Pipe Irrigation [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Pipe Sinchai
technologies_1599 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Karki Nimisha
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Niraula Archana
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Anish Adhikari
Kathmandu University
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Kathmandu University (KU) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Pipeline Irrigation [尼泊尔]
The process and measures taken to draw water from nearby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
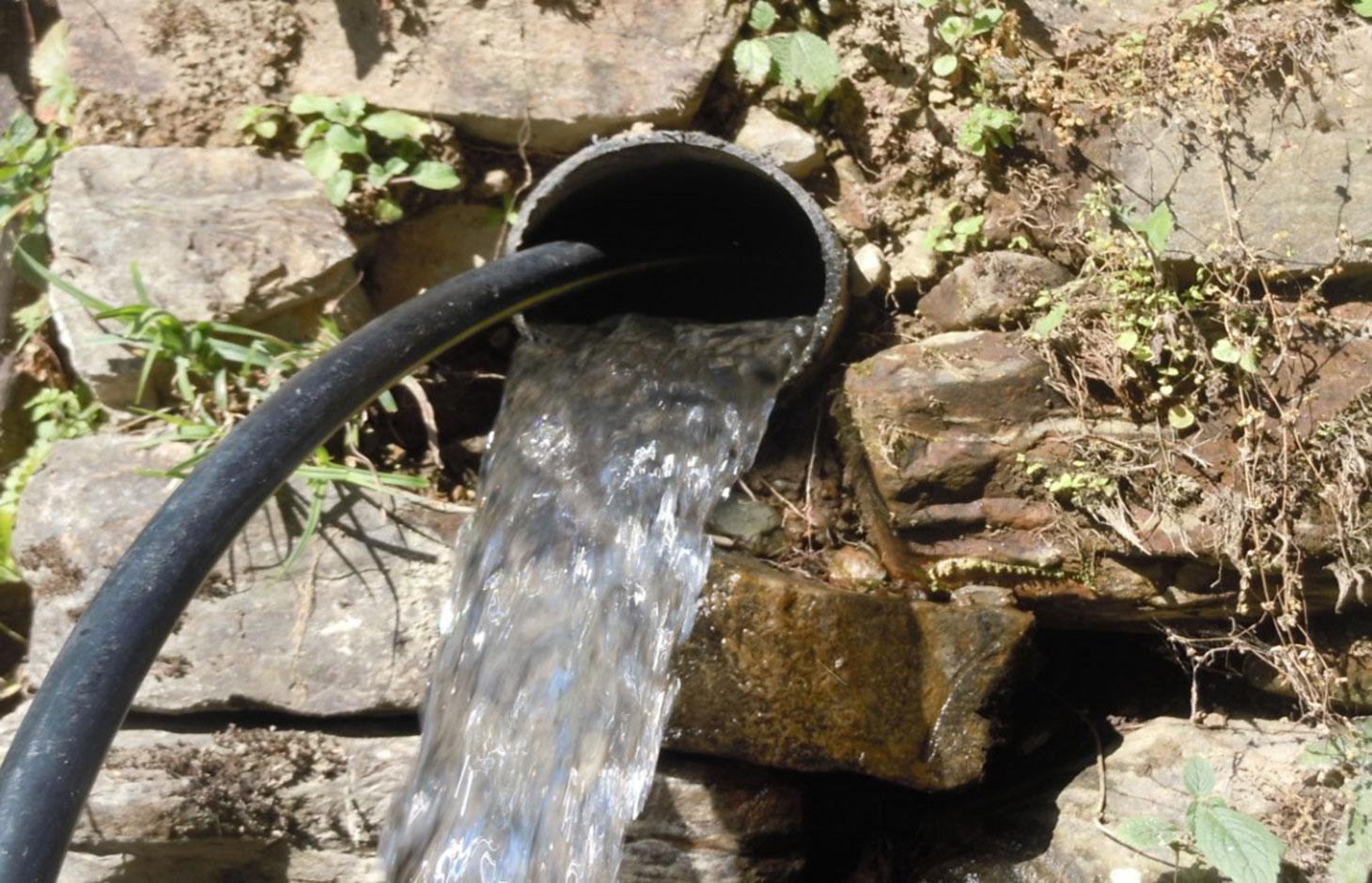
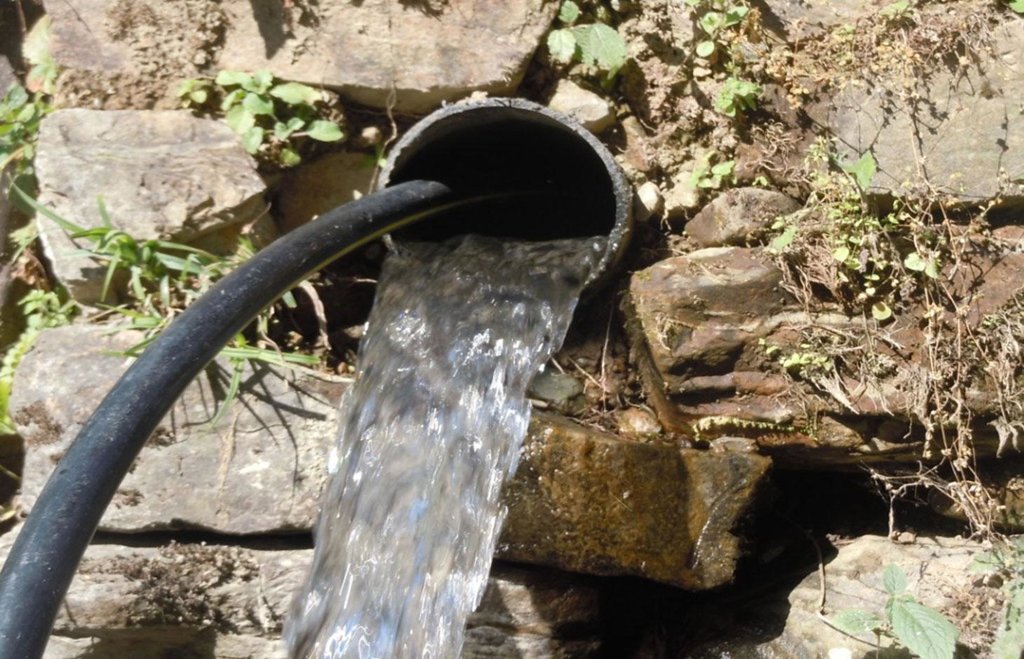
Waterways and pipelines to draw water from closeby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
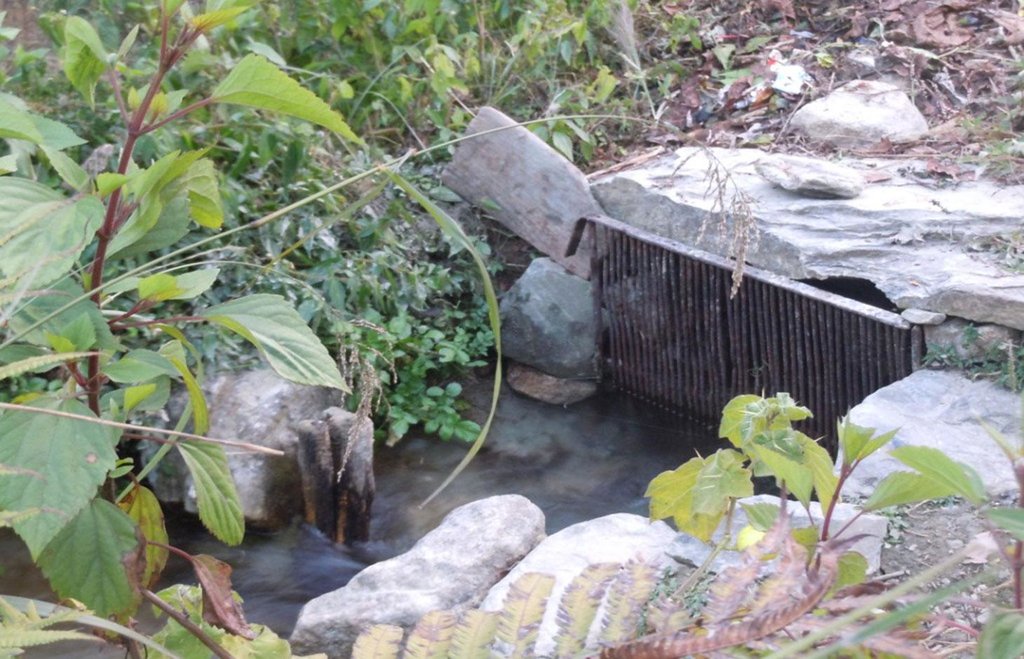
The technology involves the construction of diversion and waterways from the rivers to draw ample water sufficient for distribution to the different houses of the V.D.C .
Water is drawn from two rivers via three routes, one route from 'Polsing' river and the two other from 'Ghatte river' .
In the upper areas, open digging is done up to 700 meters from the source and waterways are created.
However, in lower areas due to more stones, creation of waterways was not possible, hence pipelines had to be created over 425 meters.
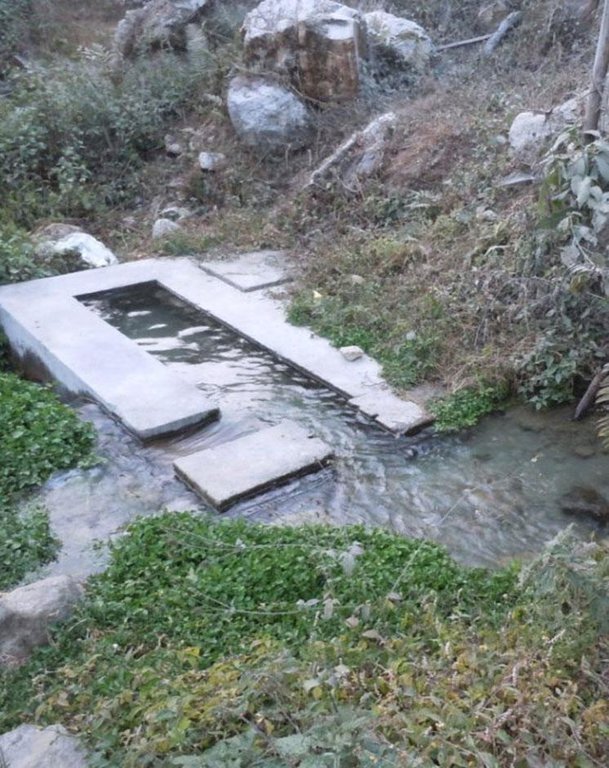
The pipeline opens in each house into a small reservoir for use in irrigation and household.
Purpose of the Technology: Mainly for conservation of land and soil along with provision of water to agricultural land.
Before the implementation of this technology, land was semi arid with few perennial crops.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Initially established and then managed by the combined effort of the users. All activities done voluntarily using easily available tools of daily usage by members of the households who benefit and make use of the technology. The only costs made were for the purpose of making pipelines which was borne half by the government and half by the land-users themselves.
No maintenance activities have been carried out so far, yet monthly collection of Rs 20 is done from each house which is stored for future use.
Natural / human environment: Chyamrangbesi VDC is a valley with subtropical type of climate. Precipitation level ranges from 750mm to 1500mm for about four months during the monsoons. The winters are dry however and hence the growing period is from 79 to 179 days, making the area semi-arid depending on the agro-climate division. Since the area falls on hill slopes with 8.16% steep so the technology is applied with convex manner.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
区域/州/省:
Chyamrangbesi
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kavre
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
28.97
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 28.97 km2.
Same technology covers entire area with water source
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Initial work started in 2004, improvements in the technology each year
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 多年一作(非木材)
每年的生长季节数:
- 3
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 150, Longest growing period from month to month: Karthik (October) - Chaitra (April) Second longest growing period in days: 120, Second longest growing period from month to month: Asadh(June) - Ashwin (September)

水道、水体、湿地
- 排水管道、水道
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land semi-arid and dry, hence only few selected crops could be grown due to lack of sufficient water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Land could not be utilised properly due to lack of sufficient water for crops, dry condition.
Future (final) land use (after implementation of SLM Technology): Other: Ow: Waterways, drainage lines, ponds, dams
3.3 由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?
由于技术的实施,土地使用是否发生了变化?:
- 是(请在技术实施前填写以下有关土地利用的问题)

农田
- 一年一作
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 灌溉管理(包括供水、排水)
- 引水和排水
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

结构措施
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
- S5:大坝、集水斗、水池
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Ha:干旱化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development (Construction of roads, not properly engineered, difficult to travel by and highly risky.), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (In the 3 months of monsoon), inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …) (Roads construction and its use by large vehicles frequently)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
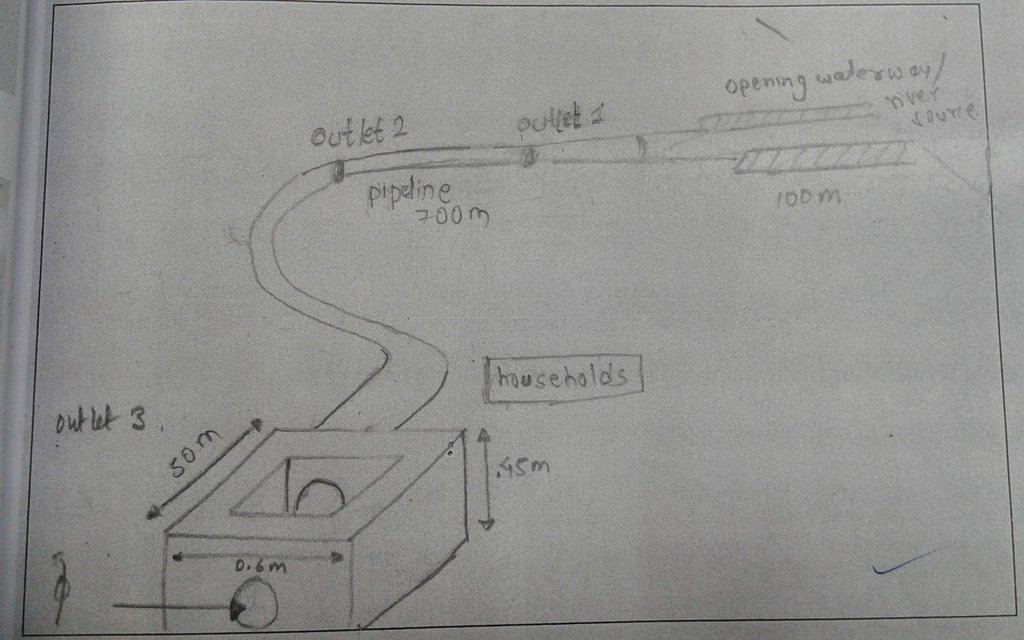
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
The drawing shows the path followed by the pipe irrigation, the various feautres
Location: Chamryangbesi VDC
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Designed by engineers
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Constructed by land users)
Main technical functions: improvement of ground cover, water harvesting / increase water supply, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Secondary technical functions: stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), water spreading, increase of biomass (quantity)
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100
Waterway
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): n/a
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 700
Dam/ pan/ pond
Vertical interval between structures (m): n/a
Spacing between structures (m): 50
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.45
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.6
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 50
Construction material (earth): soil excavated and used to make bunds of the water ways
Construction material (concrete): used to make small reservoirs in houses
Construction material (other): pipes : to transfer water from the source to houses
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 15%
If the original slope has changed as a result of the Technology, the slope today is: 0%
作者:
Anish Adhikari
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
rupees
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
98.47
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Farmers cut into land from the source in suitable directions to bring water to their houses | Dry season |
| 2. | Fitting of pipes | dry season |
| 3. | Construct small openings/reservoirs | dry season |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Farmers cut into land from the source in suitable directions to bring water to their houses | mandays | 45.0 | |||
| 劳动力 | Fitting of pipes | mandays | 15.0 | |||
| 劳动力 | Construct small openings/reservoirs | mandays | 15.0 | |||
| 施工材料 | Pipe + cement | ha | 1.0 | 50.0 |
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Area to be covered by the pipeline and distance from the source are the most determinate factors.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Monsoon rains, dry winter
农业气候带
- 半干旱
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 凸形情况
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Varies from shallow to deep
Soil texture: Soil texture varies from place to place
Soil fertility: Medium (ranked 1, varies according to water availability) and low (ranked 2)
Topsoil organic matter: Use of manure necessary for maintaining productivity
Soil drainage/infiltration: Good
Soil water storage capacity: Medium (No groundwater found)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
过量
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, Groundwater use not much evident) and <5m (ranked 2)
Availability of surface water: Excess (ranked 1, Floods occurs in case of heavy seasonal rainfall; supply of water is good and sufficient) and good (ranked 2)
Water quality (untreated): Good drinking water (perennial surface water distributed through pipelines)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
- 丰富
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 100-200 persons/km2
Annual population growth: > 4%; 5%
40% of the land users are rich.
60% of the land users are average wealthy.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 中等规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
饲料生产
饲料质量
畜牧生产
木材生产
生产故障风险
生产区域
能源生产
注释/具体说明:
Water Mill ('Pani Ghatta')
水资源可用性和质量
饮用水的可用性
饮用水的质量
家畜用水的可用性
家畜用水的质量
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
健康状况
文化机会
娱乐机会
社区机构
国家机构
SLM/土地退化知识
冲突缓解
社会经济弱势群体的情况
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
水质
水的回收/收集
地表径流
多余水的排放
地下水位/含水层
蒸发
土壤
土壤水分
土壤覆盖层
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
养分循环/补给
盐度
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
植物多样性
动物多样性
有益物种
栖息地多样性
害虫/疾病控制
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
火灾风险
风速
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
旱季稳定可靠的水流
下游洪水
下游淤积
地下水/河流污染
缓冲/过滤能力
风力搬运沉积物
对邻近农田的破坏
对公共/私人基础设施的破坏
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 不好 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 未知 |
注释:
In cases of excess water availability, pipelines have been made to divert water to mills , that uses water to rotate blades and grind crops.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology. Every year the irrigation line is being increased to encompass more houses of the VDC
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Water is equally available to all the households, with minor level decrease in the dry season. |
| The crop, fodder production has increased |
| Reduced top soil loss due to erosion |
| Maintenance requirement minimum |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| More houses could be Incorporated in the technology | Involvement of more local inhabitants so more households could benefit from the technology |
| Lack of Monitoring by Experts | Monitoring of SLM Experts could help improve the existing system to make it more sustainable and efficient. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
02/12/2012
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Pipeline Irrigation [尼泊尔]
The process and measures taken to draw water from nearby rivers for irrigation and household purposes.
- 编制者: Sabita Aryal
模块
无模块