Mulberry cultivation for silkworm [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Resham kiro ko lagi kimbu khati
technologies_1226 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Jayaswal Ekta
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
土地使用者:
Singtang Gangalal
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The plantation of mulberry plants which are allowed to grow for the production of nutrients leaves for silkworm mulberry cultivation for silkworm.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
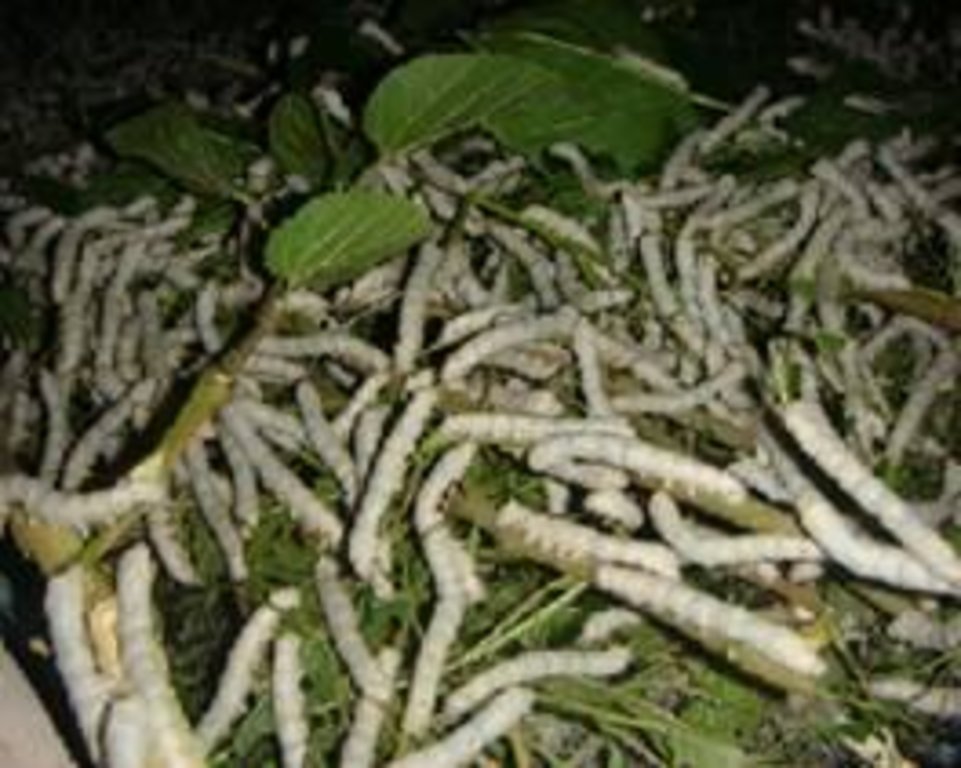
After the plantation of mulberry plants. They are ready to be eaten by silkworm. Firstly, silkworm eggs must be stay between 25 to 31 "C in tray or petric dish. In this area silkworm are brought from silkworm industry of khopasi. The larvae must be transfer to clean tray with freash food. A time came in larval stage when larvae eats huge amount of mulberry and grow more than 5cm long. After enough eating, larvae raise their heads as it shows sign for cocoon formation. Then, the worm is kept in another circular bamboo which will make cocoon more uniform in slope and easier to collect silkworm by contracting secrets from an opening under its mouth a steady stream of liquid silk coated with sericine which darkens on exposure. It takes 25 days to form cocon.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of planting mulberry plant is for producing silkworm to increases economic condition of farmer.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For over two years people have been implementing these technology.They took training from the khopasi silkworm institution.They have get external inputs.While getting training,maintenance has been carried out when the plants are not grown enough.While producing the silkworm (larva to cocoon) maintenance is carried out as keeping them in clean environment without reaching another species around them.
Natural / human environment: The natural environment is tropical with temperature ranging from 20 to 25°C .The population density is sparse with the community relying heavily on agriculture.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Chamryang Besi
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavre
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 29.27 km2.
This chamrang besi is small VDC with small populatio lacated in kavre district
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 50多年前(传统)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 作为传统系统的一部分(> 50 年)
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- wheat, tomatoes
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 35; Longest growing period from month to month: baisakh(1-30) and bhadra(1-30)

森林/林地
- (半天然)天然森林/林地
- 植树造林
(半天然)天然森林/林地:具体说明管理类型:
- 轮垦
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It decreases the number of crops in surrounding and it also kills the insect afte the formation of cocoon so in certain amount affects the environment.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduce the cropping land
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Plantation forestry: Yes
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 混合雨水灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, population pressure, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, discharges (point contamination of water), release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), change in temperature, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, poverty / wealth, labour availability, education, access to knowledge and support services, war and conflicts, governance / institutional
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Trees/ shrubs species: planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: fruit trees (mulberry plant)
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bringing plant from khopasi | Early june/july |
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bringing silkworm in time of production | late april |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 设备 | Bringing silkworm | silkworms | 2000.0 | 0.01 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 20.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 20.0 | |||||
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is labour for bringing plants from khopasi, quality of mulberry leaves, quality of silkworm etc.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 高(>3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
不可用
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: Infiltration is very low but surface flow is high
Availability of surface water: During rainy season excess water flow
Water quality (untreated): Some portion of the water is used for agriculture, but most time the water is unused
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 商业/市场
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No, there is not any difference because all the people can do it
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
One house has at least 20 rapani
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
木材生产
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
文化机会
冲突缓解
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地表径流
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
养分循环/补给
土壤有机物/地下C
其它生态影响
hazard towards adverse events
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
长期回报:
中性/平衡
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
轻度消极
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Provide the facility of fodders for animals |
| Waste product comes from the use as food for animals |
| Increase water resources |
| water product also serves as a good fertilizer |
| Improve little economic status |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increase the economic status of farmer |
| Provided the facilities |
| Decrease soil erosion |
| wastes could we good fertilizer |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| waste of time if larvae of silkworm cannot grow properly | while keeping larva place should properly clean. |
| Time taking process as cocoon formation takes around 25 days | keep larva away from other inscers. It can be done covering the disk with net. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/01/2015
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块