In situ mulching of coffee using Cordia Abbysinica [Tanzanie]
- Création :
- Mise à jour :
- Compilateur : Bertha Munyaga
- Rédacteur : –
- Examinateur : Alexandra Gavilano
Kgutela igitutu ckimwani
technologies_1191 - Tanzanie
Voir les sections
Développer tout Réduire tout1. Informations générales
1.2 Coordonnées des personnes-ressources et des institutions impliquées dans l'évaluation et la documentation de la Technologie
Spécialiste GDT:
Spécialiste GDT:
Nom du projet qui a facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
The Transboundary Agro-ecosystem Management Project for the Kagera River Basin (GEF-FAO / Kagera TAMP )Nom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - ItalieNom du ou des institutions qui ont facilité la documentation/ l'évaluation de la Technologie (si pertinent)
FAO Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO Food and Agriculture Organization) - Italie1.3 Conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées
Le compilateur et la(les) personne(s) ressource(s) acceptent les conditions relatives à l'utilisation par WOCAT des données documentées:
Oui
2. Description de la Technologie de GDT
2.1 Courte description de la Technologie
Définition de la Technologie:
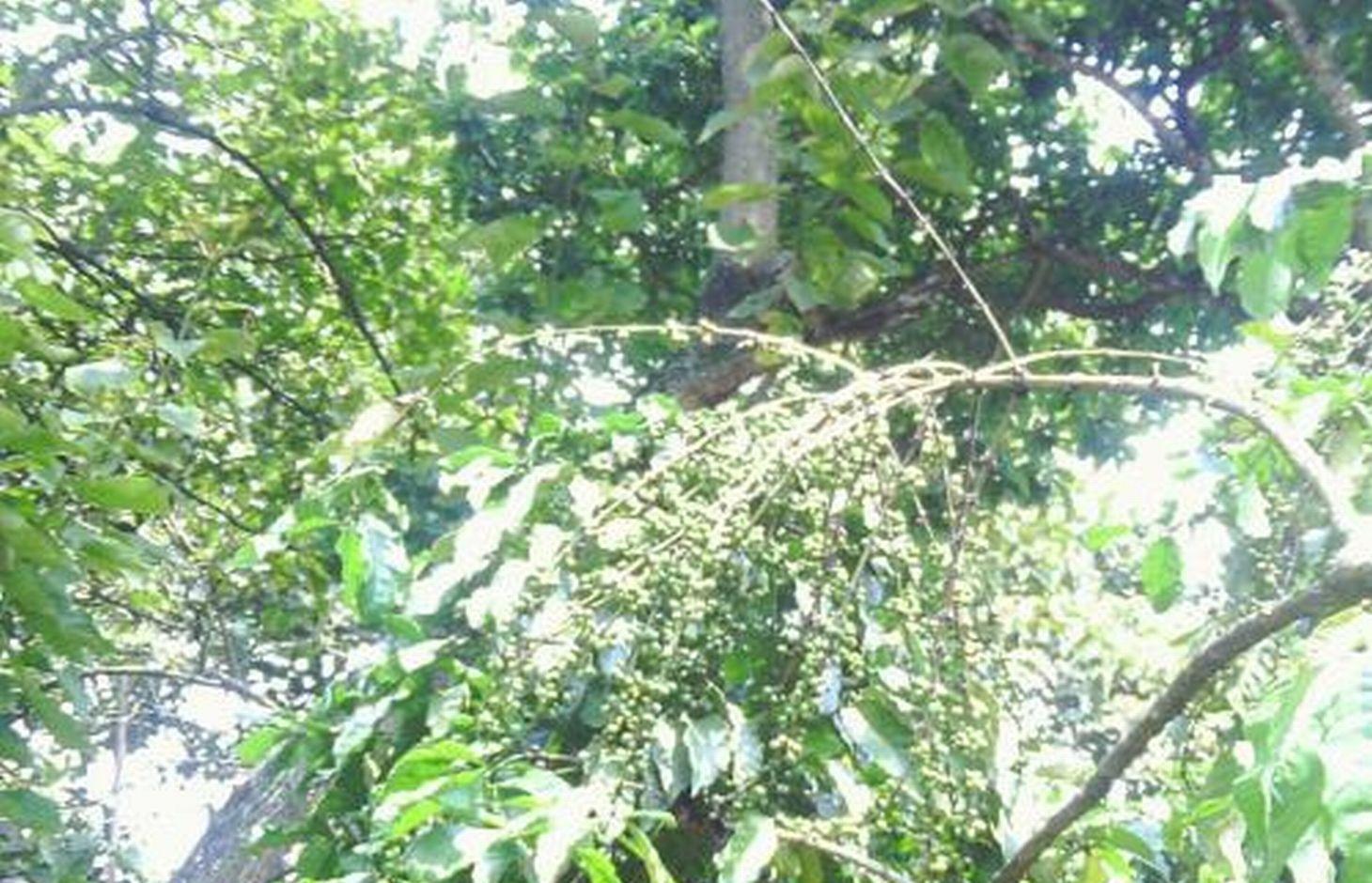
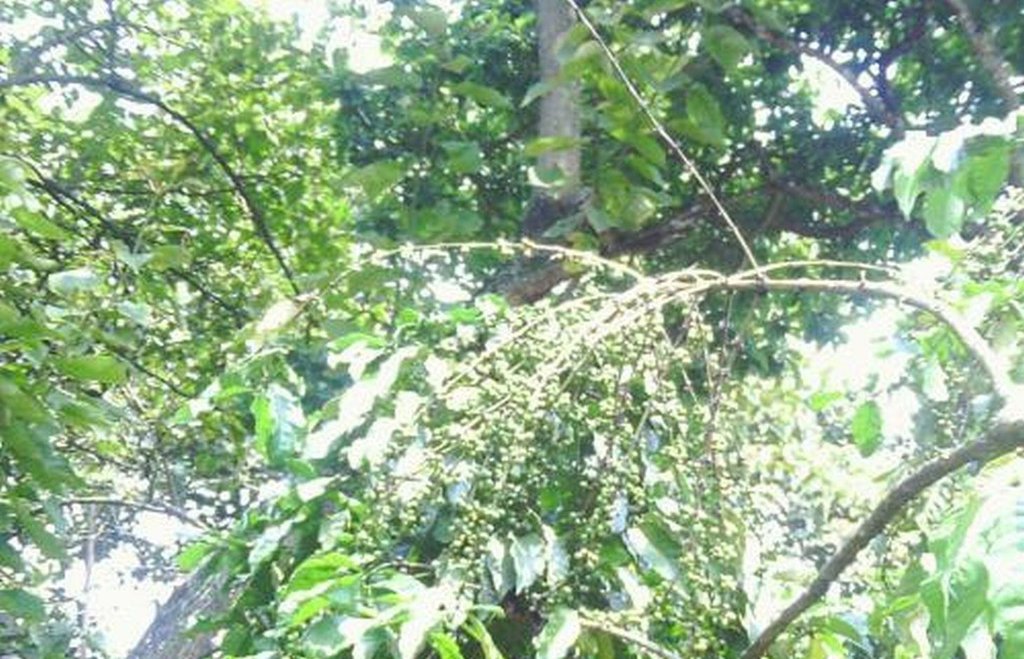
Use of indigenous trees to provide shade and leaves droppings as mulch for coffee production
2.2 Description détaillée de la Technologie
Description:
Establishment of Robusta coffee farms by an individual,on a cropland by mixing indigenous tree spp which provide a shade and dropping leaves save as natural mulch.The technology has been developed through land user initiatives over 40 years ago. Establishment activities include land clearing and preparation,preparation of holes,seed collection and planting which involve family labor Seeds are collected from neighboring village from mature trees. Holes are prepared randomly about 4 meters apart. No inputs are applied at the establishment stage only hand tools are used (hand hoe, matchet)
Shade trees are planted after establishment of coffee which are randomly planted, tree spp dominating is Cordia abbysinica which has broader leaves and easy to decompose.Other tree spp included are Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii.
Maintenance include weeding which is done by pulling weeds by hand or using hand hoe at early stage after establishment because few leaves have dropped. The farm is mainly meant for coffee production however,few crops which are cassava bananas, fruit trees Jack fruit, Mangoes, Citrus spp which are planted in the peripherals,and Dracaena sppplanted to demarcate the farm along road side.
Pruning of tree branches is done before the shade is heavy as to allow ventilation.Coffee pruning is done to an individual tree depending on number of branches it has at time of harvesting, normally 4 branches are left. Bending of coffee branches is practiced to avoid branch breaking during harvesting.
Settlement is within the farm with few livestock which are sheep, cattle and chicken.
Purpose of the Technology: To increase coffee production by mixing coffee with indigenous tree spp which drop / shed its leaves.Selected trees are those broad leaved which its leaves decompose easily hence improve soil fertility and due to high accumulation of dropped leaves there is an increase in soil moisture content.
Trees act as wind break hence no flower drop.Dracaena spp are planted very close along the road side to demarcate his plot from neighbors and public infrastructure and this helps to reduce land conflicts among neighbors and community as well.
Hand weeding is done as the technology suppress weeds to the big shade.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A farmer bought a piece of land from the village government.Establishment activities include land clearance by removal of shrubs using a matchet.This is followed by land preparations and planting holes which are 30cm depth and 30cm width. These activities are done from May to July by family labor.Planting is normally done between September and October by collecting seedlings from mature trees in neighbors fields.Planting of indigenous tree spp is done randomly after coffee planting to allow ventilation 80 different spps are planted in 1.5 acres. Seeds and seedlings are obtained from neighbors farms.Maintenance includes weeding which is done using family labor who use hand hoe. This is done twice a year in May and December to January. Pruning and bending of coffee tree branches is done once per year after harvesting of coffee as well as trees in June and July using a matchet. Each coffee tree is treated individually only 4 branches are allowed per tree. Bending is done to avoid breaking of branches during coffee harvesting.
Gap filling is done few months after transplanting between February and March at the beginning of long rains. and this was followed pruning and bending of coffee branches.
Demarcation of coffee farm using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of his farm along the road.
Natural / human environment: Land use type: Establishment of coffee has been done on crop land.
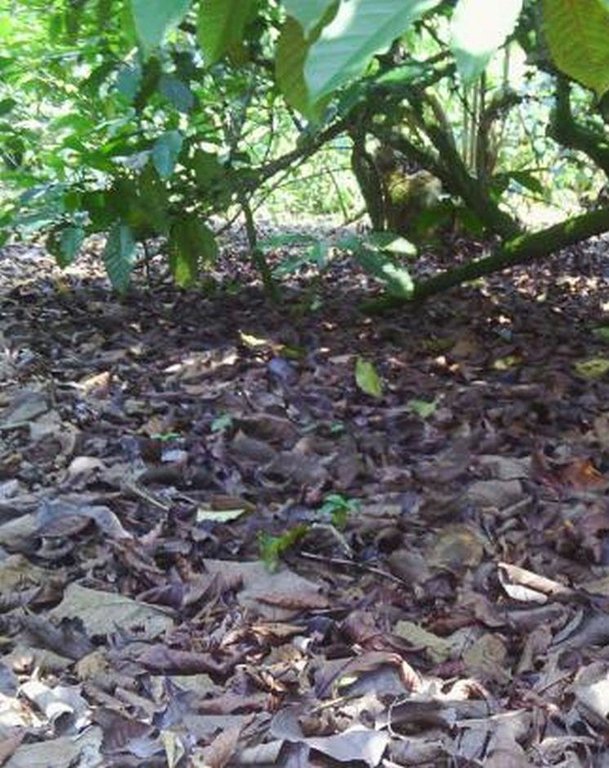
Agronomic: Natural mulch from leaves falling on ground.
Vegetative: Demarcation of boundary using Dracaena spp.
Climatic zone: Sub humid more than 269 growing days.
slope: 2-5% gentle slope
Soil type: Clay loam
Soil depth: Deep
Tools and inputs: Hand hoes,bush knife,axe, seeds and cuttings.
Land ownership: Individually owned.
2.3 Photos de la Technologie
2.5 Pays/ région/ lieux où la Technologie a été appliquée et qui sont couverts par cette évaluation
Pays:
Tanzanie
Région/ Etat/ Province:
Tanzania
Autres spécifications du lieu:
Ngara District
Spécifiez la diffusion de la Technologie:
- répartie uniformément sur une zone
S'il n'existe pas d'informations exactes sur la superficie, indiquez les limites approximatives de la zone couverte:
- < 0,1 km2 (10 ha)
Commentaires:
Boundary points of the Technology area: 236229742E 236229740E 236229639E 236229639E
9726279N 9726387N 9726293N 9726392N
Map
×2.6 Date de mise en œuvre de la Technologie
Si l'année précise est inconnue, indiquez la date approximative: :
- il y a entre 10-50 ans
2.7 Introduction de la Technologie
Spécifiez comment la Technologie a été introduite: :
- par le biais de projets/ d'interventions extérieures
Commentaires (type de projet, etc.) :
The technology was adopted from Muleba district and adapted in Kirusya village
3. Classification de la Technologie de GDT
3.2 Type(s) actuel(s) d'utilisation des terres, là où la Technologie est appliquée

Terres cultivées
- Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses)
- Plantations d’arbres ou de buissons
Cultures pérennes (non ligneuses) - Précisez les cultures:
- bananier/plantain/abaca
Plantations d'arbres et d'arbustes - Précisez les cultures:
- avocat
- citron
- café, cultivé en plein champ
- manguier, mangostane, goyave
- Cordia abbysinica, Erythrina,Meosopsis eminii,Ficus thornngii,Makhamia lutea and Tephrosia vogelii, Jack fruit, Mandarines
Nombre de période de croissance par an: :
- 2
Précisez:
Longest growing period in days: 120Longest growing period from month to month: September-DecemberSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: March-May

Pâturages
- Tethering: rapid decline of land due to expansion of settlements and crop production
Type d'animal:
- ovins
- cattle, chicken
Commentaires:
Livestock density (if relevant):
10-25 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion, water loss/moisture stress, loss of nutrients through leaching and flower drop which lead to reduced yield.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Poor soil fertility and water stress
3.4 Approvisionnement en eau
Approvisionnement en eau des terres sur lesquelles est appliquée la Technologie:
- pluvial
3.6 Mesures de GDT constituant la Technologie

pratiques agronomiques
- A1: Couverture végétale/ du sol
- A2: Matière organique/ fertilité du sol
- A3: Traitement de la couche superficielle du sol
A3: Différenciez les systèmes de travail du sol:
A 3.2: Reduced tillage (> 30% soil cover)

pratiques végétales
- V1: Couverture d’arbres et d’arbustes

modes de gestion
- M3: Disposition/plan en fonction de l'environnement naturel et humain
Commentaires:
Type of agronomic measures: mulching, manure / compost / residues, minimum tillage
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 Principaux types de dégradation des terres traités par la Technologie

érosion hydrique des sols
- Wt: perte de la couche superficielle des sols (couche arable)/ érosion de surface

dégradation chimique des sols
- Cn: baisse de la fertilité des sols et réduction du niveau de matière organique (non causée par l’érosion)

dégradation biologique
- Bc: réduction de la couverture végétale
Commentaires:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (indigenous tree,fruits and coffee. (shrubs)), change in temperature (Loss of water due to evapo transpiration), labour availability (Vegetation degradation)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall (Change of seasonal rainfall), wind storms / dust storms (De flowering leading to production loss)
3.8 Prévention, réduction de la dégradation ou réhabilitation des terres dégradées
Spécifiez l'objectif de la Technologie au regard de la dégradation des terres:
- prévenir la dégradation des terres
- réduire la dégradation des terres
4. Spécifications techniques, activités, intrants et coûts de mise en œuvre
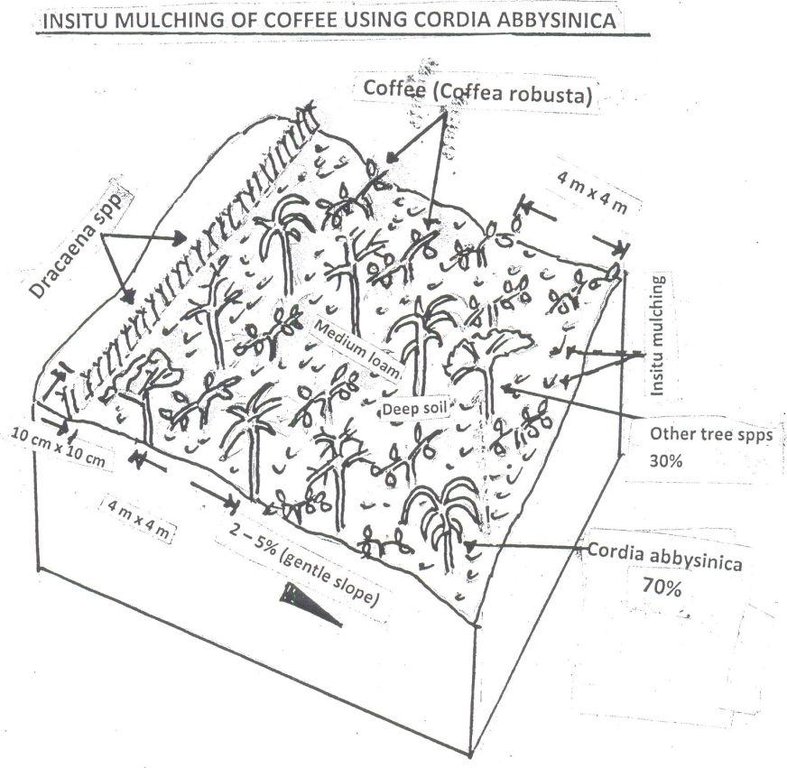
4.1 Dessin technique de la Technologie
Spécifications techniques (associées au dessin technique):
Indigenous tree are randomly planted and Cordia Abbysinica accounts for 70% of the indegenous tree spps. Demarcation of a coffee farm is done using Dracaena (shrub) done on one side of the farm along the road. Natural mulching is done by tree leaves/debris falling on ground. Slope category range from 2-5% gentle slope. Average spacing of Robusta coffee is 4m x 4m.
Location: Karushya Nyamigango. Ngara/Kagera/Tanzania
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil
Secondary technical functions: reduction in wind speed
Mulching
Material/ species: leavesof indigenous trees drop
Quantity/ density: 6 cm depth
Remarks: natural falling and irregular aligment
Manure / compost / residues
Material/ species: indigenous trees
Minimum tillage
Material/ species: Hand pulling sometimes use simple tools.
Aligned: -along boundary
Number of plants per (ha): 1,000
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 375
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 3
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 60
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia abbysinica, Ficus spp,Erythrina spp,Makhamia spp,Tephrosia spp Maesopsis spp (planted)
Fruit trees / shrubs species: avocado, mandarine,
Perennial crops species: Coffee
Other type of management: (Land protection and demarcation)
Planting Dracaena along the road side
Auteur:
Allan Bubelwa, P.O.Box 38 Kyaka Missenyi Kagera Tanzania
Date:
10/04/2014
4.2 Informations générales sur le calcul des intrants et des coûts
autre/ monnaie nationale (précisez):
Tanzanian shillings
Indiquez le taux de change des USD en devise locale, le cas échéant (p.ex. 1 USD = 79.9 réal brésilien): 1 USD = :
1600,0
Indiquez le coût salarial moyen de la main d'œuvre par jour:
3000.00
4.3 Activités de mise en place/ d'établissement
| Activité | Calendrier des activités (saisonnier) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hole preparation | Nov. |
| 2. | Seed collection and preparation | Nov to Dec |
| 3. | Seedling planting | Dec |
| 4. | Demarcation and excavation of small trench | September-before long rains |
| 5. | Preparation of cuttings | September-December |
| 6. | Actual planting | September-December |
| 7. | labour | |
| 8. | pangas (matchet) | |
| 9. | handhole | |
| 10. | tree & coffee seedlings |
4.4 Coûts et intrants nécessaires à la mise en place
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | 1,0 | 2510,4 | 2510,4 | 100,0 | |
| Equipements | tools | 1,0 | 21,88 | 21,88 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | seeds | 1,0 | 31,25 | 31,25 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | seedlings | 1,0 | 61,73 | 61,73 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie | 2625,26 | |||||
| Coût total de mise en place de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 1,64 | |||||
Commentaires:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 Activités d'entretien/ récurrentes
| Activité | Calendrier/ fréquence | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Pruning-Trees-Coffee | After harvesting, June-July |
| 2. | Weeding | after long rain season |
| 3. | Gap filling | March,during short rains |
| 4. | Bending and layering | Once after harvesting |
| 5. | Gap filling | before short rains |
| 6. | Prunning | Dry season |
4.6 Coûts et intrants nécessaires aux activités d'entretien/ récurrentes (par an)
| Spécifiez les intrants | Unité | Quantité | Coûts par unité | Coût total par intrant | % du coût supporté par les exploitants des terres | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Main d'œuvre | labour | 1,0 | 63,63 | 63,63 | 100,0 | |
| Matériel végétal | seedlings | 1,0 | 33,05 | 33,05 | 100,0 | |
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie | 96,68 | |||||
| Coût total d'entretien de la Technologie en dollars américains (USD) | 0,06 | |||||
Commentaires:
Machinery/ tools: Hand hoe, panga (matchet) and axe, Panga (Matchet), hand hoe and axe
The cost assesment was completed on 18 February 2014. The cost of labour can be reduced during the onset of rain when the soil is a bit workable.
4.7 Facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts
Décrivez les facteurs les plus importants affectant les coûts :
Labour
5. Environnement naturel et humain
5.1 Climat
Précipitations annuelles
- < 250 mm
- 251-500 mm
- 501-750 mm
- 751-1000 mm
- 1001-1500 mm
- 1501-2000 mm
- 2001-3000 mm
- 3001-4000 mm
- > 4000 mm
Zone agro-climatique
- subhumide
Thermal climate class: tropics. All months above 18°C
5.2 Topographie
Pentes moyennes:
- plat (0-2 %)
- faible (3-5%)
- modéré (6-10%)
- onduleux (11-15%)
- vallonné (16-30%)
- raide (31-60%)
- très raide (>60%)
Reliefs:
- plateaux/ plaines
- crêtes
- flancs/ pentes de montagne
- flancs/ pentes de colline
- piémonts/ glacis (bas de pente)
- fonds de vallée/bas-fonds
Zones altitudinales:
- 0-100 m
- 101-500 m
- 501-1000 m
- 1001-1500 m
- 1501-2000 m
- 2001-2500 m
- 2501-3000 m
- 3001-4000 m
- > 4000 m
5.3 Sols
Profondeur moyenne du sol:
- très superficiel (0-20 cm)
- superficiel (21-50 cm)
- modérément profond (51-80 cm)
- profond (81-120 cm)
- très profond (>120 cm)
Texture du sol (de la couche arable):
- grossier/ léger (sablonneux)
Matière organique de la couche arable:
- abondant (>3%)
5.4 Disponibilité et qualité de l'eau
Profondeur estimée de l’eau dans le sol:
> 50 m
Disponibilité de l’eau de surface:
bonne
Qualité de l’eau (non traitée):
eau potable
5.5 Biodiversité
Diversité des espèces:
- moyenne
5.6 Caractéristiques des exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
Orientation du système de production:
- commercial/ de marché
Revenus hors exploitation:
- moins de 10% de tous les revenus
Niveau relatif de richesse:
- moyen
Individus ou groupes:
- individu/ ménage
Niveau de mécanisation:
- travail manuel
Genre:
- hommes
Indiquez toute autre caractéristique pertinente des exploitants des terres:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Tree and coffee pruning is done by men because it needs climbing
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy and own 80% of the land (He is getting income from coffee).
20% of the land users are poor and own 20% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Most of the residents are permanent farmers
5.7 Superficie moyenne des terres utilisées par les exploitants des terres appliquant la Technologie
- < 0,5 ha
- 0,5-1 ha
- 1-2 ha
- 2-5 ha
- 5-15 ha
- 15-50 ha
- 50-100 ha
- 100-500 ha
- 500-1 000 ha
- 1 000-10 000 ha
- > 10 000 ha
Cette superficie est-elle considérée comme de petite, moyenne ou grande dimension (en se référant au contexte local)?
- petite dimension
5.8 Propriété foncière, droits d’utilisation des terres et de l'eau
Propriété foncière:
- individu, sans titre de propriété
Droits d’utilisation des terres:
- individuel
Droits d’utilisation de l’eau:
- communautaire (organisé)
Commentaires:
Water is accessed friendly, land is inherited.
5.9 Accès aux services et aux infrastructures
santé:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
éducation:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
assistance technique:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
emploi (par ex. hors exploitation):
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
marchés:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
énergie:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
routes et transports:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
eau potable et assainissement:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
services financiers:
- pauvre
- modéré
- bonne
6. Impacts et conclusions
6.1 Impacts sur site que la Technologie a montrés
Impacts socio-économiques
Production
production agricole
Quantité avant la GDT:
16bags/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
58 bags/ha
production fourragère
production de bois
Quantité avant la GDT:
3cub.m/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
12cub.m/ha
Revenus et coûts
dépenses pour les intrants agricoles
Quantité avant la GDT:
62 kg/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
0 kgs/ha
charge de travail
Quantité avant la GDT:
15 md/ha
Quantité après la GDT:
2 md/ha
Impacts socioculturels
sécurité alimentaire/ autosuffisance
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
improved
situation sanitaire
Quantité avant la GDT:
little
Quantité après la GDT:
inreased
opportunités culturelles
possibilités de loisirs
Quantité avant la GDT:
none
Quantité après la GDT:
available
connaissances sur la GDT/ dégradation des terres
apaisement des conflits
Quantité avant la GDT:
none
Quantité après la GDT:
available
Impacts écologiques
Cycle de l'eau/ ruissellement
quantité d'eau
qualité de l'eau
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
ruissellement de surface
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
Sols
humidité du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
couverture du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
perte en sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
high
encroûtement/ battance du sol
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
medium
Biodiversité: végétale, animale
biomasse/ au dessus du sol C
Réduction des risques de catastrophe et des risques climatiques
risques d'incendies
6.2 Impacts hors site que la Technologie a montrés
inondations en aval
envasement en aval
dommages sur les champs voisins
Quantité avant la GDT:
low
Quantité après la GDT:
medium
dommages sur les infrastructures publiques/ privées
6.3 Exposition et sensibilité de la Technologie aux changements progressifs et aux évènements extrêmes/catastrophes liés au climat (telles que perçues par les exploitants des terres)
Changements climatiques progressifs
Changements climatiques progressifs
| Saison | Augmentation ou diminution | Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| températures annuelles | augmente | bien |
Extrêmes climatiques (catastrophes)
Catastrophes météorologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| pluie torrentielle locale | bien |
| tempête de vent locale | bien |
Catastrophes climatiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| sécheresse | bien |
Catastrophes hydrologiques
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| inondation générale (rivière) | pas connu |
Autres conséquences liées au climat
Autres conséquences liées au climat
| Comment la Technologie fait-elle face à cela? | |
|---|---|
| réduction de la période de croissance | pas connu |
Commentaires:
Introduction of contour ridge
6.4 Analyse coûts-bénéfices
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts de mise en place (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Quels sont les bénéfices comparativement aux coûts d'entretien récurrents (du point de vue des exploitants des terres)?
Rentabilité à court terme:
positive
Rentabilité à long terme:
très positive
Commentaires:
In 10 years he has obtained more money from sales of coffee and tree products
6.5 Adoption de la Technologie
Commentaires:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités de la Technologie
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue de l'exploitant des terres |
|---|
|
Increased production How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Easy maintenance acctivities e.g. easy to keep weeds under control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Fuel wood availability How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Availability of fruits How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improved kowlledge regarding SLM and soil erosion How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
| Points forts/ avantages/ possibilités du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé |
|---|
|
This is cheap and affordable technology which can be used by smallholder farmers How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote technology among other farmers |
|
Large potential for increased income (higher coffee yields) How can they be sustained / enhanced? Ditto |
|
Improve soil fertility How can they be sustained / enhanced? Promote crop and livestock intergration (manure production) |
|
Increased soil moisture How can they be sustained / enhanced? Appropriate maintenance acttivities |
|
Erosion control How can they be sustained / enhanced? Maintain sufficient soil cover |
6.8 Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques de la Technologie et moyens de les surmonter
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue de l’exploitant des terres | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Land competition with food crops | Promote technology among other farmers |
| High cost of tools, especially pruning scissors | Provide required tools |
| Faiblesses/ inconvénients/ risques du point de vue du compilateur ou d'une autre personne ressource clé | Comment peuvent-ils être surmontés? |
|---|---|
| Risk to fire during dry season | Introduce fire breaks |
| In areas where frost persist can lead to fungal diseases if not well pruned | Improve pruning |
7. Références et liens
7.1 Méthodes/ sources d'information
7.2 Références des publications disponibles
Titre, auteur, année, ISBN:
Kagera TAMP project website
Disponible à partir d'où? Coût?
http://www.fao.org/nr/kagera/en/
Liens et modules
Développer tout Réduire toutLiens
Aucun lien
Modules
Aucun module trouvé