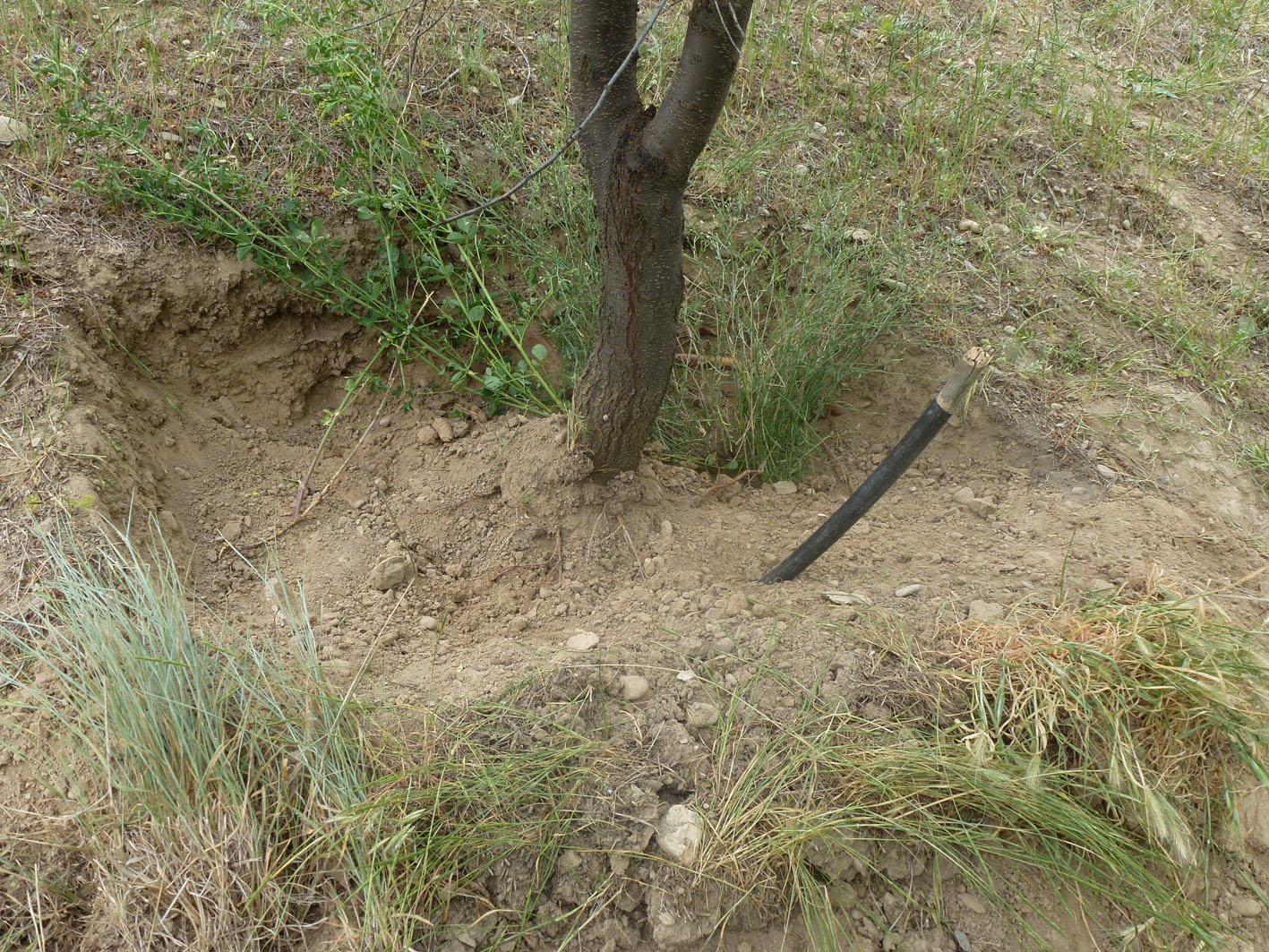
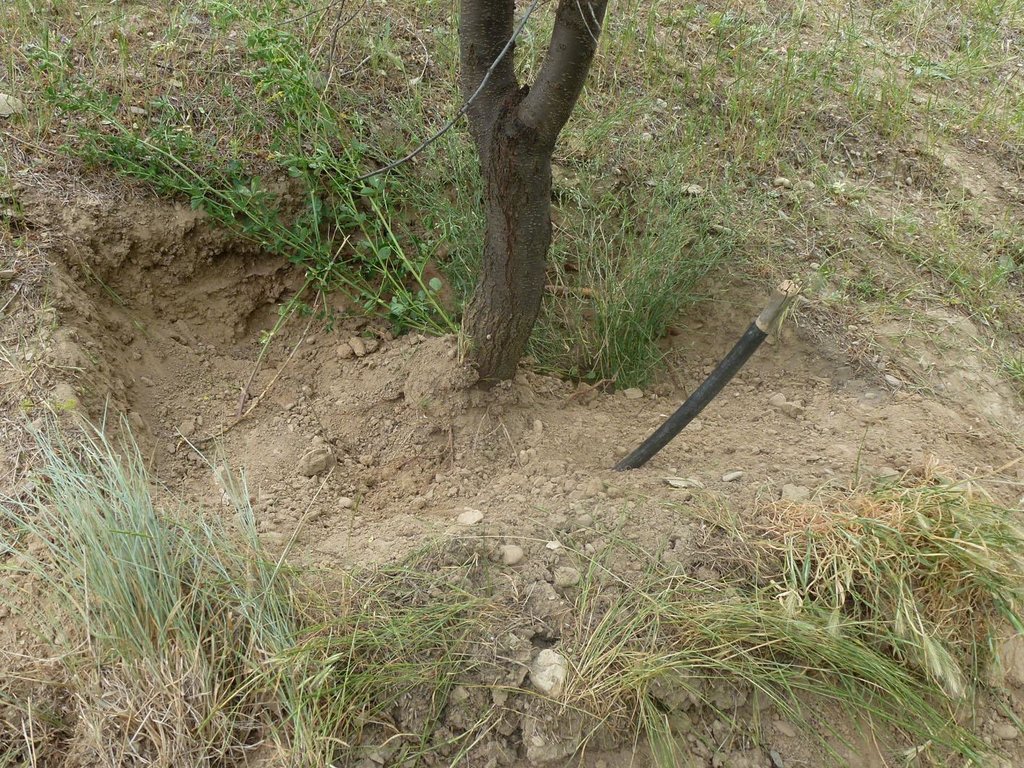
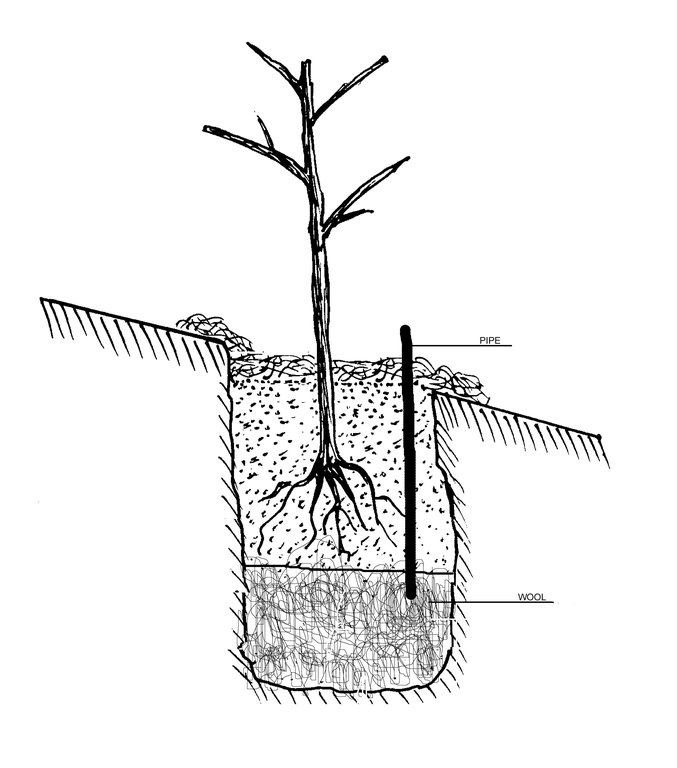
A woollen water retention bed installed under the roots of a tree irrigated by a pipe feed. [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sa'dy Odinashoev
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano, Joana Eichenberger
technologies_1508 - 塔吉克斯坦
- A woollen water retention bed installed under the roots of a tree irrigated by a pipe feed.: March 21, 2017 (inactive)
- A woollen water retention bed installed under the roots of a tree irrigated by a pipe feed.: July 28, 2017 (inactive)
- A woollen water retention bed installed under the roots of a tree irrigated by a pipe feed.: Nov. 2, 2021 (public)
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
土地使用者:
Esanov Ahmad
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Pilot Program for Climate Resilience, Tajikistan (WB / PPCR)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
The use of sheep's wool placed below the roots of fruit trees, to retain the water fed from a surface pipe.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
A bed of wool is placed within the hole before a fruit sapling is planted. The wool is fed water via a plastic pipe, which is used to saturate the wool with irrigated water. This provides a prolonged source of moisture for the trees which subsequently helps the tree survive intense dry periods and improves fruit yields.
This technology could also be applied using hay or pressed sawdust as an alternative to the wool to store the water.
Purpose of the Technology: The purpose was to implement a sustainable cost effective and easy irrigation process that will help increase fruit production in the Pejikant region of Tajikistan during the long hot dry summer periods. The process utilises readily locally available natural materials that are environmentally friendly.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: A 1m deep hole is prepared to plant the tree inside. Placed at the foot of the hole is layer of natural wool, approximately 10kg, and a plastic pipe is installed running from the wool layer to the above the surface. On top of the wool a bed of organic compost and/or high quality soil is placed to assist the growth and the sapling is planted in this. The sapling is then watered through the pipe. It is estimated that 10kg of wool will retain around 8 litres of water.
Natural / human environment: This region has low levels of annual precipitation and poor soil quality. Therefore, the land users are reliant on devising ways to improve the soil quality and irrigation practices to increase the amount of land that can be cultivated. With an increasing population and a heavy relaince on the land to support the people, there is a strong desire to bring into production land that in its current state is unproductive.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
Tajikistan, Sughd
有关地点的进一步说明:
Penjakent, Toshmunor
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land users developed this technology.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 乔木与灌木的种植
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 270Longest growing period from month to month: October-JuneSecond longest growing period in days: 90Second longest growing period from month to month: July-Septeber

森林/林地
植树造林:说明树种的起源和组成:
- 混交品种
产品和服务:
- 水果和坚果
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): The soil structure is very poor, with low density vegetation cover.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): There is a lack of irrigation water for the vegetation.
Plantation forestry: Fruit orchards
Forest products and services: fruits and nuts
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
注释:
Main measures: structural measures
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bq:数量/生物量减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Et: loss of topsoil, Bq: quantity / biomass decline, Ha: aridification
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing (Increasing numbers of livestock), other human induced causes (specify) (Disintegration of the irrigation system), change in temperature, war and conflicts (After the collapse of Sovet Union the irrigation pipes were stolen)
Secondary causes of degradation: change of seasonal rainfall, droughts
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.7
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | A 1m deep hole is prepared to plant the tree inside. | spring |
| 2. | Placing approximately 10kg of wool at the foot of the hole | spring |
| 3. | installing of plastic pipe from the wool layer to the above surface | spring |
| 4. | On top of the wool a bed of organic compost and/or high quality soil is placed to assist the growth | spring |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Digging hole | Persons/day | 0.1 | 20.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Plastic pipe | meter | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6.0 | |||||
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
The costs previously are based on the cost for providing enough pipe for one tree.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
In this situation, the wool is free to the farmers as they obtain it from their own sheep.
The labour is provided free of charge by the farmers themselves.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average: Also hilly
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is very low
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
非农收入:
- > 收入的50%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 10-50 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
100% of the land users are poor.
Market orientation of production system: Self consumption of fruits
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 租赁
用水权:
- 租赁
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
木材生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
收入和成本
农业收入
工作量
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
SLM/土地退化知识
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
It has helped improve the fruit harvests on land that was becoming increasingly degraded and would in the future be unsuitable for farming practices.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水的回收/收集
地表径流
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The impacts can be seen within the first growing season.
6.5 技术采用
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
注释:
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Some other people and projects expressed an interest.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| It improves the fruit harvest. |
|
It is easy to buy the wool. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Wool could be made available to other orchards. |
| It is cheap and easy to implement. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
It reduces the number of times the trees need to be irrigated. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The technology is so easy to implement, the information should be dispersed to other farmers. |
| It improves the soil moisture content of the orchards. |
|
The technology could be applied in very dry, desert conditions How can they be sustained / enhanced? It could be used in the more dry arid areas of the country. |
|
It increases the length of the planting season, as it holds the water in the ground for longer. How can they be sustained / enhanced? To implement the technology across a wider area. |
|
It can be applied to older, established trees, not just seedlings. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Educate the farmers about these methods. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| It still reliant on some water being available at crucial times of the year. | Piped irrigation to the land plot |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块