Gully rehabilitation [塔吉克斯坦]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Qobiljon Shokirov
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1541 - 塔吉克斯坦
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Boev Jahonbek
Tajik Soil Institute
塔吉克斯坦
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Tajik Soil Insitute (Tajik Soil Institute) - 塔吉克斯坦有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
NCCR North-South (NCCR North-South) - 吉尔吉斯斯坦1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [塔吉克斯坦]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- 编制者: Gulniso Nekushoeva
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
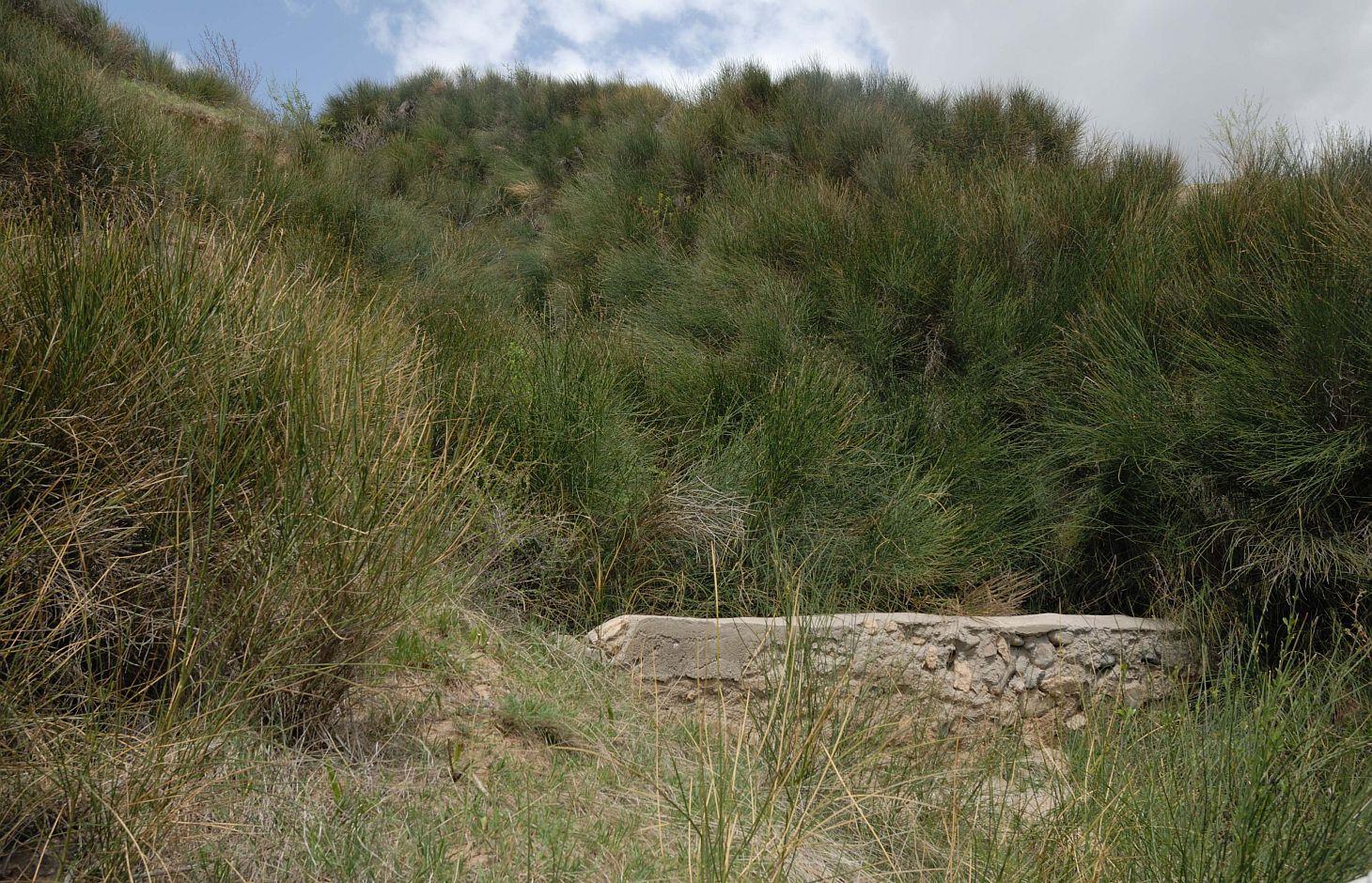
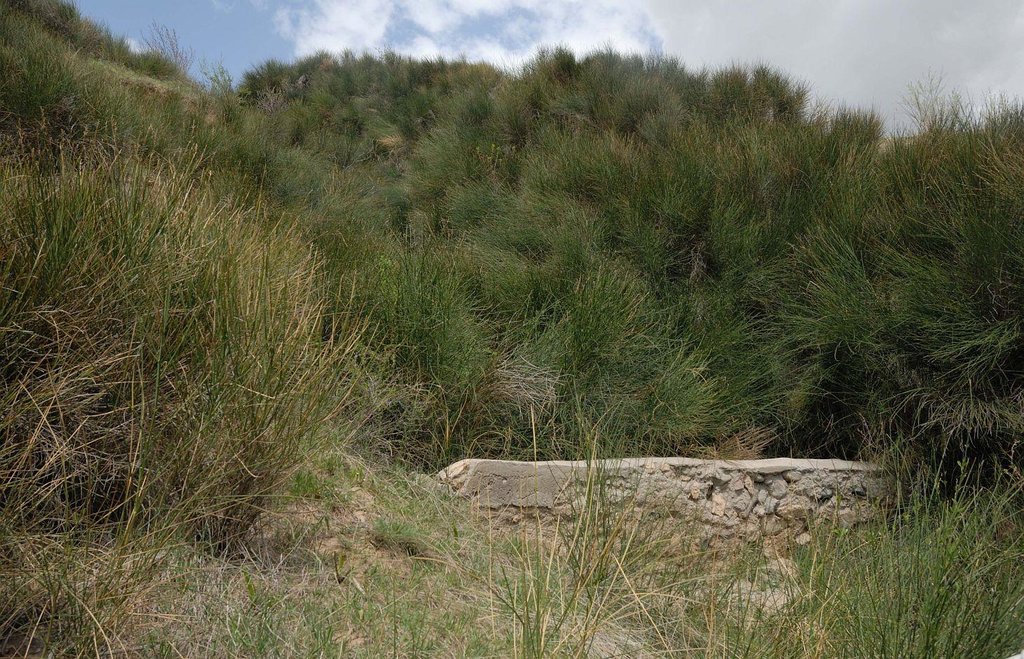
Gullies are stabilized through the establishment of a gabion and the plantation of spanish drok (Spartium junceum L).
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
The research station of the Soil Science Institute tested the stabilisation of large gullies created by water erosion through the plantation of Spanish drok (Spartium junceum L). The plantation of Spanish drok was introduced in 1972 for the first time in the research field station. Spanish drok is a perennial plant and has the ability of spreading fast through its roots and also via seeds. Most of the gullies are covered with Spanish drok by now. In total 150,000 seedlings were planted at the research station.
Purpose of the Technology: Water erosion is highly threatening croplands by washing away the fertile topsoil. Severe gullies have formed on the hilly slopes. The research station of the soil institute therefore selected a number of gullies to test different techniques of rehabilitation.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: In a first step a survey of gullies in the vicinity of the research station was conducted in order to determine an appropriate place for testing the stabilization. Spanish drok was planted and spread very fast through vegetative underground reproduction until the whole gully was covered. A gabion made out of stone and concrete was constructed at the foot of the gully. It contains a pipe to allow for outflow of excess water. Maintenance of the technology is less cost efficient and doesn't involve much cost associated activities.
Natural / human environment: The positive results of the implementation of this technology are very important as there is a great need for spreading it to other areas suffering from the same problems in Tajikistan. Spanish drok is generally not available in Tajikistan. Nowadays, the research station is providing seedlings for sale to interested farmers with a cost of roughly $ 0.40 per seedling.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
塔吉克斯坦
区域/州/省:
RRS
有关地点的进一步说明:
Javanon, Karsang
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 10-50年前
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
注释(项目类型等):
through the Karsang field research station
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- spanish drop
具体说明:
Longest growing period from month to month: April through November
注释:
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): loss of arable land, development of gullies, water erosion
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wg:冲沟侵蚀/沟蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wg: gully erosion / gullying, Wo: offsite degradation effects
Main causes of degradation: overgrazing, Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (It usually rains in March-April with duration of 20-45 minutes)
Secondary causes of degradation: wind storms / dust storms (Wind storms in winter), droughts (Hot summer months without rain)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
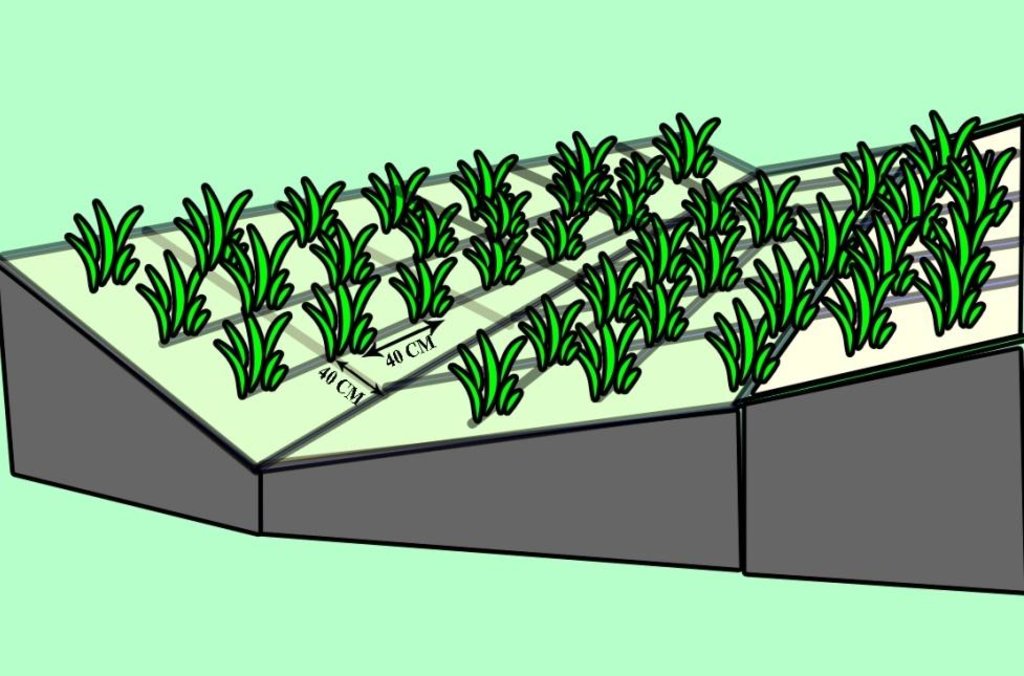
Scheme of how the Spanish Drok was planted on a eroded slopes of Karsang Research Field Station.
Location: Karsang Research Field Station. Javonon, Karsang
Date: 16-07-2012
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate
Main technical functions: control of concentrated runoff: retain / trap, improvement of ground cover, stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Scattered / dispersed
Number of plants per (ha): 5000
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.2
Trees/ shrubs species: Spanish drop.
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 25%
Wall/ barrier
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 1.2
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.2
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 3.5
Construction material (stone): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
Construction material (concrete): stone and concrete was used for the establishment of the gabion
作者:
Q. Shokirov
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Somoni
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
4.5
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
7.00
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selection of area | early spring |
| 2. | Planting of spanish drop | early march |
| 3. | Construction of gabion |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Selection of area | Persons/day | 30.0 | 30.0 | 900.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Planting of spanish drop | Persons/day | 36.0 | 30.0 | 1080.0 | |
| 劳动力 | Construction of gabion | Gabion | 1.0 | 700.0 | 700.0 | |
| 施工材料 | Stones | Gabion | 1.0 | 800.0 | 800.0 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 3480.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 773.33 | |||||
如果土地使用者负担的费用少于100%,请注明由谁负担其余费用:
Tajik Soil Institue
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 1 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | As the plant spreads through root propagation, the dispersal has to be limited by removing some of the plants every year |
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
buying seeds, tools, additional labor cost needs to be filled out more.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凹陷情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is low
Soil drainage / infiltration is medium
Soil water storage capacity is low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
10% of the land users are average wealthy.
90% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
Research station belongs to the State, but land is leased to the local farmers for use.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Spanish drok is used as firewood, increased availability
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
Prevents gullies from spreading and destroying production area
收入和成本
工作量
注释/具体说明:
No need to take care of eroded land every year
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Farmers are aware of erosion problems and benefits of Spanish drok
Livelihood and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
Many farmers have now understanding of mitigating soil erosion by water with the use of Spanish Drok.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
栖息地多样性
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游洪水
缓冲/过滤能力
对邻近农田的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
Full establishment of the Spanish drok takes about 10 years, however, through the establishment of the gabion some immediate benefits occur
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
NA
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 0-10%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology was implemented through the research station using their employees.
There is a little trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Earlier Spanish drok was not yet known among the farmers as it is an exotic species. A handful of farmers have been interested and adopted the technology in their plots. According to farmers from the station more people are interested applying such technologies as a protection for soil erosion and establishment of gabions.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Affordable technology for land restoration and degraded plots. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Effectively puts a halt to water erosion. |
| The bushes provide valuable firewood for the local land users. |
| A special microclimate is created through the establishment of the plants with humidity being preserved all year long and birds and bees seem to use it as a preferred habitat. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| The planting material is generally not available in Tajikistan, only now the research station is selling it to interested farmers, however, availability is still very localised. | Farmer to farmer spreading of planting material in addition to providing planting material to the different tree nurseries in the country. |
| Spanish drok is very easily inflammable in the dry summermonths due to essential oils which can pose a potential risk. | Good care has to be taken during the dry period and maybe some warning signs put up to tell people not to drop their cigarette stumps. |
| For the coverage of a whole gully with spanish drok about 10 years are needed as it happens through natural root propagation. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Field research station for analysing soil conservation measures [塔吉克斯坦]
Research Station of the Tajik Academy of Agrarian Science, Soil Institute conducting research on soil conservation and productivity in the rainfed hill zones of central Tajikistan.
- 编制者: Gulniso Nekushoeva
模块
无模块