Ex-post and ex-ante soil sealing maps [波兰]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Tomasz Miturski
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: Fabian Ottiger, Alexandra Gavilano
Mapy procesu zasklepiania gleb (Polish)
technologies_1716 - 波兰
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Preventing and Remediating degradation of soils in Europe through Land Care (EU-RECARE )有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation (Institute of Soil Science and Plant Cultivation) - 波兰1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

The prevention of soil sealing [波兰]
The prevention of soil sealing is an approach in which stakeholders are making spatial planning decisions based on the new map of soil sealing, in case of protecting the most valuable soils.
- 编制者: Tomasz Miturski
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Ex-post and ex-ante soil sealing maps
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
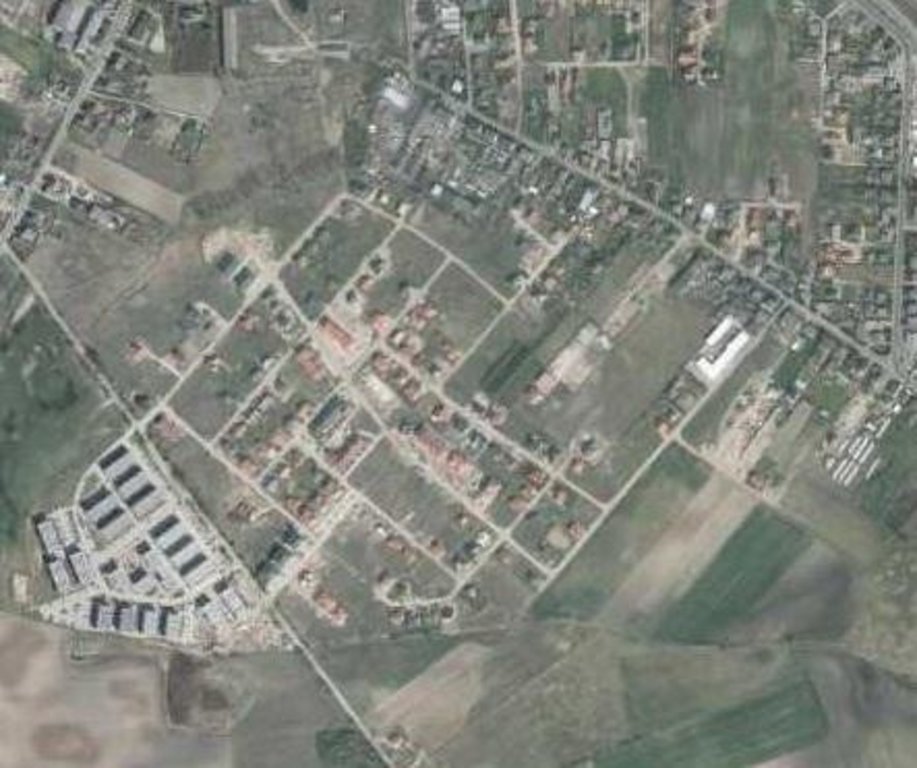
The technology utilizes soil agricultural maps and provides information on quality of sealed soils.
It involves cellular automata software to build the model of land use change and produce the forecasts for various soil protection scenarios.
Spatial development of the functional areas. These are mostly areas of soil protection for food production purposes. The delineation is based on land productivity information (present on soil-agricultural maps), distribution of high nature value areas, need for establishment of “green rings” around the bigger cities.
The maps will be sent to the municipal authorities, with a scientific comment on the problem. The technology enables determining the scale of the soil sealing threat in the province, also what is the soil quality class of the area of interest. In the municipalities with the greatest soil sealing problem and with perspective to expand in the future, there is a need for new legal regulations to force soil protection in local spatial plans. The regional spatial planning office should become a coordinator for the local spatial planning offices, to raise the knowledge about how to use soil digital maps in spatial planning, especially in the case of protecting the soil against soil sealing process. For the municipalities, large scale maps are produced, which contain results of soil sealing forecasting model.
Land use maps of at least 10-meter resolution are produced for two historical periods through classification of the satellite images and using available local land use information. The information on land use change is superimposed on maps characterizing soil quality in order to detect to what extend the urbanization took place on valuable soils. The new sealed area, reflecting the built up sprawl of at least last 15 years, consists with expansion of the following land use classes: continuous residential area, commercial/industrial area and transport facilities. The soils under these new land use types fully lost their environmental functions.
In the soil sealing forecasts the Cellular Automata-based Metronamica model is used. The software was developed and provided by the Research Institute from Knowledge Systems (RIKS) from Maastricht, The Netherlands. The software utilizes cellular automata model to spatially distribute areas of particular land use classes with assumption that the neighborhood of a cell (surrounding cells) influences the transition of this cell into other land use class in the next time step. The method utilizes land use maps and soil quality maps.
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
波兰
区域/州/省:
Poland/Great Poland province
有关地点的进一步说明:
Poznań
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果技术均匀分布在一个区域,则指定覆盖的区域(单位为平方千米):
199.0
如果不知道精确的区域,请注明大致覆盖的区域:
- 100-1,000 平方千米
注释:
Total area covered by the SLM Technology is 199 km2.
Map
×2.6 实施日期
如果不知道确切的年份,请说明大概的日期:
- 不到10年前(最近)
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 在实验/研究期间
- 通过项目/外部干预
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 创造有益的经济影响
- 创造有益的社会影响
- Create and spread knowledge
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
具体说明:
Longest growing period in days: 215, Longest growing period from month to month: April - October

牧场
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Preferential sealing of most productive soils.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 减少基于生态系统的灾害风险
- Creating and sharing knowledge
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

管理措施
- M2:改变管理/强度级别
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

物理性土壤退化
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失
注释:
Main causes of degradation: urbanisation and infrastructure development, population pressure, governance / institutional
Secondary causes of degradation: inputs and infrastructure: (roads, markets, distribution of water points, other, …)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
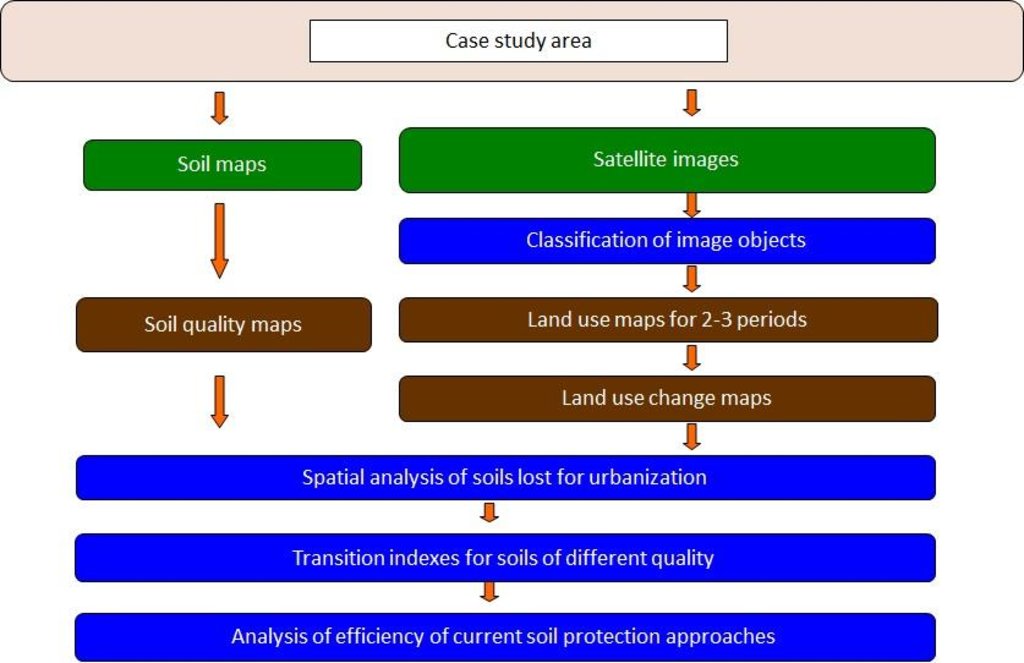
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
This is a schema for soil sealing maps developement.
Technical knowledge required for land users: moderate (Developers)
Technical knowledge required for Administration: high
Technical knowledge required for Researchers: high
Main technical functions: improvement of surface structure (crusting, sealing), increase of infiltration, spatial arrangement and diversification of land use
Secondary technical functions: improvement of water quality, buffering / filtering water
Change of land use type: Limited conversion of agricultural land into urban purposes.
Change of land use practices / intensity level: Steering new constructions to soils with less functions. Limited sealing of high quality soils.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Thermal climate class: temperate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Soil fertility: High
Soil drainage/infiltration: Medium (ranked 1) and poor (ranked 2)
Soil water storage capacity: Medium
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
< 5米
地表水的可用性:
好
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业)
个人或集体:
- 员工(公司、政府)
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Population density: > 500 persons/km2
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 大规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
水资源可用性和质量
灌溉用水的可用性
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
灌溉用水的质量
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
娱乐机会
注释/具体说明:
comparing to baseline scenario
SLM/土地退化知识
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
土壤
土壤流失
土壤结壳/密封
土壤压实
生物多样性:植被、动物
栖息地多样性
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
水资源可用性
下游洪水
6.5 技术采用
注释:
There are examples of land use and soil maps for spatial planing in cities of Central Europe, e.g. Stuttgart. it is impossible to assess the percentage of users.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Analysis of various scenarios possible |
| Decisions in spatial planning based on empirical data in spatial format |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Lack of regulations forcing use of the technology | Pressenting examples of implementation in order to encourage to apply at local level strategies |
| Potential errors in forecasts | Improving the data quality and model effectiveness. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
- 与土地使用者的访谈
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
28/02/2015
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

The prevention of soil sealing [波兰]
The prevention of soil sealing is an approach in which stakeholders are making spatial planning decisions based on the new map of soil sealing, in case of protecting the most valuable soils.
- 编制者: Tomasz Miturski
模块
无模块