
10 mandays
注释/具体说明:
Cutting mulching grasses are income generating activities for young men and women.
livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Improved coffee/banana mulching increases farm income. Additional revenue is spent for child’s education and health services
Working in distant unconducive environment
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤压实
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
注释/具体说明:
Soil's living organisms
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Surface water run-off is combated in the area, hence neighbor's fields face only rain direct rain drops.
Nutrient transfer from grassland to crop land
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
| 未知 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
No establishment costs, recurrent costs for mulching Technology for three years consecutively, can increase productivity in two folds and be maintained for more than ten years.
6.5 技术采用
- > 50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1766 households (68 percent of land users in stated area)
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
1766 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: There are farmers who apply dried banana leaves and pseudo stem as mulch.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: The adoption is moderate simply because of increasing cost of mulching grasses compared to produce farm gate price increase. Furthermore the labour force is dominated by the elderly.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increase in soil moisture especially during the dry season How can they be sustained / enhanced? Perform regularly maintenance activities |
|
Reduced weeds How can they be sustained / enhanced? Apply mulch grasses at the depth of 15 cm twice a year for the first 3 years consecutively |
|
Fertility increase How can they be sustained / enhanced? Soft loan of livestock to be provided to farmers |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Esy to implement and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote extended use of the technology (knowledge sharing) |
|
Multiple ecological benefits: improved soil organic matter, soil moisture and soil biodiversity How can they be sustained / enhanced? Educate farmers on diversified mulching materials and systems e.g. intercropping, cover crops, minimum tillage |
|
Prevent soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Combine other conservation technologies e.g. contour construction with mulching. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Does not stay longer, it can persist for one season, hence requires twice application | Apply the correct quality and quantity material. |
| Not readily available to all farmers simply because range land has been allocated to well to do farmers. |
Land tenure system and land use planning should be revisited |
| Increased manual labour (cutting, transportation spreading) | Plant grasses like vertiva |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Grass mulch available only to farmers with grassland | Other measures should be encouraged (use of chopped banana,pseudo stem, leaves and sheaths) |
| Degradation of grassland | Promotion of SLM Technologies for grassland conservation |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.3 链接到网络上的相关信息
标题/说明:
Kagera TAMP project website
URL:
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Indigenous knowledge transfer [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
Indigenous knowledge transfer, is a common phenomena in farming societies whereby elders taught younger generations the practical aspects in production and emphasizes the norms and proms in folk story tales.
- 编制者: Godfrey Baraba
模块
无模块