Cultivation of Hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in the watershed [阿富汗]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Aqila Haidery
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Alexandra Gavilano
Kesht Angoza da abriza
technologies_1306 - 阿富汗
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
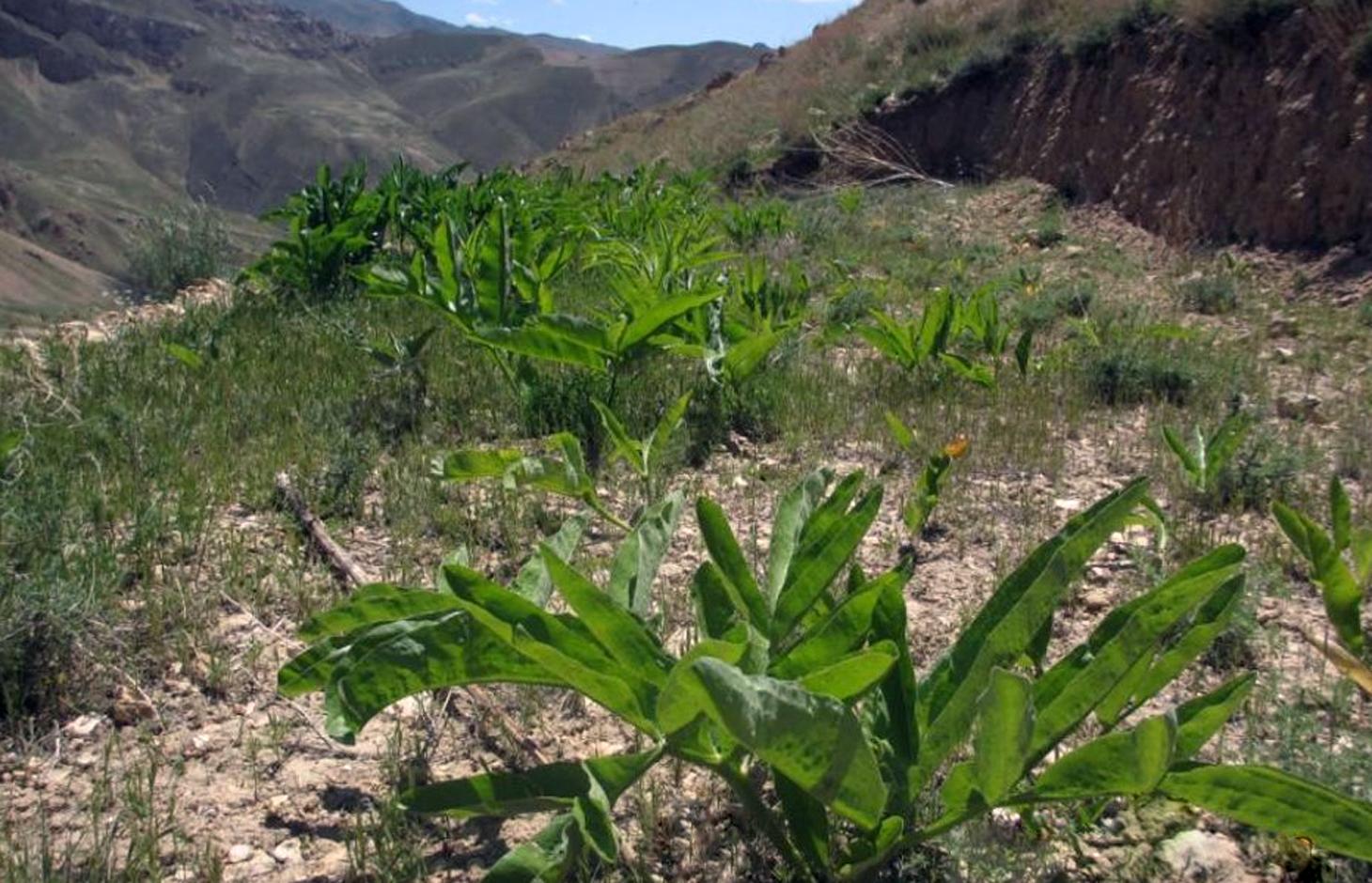
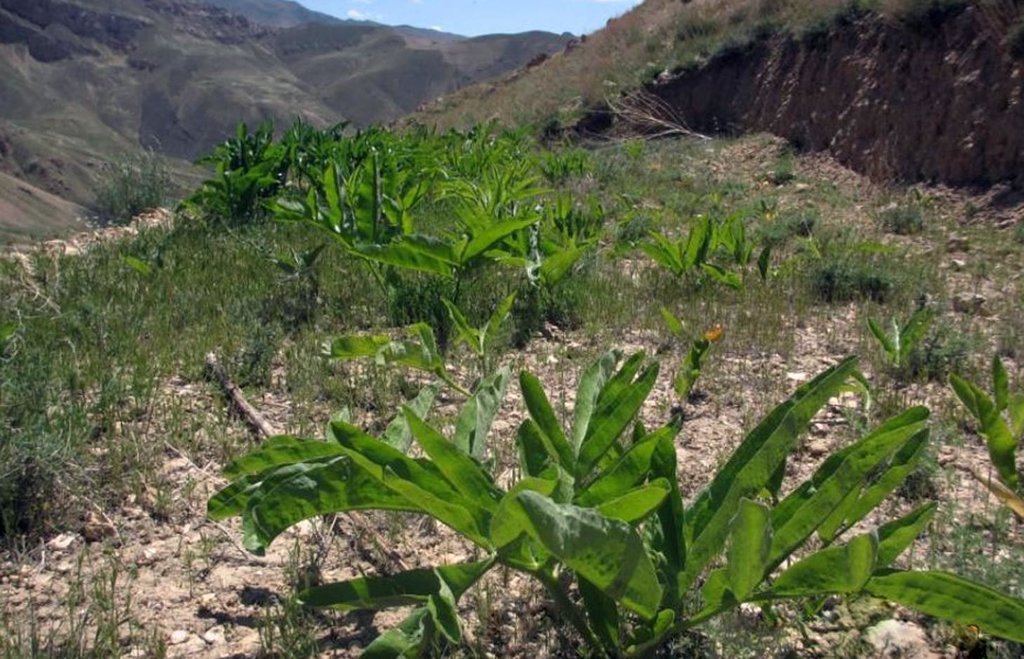
Ferula assa-foetida is an important medicinal plant, a valued cash crop and a native plant of Afghanistan’s range-lands.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Cultivation of hing (Ferula assa-foetida) in watersheds is documented by the Sustainable Land Management Project which is implemented by HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and funded by the Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation (SDC). Ferula assa-foetida, or hing, is a medicinal plant that grows well in shallow sandy and alkaline soils in semi-arid climates and at high altitudes and is a native plant of Afghanistan’s upper catchment areas. Due to the enduring conflict and the consequent breakdown of community-managed grazing in upper catchment areas, most range-lands in Afghanistan are been seriously degraded. Uncontrolled grazing of animals and growing cereal crops on range-lands are the main contributors to the loss of vegetation coverage in upper catchments. One of the negative consequences are flash floods occurring several times a year, damaging agricultural lands, irrigation canals, houses and other infrastructure while often also causing fatalities.
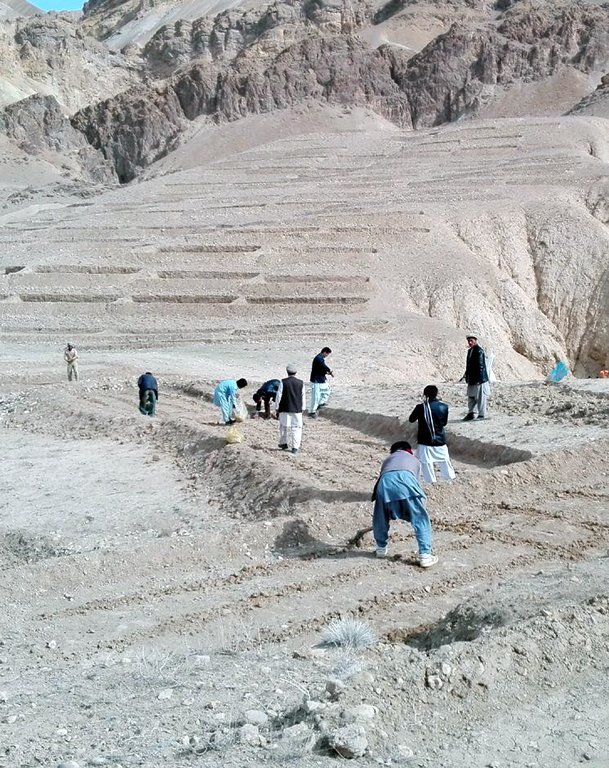
In order to decrease the risk of flash floods, improve pastures and extend cash crop cultivation in upper catchment areas, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation has implemented community-based watershed activities such as structural and agronomic measures to control water runoff.
Hing has been identified as a suitable agronomic measure in watershed management in Saighan district. HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation and the target communities selected hing as a valuable cash crop and a suitable plant for watershed rehabilitation. Today, hing is cultivated on 1,400,000 m2 (140 ha) in nine watersheds and with the participation of 1500 families. The growing period of hing depends on the local climate but tends to be 5-10 years and culminates in the pants’ flowering. During the first five years hing has grey colored leaves. Later a stem appears and grows more than a meter high. The stem is large and yellow and at the end of the main and subordinate stems are yellow flowers. The width of the hing root varies between 7-15 cm and usually goes as deep as 30-40 cm into the soil. Hing plantations have been established with the involvement of the local communities and are managed by the responsible watershed committee. The harvest of hing is organized by the watershed committee and all households have the right to participate and sell hing for income generation. To maintain watershed activities, such as hing cultivation, a safe box has been created for each community-managed watershed. The watershed committee manages the safe box and collects funds for maintenance, community development and emergency projects, according to the watershed management plan which has been developed by the local communities with support of HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation.
Natural / human environment: Bamyan is a remote province of Afghanistan with a high poverty rate. It has a semi-arid climate with cold winters and hot and dry summers. During winter, temperatures can drop below -22 degrees. Summer temperatures can reach to 34 degrees in the month of July. The average annual rainfall in the area is about 230 mm and some years can be very dry. 90% of the population relies on subsistence agriculture for their livelihoods and off-farm activities are marginal. The growing season in Saighan district is relatively short from April to October and farmers can produce only one crop per year. Farmers with access to irrigation water cultivate cash crops, for example potato and vegetables, in addition to staple (wheat) and fodder crops. Those without access to irrigation water cultivate wheat and fodder crops only. Water scarcity from May to September may result in a lack of high value crops.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
阿富汗
区域/州/省:
Bamyan
有关地点的进一步说明:
Saighan
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
1.4
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
- Re-introduction
注释(项目类型等):
The technology was introduced since 2012
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农牧业(包括农牧结合)

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
多年生(非木质)作物 - 指定作物:
- 药用、芳香、杀虫植物 - 多年生植物

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Lack of management in upper catchment area over the last decades resulted in a severe loss of vegetation and in the loss of biodiversity. Uncontrolled grazing of animals during the spring season prevented seed production of domestic plants. Hot temperature in summer burnt the remaining parts of domestic plants. Each year, the soil is washed away by heavy rainfalls creating gulleys which further reduced the vegetation cover.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): The users of watershed areas cut shrubs for fuel and graze their animals. The lack of alternatives left them to overuse resources in upper catchment areas during war and conflict.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Cropland: Cp: Perennial (non-woody) cropping
Number of growing seasons per year: 1
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: March to July
Livestock density: 10-25 LU /km2
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
否

牧场
- Extensive grazing
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- cultivation of medical plants
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, mixed cropping / intercropping, cover cropping
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main causes of degradation: crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The upper catchment area have broken to agricultural lands), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Domestic shrubs have been cut and have been used for fuel energy), overgrazing (Without management people grazed their animals in spring season and prevented from the plant seed production.), war and conflicts (3 decades internal wars in Afghanistan)
Secondary causes of degradation: droughts (Continiuosly 3 drought years also had a rule for burning plants in upper catchment areas), poverty / wealth (During internal wars, people were not able to go in other provinces and only they had access to agriculture land and livestock for their livelihood)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
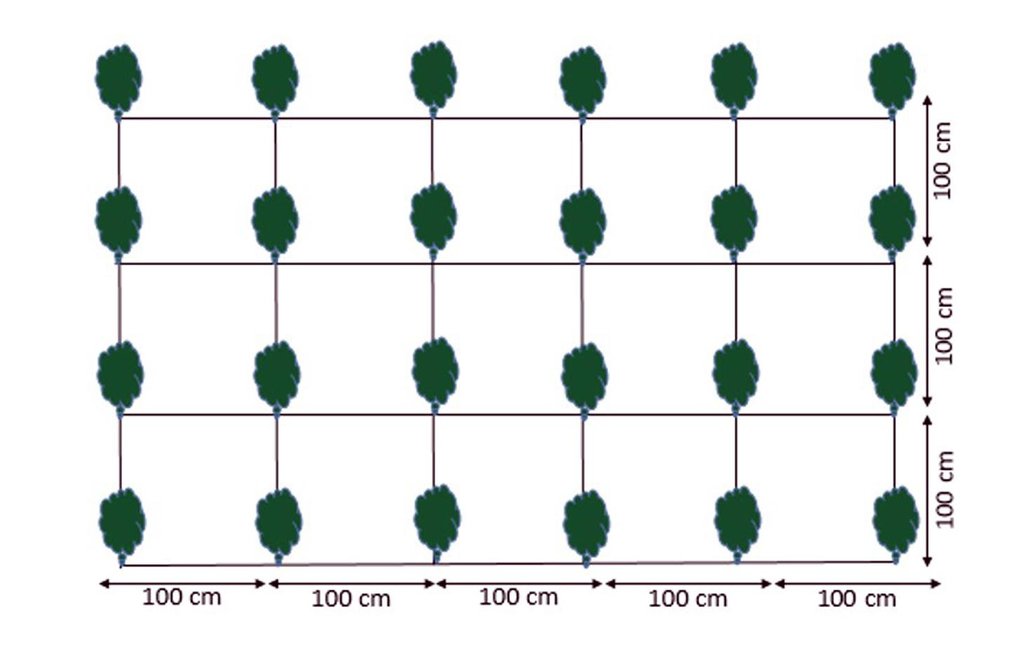
Cultivation plan of Ferula assa-foetida:
Plant to plant distance 100 cm.
Line to line distance 100 cm.
Seed depth 1-1.5 cm with;
3-6 seeds in one spot.
Location: Saighan watersheds. Bamyan
Date: 18/04/2016
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, Increase vegetation cover through cash crop
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida
Quantity/ density: 4 plant/m2
Remarks: plant to plant and line to line 100 cm
Mixed cropping / intercropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other domestic plants
Quantity/ density: 1 m2
Remarks: Growing domestic plants between Ferula assa-foetida plants
Cover cropping
Material/ species: Ferula assa-foetida and other plants cover the naked area
作者:
Shabir Shahem, HELVETAS Swiss Intercooperation, Afghanistan
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Afghani
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
67.69
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
5.17
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 12.92 | 12.92 | 25.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 115.0 | 115.0 | 25.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 127.92 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 1.89 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Hiring guard for protection of watershed from uncontrolled grazing |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
In 2015, the government of Tajikistan did not limit the export of seeds to Afghanistan.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Good quality seeds are available in Tajikistan. If the government of Tajikistan limits exporting seeds to Afghanistan, seed costs may increase.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 团体/社区
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
10% of the land users are rich.
35% of the land users are average wealthy.
45% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: The importance of off-farm income is marginal. However, hing cultivation in the watershed presents a viable opportunity to generate income off-farm for the involved communities. Hing can contribute up to >50% of off-farm income.
The watershed belongs to the communities and all households have the same rights.
The income is saved in a communal safe box and is spent for community development and emergency issues.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 社区/村庄
土地使用权:
- 社区(有组织)
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Watershed committee manage the income of Ferula assa-foetida productions through safe box investment
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Improve the economic opportunities of the community to generate income
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
5
SLM之后的数量:
25
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation coverage
土壤
土壤水分
SLM之前的数量:
10
SLM之后的数量:
30
注释/具体说明:
When the plants grow more, cover area and infilterate runoff
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
5
SLM之后的数量:
50
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation coverage
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Vegetation coverage
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Reduction of flash flood protect lower part resources
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
Should be cultivated away from flood stream area.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The estabIishment costs are high because hing yields only after five years. However, the investments and maintenance costs are quickly returned once hing can be harvested.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
750 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
In this calculation, the total number of families in 13 villages are considered.
There is no trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The establishment costs are too high.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increase in production of the valuable plants in the upland areas. |
| Protection of the lower lands from the risk of flash floods. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Introduction and increase in valuable cash crop cultivation in unproductive lands. |
| New income opportunity and increase in income of the community members. |
| Reducing flash flood through increasing vegetation coverage |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The watershed area is common land. | Need active watershed committee members to manage well (good governance). |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| People lack alternatives and have therefore no stake to protect the upland areas. | Negotiation with herders to reduce the number of their livestock because of introduction of as new alternative source of income. |
| Tangible benefits are only visible after five years. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
17/04/2016
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块