Trees in the riparian area as a protective and aesthetic advantage at Naro Moru River [肯尼亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Manuel Fischer
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
technologies_1580 - 肯尼亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
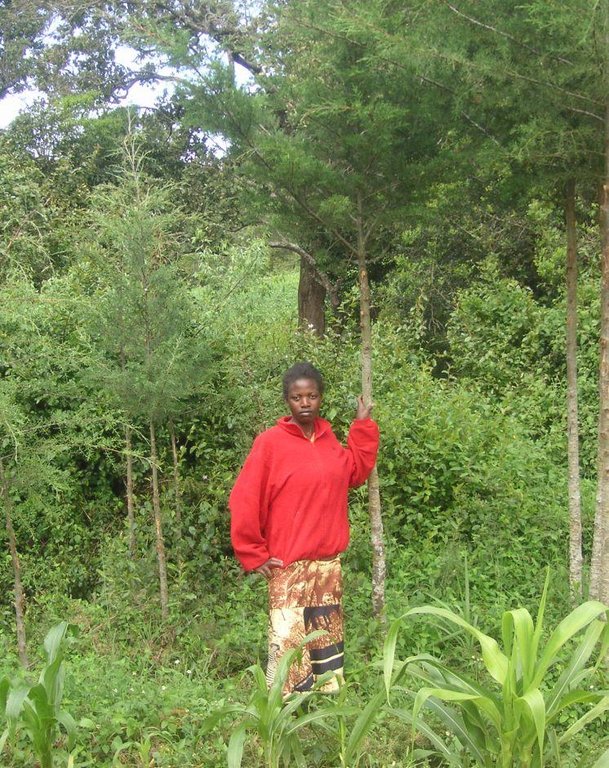
土地使用者:
Wanjiru Cecilia
肯尼亚
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Trees are planted along the riparian zone to stabilize the riverbank and to prevent degradation. The wood can be used to establish a building or to generate income on the market.
2.2 技术的详细说明
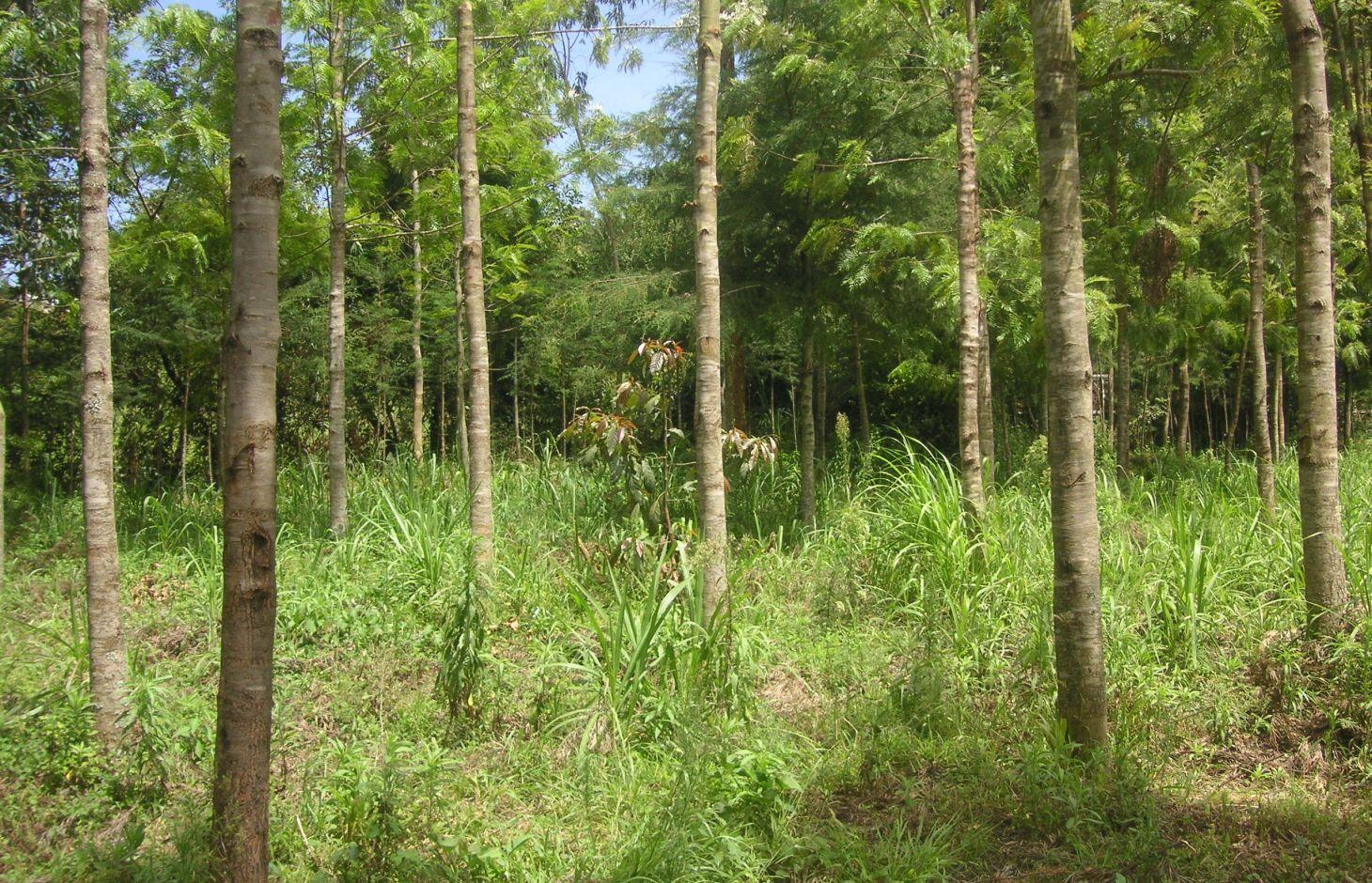
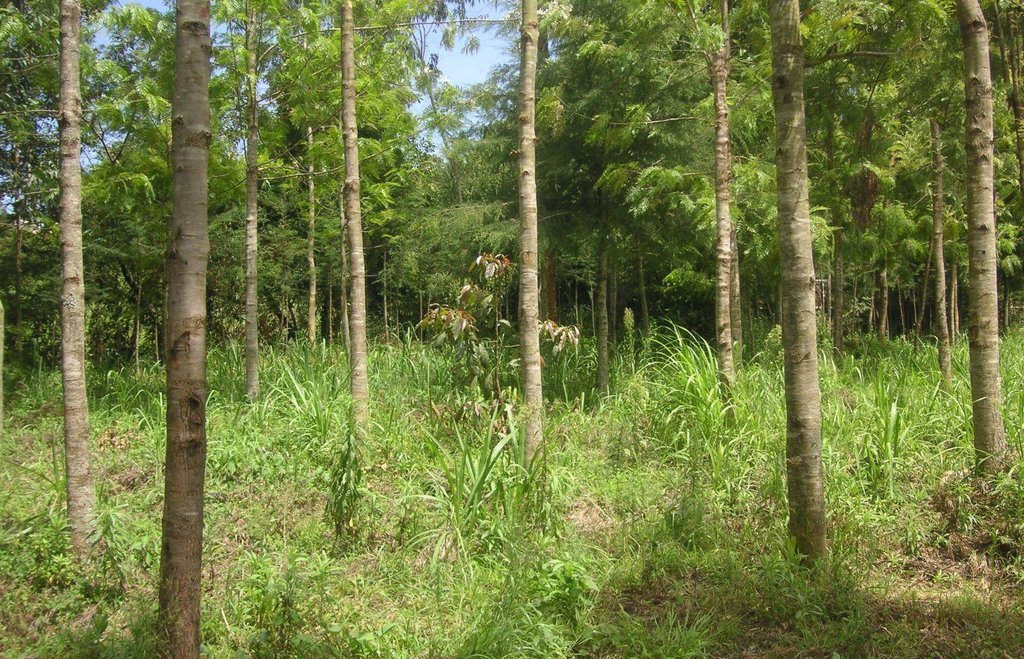
说明:
At the foot slopes of Mt. Kenya a farmer has developed a technology to protect the own land plot from riverbank erosion. The technology consists of three main measures: A wall along the riverbed, trees that are aligned on the wall as well as beside it and Napier grass wildly scattered between the trees. The wall was built on a highly exposed spot of the riverbank. Trees along and beside the wall ensure its stability. The combination of the two measures results in an effective protection of the riverbank in terms of erosion. Side effects of the technology are higher runoff during the dry season, better water quality due to less erosion and an improved riparian habitat for animals and plants.
Purpose of the Technology: For a small scale farmer, planting of trees can have advantages in an economic, an ecologic and an aesthetic point of view. The trees stabilize the soil, allow the riparian vegetation to establish, and prevent major damages through flooding. Furthermore, there are several advantages of an intact riparian zone, such as enhanced biodiversity, increased water quality as well as retention of agrochemicals. The trees also work as a kind of bank account, since the prices for wood are quite high. Trees can be cut and sold from time to time to generate an income that can be used for further investments like local entrepreneurship or building houses for family members. Last but not least, the farmer emphasized the beautiful appearance of the trees including the relatively cool micro- climate the trees are able to provide during the hot months of the dry period.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: The trees were planted during the rainy season. Braches are pruned regularly and provide mulch material as well as fire wood. When trees are reaching maturity they will selectively be cut and replanted. The Napier grass is cut regularly for fodder to be feed to animals. At this particular time, there is a regular hay yield (weed). Seedlings for trees and the grasses are produced on site. Occasional pruning ensures fuel wood supply.
Natural / human environment: The plot is situated at the western side of Mt. Kenya in its foot zone, a moderate hilly region. Actually, the foot zone is a transition area between the humid mountain forest above elevations of 2500 m.a.s.l and the semi-arid savannah zone below 2000 m a.s.l. Although the region is located in the rain shadow of Mt. Kenya, there is just enough precipitation (740mm) to sustain rain fed agriculture and the farmers even benefit from a water project. During the last decades, the region has experienced a still continuing population growth which increases population pressure in the area. The good accessibility and the moderate tourism allow even off-farm income-generation.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
肯尼亚
区域/州/省:
Kenya/Central Province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Naro Moru
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
The land user has enough space to afforest along the riparian. The main goals are to stabilise the riparian soil and to produce wood for use in the future.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 农林业

农田
- 一年一作
年作 - 具体指明作物:
- 饲料作物 - 草
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 90 Longest growing period from month to month: april to may Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: october to november

森林/林地
- 植树造林
树木类型:
- 柏木属物种
- 银桦
产品和服务:
- 木材
- 薪材
- 自然保持/保护
- 娱乐/旅游
注释:
Trees/ shrubs species: Cypress, Grevillea, indigenous trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Napier grass
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Surface water pollution and riverbank degradation as well as a diminished habitat of riparian flora and fauna.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): An unstable riparian zone being eroded by the river and unattractive aesthetics.
Problems / comments regarding forest use: The purpose of the forest is mainly in a protective way. Later on, as soon as the trees are large enough, selective felling for construction is planned.
Forest products and services: timber, fuelwood, nature conservation / protection, recreation / tourism
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Forests / woodlands: Fp: Plantations, afforestations
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 天然和半天然森林管理
- 改良的地面/植被覆盖
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

结构措施
- S6:墙、障碍物、栅栏、围墙
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures
Secondary measures: structural measures
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -linear, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bs:质量和物种组成/多样性的下降

水质恶化
- Hp:地表水水质下降
- Hw:湿地缓冲能力下降
注释:
Main type of degradation addressed: Wr: riverbank erosion, Bs: quality and species composition /diversity decline, Hp: decline of surface water quality
Secondary types of degradation addressed: Wt: loss of topsoil / surface erosion, Bc: reduction of vegetation cover, Hw: reduction of the buffering capacity of wetland areas
Main causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use, population pressure, education, access to knowledge and support services
Secondary causes of degradation: floods
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
注释:
Secondary goals: mitigation / reduction of land degradation
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Indigenous trees, a wall and Napier grass are installed between the agricultural land and the river. The wall prevents erosion at a very endangered spot. The trees and the grass provide fodder and wood.
Location: Naro Moru. Nyeri / Central Province
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase of infiltration, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, stabilization of riverbank by trees and grasses
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides)
Aligned: -linear
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 200
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 0
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 2
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): 800
Trees/ shrubs species: Cypress, Grevillea, indigenous trees
Fruit trees / shrubs species: Napier grass
Wall/ barrier
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.5m
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 2m
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 10m
作者:
Manuel Fischer
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.70
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Setting up a tree nursery | |
| 2. | Planting seedlings | during rainy season |
| 3. | Establishment of wall |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Setting up a tree nursery | Persons/day | 5.0 | 3.3333 | 16.67 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Planting seedlings | Persons/day | 25.0 | 3.3333 | 83.33 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Establishment of wall | Persons/day | 5.0 | 3.3333 | 16.67 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 116.67 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 116.67 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Replanting trees that dried up | |
| 2. | Cutting the Napier grass and pruning trees | during the rainy seasons = 4 months a year. 3 times a month |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Replanting trees | Persons/day | 3.0 | 3.3333 | 10.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cutting the Napier grass and pruning trees | Persons/day | 12.0 | 3.33333 | 40.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 50.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 50.0 | |||||
注释:
Establishment has been carried out over a time period of 5 years. Considering this time frame, the establishment costs are smaller than the maintenance costs.
The costs per hectare were calculated for a riparian area with the length of 100 m and a width of 10 m, since hectares are difficult to apply in a riparian context. The determining factor for the costs is labour. In this case, the labour costs are quite high because the seedlings were produced in the own nursery. This explains the high labour costs. Some of the seedlings had to be replanted, because they dried up. The required equipment like a spade is available on nearly every farm or can be borrowed from neighbours and is thus not added to the costs.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
NS-Daten Eliza
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics. source: http://en.climate-data.org/location/103473/
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Altitudinal zone: 2020
Slopes on average: Land plot has a slope between 5% and 9%
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil texture: mixture, because it is not red
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity very low - low
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: <5 mjust along the river, deeper ground water level 50-100m
Water quality (untreated): From a water project
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Species diversity: Also medium
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: A clan uses the land commonly. Besides the base family (mother, father, son), the grandmother and an uncle use parts of the land. All of them apply the protective technologies in the riparian.
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
Average area of land owned or leased by land users applying the Technology: < 0.5 ha for Riparian forest.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
Mostly small scale farmers are using the land.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Napier grass yield has increased
木材生产
注释/具体说明:
Before, there was only little wood production
社会文化影响
SLM/土地退化知识
Aesthetics
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
多余水的排放
土壤
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
生物多样性:植被、动物
有益物种
减少气候和灾害风险
洪水影响
其它生态影响
Riverbank erosion
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
| 局地风暴 | 好 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
非常消极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
非常积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
1 household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The WRUA has been distributing seedlings among the riparian farmers. Quantification is not possible.
100% of land user families have adopted the Technology without any external material support
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
There is a recreational aspect of the riparian zone. Especially during hot days the farmer is enjoying the slightly colder temperatures because of the canopy and the cooling stream. The aesthetic aspects of the riparian are also enhanced. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If the canopy of the riparian is maintained, it can serve still as recreation area and convince with beautiful looks. |
|
Long term benefits in terms of wood and timber provided by the trees. How can they be sustained / enhanced? If trees are not chopped too early, they will have a good price on the market. |
|
The maintenance of the riparian is not tiring and still gives a good harvest. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Benefits can be sustained by continuing the management practices. |
|
Diversification: Formerly, there was maize at the river, but it died due to cold temperatures. Forests do not die due to frost. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Every plant has its special needs that should be kept in mind. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
Wood production through selective felling is sustainable. How can they be sustained / enhanced? No widespread felling of trees, only selective intervention. |
|
Fodder production enables the keeping of cattle. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Before dry periods, some fodder should be stored to ensure fodder supplies. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| There is less crop yield, because an area of the plot was formerly used for maize production and now it is part of the riparian. | The productive and protective benefits of the riparian overcome decreased size of the agricultural plot. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块