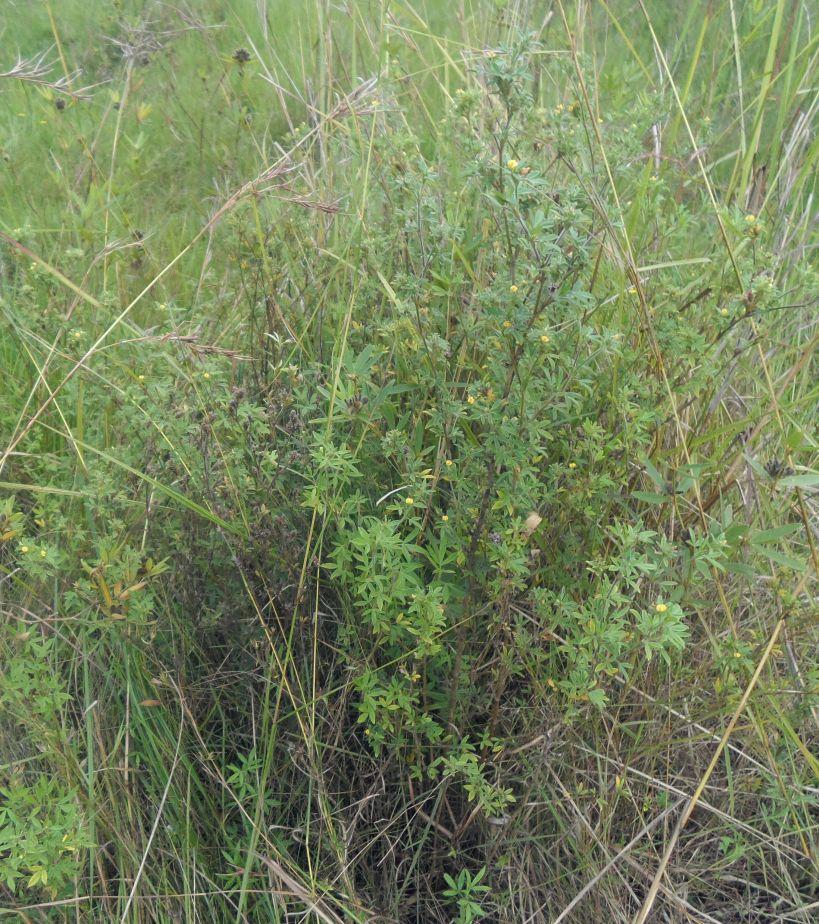
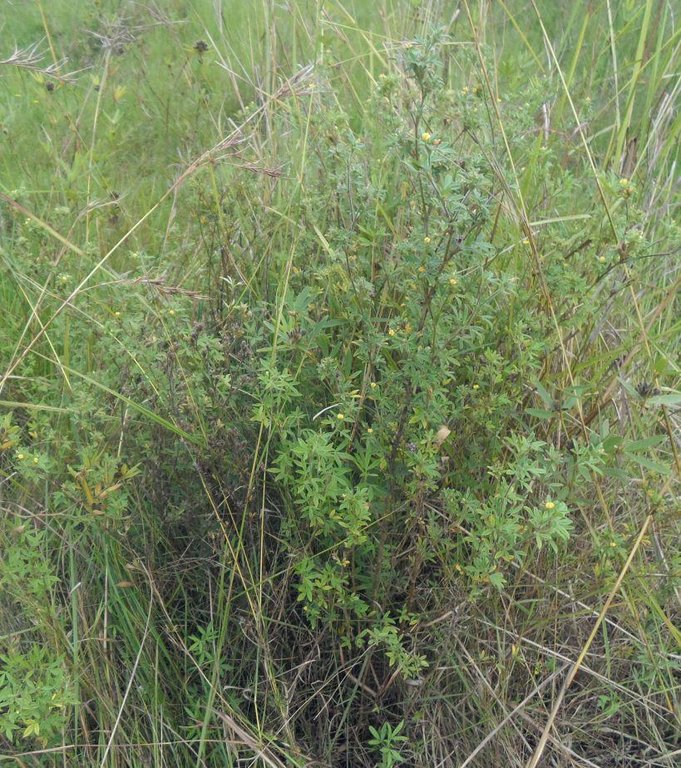
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and regeneration of cut and carry materials. [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: ALLAN BUBELWA
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Eneo lililotengwa na kwa ajili hifadhi ya mto na kuvuna malisho na matandazo
technologies_1607 - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Member of the district council:
Egidius Pancras
Missenyi Disrict Council Kagera Tanzania
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Bukoba district council (Bukoba district council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Missenyi District Council (Missenyi District Council) - 坦桑尼亚联合共和国1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷
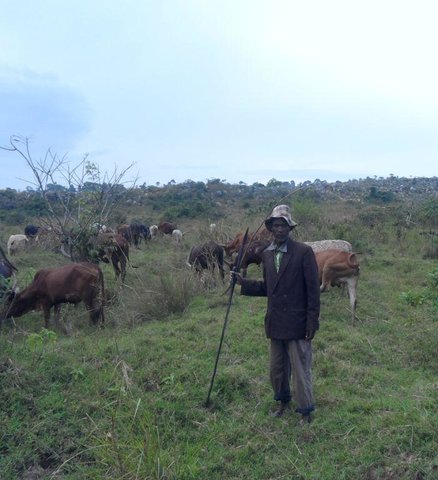

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- 编制者: ALLAN BUBELWA
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Area enclosures for protection of riverine ecosystem and purposeful regeneration of mulching and pasture materials for cut and carry
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Area enclosure is done in low grazing range lands of average slope 2 – 5%. Enclosure is done by demarcating the fragile land that has direct impact to the riverine ecosystem. The land is exposed to degradation through overgrazing and soil compaction by livestock, bush fire, river bank erosion and reduced quality of pasture spps. Demarcation is done by planting trees in identified area situated about 300 meters from the riverine buffer zone. The preferred plants are Ficus thonigii. The average space between trees is 2 meters. Physical enclosure is supported and enhanced by use of protective bylaws. Reseeding of nutritious pasture species is also done and the area is left under protection for growth and regeneration of mulch, pastures and other vegetation to take place. The common pasture species reseeded are Leucaena spp, cannavaria brazile, clitoria tenatea, sesbania sesban, stylothensis, cajanus cajan, chloris gayana, branchalia spps . Direct grazing is prohibited and mulch and pasture materials are accessed through controlled and organized cut and carry.
Area enclosure is meant for rehabilitation of the riverine ecosystem and prevention of further degradation. Mulch and high nutritious pasture materials that are accessed through organized cut and carry procedures improve crop and animal productivity and have both direct and indirect impact to diversification of income sources and thus play significant role in putting the triple win solution into reality.
Purpose of the Technology: Purpose: 1) To improve vegetative cover, reduce soil erosion and prevent and rehabilitate degradation of the riverine ecosystem 2) Ensure sustainable availability and accessibility of mulch and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity 3) Promote use of environmental friendly exploitation of land resources (i.e. mulch, pasture, grass carpeting and other materials) and 4) Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources.
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Establishment and recurrent activities includes: area identification and measurement; slashing and land preparation for boundary tree planting and pasture reseeding; collection of planting materials and planting along defined boundaries for demarcation; procurement of seed and reseeding of nutritious and palatable pasture species; selective weeding; area reshaping and gap filling.
Natural / human environment: Bio-physically the area is semi natural grassland with grasses and shrubs trees. The technology is a combination of management and vegetative measure (area enclosure, demarcation using ficus thonigii and reseeding of nutritious pasture). Climatic zone is sub humid with 210 length of growing period (LGP). Slope category is gentle lying between 2-5%. Soil texture is fine heavy (clay) with medium soil depth.
Social economic wise the area is dominated by handy tools typology of mechanization. Production system is mixed (both for subsistence and commercial purposes). Inputs used includes tools (hand hoe, machete, sickles, spade and mattock), light and heavy labour, pasture seeds and tree planting materials with average annual costs of 1084.3 USD per hectare. Land ownership in technological area is communal.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
坦桑尼亚联合共和国
区域/州/省:
Tanzania/Kagera
有关地点的进一步说明:
Missenyi distict/Minziro ward/Minziro village
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
Includes enclosed and demarcated area closer and around the riverine ecosystem.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
The technology is a result of the recent SLM participatory dialogues made between land users and SLM specialist (external experts). In these dialogues both endogenous and technical knowledge based were given equal weight and were combined in a complementary manner. Land users alos were empowered to take self initiative and ownership of the decision making process.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保护生态系统
- 保持/提高生物多样性
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型
同一土地单元内混合使用的土地::
是
具体说明混合土地使用(作物/放牧/树木):
- 林牧业

农田
每年的生长季节数:
- 2
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 120, Longest growing period from month to month: September to December Second longest growing period in days: 90 Second longest growing period from month to month: March to May

牧场
粗放式放牧:
- 游牧
- 半游牧畜牧业
集约放牧/饲料生产:
- 收割和携带/零放牧
动物类型:
- 山羊
- 绵羊

森林/林地
- Ficus thonigii
注释:
Livestock density (if relevant):
50-100 LU /km2
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Soil erosion due to downstream run off exacerbated by loss of vegetation cover due to bush fire and soil compaction caused by overgrazing, degradation of the riverine ecosystem caused by River bank erosion, land bareness and exposure to direct sunlight and excessive unproductive loss of both green and blue water.
Major land use problems (land users’ perception): River pollution, erosion of the river bank, land bareness and reduction of mulching and pasture materials.
Nomadism: People with large herd of animal move with their animals in search of adequate pasture
Semi-nomadism / pastoralism: Exercised with people with few stock.
Cut-and-carry/ zero grazing: done by farmers who usuall keep dairy goats and cattles.
Grazingland comments: Area enclosure is largely meant to control land degradation of the riverine ecosystem through overgrazing by people who own large number of stocks at the same time promote organized, sustainable and environmental friendly exploitation of the fragile land lands (e.g. controlled cut and carry rather than direct grazing in the riverine ecosystem).
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 区域封闭(停止使用,支持恢复)
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V2:草和多年生草本植物

管理措施
- M7:其它
注释:
Main measures: vegetative measures, management measures
Specification of other management measures: Area enclosure to promote vegetative regeneration and organized use
Type of vegetative measures: aligned: -along boundary, scattered / dispersed
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wr:河岸侵蚀

物理性土壤退化
- Pc:压实

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management (Compaction due to overstocking, accerated runoff and erosion.), crop management (annual, perennial, tree/shrub) (Reduction of mulching and pasture materials), deforestation / removal of natural vegetation (incl. forest fires) (Rampant bush fire), over-exploitation of vegetation for domestic use (Un0rganize exploitation of mulching materials), overgrazing (Uncontrolled grazing), disturbance of water cycle (infiltration / runoff) (Loss of green water through unproductive evaporation and blue water through ruoff as well as evaporation), population pressure (Exessive eploitation of the grassland and forests in the riverine ecosystem), poverty / wealth (Reliance on wood as the sole source of fuel), education, access to knowledge and support services (Inadequate acess to extension service due to shortage of extension staff), governance / institutional (Weak and inactive institutions to deal with environmental issues)
Secondary causes of degradation: change in temperature (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), change of seasonal rainfall (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), Heavy / extreme rainfall (intensity/amounts) (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire), droughts (Climatic change and variability due to green gas emmision caused by bush fire)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
- 修复/恢复严重退化的土地
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: moderate (Is simply retraining on some principles of sustainable land management, law and rules guiding the fragile ecosystems, participatory training skills and grassroots facilitation skills.)
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Largely exposure to act and policies guiding the fragile ecosystems and learning by doing on the job,)
Main technical functions: control of raindrop splash, control of dispersed runoff: impede / retard, control of concentrated runoff: impede / retard, improvement of ground cover, improvement of topsoil structure (compaction), stabilisation of soil (eg by tree roots against land slides), increase / maintain water stored in soil, improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water, sediment retention / trapping, sediment harvesting, promotion of vegetation species and varieties (quality, eg palatable fodder)
Aligned: -along boundary
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs
Number of plants per (ha): 400
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): 1 m
Scattered / dispersed
Vegetative material: T : trees / shrubs, G : grass
Number of plants per (ha): various
Vertical interval between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Spacing between rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Vertical interval within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Width within rows / strips / blocks (m): various
Trees/ shrubs species: ficus thonigii planted arround the boundary and leguminous pasture shrubs planted within the area (stlothensis, lucaena spps)
Grass species: Randomly planted (chloris gayana, desmodium spp and Calliandra)
Slope (which determines the spacing indicated above): 2 - 5%%
Gradient along the rows / strips: 2 - 5%%
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Introduction of organized cut and carry exploitation of mulching and pasture materials
Other type of management: Boundary enclosure, law enforcement
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
Tanzanian shillings
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
1700.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
1.12
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site/boundary identification | October |
| 2. | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | October |
| 3. | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | November |
| 4. | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Once |
| 5. | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | once |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Site/boundary identification | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.13333 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Site preparation for reseeding and demarcation (slashing, selective tilling, hole digging) | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | |
| 劳动力 | Planting of demarcation trees, leguminous shrubs and grass pasture | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | |
| 劳动力 | Fertilizer application (DAP) | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.13333 | 17.0 | |
| 设备 | Tools | Number | 5.0 | 3.0 | 15.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | ha | 1.0 | 235.29 | 235.29 | |
| 植物材料 | Seedlings | ha | 1.0 | 117.65 | 117.65 | |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | kg | 125.0 | 0.588 | 73.5 | |
| 其它 | Meeting on awareness creation and formalization of the practice (change of resource use practice) | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.9213 | 58.82 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 651.9 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 0.38 | |||||
注释:
Duration of establishment phase: 2 month(s)
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Selective weeding and gap filling | Once |
| 2. | Supervision and monitoring | monthly |
| 3. | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Weekly |
| 4. | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Weekly |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Selective weeding and gap filling | Mandays | 15.0 | 1.76466 | 26.47 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Supervision and monitoring | Mandays | 15.0 | 3.53 | 52.95 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Organized cut and carry of Mulching and pasture materials | Mandays | 10.0 | 17.647 | 176.47 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | monitoring area closure and organized cut and carry | Mandays | 10.0 | 17.647 | 176.47 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 432.36 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 0.25 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: machete and sickles.
The costs were calculated per unit of ha as per 13/06/2014.
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
labour is the most determinant factor.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Short rains (september to December), March to May long rains. Length of dry periods January, February, June, July and August.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: tropics. Temperature grater than 20°C, LGP is 210 days
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Landforms: Plateau/plains (ranked 1, is largely applied in extended cancave lower range land pouring water to the river) and footslopes (ranked 2, partly includes the convex the convex hill slopes)
Slopes on average: Gentle (The area is largely extended gentle sloppy lower range land plateau receiving water from the the upper landscape and draining into the lower Ngono river which drains into Kagera river)
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 粗粒/轻(砂质)
- 细粒/重质(粘土)
表土有机质:
- 低(<1%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil depth on average: Moderately deep (ranked 1, The lower range land is moderately deep it receives eroded soil from the upper and mid sloppy landscape) and shallow (ranked 2, largely include the the area between the upper and lower mid landscape)
Soil texture: Coarse/light (ranked 1, the lower side is largely light sandy soil) and fine/heavy (ranked 2, some patches fine clay soil)
Soil fertility: Low (Nutrient eroded by runoff into the river)
Topsoil organic matter: Low (top soil eroded by runoff into the river)
Soil drainage / infiltration: Medium (ranked 1, caused by the dominance of sand soil) and poor (ranked 2, due to trampling by animals)
Soil water storage capacity: Low (due to the dominance of sand soil)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
表面上
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
不良饮用水(需要处理)
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Ground water table: On surface (ranked 1, along the flowing river Ngono) and <5m (ranked 2, the area is within the riverine ecosystem)
Availability of surface water: Medium (The main water source is Kagera river with water flows all year round)
Water quality (untreated): Poor drinking water (treatment required, Kagera river receives partly receives water drained from the upper kibanja, Kikamba and other distant places. Kagera river water therefore is contaminated can not be consumed untreated)
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 低
关于生物多样性的注释和进一步规范:
Overgrazing has left the area with disappearance of some palatable and nutritious pastures, bushfire and deforestation also has disturbed tree and shrub composition and the soil microbiology.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Land users applying the Technology are mainly common / average land users
Population density: 50-100 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 1% - 2%
30% of the land users are very rich and own 35% of the land.
60% of the land users are average wealthy and own 50% of the land.
10% of the land users are poor.
and own 15% of the land.
Off-farm income specification: Generally 90% relies on agriculture as their main source of livelihood. Only a few are engaged in off-farm activities like petty trading, kiosk, brick making e.t.c.
Market orientation: Mixed (Livestock are largely kept for domestic use e.g. milk, meat and manure and parlty for commercial purposes)
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
There is shortage of grazing land. People with large animal herd move with their animals in search of better pasture.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 自由进入(无组织)
注释:
In Tanzania land is a state property. Land use right is largely individual not titled and is acquired through inheritance or purchase through traditional or customary procedures.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
SLM之前的数量:
5.0 ton/ha
SLM之后的数量:
6-7.0 ton/ha
注释/具体说明:
due to the availability and use of mulching by some farmersmaterials
饲料生产
SLM之前的数量:
2 acres/annum
SLM之后的数量:
10 acre/annum
注释/具体说明:
area enclosure and decline of forest fire
饲料质量
SLM之前的数量:
3
SLM之后的数量:
8
注释/具体说明:
increase in the number of nutritiuos pasture species due to reseeding
畜牧生产
SLM之前的数量:
1200litres/cow/yeer
SLM之后的数量:
2000litres/cow/year
注释/具体说明:
Contribution of nutritious cut and carry pastures
收入和成本
农业投入费用
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
availability of manure from animal kept under zore grazing
收入来源的多样性
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Income accrued from sell of mulching and pasture materials.
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
improved diet due to varied food availability (avalability of milk)
社区机构
SLM之前的数量:
weak
SLM之后的数量:
strong
注释/具体说明:
empowerment and capacity building of environmental committee.
SLM/土地退化知识
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Knoledge over controll of riverine resources.
冲突缓解
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
Improved livelihoods and human well-being
注释/具体说明:
The technology has contributed to availability and accessibility to mulching and nutritious pasture that are need for increased crop and livestock productivity. This has both direct and indirect impact on the income of the community and hence livelihood (e.g. ability to meet education and health expenses).
生态影响
水循环/径流
水量
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Reduction in uproductive loss of both green and blue water.
地表径流
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Resultant of vergetation cover
蒸发
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Reduce uproductive evaporation due vegetation cover
土壤
土壤覆盖层
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Improved vegetation cover
土壤流失
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Cotrolled soil erosion due to runoff
土壤结壳/密封
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
土壤压实
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Reduced overgrazing and animla trumpling
生物多样性:植被、动物
生物量/地上C
SLM之前的数量:
low
SLM之后的数量:
high
注释/具体说明:
Controlled fire burning
减少气候和灾害风险
碳和温室气体的排放
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Controled bush fire
火灾风险
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
harzards due to bush fire but reduced due to enclosure, fire break and use of bylaws.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
下游淤积
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
地下水/河流污染
SLM之前的数量:
high
SLM之后的数量:
low
注释/具体说明:
Resultant of improved vegetation cover and controlled erosion
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 未知 |
| 局地风暴 | 未知 |
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 不好 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 比较和缓的(河道)洪水 | 未知 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
注释:
The technology was modified to become more tolerant through organized cut and carry of mulching and pasture materials.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
Mulching and pasture have short maturing period and this causes land users to realize rewards right from the beginning of the technology and the benefit increases more with time.
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on acceptance with external material support: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
Comments on spontaneous adoption: The technology is applied only on communally owned area nearby the fragile reverine ecosystem. Implementation is done by empowered community based on and guided with decision reached by the whole community and law reinforcement. Is not based on individual voluntarism and option.
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: As a result of benefit realization of the use of technology, there a growing acceptance and spontaneous adoption by the whole community
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology prevent degradation of the river bank and disappearance of palatable and nutritious pasture |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Area enclosure complimented with reinforcement of bylaws reduce fire incidences and helps in sequestration of carbon both above and below the ground and reduce the effect of green gas emission. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of feed to animals kept in farm under zero grazing (e.g. dairy goats and cattle) and control unproductive loss of manure. |
| Area enclosure and organized cut and carry feeding ensure availability of mulching materials needed in production of banana and other crops. |
| Promote direct and indirect diversification of income sources to the rural poor. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Time consuming and labour heavy especially to environmental committee members. | Device motivation and incentive system at the grassroots. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Emergency and dominance of invasive species | Liaise with research to find alternative and beneficial use of invasive species. |
| Needs committed people who can spend their valuable time in promotion of the technology. | Use SLM related incentives and promotion e.g. support with dairy goat to people who actively participate in promotion of the technology (as part of crop livestock integration) . |
| Takes time to inculcate self initiatives and ownership | Systematize and Operationalize into existing systems |
| Needs attitude and behavioral change (is not normal traditional for rural people to cultivate grass). | Encourage change of mindset by enabling farmers understanding of the principle behind pasture establishment. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
03/06/2014
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Active participation of herder leader (WAKONDO) in management … [坦桑尼亚联合共和国]
Prevention and mitigation of the grazing land and riverine ecosystems through mandatory grassroots meetings, law enforcement and active participation and empowerment of herder leaders’ (masters of the most resource destructive group)
- 编制者: ALLAN BUBELWA
模块
无模块