In situ mulching of coffee using Cordia Abbysinica [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Bertha Munyaga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Kgutela igitutu ckimwani
technologies_1191 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - 意大利有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - 意大利1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
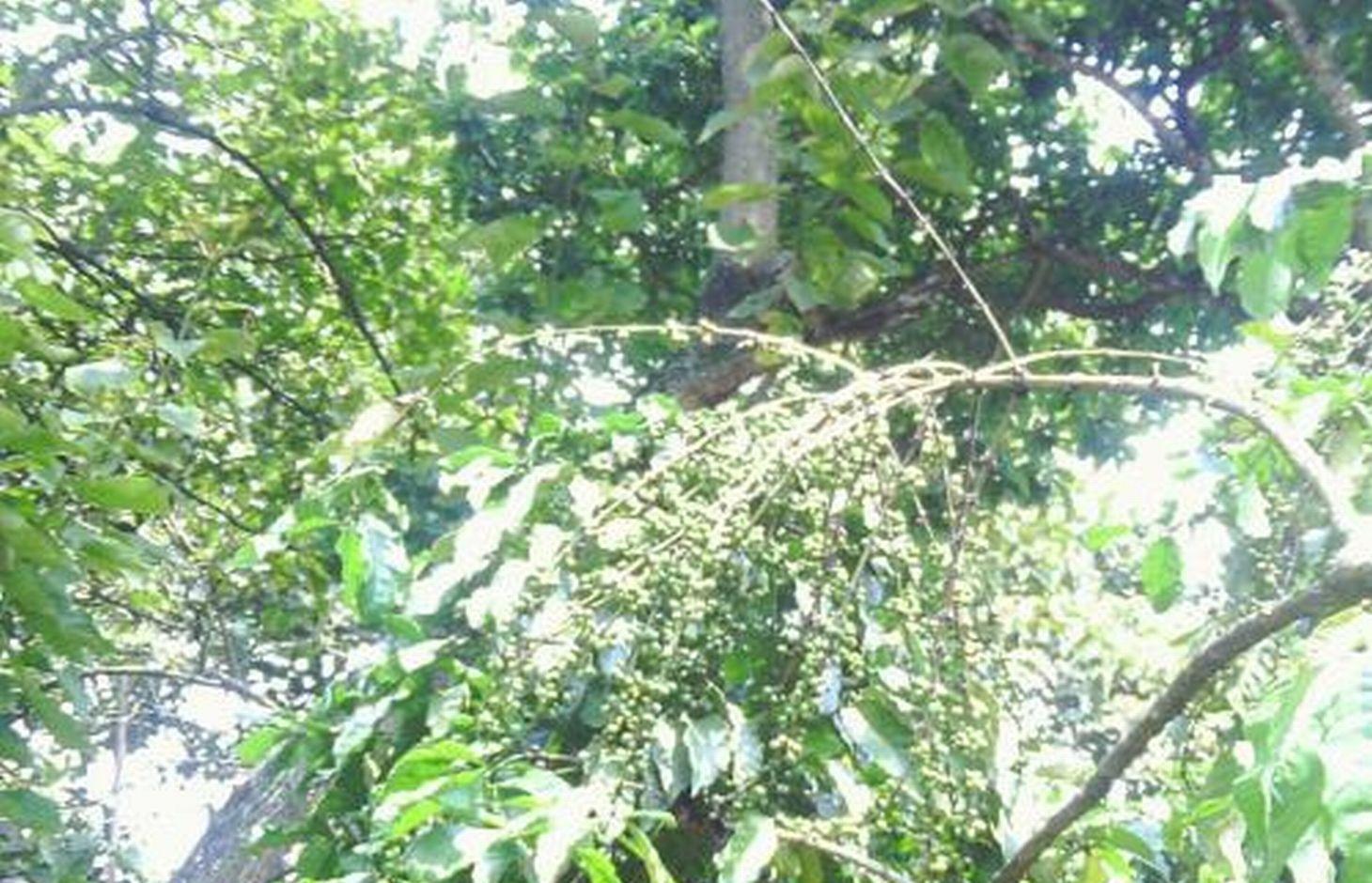
Use of indigenous trees to provide shade and leaves droppings as mulch for coffee production
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
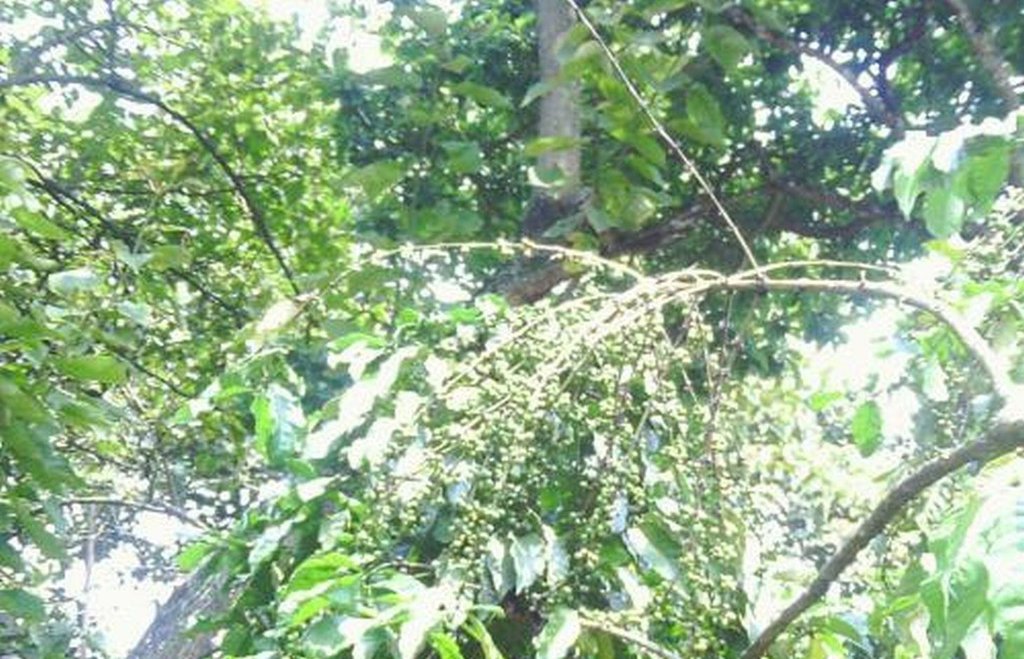
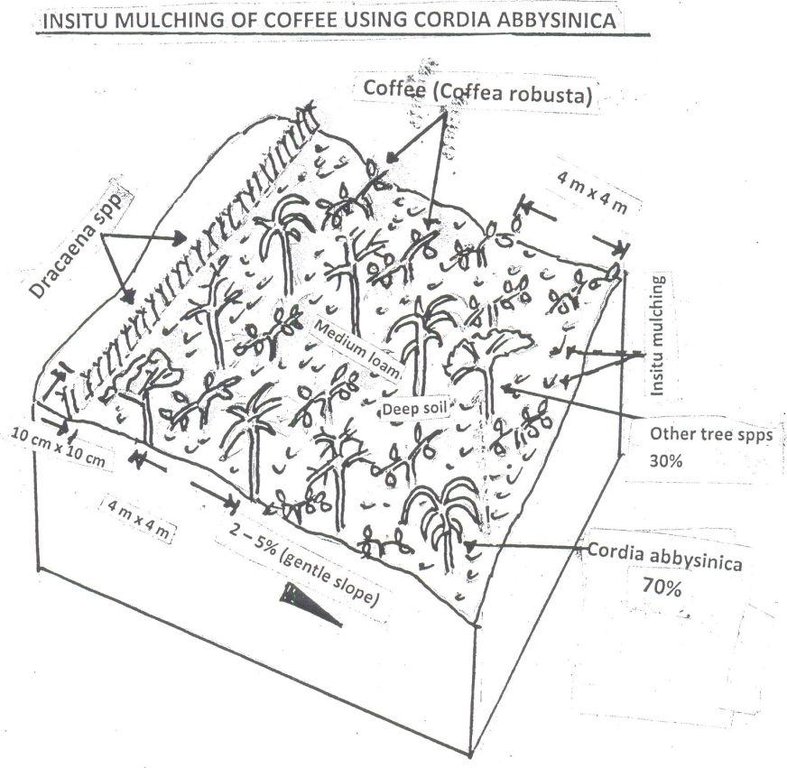
Establishment of Robusta coffee farms by an individual,on a cropland by mixing indigenous tree spp which provide a shade and dropping leaves save as natural mulch.The technology has been developed through land user initiatives over 40 years ago. Establishment activities include land clearing and preparation,preparation of holes,seed collection and planting which involve family labor Seeds are collected from neighboring village from mature trees. Holes are prepared randomly about 4 meters apart. No inputs are applied at the establishment stage only hand tools are used (hand hoe, matchet)
Shade trees are planted after establishment of coffee which are randomly planted, tree spp dominating is Cordia abbysinica which has broader leaves and easy to decompose.Other tree spp included are Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii.
Maintenance include weeding which is done by pulling weeds by hand or using hand hoe at early stage after establishment because few leaves have dropped. The farm is mainly meant for coffee production however,few crops which are cassava bananas, fruit trees Jack fruit, Mangoes, Citrus spp which are planted in the peripherals,and Dracaena sppplanted to demarcate the farm along road side.
Pruning of tree branches is done before the shade is heavy as to allow ventilation.Coffee pruning is done to an individual tree depending on number of branches it has at time of harvesting, normally 4 branches are left. Bending of coffee branches is practiced to avoid branch breaking during harvesting.
Settlement is within the farm with few livestock which are sheep, cattle and chicken.
Purpose of the Technology: To increase coffee production by mixing coffee with indigenous tree spp which drop / shed its leaves.Selected trees are those broad leaved which its leaves decompose easily hence improve soil fertility and due to high accumulation of dropped leaves there is an increase in soil moisture content.
Trees act as wind break hence no flower drop.Dracaena spp are planted very close along the road side to demarcate his plot from neighbors and public infrastructure and this helps to reduce land conflicts among neighbors and community as well.
Hand weeding is done as the technology suppress weeds to the big shade.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A farmer bought a piece of land from the village government.Establishment activities include land clearance by removal of shrubs using a matchet.This is followed by land preparations and planting holes which are 30cm depth and 30cm width. These activities are done from May to July by family labor.Planting is normally done between September and October by collecting seedlings from mature trees in neighbors fields.Planting of indigenous tree spp is done randomly after coffee planting to allow ventilation 80 different spps are planted in 1.5 acres. Seeds and seedlings are obtained from neighbors farms.Maintenance includes weeding which is done using family labor who use hand hoe. This is done twice a year in May and December to January. Pruning and bending of coffee tree branches is done once per year after harvesting of coffee as well as trees in June and July using a matchet. Each coffee tree is treated individually only 4 branches are allowed per tree. Bending is done to avoid breaking of branches during coffee harvesting.
Gap filling is done few months after transplanting between February and March at the beginning of long rains. and this was followed pruning and bending of coffee branches.
Demarcation of coffee farm using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of his farm along the road.
Natural / human environment: Land use type: Establishment of coffee has been done on crop land.
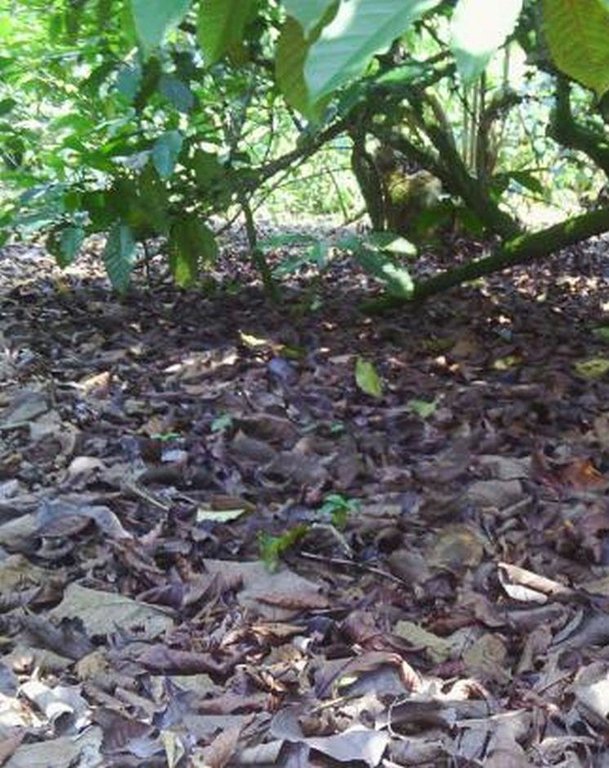
Agronomic: Natural mulch from leaves falling on ground.
Vegetative: Demarcation of boundary using Dracaena spp.
Climatic zone: Sub humid more than 269 growing days.
slope: 2-5% gentle slope
Soil type: Clay loam
Soil depth: Deep
Tools and inputs: Hand hoes,bush knife,axe, seeds and cuttings.
Land ownership: Individually owned.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Tanzania
有关地点的进一步说明:
Ngara District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Boundary points of the Technology area: 236229742E 236229740E 236229639E 236229639E
9726279N 9726387N 9726293N 9726392N
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was adopted from Muleba district and adapted in Kirusya village
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 香蕉/芭蕉/蕉麻
乔木和灌木种植 - 指定作物:
- 鳄梨
- 柑橘属
- 咖啡,露天种植
- 芒果、山竹果、番石榴
- Cordia abbysinica, Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii, Jack fruit, Mandarines
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September-DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May

牧场
- Tethering: rapid decline of land due to expansion of settlements and crop production
动物类型:
- 绵羊
- cattle, chicken
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, water loss/moisture stress, loss of nutrients through leaching and flower drop which lead to reduced yield.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor soil fertility and water stress
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
- A3:土壤表面处理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M3:根据自然和人文环境进行布局
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (indigenous tree,fruits and coffee. (shrubs)), change in temperature (Loss of water due to evapo transpiration), labour availability (Vegetation degradation)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Change of seasonal rainfall), wind storms / dust storms (De flowering leading to production loss)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Indigenous tree are randomly planted and Cordia Abbysinica accounts for 70% of the indegenous tree spps. Demarcation of a coffee farm is done using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of the farm along the road. Natural mulching is done by tree leaves/debris falling on ground. Slope category range from 2-5% gentle slope. Average spacing of Robusta coffee is 4m x 4m.
Location: Karushya Nyamigango. Ngara/Kagera/Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: leavesof indigenous trees drop
Quantity/ density: 6 cm depth
Remarks: natural falling and irregular aligment
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: indigenous trees
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand pulling sometimes use simple tools.
Aligned: -along boundary
Number of plants per (ha): 1,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 375
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia abbysinica, Ficus spp,Erythrina spp,Makhamia spp,Tephrosia spp Maesopsis spp (planted)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: avocado, mandarine,
Perennial crops species: Coffee
Other type of management: (Land protection and demarcation)
Planting Dracaena along the road side
作者:
Allan Bubelwa, P.O.Box 38 Kyaka Missenyi Kagera Tanzania
日期:
10/04/2014
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tanzanian shillings
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1600.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3000.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hole preparation | Nov. |
| 2. | Seed collection and preparation | Nov to Dec |
| 3. | Seedling planting | Dec |
| 4. | Demarcation and excavation of small trench | September-before long rains |
| 5. | Preparation of cuttings | September-December |
| 6. | Actual planting | September-December |
| 7. | labour | |
| 8. | pangas (matchet) | |
| 9. | handhole | |
| 10. | tree & coffee seedlings |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | 1.0 | 2510.4 | 2510.4 | 100.0 | |
| 设备 | tools | 1.0 | 21.88 | 21.88 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seeds | 1.0 | 31.25 | 31.25 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | 1.0 | 61.73 | 61.73 | 100.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2625.26 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1.64 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning-Trees-Coffee | After harvesting, June-July |
| 2. | Weeding | after long rain season |
| 3. | Gap filling | March,during short rains |
| 4. | Bending and layering | Once after harvesting |
| 5. | Gap filling | before short rains |
| 6. | Prunning | Dry season |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | 1.0 | 63.63 | 63.63 | 100.0 | |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | 1.0 | 33.05 | 33.05 | 100.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 96.68 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.06 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, panga (matchet) and axe, Panga (Matchet), hand hoe and axe
The cost assesment was completed on 18 February 2014. The cost of labour can be reduced during the onset of rain when the soil is a bit workable.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Labour
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Tree and coffee pruning is done by men because it needs climbing
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (He is getting income from coffee).
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the residents are permanent farmers
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Water is accessed friendly, land is inherited.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
16bags/ha
SLM之后的数量:
58 bags/ha
饲料生产
木材生产
SLM之前的数量:
3cub.m/ha
SLM之后的数量:
12cub.m/ha
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
62 kg/ha
SLM之后的数量:
0 kgs/ha
工作量
SLM之前的数量:
15 md/ha
SLM之后的数量:
2 md/ha
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
improved
健康状况
SLM之前的数量:
little
SLM之后的数量:
inreased
文化机会
娱乐机会
SLM之前的数量:
none
SLM之后的数量:
available
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
SLM之前的数量:
none
SLM之后的数量:
available
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
土壤结壳/密封
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
medium
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
减少气候和灾害风险
火灾风险
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
下游淤积
对邻近农田的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
medium
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
Introduction of contour ridge
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
In 10 years he has obtained more money from sales of coffee and tree products
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Easy maintenance acctivities e.g. easy to keep weeds under control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Fuel wood availability How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Availability of fruits How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improved kowlledge regarding SLM and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
This is cheap and affordable technology which can be used by smallholder farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Large potential for increased income (higher coffee yields) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote crop and livestock intergration (manure production) |
|
Increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate maintenance acttivities |
|
Erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain sufficient soil cover |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Land competition with food crops | Promote technology among other farmers |
| High cost of tools, especially pruning scissors | Provide required tools |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Risk to fire during dry season | Introduce fire breaks |
| In areas where frost persist can lead to fungal diseases if not well pruned | Improve pruning |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块