Artificial Grassed Waterway [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Paul Kahiga
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Grassed waterways
technologies_1320 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Chege Timothy
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Gathenya Mwangi
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Home Patrick
Jomo Kenyatta University of Agriculture and Technology
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Wamuongo Jane
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
肯尼亚
SLM专业人员:
Karanja Andrew
Kenya Agricultural Research Institute
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
KARI Headquarters (KARI Headquarters) - 肯尼亚有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Jomo Kenyatta University (Jomo Kenyatta University) - 肯尼亚1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Artificial grassed waterways are constructed waterways established for transportation of concentrated flow at safe velocities using adequate vegetation.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
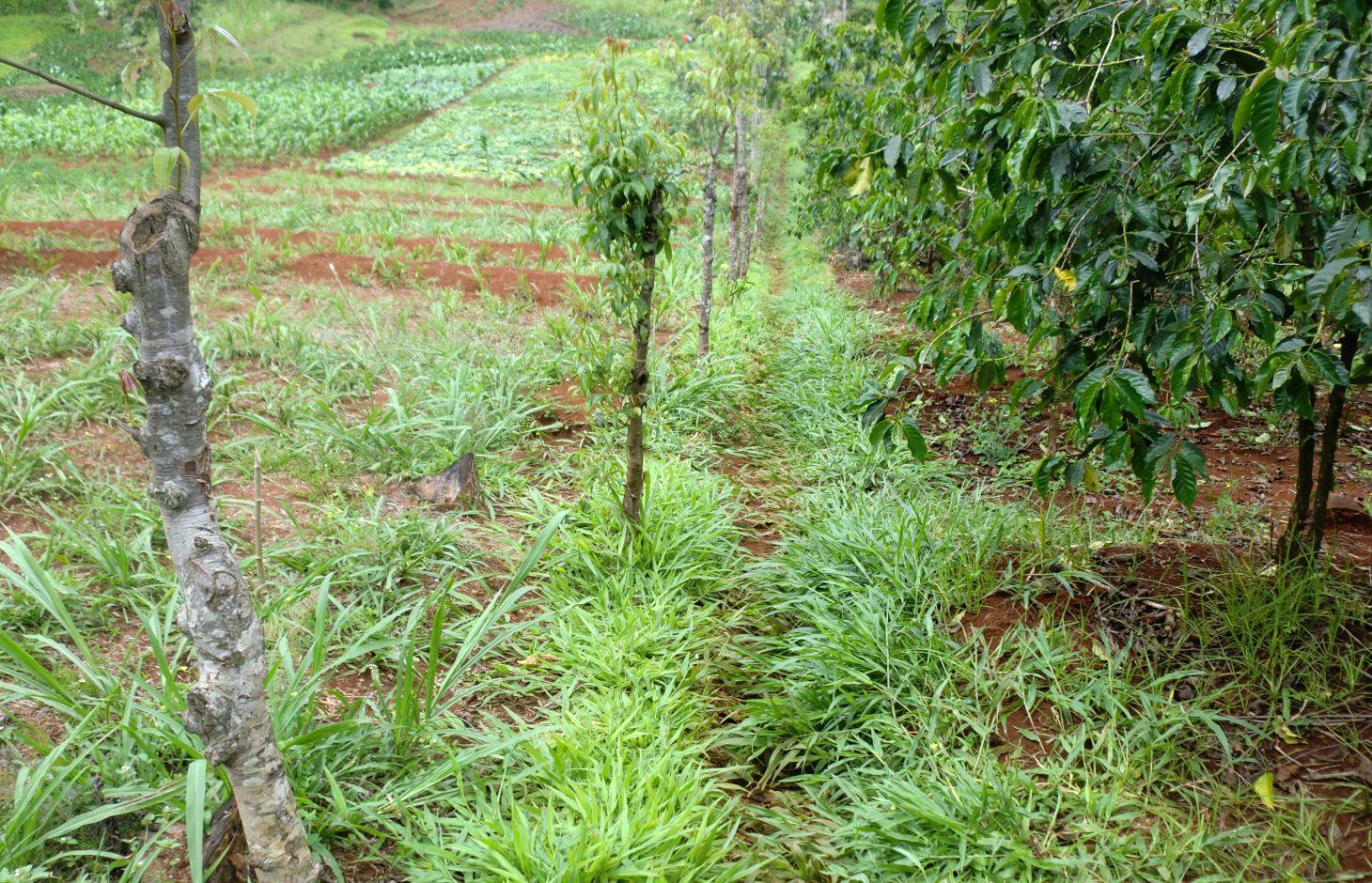
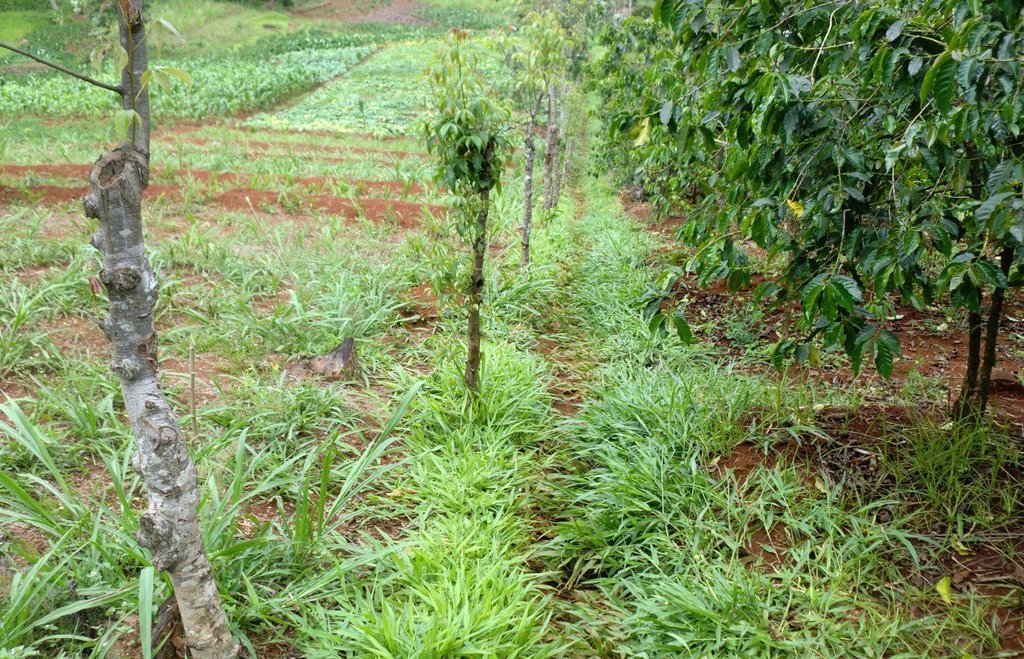
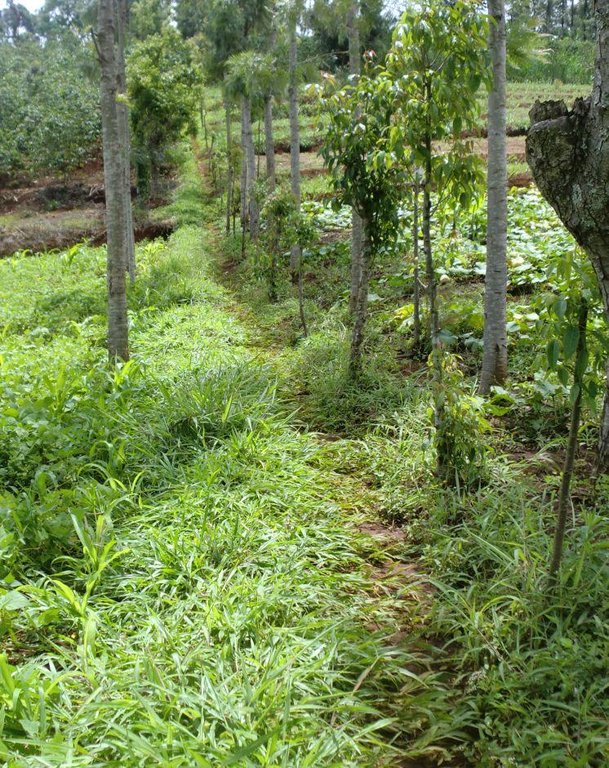
Grassed waterways are natural or constructed channels established for transport of concentrated flow at safe velocities using adequate vegetation. They are generally broad and shallow by design to move surface water across farms without causing soil erosion. The vegetative cover slows the water flow, minimizing channel surface erosion. When properly constructed, grassed waterways can safely transport large water flows down slope. These waterways can also be used as outlets for water released from contoured and terraced systems and from diverted channels. This practice reduces sedimentation of nearby water bodies and pollutants in runoff.
Purpose of the Technology: In Embu District, waterways are constructed to act both as a channel of disposing run-off into the river and a foot path. The type of vegetation that is used in this district is fodder grass called paspalum. They are used on slopes of less than 20% and where flow velocities do not exceed 1.8 m/s. They are also suitable in areas where rainfall intensities are high and excess run-off is frequent, such as slopes in humid regions, in semi-arid or arid regions where soil infiltration rates are low and run-off is concentrated, where cultivated fields have been treated with various types of terracing systems and drainage is necessary and on non-cultivated lands to connect run-off drainage structures such as diversions, cut-off ditches. Advantages of grassed waterways include flood damage prevention; erosion control; aesthetic value; water quality improvement; design based on landowner’s/farmer’s experience; soluble contaminant flow retardation; and dispersion of concentrated flow, thereby minimizing gully erosion.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Limitations of this practice include the cost of installation (e.g., grading slopes and vegetation establishment), loss of acreage for pasture or crops and the variability of effectiveness due to the uncertainty of runoff rate and frequency. Disadvantages of a grassed waterway include working around it with farm equipment, vegetative growth may be troublesome and the depth of the waterway limits it as a tile drainage outlet. The construction of the waterway will depend on the soil’s erosive potential. For example, a shallower waterway will result in an area with more erodible soil. Depending on the equipment and labor costs, grading, seed and fertilizer selected, the cost of establishing grassed waterways will vary. However in most cases where no additional structures are constructed on the waterway, grassed waterways are cheap to construct. Potential returns include fodder for feeding the farmers animals which is very common in Embu North District.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Eastern Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Embu North District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 1-10 平方千米
Map
×2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷物类 - 玉米
- 饲料作物 - 草
- 蔬菜 - 叶菜(色拉、卷心菜、菠菜和其他)
- coffee
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90, Longest growing period from month to month: May to July
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion on water ways
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion from the runoff
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
- 地表水管理(泉、河、湖、海)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A1:植被和土壤覆盖层
- A3:土壤表面处理
A3:区分耕作制度:
A 3.1:免耕
注释:
Type of agronomic measures: better crop cover, zero tillage / no-till
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
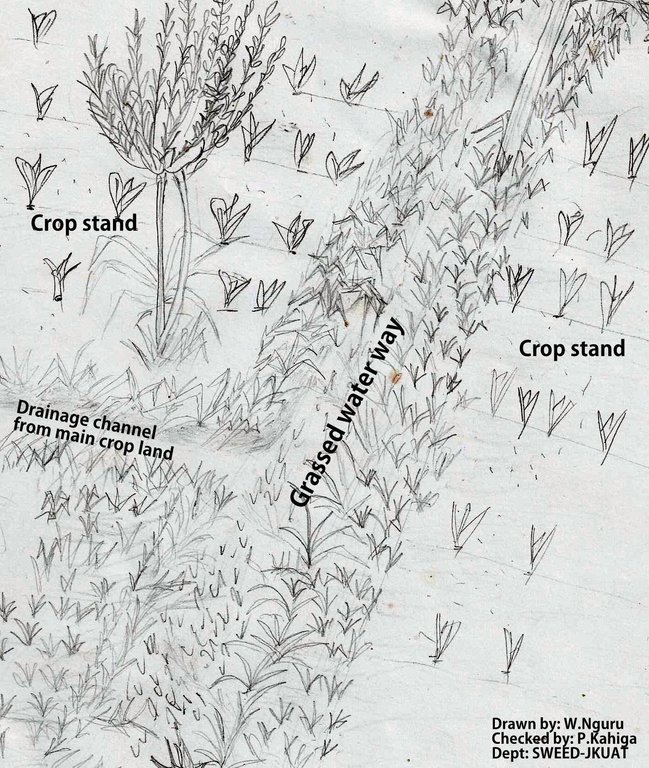
The technical drawing on the left shows a typical artificial grassed water way. Farmers plant grass along a pathway that acts as a both foot path and waterway to drain runoff from the main crop land along a drainage channel. Some times it is constructed along a boundary between to farms. As water flows down the slope through the grassed water way, the soil particles are filtered by the grass.
Location: Embu North District. Eastern
Date: 02/09/2011
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover
Secondary technical functions: increase of surface roughness
Better crop cover
Material/ species: Fodder grass
Quantity/ density: t/ha
Remarks: scattered
Zero tillage / no-till
Material/ species: Planting hole is made only where the grass is planted
作者:
Paul Kahiga, 62000-00200, Nairobi
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Kshs
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
100.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Purchase of gras seeds |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Planting grass | ha | 1.0 | 10.0 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Grass seeds | ha | 1.0 | 25.0 | 25.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 55.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.55 | |||||
注释:
Life span of the product (grass): 1 year
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Reseeding | 1 |
| 2. | Replanting of grass vines | 1 |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Reseeding | 10m | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Replanting of grass vines | 500, | 1.0 | 2.5 | 2.5 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 5.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.05 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Jembes and pangas
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
costs of grass seeds or plantings and labour during planting
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: Medium
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 100% of the land.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
畜牧生产
土地管理
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM/土地退化知识
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Fodder grass, pathways and acts as boundaries
生态影响
水循环/径流
水质
地表径流
多余水的排放
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Depends on the type of grass
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
缓冲/过滤能力
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: They do it on their own
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| In the artificial grassed water ways, the grass used is also used as a fodder grass. |
| The grass prevents soil erosion on the drainage channels. |
| Once the grass have been established, maintenance cost is relatively low. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Paspalum grass roots are favorite for moles which eat up other crops. | Use of grass or vegetation that is not favorite for moles |
| Sometimes, waterways may abstract passage of farm machinery | Avoid crossing the waterway with heavy machinery when the soils are wet. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
08/02/2011
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块