Rotational Grazing [土耳其]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Mehmet Zengin
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Kontrollü Otlatma (Turkish)
technologies_1398 - 土耳其
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Allowing livestocks to graze in pasturelands in a periodic and regular manner.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
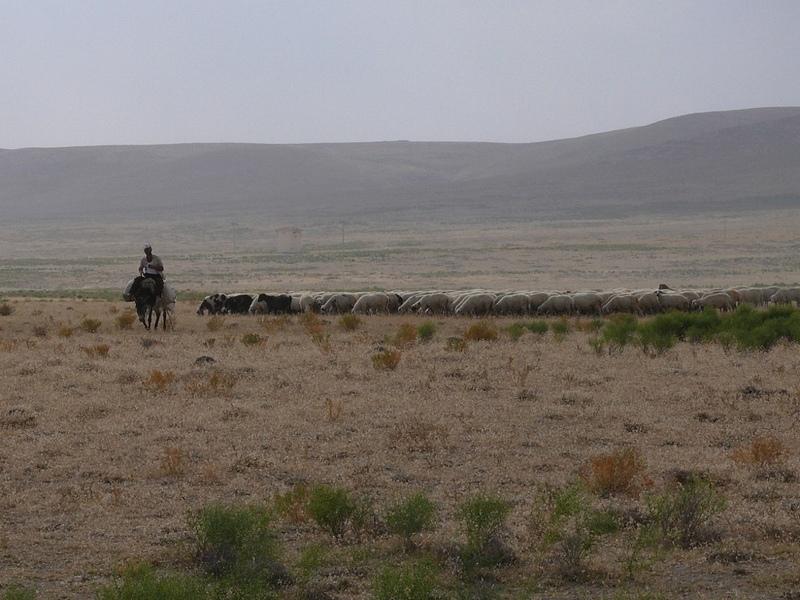
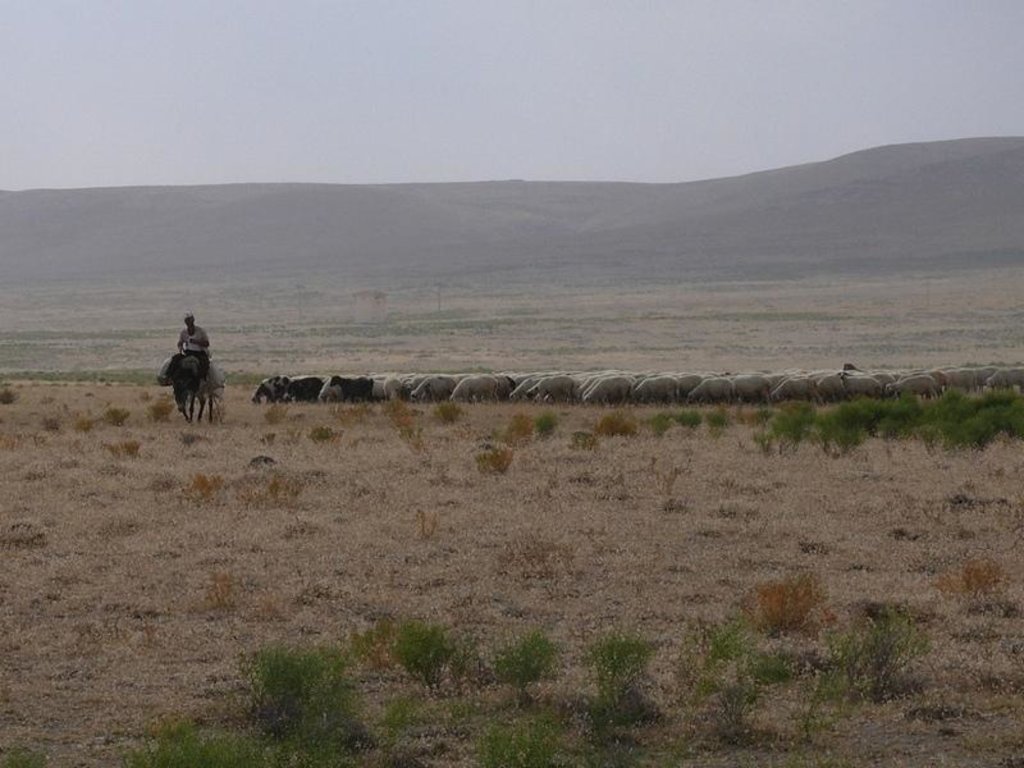
Sheep breeding has been very common for a long time in the Karapinar district. Sheep grazes in 50 km2 pasture area within the DESIRE hotspot during summers and they are fed in stables in winters. Pasture areas are degraded due to lack of rain, overgrazing and no-remediation. Farmers allow their livestock to go out from early spring onwards due to expensive feed costs in stables. A pasture can not feed sheep efficiently due to high numbers of sheep, early grazing and soil weakness due to high wind erosion. If a part of pasture is grazed one year, the remaining parts will be grazed coming year, in this way pastures are rested in rotation. So, in rested pastures soil erosion will be minimum since herb growth is good for the next year.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
土耳其
区域/州/省:
Konya
有关地点的进一步说明:
Karapinar
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 50 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 谷类 - 大麦
- 谷类 - 小麦(春季)
- 谷类 - 小麦(冬季)
- 饲料作物 - 三叶草
- 根/块茎作物 - 甜菜
- corn
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 240Longest growing period from month to month: Oct - MaySecond longest growing period in days: 180Second longest growing period from month to month: May - Oct

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 半游牧畜牧业
动物类型:
- 绵羊
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Annual precipitation is low (270 mm) while evaporation is high (750 mm) per year. Soils are thin because of wind deflation and degradation. As a result soil fertility is low and biomass is very poor. Negatively, farmers grow plants that need lots of water. Strip farming has not been performed and drip irrigation is not preferred method.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Irrigation water is scarce, pasture lands are very poor, electricity for irrigation is very expensive.
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: sheep in natural pastures.
Livestock is grazing on crop residues
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Water supply: rainfed
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 畜牧业和牧场管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- Rotational grazing
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施

管理措施
注释:
Main measures: management measures
Secondary measures: vegetative measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降
- Bl:土壤寿命损失
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Bh: loss of habitats
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Bl: loss of soil life
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Controlled grazing must be performed immediately.), droughts (Yearly temperature is increasing.), population pressure (Population increases parallel to the labourlessness.)
Secondary causes of degradation: disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Annual rain is low.), over abstraction / excessive withdrawal of water (for irrigation, industry, etc.) (Groundwater is excessively used to irrigate plants of high water demand.)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
注释:
Main goals: rehabilitation / reclamation of denuded land
Secondary goals: prevention of land degradation, mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, reduction in wind speed
Secondary technical functions: increase in organic matter, increase in nutrient availability (supply, recycling,…), increase of infiltration, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: C : perennial crops
Number of plants per (ha): 5000000
Perennial crops species: graminea and laguminosa
Layout change according to natural and human environment: densely herb growing
Major change in timing of activities: rotational grazing
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Turkish Liras
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1.3
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
17.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | sowing | early spring / once |
| 2. | fertilizing | early spring / once |
| 3. | Farmers training | winter / once |
| 4. | Barbed wire | winter / once |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 23.0 | 23.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 105.0 | 105.0 | 10.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | ha | 1.0 | 39.0 | 39.0 | 10.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 167.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 128.46 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 6 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | fertilizing | early spring / once a year |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | ha | 1.0 | 45.0 | 45.0 | 50.0 |
| 设备 | Machine use | ha | 1.0 | 16.0 | 16.0 | 10.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 61.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 46.92 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: tractor, fertilizing machine, tractor, screw
The cost were calculated according to prices of 2008 for seed, fertilizer and labour.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Seed and fertilizer costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Winter / 8 months
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: boreal
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is: Very low-low
Soil drainage/infiltration is: Medium
Soil water storage capacity is: Medium-very low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
仅供农业使用(灌溉)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: 5-50m (it decrease in summer and increase in winter)
Availability of surface water: poor/none (it is high in winter and very low in summer)
Seasonability of water quality and source of water pollution: For agricultural use only (irrigation) (Commonly ground water is used for agriculture. It is more saline in summer than winter seasons.)
Seasonability of water quality and source of water pollution: poor drinking water (treatement required) (Its quality is good in winter, while that of is bad in summer. Usually ground water.)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
机械化水平:
- 机械化/电动
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
70% of the land users are average wealthy and own 70% of the land.
30% of the land users are poor and own 30% of the land.
Market orientation: The production is slightly subsidised
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: 15-50 ha, 50-100 ha
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
500
SLM之后的数量:
650
注释/具体说明:
kg/da
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
500
SLM之后的数量:
650
注释/具体说明:
kg/da
饲料质量
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
moderate
畜牧生产
SLM之前的数量:
15
SLM之后的数量:
23
注释/具体说明:
sheep/da
生产故障风险
SLM之前的数量:
modarate
SLM之后的数量:
low
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水需求
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
170
SLM之后的数量:
130
注释/具体说明:
Numbers in USD. Cost for one sheep.
农业收入
SLM之前的数量:
30000 USD
SLM之后的数量:
50000 USD
注释/具体说明:
Income per year
社会文化影响
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
moderate
国家机构
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
moderate
冲突缓解
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
moderate
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
土壤有机物/地下C
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
植物多样性
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
风速
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
风力搬运沉积物
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
对邻近农田的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
modarate
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
注释:
Planting shrub species as rows perpendicular to wind direction which are tolaerant to drought and dust storms. So the other plants can survive more and soil erosion by wind will decrease.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Pasture maintenance costs are low. Only rotational grazing is done and seeding and fertilizing were realized periodically.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
145
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
50% of land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
145 land user families have adopted the Technology with external material support
Comments on acceptance with external material support: Sheep owners supported this technology idea. Because rotational grazing and pasture improving are easy and cheap.
10% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
30 land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
Comments on spontaneous adoption: Sheep owners or farmers liked rotational grazing model, but they had no knowledge about it. Government Farming Organization gave knowledge about the application of this measure.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: In both Karapınar and vicinity, farmers learned the new grazing technology and its benefits. Pasture grazing conflicts decreased gradually. The technology in question was a model for around settlements.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The conservation is easy to apply. How can they be sustained / enhanced? With education, and care, they can sustain the method. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Low expensive, usable and adoptable How can they be sustained / enhanced? No overgrazing, animal density mustn't be inceased. Instead, the government should support new seeding and fertilizing expenses and give knowledge about new techniques. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of pasture at initial phase of the method. | Feed crops production like sillage corn, welch or clover. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Conflicts among farmers. | With training they can overcome this problem. And they did not preserve new pasture areas sowed to graze their sheep. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块