Mulberry cultivation for silkworm [เนปาล]
- ผู้สร้างสรรค์:
- การอัพเดท:
- ผู้รวบรวม: Sabita Aryal
- ผู้เรียบเรียง: –
- ผู้ตรวจสอบ: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Resham kiro ko lagi kimbu khati
technologies_1226 - เนปาล
ดูส่วนย่อย
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมด1. ข้อมูลทั่วไป
1.2 รายละเอียดที่ติดต่อได้ของผู้รวบรวมและองค์กรที่เกี่ยวข้องในการประเมินและการจัดเตรียมทำเอกสารของเทคโนโลยี
ผู้เชี่ยวชาญ SLM:
Jayaswal Ekta
Kathmandu University
เนปาล
ผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Singtang Gangalal
ชื่อขององค์กรซึ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการทำเอกสารหรือการประเมินเทคโนโลยี (ถ้าเกี่ยวข้อง)
Kathmandu University (KU) - เนปาล1.3 เงื่อนไขการใช้ข้อมูลที่ได้บันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT
ผู้รวบรวมและวิทยากรหลักยอมรับเงื่อนไขเกี่ยวกับการใช้ข้อมูลที่ถูกบันทึกผ่านทาง WOCAT:
ใช่
1.4 การเปิดเผยเรื่องความยั่งยืนของเทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้
เทคโนโลยีที่ได้อธิบายไว้นี้เป็นปัญหาของความเสื่อมโทรมโทรมของที่ดินหรือไม่ จึงไม่ได้รับการยอมรับว่าเป็นเทคโนโลยีเพื่อการจัดการที่ดินอย่างยั่งยืน:
ไม่ใช่
2. การอธิบายลักษณะของเทคโนโลยี SLM
2.1 การอธิบายแบบสั้น ๆ ของเทคโนโลยี
คำจำกัดความของเทคโนโลยี:
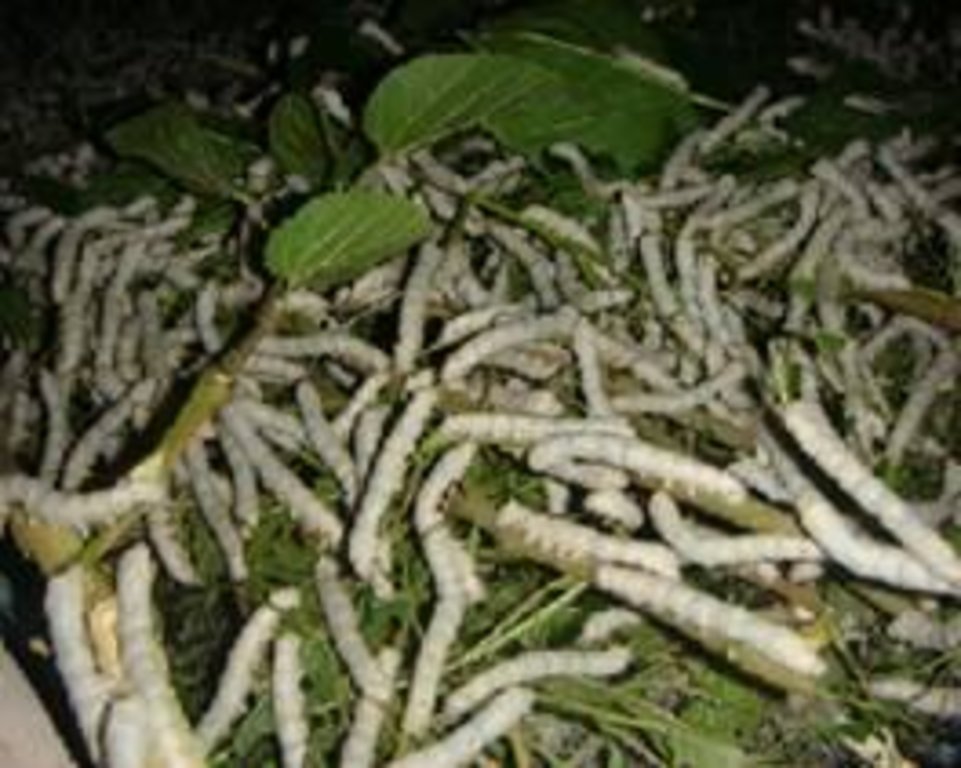
The plantation of mulberry plants which are allowed to grow for the production of nutrients leaves for silkworm mulberry cultivation for silkworm.
2.2 การอธิบายแบบละเอียดของเทคโนโลยี
คำอธิบาย:
After the plantation of mulberry plants. They are ready to be eaten by silkworm. Firstly, silkworm eggs must be stay between 25 to 31 "C in tray or petric dish. In this area silkworm are brought from silkworm industry of khopasi. The larvae must be transfer to clean tray with freash food. A time came in larval stage when larvae eats huge amount of mulberry and grow more than 5cm long. After enough eating, larvae raise their heads as it shows sign for cocoon formation. Then, the worm is kept in another circular bamboo which will make cocoon more uniform in slope and easier to collect silkworm by contracting secrets from an opening under its mouth a steady stream of liquid silk coated with sericine which darkens on exposure. It takes 25 days to form cocon.
Purpose of the Technology: The main purpose of planting mulberry plant is for producing silkworm to increases economic condition of farmer.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: For over two years people have been implementing these technology.They took training from the khopasi silkworm institution.They have get external inputs.While getting training,maintenance has been carried out when the plants are not grown enough.While producing the silkworm (larva to cocoon) maintenance is carried out as keeping them in clean environment without reaching another species around them.
Natural / human environment: The natural environment is tropical with temperature ranging from 20 to 25°C .The population density is sparse with the community relying heavily on agriculture.
2.3 รูปภาพของเทคโนโลยี
2.5 ประเทศภูมิภาค หรือสถานที่ตั้งที่เทคโนโลยีได้นำไปใช้และได้รับการครอบคลุมโดยการประเมินนี้
ประเทศ:
เนปาล
ภูมิภาค/รัฐ/จังหวัด:
Chamryang Besi
ข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมของสถานที่ตั้ง :
Kavre
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 29.27 km2.
This chamrang besi is small VDC with small populatio lacated in kavre district
Map
×2.6 วันที่การดำเนินการ
ถ้าไม่รู้ปีที่แน่นอน ให้ระบุวันที่โดยประมาณ:
- มากกว่า 50 ปี (แบบดั้งเดิม)
2.7 คำแนะนำของเทคโนโลยี
ให้ระบุว่าเทคโนโลยีถูกแนะนำเข้ามาอย่างไร:
- เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของระบบแบบดั้งเดิมที่ทำก้นอยู่ (> 50 ปี)
3. การจัดประเภทของเทคโนโลยี SLM
3.1 วัตถุประสงค์หลักของเทคโนโลยี
- สร้างผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจที่เป็นประโยชน์
3.2 ประเภทของการใช้ที่ดินในปัจจุบันที่ได้นำเทคโนโลยีไปใช้

พื้นที่ปลูกพืช
- การปลูกพืชล้มลุกอายุปีเดียว
- การปลูกพืชยืนต้นที่ไม่มีเนื้อไม้
Annual cropping - Specify crops:
- cereals - maize
- vegetables - leafy vegetables (salads, cabbage, spinach, other)
- wheat, tomatoes
จำนวนของฤดูเพาะปลูกต่อปี:
- 2
ระบุ:
Longest growing period in days: 35; Longest growing period from month to month: baisakh(1-30) and bhadra(1-30)

ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่ากึ่งธรรมชาติ / พื้นที่ทำไม้
- ป่า/พื้นที่ทำไม้
(Semi-)natural forests/ woodlands: Specify management type:
- การเกษตรแบบไร่เลื่อยลอย (Shifting cultivation)
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): It decreases the number of crops in surrounding and it also kills the insect afte the formation of cocoon so in certain amount affects the environment.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Reduce the cropping land
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: Yes
Plantation forestry: Yes
Constraints of infrastructure network (roads, railways, pipe lines, power lines)
3.4 การใช้น้ำ
การใช้น้ำของที่ดินที่มีการใช้เทคโนโลยีอยู่:
- น้ำฝนร่วมกับการชลประทาน
3.5 กลุ่ม SLM ที่ตรงกับเทคโนโลยีนี้
- การเลี้ยงผึ้ง การเพาะเลี้ยงสัตว์น้ำ สัตว์ปีก ฟาร์มกระต่าย ฟาร์มหนอนไหม
3.6 มาตรการ SLM ที่ประกอบกันเป็นเทคโนโลยี

มาตรการอนุรักษ์ด้วยวิธีพืช
- V1: ต้นไม้และพุ่มไม้คลุมดิน
3.7 รูปแบบหลักของการเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดินที่ได้รับการแก้ไขโดยเทคโนโลยี

การเสื่อมโทรมของดินทางด้านชีวภาพ
- Bc (Reduction of vegetation cover): การลดลงของจำนวนพืชที่ปกคลุมดิน
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, industrial activities and mining, urbanisation and infrastructure development, over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.), change of seasonal rainfall, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts), wind storms / dust storms, floods, droughts, population pressure, inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
Secondary causes of degradation: overgrazing, discharges (point contamination of water), release of airborne pollutants (urban/industry…), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff), change in temperature, other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify, land tenure, poverty / wealth, labour availability, education, access to knowledge and support services, war and conflicts, governance / institutional
3.8 การป้องกัน การลดลง หรือการฟื้นฟูความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
ระบุเป้าหมายของเทคโนโลยีกับความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน:
- ป้องกันความเสื่อมโทรมของที่ดิน
4. ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค กิจกรรมการนำไปปฏิบัติใช้ ปัจจัยนำเข้า และค่าใช้จ่าย
4.1 แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี
ข้อมูลจำเพาะด้านเทคนิค (แบบแปลนทางเทคนิคของเทคโนโลยี):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: high
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, increase of surface roughness, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, water harvesting / increase water supply, water spreading, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: drain / divert, reduction of slope angle, reduction of slope length
Trees/ shrubs species: planted
Fruit trees / shrubs species: fruit trees (mulberry plant)
4.2 ข้อมูลทั่วไปเกี่ยวกับการคำนวณปัจจัยนำเข้าและค่าใช้จ่าย
ระบุสกุลเงินที่ใช้คำนวณค่าใช้จ่าย:
- USD
4.3 กิจกรรมเพื่อการจัดตั้ง
| กิจกรรม | Timing (season) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bringing plant from khopasi | Early june/july |
4.5 การบำรุงรักษาสภาพหรือกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำ
| กิจกรรม | ช่วงระยะเวลา/ความถี่ | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Bringing silkworm in time of production | late april |
4.6 ค่าใช้จ่ายของปัจจัยนำเข้าและกิจกรรมที่เกิดขึ้นเป็นประจำที่ต้องการการบำรุงรักษา (ต่อปี)
| ปัจจัยนำเข้า | หน่วย | ปริมาณ | ค่าใช้จ่ายต่อหน่วย | ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดต่อปัจจัยนำเข้า | %ของค่าใช้จ่ายที่ก่อให้เกิดขึ้นโดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| อุปกรณ์ | Bringing silkworm | silkworms | 2000.0 | 0.01 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| ค่าใช้จ่ายทั้งหมดของการบำรุงรักษาสภาพเทคโนโลยี | 20.0 | |||||
| Total costs for maintenance of the Technology in USD | 20.0 | |||||
4.7 ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่าย
ปัจจัยสำคัญที่สุดที่มีผลกระทบต่อค่าใช้จ่ายต่างๆ:
The most determinate factor affecting the cost is labour for bringing plants from khopasi, quality of mulberry leaves, quality of silkworm etc.
5. สิ่งแวดล้อมทางธรรมชาติและของมนุษย์
5.2 สภาพภูมิประเทศ
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลาดชัน:
- ราบเรียบ (0-2%)
- ลาดที่ไม่ชัน (3-5%)
- ปานกลาง (6-10%)
- เป็นลูกคลื่น (11-15%)
- เป็นเนิน (16-30%)
- ชัน (31-60%)
- ชันมาก (>60%)
ธรณีสัณฐาน:
- ที่ราบสูง/ที่ราบ
- สันเขา
- ไหล่เขา
- ไหล่เนินเขา
- ตีนเนิน
- หุบเขา
ระดับความสูง:
- 0-100 เมตร
- 101-500 เมตร
- 501-1,000 เมตร
- 1,001-1,500 เมตร
- 1,501-2,000 เมตร
- 2,001-2,500 เมตร
- 2,501-3,000 เมตร
- 3,001-4,000 เมตร
- > 4,000 เมตร
5.3 ดิน
ค่าเฉลี่ยความลึกของดิน:
- ตื้นมาก (0-20 ซ.ม.)
- ตื้น (21-50 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกปานกลาง (51-80 ซ.ม.)
- ลึก (81-120 ซ.ม.)
- ลึกมาก (>120 ซ.ม.)
เนื้อดิน (ดินชั้นบน):
- ปานกลาง (ดินร่วน ทรายแป้ง)
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน:
- สูง (>3%)
(ถ้ามี) ให้แนบคำอธิบายเรื่องดินแบบเต็มหรือระบุข้อมูลที่มีอยู่ เช่น ชนิดของดิน ค่า pH ของดินหรือความเป็นกรดของดิน ความสามารถในการแลกเปลี่ยนประจุบวก ไนโตรเจน ความเค็ม เป็นต้น:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is high
5.4 ความเป็นประโยชน์และคุณภาพของน้ำ
ระดับน้ำใต้ดิน:
ที่ผิวดิน
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน:
เกินพอ
คุณภาพน้ำ (ที่ยังไม่ได้บำบัด):
ใช้ประโยชน์ไม่ได้
ความคิดเห็นและข้อมูลจำเพาะเพิ่มเติมเรื่องคุณภาพและปริมาณน้ำ:
Ground water table: Infiltration is very low but surface flow is high
Availability of surface water: During rainy season excess water flow
Water quality (untreated): Some portion of the water is used for agriculture, but most time the water is unused
5.6 ลักษณะของผู้ใช้ที่ดินที่นำเทคโนโลยีไปปฏิบัติใช้
แนวทางการตลาดของระบบการผลิต:
- ทำการค้า/การตลาด
ระดับของความมั่งคั่งโดยเปรียบเทียบ:
- พอมีพอกิน
เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน:
- เป็นรายบุคคล/ครัวเรือน
ระดับของการใช้เครื่องจักรกล:
- งานที่ใช้แรงกาย
- การใช้กำลังจากสัตว์
ระบุลักษณะอื่นๆที่เกี่ยวข้องของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน:
Difference in the involvement of women and men: No, there is not any difference because all the people can do it
5.7 Average area of land used by land users applying the Technology
- < 0.5 เฮกตาร์
- 0.5-1 เฮกตาร์
- 1-2 เฮกตาร์
- 2-5 เฮกตาร์
- 5-15 เฮกตาร์
- 15-50 เฮกตาร์
- 50-100 เฮกตาร์
- 100-500 เฮกตาร์
- 500-1,000 เฮกตาร์
- 1,000-10,000 เฮกตาร์
- >10,000 เฮกตาร์
พิจารณาว่าเป็นขนาดเล็ก กลาง หรือขนาดใหญ่ (ซึ่งอ้างอิงถึงบริบทระดับท้องถิ่น):
- ขนาดเล็ก
แสดงความคิดเห็น:
One house has at least 20 rapani
5.9 การเข้าถึงบริการและโครงสร้างพื้นฐาน
สุขภาพ:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การศึกษา:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
ความช่วยเหลือทางด้านเทคนิค:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
การจ้างงาน (เช่น ภายนอกฟาร์ม):
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
น้ำดื่มและการสุขาภิบาล:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
บริการด้านการเงิน:
- จน
- ปานกลาง
- ดี
6. ผลกระทบและสรุปคำบอกกล่าว
6.1 ผลกระทบในพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (On-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ผลกระทบทางด้านเศรษฐกิจและสังคม
การผลิต
การผลิตพืชผล
การผลิตพืชที่ใช้เลี้ยงปศุสัตว์
การผลิตไม้
รายได้และค่าใช้จ่าย
รายได้จากฟาร์ม
ผลกระทบด้านสังคมวัฒนธรรมอื่น ๆ
โอกาสทางวัฒนธรรม
การบรรเทาความขัดแย้ง
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยา
วัฐจักรน้ำหรือน้ำบ่า
คุณภาพน้ำ
น้ำไหลบ่าที่ผิวดิน
ดิน
ความชื้นในดิน
สิ่งปกคลุมดิน
การสูญเสียดิน
การหมุนเวียนและการเติมของธาตุอาหาร
อินทรียวัตถุในดิน/ต่ำกว่าดินชั้น C
ผลกระทบด้านนิเวศวิทยาอื่น ๆ
hazard towards adverse events
6.2 ผลกระทบนอกพื้นที่ดำเนินการ (Off-site) จากการใช้เทคโนโลยี
ความเสียหายต่อพื้นที่เพาะปลูกของเพื่อนบ้าน
6.3 การเผชิญและความตอบสนองของเทคโนโลยีต่อการเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป และสภาพรุนแรงของภูมิอากาศ / ภัยพิบัติ (ที่รับรู้ได้โดยผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
การเปลี่ยนแปลงสภาพภูมิอากาศที่ค่อยเป็นค่อยไป
| ฤดู | increase or decrease | เทคโนโลยีมีวิธีการรับมืออย่างไร | |
|---|---|---|---|
| อุณหภูมิประจำปี | เพิ่มขึ้น | ไม่ค่อยดี |
6.4 การวิเคราะห์ค่าใช้จ่ายและผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับ
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการจัดตั้งเป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะยาว:
เป็นกลางหรือสมดุล
ผลประโยชน์ที่ได้รับเปรียบเทียบกับค่าใช้จ่ายในการบำรุงรักษาหรือต้นทุนที่เกิดขึ้นซ้ำอีก เป็นอย่างไร (จากมุมมองของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน)
ผลตอบแทนระยะสั้น:
ด้านลบเล็กน้อย
6.7 จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสของเทคโนโลยี
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้ใช้ที่ดิน |
|---|
| Provide the facility of fodders for animals |
| Waste product comes from the use as food for animals |
| Increase water resources |
| water product also serves as a good fertilizer |
| Improve little economic status |
| จุดแข็ง / ข้อได้เปรียบ / โอกาสในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก |
|---|
| Increase the economic status of farmer |
| Provided the facilities |
| Decrease soil erosion |
| wastes could we good fertilizer |
6.8 จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงของเทคโนโลยีและวิธีการแก้ไข
| จุดอ่อน / ข้อเสียเปรียบ / ความเสี่ยงในทัศนคติของผู้รวบรวมหรือวิทยากรหลัก | มีวิธีการแก้ไขได้อย่างไร |
|---|---|
| waste of time if larvae of silkworm cannot grow properly | while keeping larva place should properly clean. |
| Time taking process as cocoon formation takes around 25 days | keep larva away from other inscers. It can be done covering the disk with net. |
7. การอ้างอิงและการเชื่อมต่อ
7.1 วิธีการและแหล่งข้อมูล
- ไปเยี่ยมชมภาคสนาม การสำรวจพื้นที่ภาคสนาม
- การสัมภาษณ์กับผู้ใช้ที่ดิน
วันที่เก็บรวบรวมข้อมูล(ภาคสนาม) :
08/01/2015
ลิงก์และโมดูล
ขยายทั้งหมด ย่อทั้งหมดลิงก์
ไม่มีลิงก์
โมดูล
ไม่มีโมดูล