Zero grazing [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Wilson Bamwerinde
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Okurisiza hamwe
technologies_1188 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Ministry of Agriculture, Animal Industry, and Fisheries of Uganda (MAAIF) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Stall-fed livestock production is an efficient method to produce organic fertilizers (manure) for the conservation and improvement of soil fertility.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
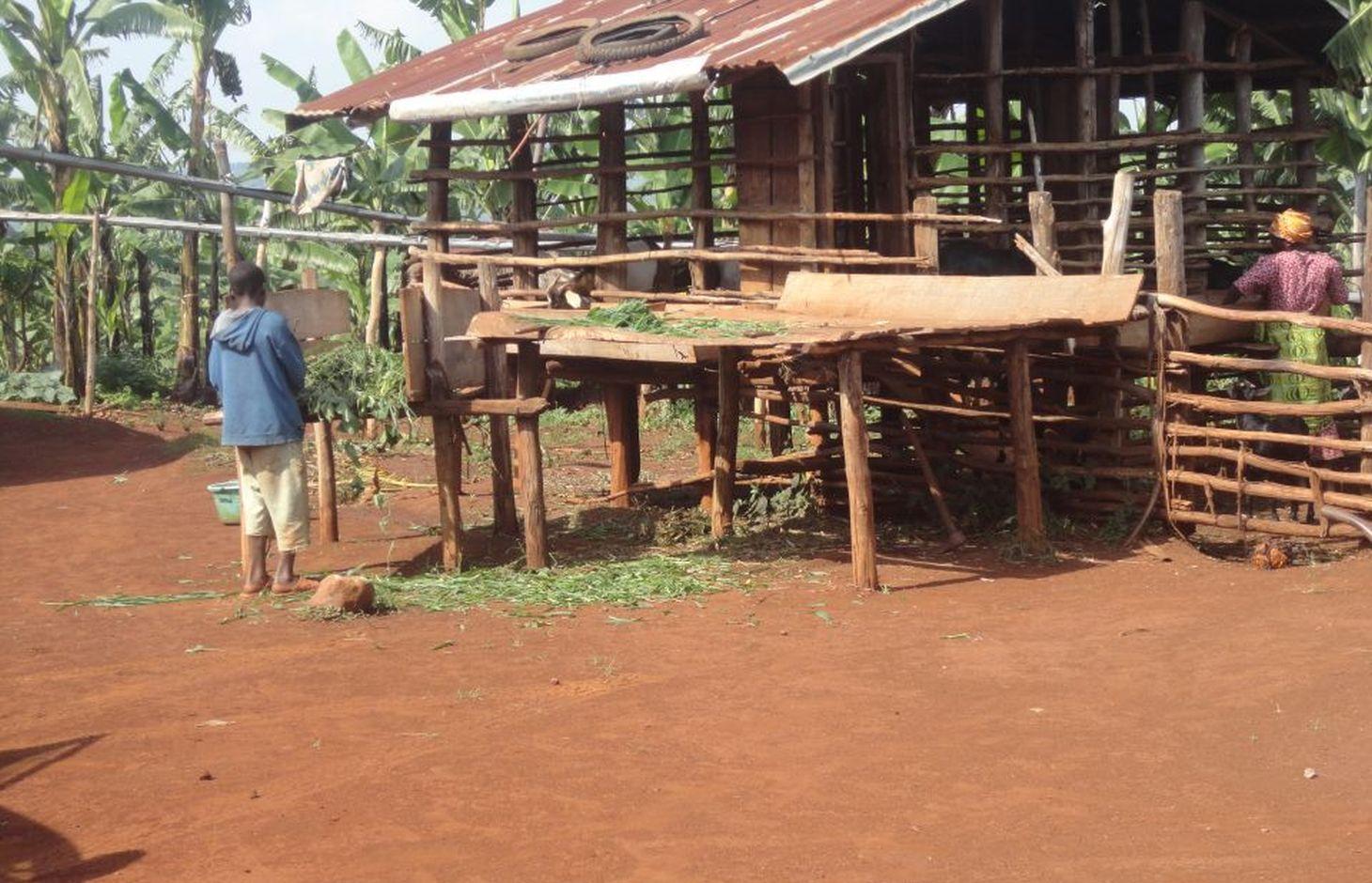
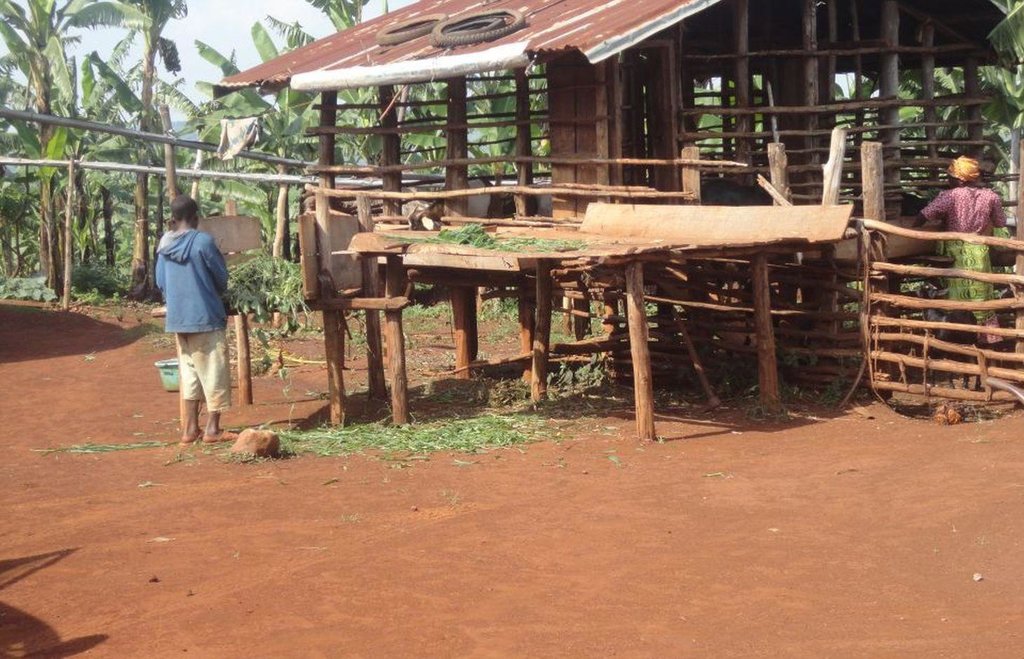
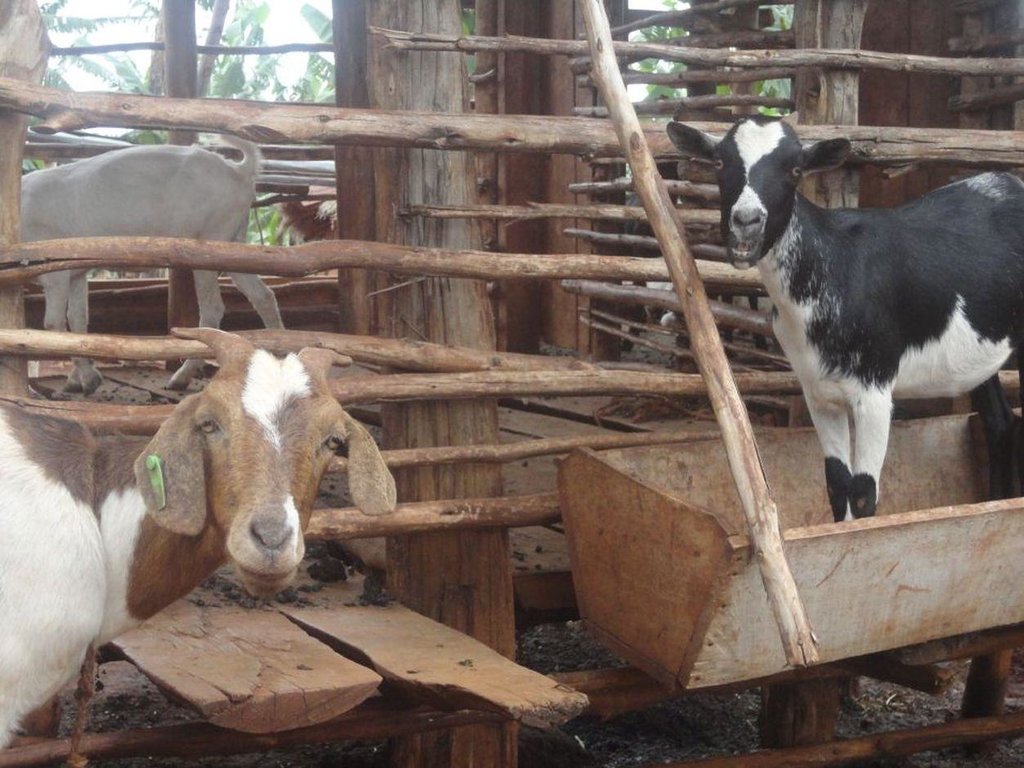
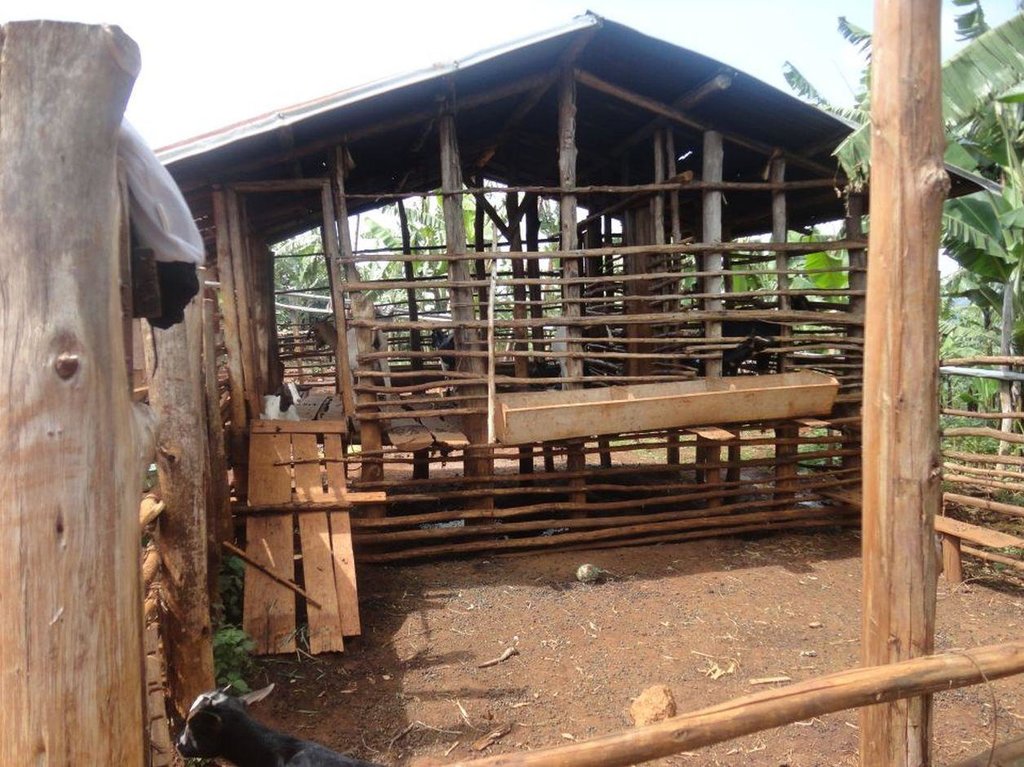
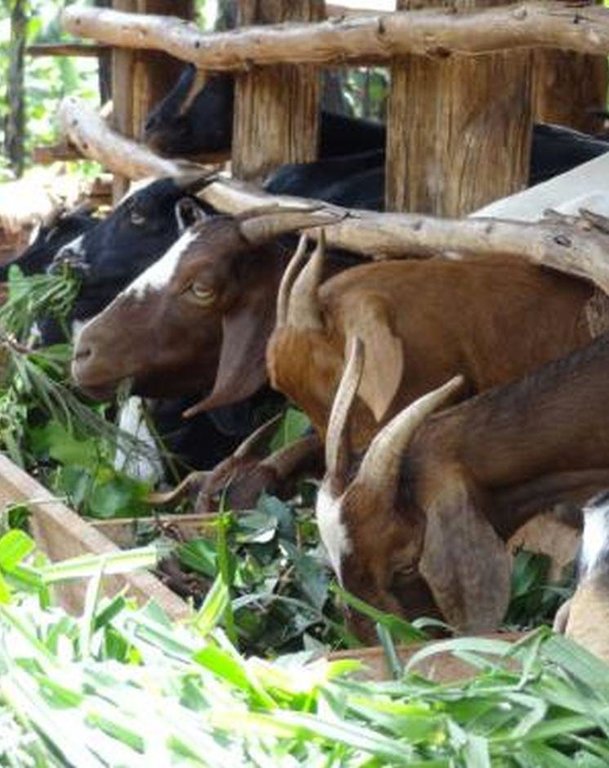
Zero-grazing has been a common livestock (cattle and pigs) management practice in most areas of south-western Uganda due to reduced communal grazing land. In the predominantly annual cropping system communities, free grazing livestock often damage crops and are a major cause of conflict. On the other hand, farmers observe that crop yields have declined season after season. For example, the bunch of bananas has grown smaller, it has smaller fingers, and many banana stands have no fruit during much of the year. The most important ways through which croplands in Rubagano are degraded include nutrient transfer through harvest and crop residue movement and use; nutrient mining whereby continuous cultivation is done with little or no replenishment; and soil and water runoff on steep slopes. Farmers know that one of the most important ways to reverse declining soil fertility is to apply manure, but it is expensive. Therefore farmers acquired goats or pigs primarily for the provision of manure for their cropland, but also as a household income generating enterprise. In stall-fed goat or pig production, The zero-grazing unit is designed in such a way that it is well ventilated and protected from wind, rain and constant direct sunshine to avoid livestock developing coughs, colds and stress. The unit has 3 major parts: the feeding and rest area, the exercise area and the manure collection area. The feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground. Below it is the manure collection area and above it, a corrugated iron roof. There is a feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area in which mixed fodder is fed to the livestock. A wooden food preparation slab for cutting and mixing fodder is in front of the feeding/rest area. The unit for housing 12 goats is 4 m by 8 m on the ground and 3 m high at the feeding area.
Purpose of the Technology: The major objective of stall-feeding is to maximize manure collection for sustaining soil fertility in cropland. Other goals are to improve household income, reduce expenditure on pests and disease management through livestock isolation from other animals and to reduce labor by cutting and storing fodder for use over a period instead of grazing in distant pastures daily.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The materials required for establishment of the zero-grazing unit for goats are wooden posts or poles, cut-off planks, wooden slats/timber, iron sheets and nails. The 4 m by 4 m feeding/rest area is raised 1 m above the ground on strong Eucalyptus or pine posts of diameter 5-10 cm. Its wall is 2 m high and is made of widely spaced cut-off planks or light wooden poles not more than 3 cm diameter nailed to strong upright posts. The floor is made of wooden slats placed 2 cm apart, big enough to allow livestock droppings to fall through but too small for adult goats’ or kids’ hooves pass, in order to avoid injury to livestock. There is a 1.5 m by 0.5 m feeding vat on each side of the feeding/rest area and a 1 m by 1 m fodder mixing wooden slab at the front. On the ground to one side of the feeding/rest area is the 4m by 4m exercise area. The unit can be constructed at any time of the year.
Natural / human environment: Regular maintenance of the unit is done to ensure the floor does not develop holes that can lead to injury of the livestock, and the roof does not leak when it rains. Increased manure collection and application increases crop yields and supports crop diversification.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Uganda
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mbarara District
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: -0.86313 30.62564; -0.86314 30.62561; -0.86316 30.62569; -0.86319 30.62567
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 0.002 km2.
There are 20 zero grazing units (goats and pigs) in the area and with a total area of about 2 hectares. The technology is being adopted slowly throughout the community.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
This technology was introduced in 2008 by NAADS and later by Africa2000 with aim to improve manure and compost production in Kagera region. Recently, Kagera TAMP project provided additional support to introduce exotic breeds of the goats and increase livestock productivity.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 豆科牧草和豆类 - 豆子
- 根/块茎作物 - 土豆
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120 Longest growing period from month to month: February to May Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: September to November

牧场
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
动物类型:
- 牛 - 奶制品
- 山羊
- pigs
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Reduction of soil organic matter content
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Decline of soil fertility and decreased crop yields
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Grazing land: Gi: Intensive grazing/ fodder production
Type of cropping system and major crops comments: other crops like peas, millet, maize and sorghum are also grown.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

牧场
注释:
Extensive grazing land
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 农畜综合管理
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
注释:
Main measures: agronomic measures, vegetative measures, management measures
Type of agronomic measures: manure / compost / residues
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Cn: fertility decline and reduced organic matter content, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Poor methods of cultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Poor agronomic practices), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Vegetation destroyed for domestic use (firewood and thatch).)
Secondary causes of degradation: education, access to knowledge and support services
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Main goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Details of zero grazing shed structure : A. Overview of the livestock shed with manure colelction area (below) B. View on the feeding arrangement with the fodder vats abouve ground level C. Deatils of the fodder vat D. Overview of the fodder preparation structures
Location: Rubagano, Mwizi, Mbarara District. Uganda
Date: 29-DEC-2013
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Comprehensive knowledge on shed construction (e.g. planning, design of shed levels) and livestock management (fodder quality, feeding, diseases))
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…)
Secondary technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: Manure (Pigs or goats)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 900
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Grass species: Pennisetum purpereum (napier grass), Calliandra Spp.)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25-30%
Change of land use type: Mixed crop and livestock husbandry
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Planting fodder in addition to traditional annual and perennial crops
作者:
Byonabye Proscovia, Kagera TAMP, Kabala
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
2600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3.85
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of tools | Wet season |
| 2. | Purchase of construction materials | |
| 3. | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | |
| 4. | Purchase of livestock | |
| 5. | Grass seed procurement and sowing | Wet season |
| 6. | Converting part of the cropland (annual and perrenial crops) into fodder production |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Construction of zero grazing shed ( including vats and manura collecion area) | ha | 1.0 | 115.4 | 115.4 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | Set | 1.0 | 115.4 | 115.4 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1.0 | 38.46 | 38.46 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1.0 | 250.0 | 250.0 | 100.0 |
| 其它 | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1.0 | 173.1 | 173.1 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 692.36 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.27 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
Lifespan of:
Tools - 1 year
Construction material - 10 years
Zero grazing shed - 1 year
Livestock - 20 years
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Cutting and carrying and application of fodder | Daily |
| 2. | Collection, composting and application of manure | Daily |
| 3. | Purchase of tools and materials for reconstruction/repairs of the shed structure | annual |
| 4. | Weeding and gapping | Seasonal |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 38.46 | 38.46 | |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 11.54 | 11.54 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Tree poles,nails,sorghum stalk | ha | 1.0 | 3.85 | 3.85 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Corrugated iron sheets | ha | 1.0 | |||
| 其它 | Livestock (3 Does) | ha | 1.0 | 18.0 | 18.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 71.85 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.03 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Panga, hoe, tree poles nails, soka jembe, spade, and wheel barrow., Hand hoe, panga.
The costs were calculated for the construction of the shed, acquisition of 3 does and establishment of fodder crops on part of cropland formerly used for annual and perrenial crops. The calculations were done for the technology in August 2011.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factors in the establishment of the technology are: labour for planting, maintaining and cutting grass and other pastures and carrying the fodder to the zero-grazing unit; labour for fetching water for the animals; and labour for removing and composting manure and spreading into the garden.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1041.00
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C.
Rubagano receives at least 6 months of rain in 2 seasons, February to May and September to November
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 1501-2000 m a.s.l. (1740 m.a.s.l)
Slopes on average: Hilly (Fairly steep slopes in places)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Shallow (Mother rock easily reached on pitting)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (Sand and stones)
Soil fertility: Low (Fertility depleted; being slowly replenished by application of technology)
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good (Water easily penetrates into the soil)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (Crops easily dry during the dry spell)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: >50m (Not possible to reach water table)
Availability of surface water: Poor/none (No surface water except when it rains)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatement required, muddy water collected by damming runoff in natural rock depressions)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Low, noticed improvements after application of the technology
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No difference in involvement of men and women.
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
14% of the land users are rich and own 37% of the land.
48% of the land users are average wealthy and own 42% of the land.
21% of the land users are poor and own 14% of the land.
17% of the land users are poor and own 7% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: There is increased yield where the technology has been applied, increasing the income generated on-site thereby reducing off-farm percentage.
Level of mechanization: Manual work (use hand hoes)
Market orientation: Mixed (Some crops are sold to generate household income. Goats will be mainly for sale)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Some households have more while others have less land.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 个人
注释:
Individual land ownership. Recent introduction of the water harvesting measures provided land owners with access to own water sources
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
10kg
SLM之后的数量:
60kg
注释/具体说明:
increased yields for beans realised.
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
生产故障风险
产品多样性
生产区域
收入和成本
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
23dollars per yr
SLM之后的数量:
92 dollars per yr.
注释/具体说明:
yields increased from sell of goats
收入来源的多样性
工作量
注释/具体说明:
As there is now a lot more activity on-farm
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation cover has been improved.
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Food security and household income have improved. This has resulted in children in these households having more time for school and in case of illness, there in some money for accessing treatment.
生态影响
土壤
土壤覆盖层
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
livestock is confined
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
注释:
Forage and fodder usually become scorched during seasons of long drought and livestock may die from lack of food. Grass is cut in the wet season while it is plentiful and turned into hay for the time of scarcity. For this, a barn unit needs to be constructed.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The benefits far outweigh the establishment and maintenance costs. The negative on short-term returns is due to the cost of the technology (construction and procuring livestock) which is a little high for the farmers in this area.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
20 on 2 hectares
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 11-50%
注释:
90% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
18 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The does were supplied to farmers using project funds.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
2 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: these farmers are rich and procured the technology without support from the project
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: 20 households in one village have adopted the technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Technology easy to establish and maintain How can they be sustained / enhanced? Proper management of the livestock |
|
Helps in soil fertility management How can they be sustained / enhanced? Good manure management |
|
Imporove soil cover and reduce soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? using the manure in a proper /recommended way i.e. using it when planting or putting it in the plot before primary cultivation |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Animals are fed on selected pasture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote the growing of that pasture |
|
The technology promotes us of organic manure How can they be sustained / enhanced? Use of compost pits to recycle the wastes into manure |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The technology may contribute to loss of vegetation | Planting pasture & other grass for feeding the animals |
7. 参考和链接
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块