Tomato Grafting [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Kalami Prabidhi Dwara Golbheda Uthapadan (Main Contributor: Purusottam Gupta, IDE Nepal)
technologies_1694 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Gupta Purusottam
IDE-Nepal, currently NEAT project
印度
SLM专业人员:
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
ICIMOD International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
iDE Nepal (iDE Nepal) - 尼泊尔1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Using the participatory market chain approach to help … [尼泊尔]
Discussions and structured interactions between farmers and the different actors involved throughout the market chain can help to stimulate joint innovations based on shared ideas and mutual trust.
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Cleft grafting can be used to produce plants that are resistant to a number of pests and diseases and are often higher yielding than the original. Tomato seedlings can be easily grafted onto resistant root stock of the wild eggplant (Solanum sysimbrifolium) to produce a disease-resistant and commercially viable crop.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
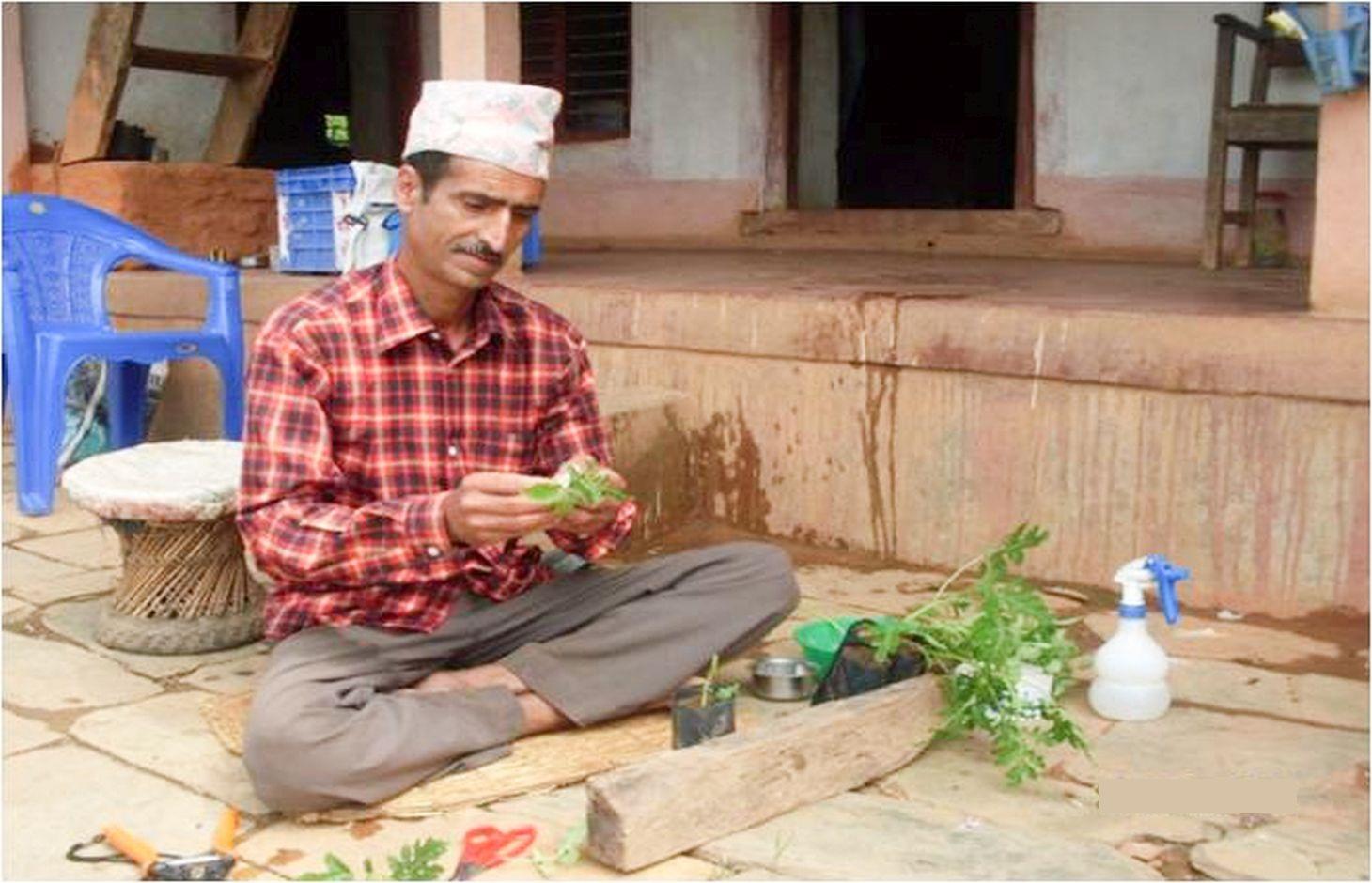
Some of Nepal's most lucrative vegetable cash crops, especially solanaceous crops such as tomato and eggplant, are particularly susceptible to attack by the root knot nematode, Meliodogyne spp, which costs Nepal's farmers millions of rupees in losses annually. In recent years, farmers found that this pest was becoming prevalent and that they could not control it permanently using either cheap or eco-friendly solutions. Researchers and development officers took up the challenge and found that grafting technology could successfully control not only the root knot nematode but also wilting disease. As a bonus, they also found that grafting can increase the yield potential of the plants and improve the overall productivity of the land.
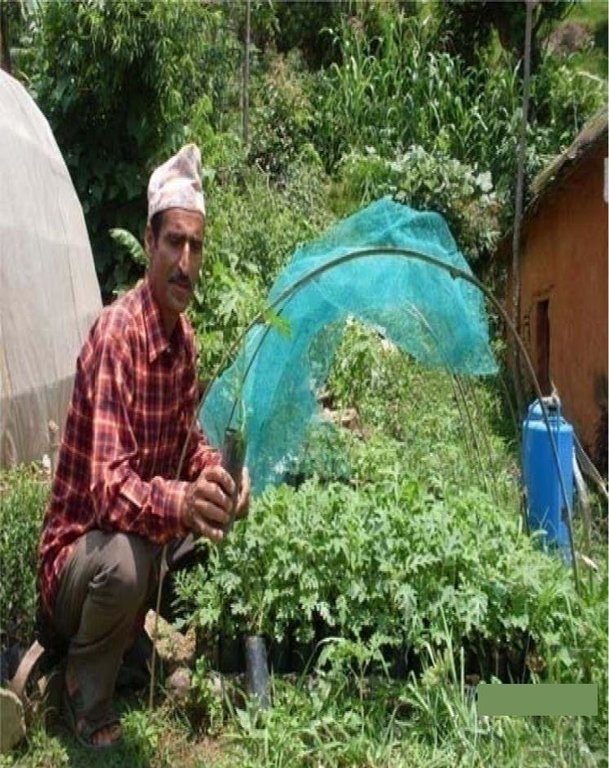
Establishment / maintenance activities and inputs: Loam and silt loam soils with a pH of 6.0–7.0 are the most suitable for this type of cultivation. Grafting technology requires two plants: the scion and the rootstock. The scion is a detached shoot or twig containing buds from the desired woody plant. The rootstock is a plant with an established healthy root system, onto which a cutting or a bud from another plant is grafted. The scion seedlings are grown in raised solarized nursery beds, where care has been taken to see that the soil has been sterilised and all soil pests have been destroyed. Robust rootstock of wild eggplant (Solanum sysimbrifolium) is appropriate for tomato propagation. The rootstock seedlings are grown in multi cell trays and transplanted when they are 20–25 cm high and have a few leaves and a pencil thick stalk. Seeds for the rootstock seedlings are sown in March/April and are ready in 6–8 weeks; scion seeds are sown in April/May and are ready for grafting in 3–4 weeks. Both scion and rootstock plants should have achieved similar stalk thicknesses at the time of grafting. Cleft grafting is carried out and the grafted seedlings kept in polypots in a closed polyhouse for 7–10 days. Then the grafted seedlings are carefully transplanted to their permanent location. The grafted plants are watered the day after they are transplanted; the extent of watering depends on how moist the soil is and on local weather conditions. The field is mulched throughout the cropping period using straw and other farm biomass materials.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Arukharka -6, Syangja District
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- tomatoes
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Insufficient water for irrigation, the soil is acidic, vegetable crops are attacked by pests and crop production is in decline.
3.4 供水
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 病虫害综合管理(包括有机农业)
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A5:种子管理,改良品种
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

生物性退化
- Bp:害虫/疾病增加,捕食者减少

水质恶化
- Hs:地表水良变化
注释:
Main causes of degradation: soil management, other human induced causes (specify) (Overuse of chemical Fertilizer), droughts
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
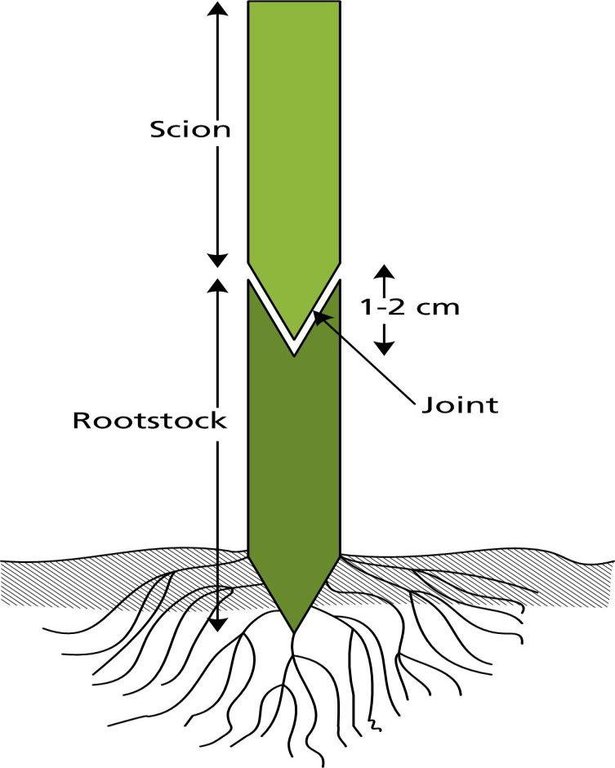
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
Schematic diagram of a tomato scion grafted on to the rootstock of a wild eggplant.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: high
Main technical functions: Reduce Pest Attack, Improve crop production
作者:
A. K. Thaku
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
NPR
如相关,注明美元与当地货币的汇率(例如1美元=79.9巴西雷亚尔):1美元=:
72.0
4.3 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 时间(季度) | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Prepare the land | |
| 2. | Prepare Scions | |
| 3. | Prepare rootstock | |
| 4. | Grafting | |
| 5. | Transplant grafted Seedling |
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Prepare the land | persons/day | 5.0 | 4.2 | 21.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Tools | unit | 1.0 | 22.0 | 22.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 28.0 | 28.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Fertilizer | unit | 1.0 | 17.0 | 17.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Compost/manure | unit | 1.0 | 65.0 | 65.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pesticide | unit | 1.0 | 21.0 | 21.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Plant tonic | unit | 1.0 | 7.0 | 7.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Polypot,grafting chamber etc | unit | 1.0 | 225.0 | 225.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 406.0 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 5.64 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Both scion and rootstock seeds are watered after sowing. The seedlings are monitored and watered as needed. (Overall labor: 16 person days) | |
| 2. | After transplanting, the grafted seedlings are watered the next day and twice weekly thereafter. As the plantlets mature, they are watered at 10-day intervals and the surface of the soil is mulched. The moisture level in the soil is monitored throughout the cropping period. | |
| 3. | Top dressing with biofertilizers (N, P, K, and vesicular arbuscular mycorrhiza VAM) and bio-hume is applied to the root zone. |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Watering scion and rootstock | persons/day | 16.0 | 4.25 | 68.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Electricity and water charger | unit | 1.0 | 8.5 | 8.5 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 144.5 | |||||
| 技术维护总成本,美元 | 2.01 | |||||
注释:
Machinery/ tools: spade, scissors, sharp scalpel, multi cell tray, hoe, plough
4.7 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
All costs and amounts are rough estimates by the technicians and authors.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility is high
Soil drainage / infiltration is good
Soil water storage capacity is medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
> 50米
地表水的可用性:
匮乏/没有
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
非农收入:
- 收入的10-50%
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: 200-500 persons/km2
Annual population growth: 0.5% - 1%
Relative level of wealth: rich, average, poor
20% of the land users are rich.
30% of the land users are average wealthy.
50% of the land users are poor.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
收入和成本
农业收入
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
其它生态影响
resistance towards pests and disease
maintaining moisture in soil
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 增加或减少 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 不好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气象灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 局地暴雨 | 好 |
其他气候相关的后果
其他气候相关的后果
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 缩短生长期 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
消极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
中性/平衡
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发的,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 91-100%
注释:
There is a strong trend towards spontaneous adoption of the Technology
Comments on adoption trend: Most (90%) of the farmers are implementing the technology voluntarily and there is a spontaneous trend for adoption. In the area studied, about 20–30 households per year are adopting this technology.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
|
The technology is highly effective at controlling pests and disease. How can they be sustained / enhanced? The wild eggplant rootstocks are somewhat difficult to graft because they are spiny. Spine-free rootstock seedlings would be easier to graft. |
|
The grafted seedlings themselves are a good source of income for farmers. How can they be sustained / enhanced? Create awareness among farmers and encourage nurseries to provide grafted seedlings. Support farmers during the start-up stage. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Grafting is time consuming and difficult because wild eggplant rootstock plants are spiny. | Need more research to identify other possible rootstock plants. |
| Grafting can be expensive and requires an initial investment in training; specialized materials are needed. Technically demanding, needs practise. Specialized materials are difficult to get. | Nurseries need to be supported and need to have access to specialized materials on time. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Using the participatory market chain approach to help … [尼泊尔]
Discussions and structured interactions between farmers and the different actors involved throughout the market chain can help to stimulate joint innovations based on shared ideas and mutual trust.
- 编制者: Shreedip Sigdel
模块
无模块