Vegetated graded soil bund [埃塞俄比亚]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Deborah Niggli, Alexandra Gavilano
Yeafer Erken (Amharic)
technologies_1601 - 埃塞俄比亚
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Water and Land Resource Centre Project (WLRC)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Community Organizations and Mobilization for Soil and Water … [埃塞俄比亚]
Community mobilization for soil and water conservation work in a watershed planning unit is an approach for collective action by organizing all active labor forces living in the kebele/peasant association into development group of 20-30 members and further divide into 1:5 work force to implement construction of soil and water …
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [埃塞俄比亚]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Vegetated graded soil bund is a soil conservation practice meant for cultivated lands and constructed by excavating graded channel on upper side and develop embankment on lower side which is planted with grass or shrub species in order to control soil erosion and drain excess runoff implemented through community mobilization.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
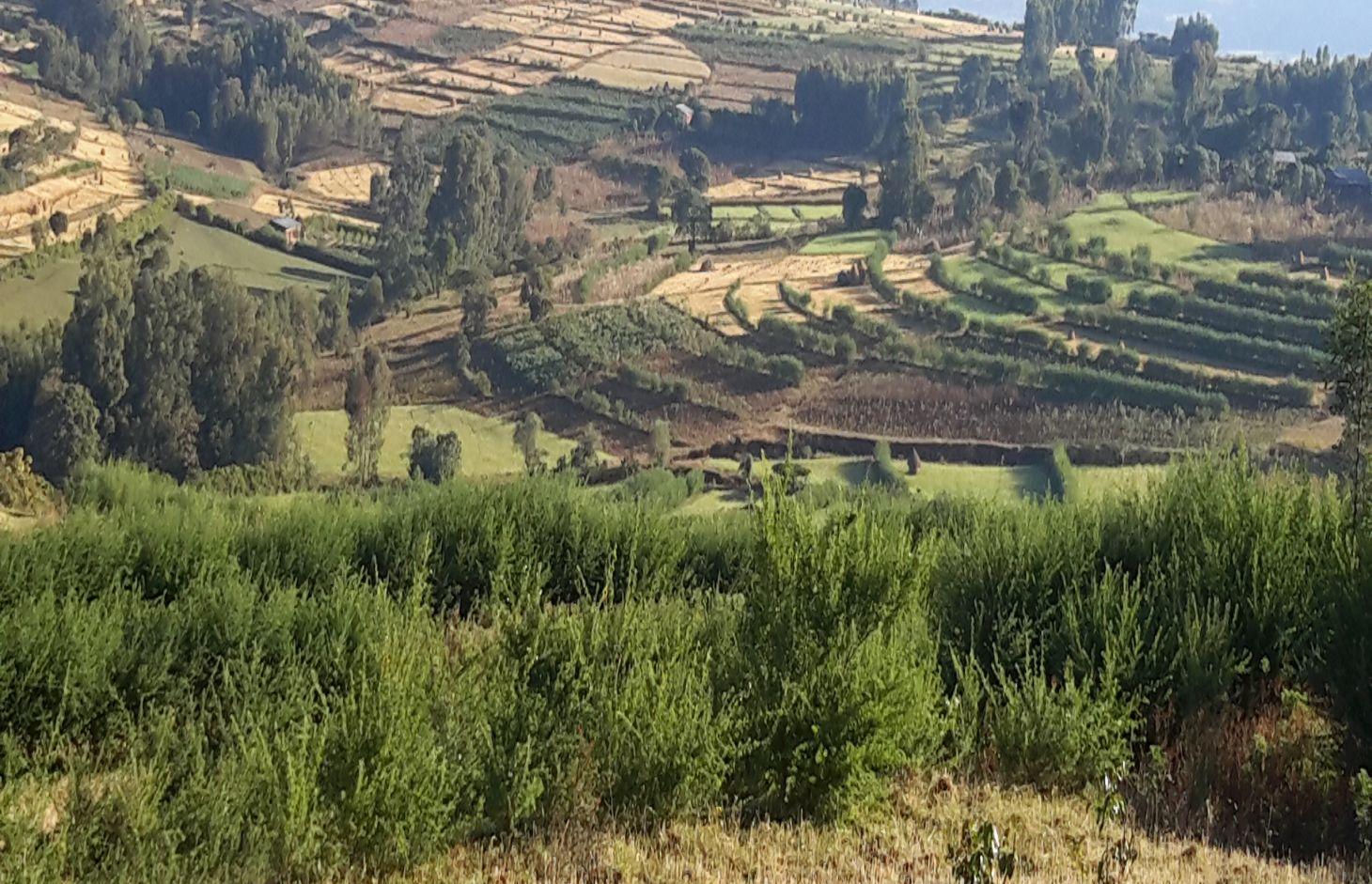
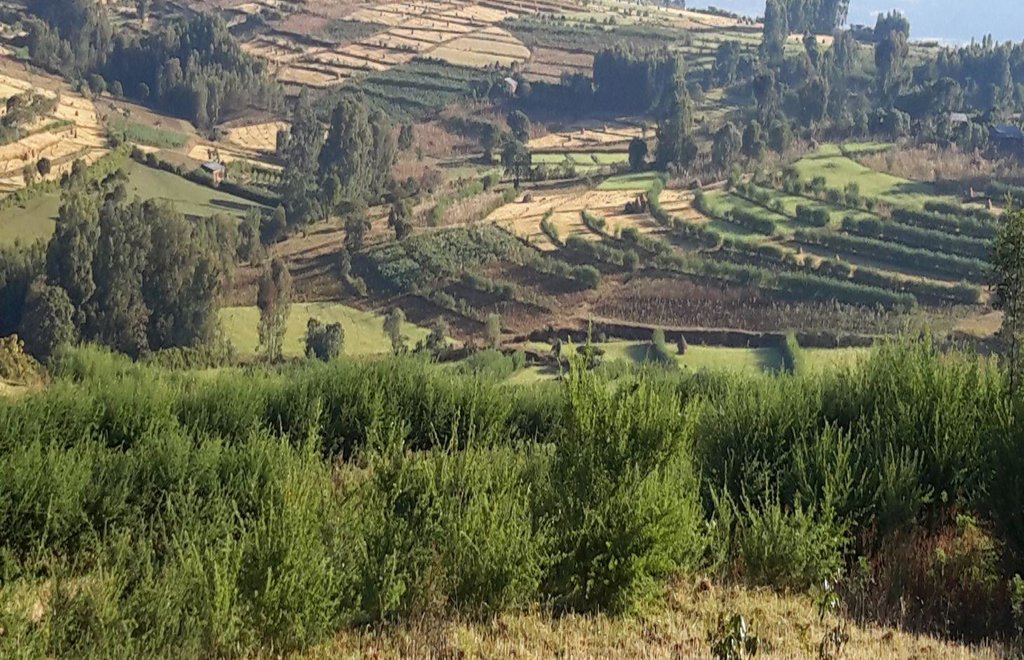
Vegetated graded soil bund is a practice or soil conservation technology for cultivated lands and constructed by excavating graded channel and form embankment. It is practiced in areas where there is excess runoff to be disposed and where there is no stones available for construction. The design specifications (ditch gradient, width and height) and layout (spacing/vertical interval) vary on the amount of excess runoff and slope of the land. Soil bund construction begins from top of the catchment. Cut off drains are constructed on top of the catchment and where needed to drain excess runoff to well stabilized natural or man-made waterways. this helps to reduce runoff impact on gullies. The bund ditch/channel should be sufficient enough to drain excess runoff safely without causing channel erosion and creating downstream damages. At same time the embankment should be stable to withstand overflows and damage due to free grazing. One technique to stabilize bunds is to plant the embankment with grass and shrub species of multiple economic value in order to compensate production area lost by bund construction. Often, the species are preferably used for livestock feed. Thus, free grazing has to be controlled. To protect damage of channels and embankments by extreme runoff and floods, frequent supervision and maintenance is required.
The purposes are:
1) Reduce nutrient loss and soil erosion by shortening the slope length,
2) Safely drain excess runoff from upstream of gully into protected waterways,
4) Produce biomass of fodder and cash values.
Vegetated graded bunds are established by doing surveying using hand level to determine the layout of the technology along the slope. During the surveying, the position of bunds (spacing) and cutoff drains and connection to waterways are determined. Bunds are laid following 0.05% gradient and up to 80 m maximum length. The specifications of the structure are: height of bund is a minimum of 60 cm after compaction; depending on the soil, base width range between 1.0 and 1.5m; top width is between 30 and 50 cm. The construction is made across different parcels owned by different land users. If there is no natural waterways and where it is appropriate, paved waterways are constructed at every 80 m or less bund length to dispose drainage water. At the beginning of the rainy season, the embankments are covered with grass and/or shrubs either by direct sowing of seeds or planting the seedlings raised in the nurseries. Monitoring of damages due to flooding and animals, maintenance of the structure as well as replanting of dead seedlings on bunds is required to sustain the soil conservation technology.
The technology is appropriately applied in high rainfall and sub-humid areas of the sub-tropics, particularly where the soil is moderately deep and poorly drained. It is constructed on cultivated lands having slopes in the range of 3-15%. The practice can be constructed by land users. It also requires collective decision and actions to drain excess runoff through waterways. The living condition depends on subsistence crop-livestock mixed farming. On average households have 5-6 family size. Crop production is meant for home consumption with small surplus for local market. The services related to water supply, energy supply, and infrastructure are low. Besides it is an asset, animals often used to cope shocks during drought periods.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
埃塞俄比亚
区域/州/省:
Amhara National Regional State (ANRS)
有关地点的进一步说明:
Mecha, Bahirdar Zuria and Yilmana Densa
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 20 km2.
The technology is applied on specific conditions within the watersheds or area of adoption
2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The soil bunds are introduced before 30-40 years, however the integration of structural and combination of vegetative measures are applied in three years period in the WLRC learning watersheds.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
- Rhamnus, Napier grass
- Cordia Africana, Polycantha, Sesbania Susban, Pigeon pea, Treelucer
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 210, Longest growing period from month to month: June-December; Second longest growing period in days: 180, Second longest growing period from month to month: June-November

牧场
- free grazing
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Land degradation due to sheet erosion, rills and gullies, soil nutrient depletion, overgrazing, shortage of fuel wood, excessive removal of crop residuals, loss of vegetation and deforestation
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): Soil erosion, soil nutrient depletion, shortage of pasture
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 充分灌溉
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 横坡措施
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

结构措施
- S2:堤、岸
- S3:分级沟渠、渠道、水道
注释:
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -graded strips
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀
- Wo:场外劣化效应

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (High tillage frequency on annual basis and steep slope cultivation), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (The cropping system is cereal based that induce erosion), overgrazing (Livestock graze on crop residues after harvesting of crops), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Extreme rainfall cause for high erosion), other natural causes (avalanches, volcanic eruptions, mud flows, highly susceptible natural resources, extreme topography, etc.) specify (Steep slopes or rugged topography), population pressure (Result in expansion of crop lands to steeper slopes)
Secondary causes of degradation: deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Deforestation of scattered trees in the farm and forests upstream of crop lands), land tenure (Insecure tenure play role not to invest on long term), poverty / wealth (Poor can not afford to invest on soil conservation on his parcel), education, access to knowledge and support services, governance / institutional
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
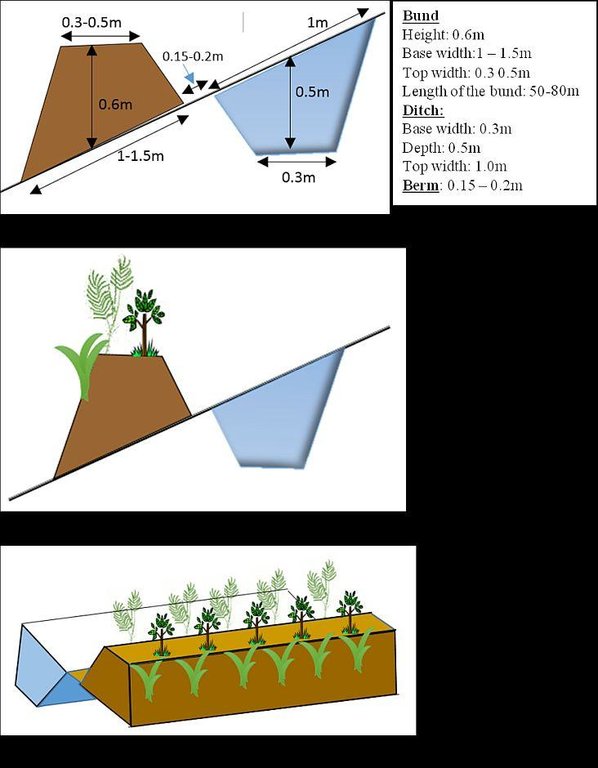
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Vegetated graded soil bund showing the excavated ditch or channel and the embankment planted with grass and shrubs
Location: Amhara Region. Mecha, Yilmana Densa, Bahir Dar Zuria and Dessie Z
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high (Layout and design specification of soil bunds and cutoff drains vary on soil types, slopes, and rainfall conditions. Experts thus should acquire knowledge on specific hydrologic conditions)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Land users need skill to layout and construct bunds, monitor structures before the occurrence of excessive damage, and do regular maintenance)
Main technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, reduction of slope length, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, increase of biomass (quantity)
Secondary technical functions: control of dispersed runoff: retain / trap, reduction of slope angle, increase / maintain water stored in soil, increase of groundwater level / recharge of groundwater
Aligned: -graded strips
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, C : perennial crops, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): T=5333, C=160, G=1600
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1-1.5
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 10-20
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): T=0.3, C=5, G=0.5
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 0.3
Trees/ shrubs species: Cordia Africana, Polycantha, Sesbania Susban, Pigeon pea, Treelucer
Perennial crops species: Rhamnus
Grass species: Napier grass
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-15%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 0.05%
Diversion ditch/ drainage
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3-0.7
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.2-2.8
Length of ditches/pits/dams (m): 100-250
Waterway
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 1.5-2.0
Bund/ bank: graded
Vertical interval between structures (m): 1-1.5
Spacing between structures (m): 10-20
Depth of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.5
Width of ditches/pits/dams (m): 0.3
Height of bunds/banks/others (m): 0.6
Width of bunds/banks/others (m): 1-1.5
Length of bunds/banks/others (m): 50-80
Construction material (earth): in-situ excavated soil
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 3-15%
Lateral gradient along the structure: 0.05%
Vegetation is used for stabilisation of structures.
作者:
Bekure Melesse, WLRC, P.O.Box 8707, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
ETH BIRR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
20.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.50
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparing planting materials | January-May |
| 2. | Preparation of planting materials | January-May |
| 3. | Transportation of grass splits/cuttings | Start of rainy season/July |
| 4. | Transporting tree seedlings | Start of rain season/July |
| 5. | Planting grass splits/cuttings | Start of rainy season/July |
| 6. | Sowing seeds on bunds | Start of rainy season/July |
| 7. | Planting tree seedlings on bunds | Starting of rainy season/July |
| 8. | Surveying (layout of structures) | After crop harvest and before first tillage operation |
| 9. | Construction of cutoff drains | January-April |
| 10. | Construction of bunds (ditch and embankment) | January-April |
| 11. | Construction of waterways | January - April |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 1107.0 | 1107.0 | 79.0 |
| 设备 | animal traction | ha | 1.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | tools | ha | 1.0 | 300.6 | 300.6 | 50.0 |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 32.0 | 32.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seeds | ha | 1.0 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | compost manure | ha | 1.0 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | stone | ha | 1.0 | 1300.0 | 1300.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | wood | ha | 1.0 | 110.0 | 110.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | earth | ha | 1.0 | 25.2 | 25.2 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 2889.8 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 144.49 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 15 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Preparation of planting materials | January - May |
| 2. | Transportation of seedlings | July |
| 3. | Re-plantation of seedlings and grass splits | July |
| 4. | Maintenance of bunds, cutoff drain and waterways | January-April |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | labour | ha | 1.0 | 279.0 | 279.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 20.0 | 20.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 299.0 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 14.95 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: Cart, plastic tubes, spade, pickaxe, hand level, graduated ranging pole, spade, pickaxe, crowbar, hammer
The costs are calculated based on the labour, seedling/seed, grass splits required per hectare
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
The cost variation in implementing vegetated soil bund is dependent upon availability of stones, workability of the soil, cost of seeds or seedlings for plantation, and distance for transporting seedlings.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Monsoon, 5-6 months rain and 6-7 dry months
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics. he lowest temperature is above 5oc but below 18oc etween November to January
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
- 低(<1%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 贫瘠
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Difference in the involvement of women and men: Women are involved in the construction of bunds with role of collecting stones, stabilize/compact the embankments and sometimes help men in excavating the earth
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 2% - 3%
80% of the land users are average wealthy.
20% of the land users are poor.
Off-farm income specification: Land users often do not have access to off-farm income unless those who are young and own small size of land go for seasonal labor to towns during the slack period
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 州
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Crop yield increase on sedimentation area of bunds
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Introduction of fodder crops on bunds
饲料质量
注释/具体说明:
Introduction of high value forage crops
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
The area used for ditch construction can be taken as a loss of land
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
In slope classes where spacing is narrow farm operation will be hindered
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Increase in income due to yield increase and fodder production
社会文化影响
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Watershed users committee established to regulate the development
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Field staffs and land users aware of erosion and soil conservation
冲突缓解
contribution to human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology aim to reduce the soil loss and improving the soil moisture to produce crops. On the other hand, the fodder production on bunds increase livestock productivity. Through improving crop and livestock productivity the livelihood of the watershed people is improved in long terms.
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
注释/具体说明:
Overall effect of bunds show increase in surface water downstreams
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
reduction of concentrated runoff
土壤
土壤水分
注释/具体说明:
Increase the rate of infiltration
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Soil loss is reduced by breaking the slope length
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
旱季稳定可靠的水流
注释/具体说明:
In good drainage soils it increases infiltrated water and interflows
下游洪水
注释/具体说明:
Since it helps to reduce concentration of runoff it contributes to reduce flooding
下游淤积
注释/具体说明:
The main function of bunds is to reduce soil loss
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
All fields are treated with integrated bund, cutoff drain and waterways
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 不好 |
注释:
The technology has sufficient drainage ditch to tolerate excess runoff occurred during heavy rainfall events. However, it is sensitive to floods unless flood management measures such as strong cutoff drains and waterways are implemented
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The short term economic benefits of the technology includes increase in fodder production and slightly crop productivity due to improved soil moisture. Whereas the long term benefit can be obtained as a result of increased yield on areas where sediment accumulation occurs as well as production of fodder on soil bunds for livestock feed
6.5 技术采用
注释:
The technology is implemented using community mobilization approach which involves all land users. All land users, who cultivate land in areas where bunds are suitable, implemented the technology. All parcels are covered with the technology/bunds except homesteads and degraded hillsides and gullies which are treated with different SLM technologies
Since the approach encourages collective action (through community organizations) to integrate different SLM technologies in the watershed level, there is no attempt by individual land users. However, there are motivations and implementation of land users on adjacent watersheds to implement the technology.
There is a moderate trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
The trend is at increasing rate although land users need material support such as multipurpose seedlings to stabilize bunds. There is shortage of supply of fodder seeds. Community nurseries are inadequate and not well supported to raise seedlings to meet community demands.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Increase in fodder production for livestock feed |
| Reduce conflict among adjacent land users (i.e., upstream and downstream land users) that arise due to concentrated runoff |
| Reduce soil erosion |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology reduces soil loss and associated nutrient loss significantly in the first 3 to 4 years and further reduce siltation of reservoirs and land degradation |
| Increase the soil moisture in the landscape/watershed |
| Improves the greenness, soil carbon and micro-climate |
| Increase level of awareness of land users to produce fodder and diversify production and income |
| Reduce the concentration of runoff and safely drain without causing damage |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Hinder farm operations like turning oxen become difficult while ploughing | It can be sustained through proper layout and allow space for human and animal paths |
| Plantation on bunds harbor birds | This can be avoided by harvesting the mature branches of the shrubs for livestock feed on seasonal basis. |
| Appearance of new weeds species along the drainage ditches | Regular weed monitoring and manual control |
| Hinders livestock to graze on crop residues | Try to use cut and carry grazing system (both crop residues and fodders) and develop forage development strategies in every possible niches |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High labor requirement to establish and maintain the technology | Increase the awareness level of land users and strength collective actions and local organizational setups |
| Small land loss for construction | Introduce production options (like fodder production) on bunds to compensate the lost land |
| It requires some years to accumulate sediment on bund area and form bench | It can be improved by modifying the design of drainage ditchs |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
12/05/2014
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Vegetated Graded Soil Bund: A Technique to Reduce Runoff Impact and Increase Soil Moisture Storage and Fodder Biomass, WLRC Brief No. 4
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
WWW.wlrc-eth.org
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Community Organizations and Mobilization for Soil and Water … [埃塞俄比亚]
Community mobilization for soil and water conservation work in a watershed planning unit is an approach for collective action by organizing all active labor forces living in the kebele/peasant association into development group of 20-30 members and further divide into 1:5 work force to implement construction of soil and water …
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse

'Cut and Carry' Grazing system or 'Zero Grazing' … [埃塞俄比亚]
Cut and carry grazing system (alternatively called zero grazing) is an approach where the community is consulted to identify and agree on areas to be closed and protected from free grazing; establish user groups are established to share the fodder biomass harvested from communal closed areas equitably; they utilize tree/shrub …
- 编制者: Gizaw Desta Gessesse
模块
无模块