Legume integration [尼泊尔]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: Richard Allen
- 编辑者: –
- 审查者: David Streiff, Alexandra Gavilano
Bali pranali ma kosebali samabesh
technologies_1753 - 尼泊尔
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
SLM专业人员:
Director
Soil Management Directorate, Department of Agriculture
尼泊尔
SLM专业人员:
Team Leader
Sustainable Soil Management Programme
尼泊尔
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Sustainable Soil Management Programme, Nepal (SSMP)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Department of Agriculture, Soil Management Directorate, Hariharbhawan Lalitpur (doasoil) - 尼泊尔有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
HELVETAS (Swiss Intercooperation)1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.5 参考关于SLM方法(使用WOCAT记录的SLM方法)的调查问卷

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [尼泊尔]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Integration of leguminous crops as intercrops on terrace risers or as relay crops
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
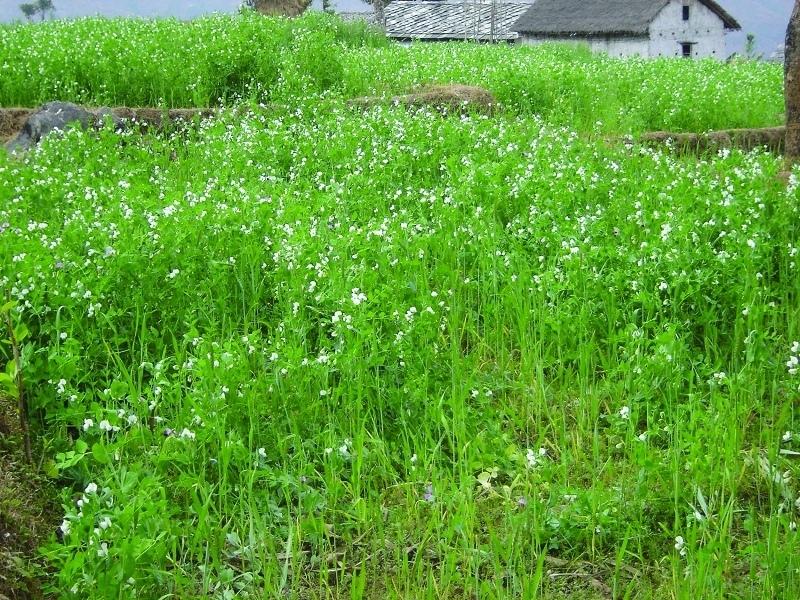
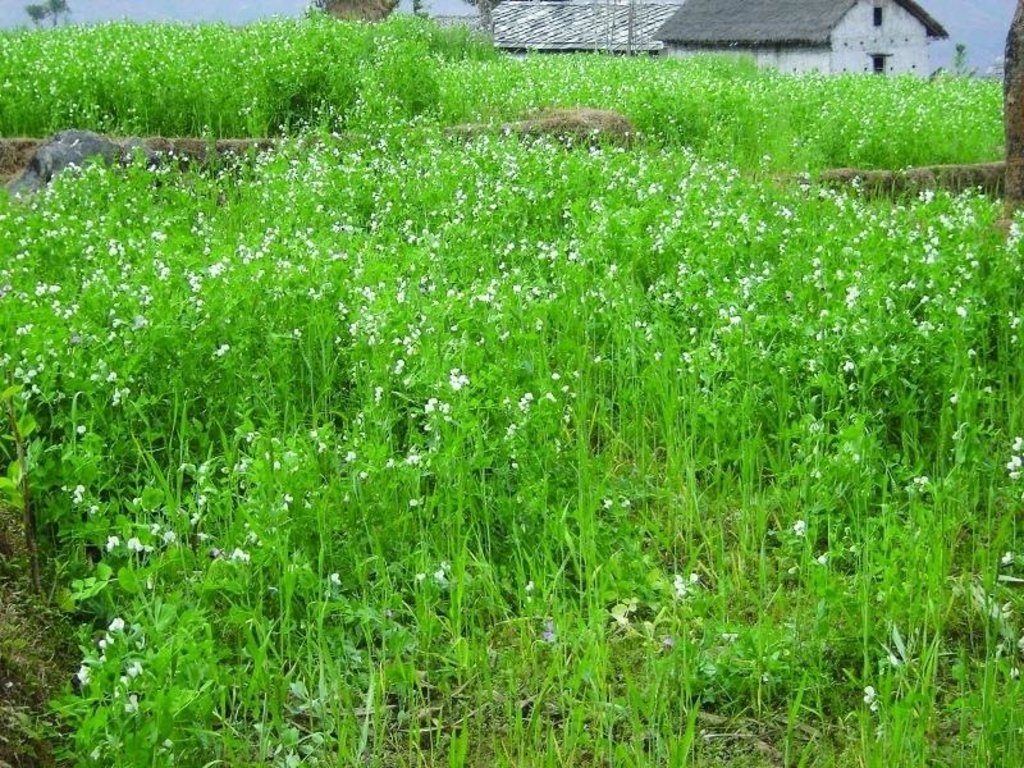
Legumes are widely grown across the hills of Nepal, with the most common being soybean, lentils, black gram, cow pea, beans, horse gram, field peas, and rice bean. They are mostly intercropped or relay cropped with cereals such as maize, millet, and rice. They are also planted on the edges of terraces and rice paddy bunds. Depending on the species, they may be grown in rain-fed or irrigated fields during the winter or summer seasons.
The majority of the legumes grown by farmers are used for food or as a cash crop. The planting of fodder legumes has become more popular with the expansion of stall-feeding and the development of a dairy industry. The planting of legumes, with the main objective of improving soil fertility is a more recent development in Nepal’s hills.
Nitrogen is the main plant nutrient element and is usually applied through commercial fertiliser where available. Legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen through bacterial nodules on their roots, then nitrogen subsequently becomes available to the following crops. It is important, therefore, not to uproot the legume crop during harvesting - it should be harvested by cutting the above ground parts leaving the roots (and the nodules) in the soil. The crop residues can be fed to livestock, used as animal bedding, applied as green manure directly to fields, or incorporated in compost. In this way most of the nitrogen that was fixed by the legume crop is returned to the soil.
Details about the different legume species and their different characteristics and uses are described in detail in SSMP, PARDYP and SSD-NARC (2000).
2.3 技术照片
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
尼泊尔
有关地点的进一步说明:
Midhills districts of Nepal
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
Map
×3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- improve soil fertility
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
注释:
Major land use problems (compiler’s opinion): Intensifying cultivation practices with either 1) inadequate application of fertilisers leading to a decline in soil fertility and the mining of soil nutrients or 2) the application of too much fertiliser causing environmental problems through excessive leaching, losses of fertiliser in surface runoff, and consequent eutrophication or nitrification of streams, ponds, or groundwater.
3.5 该技术所属的SLM组
- 土壤肥力综合管理
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
技术规范(与技术图纸相关):
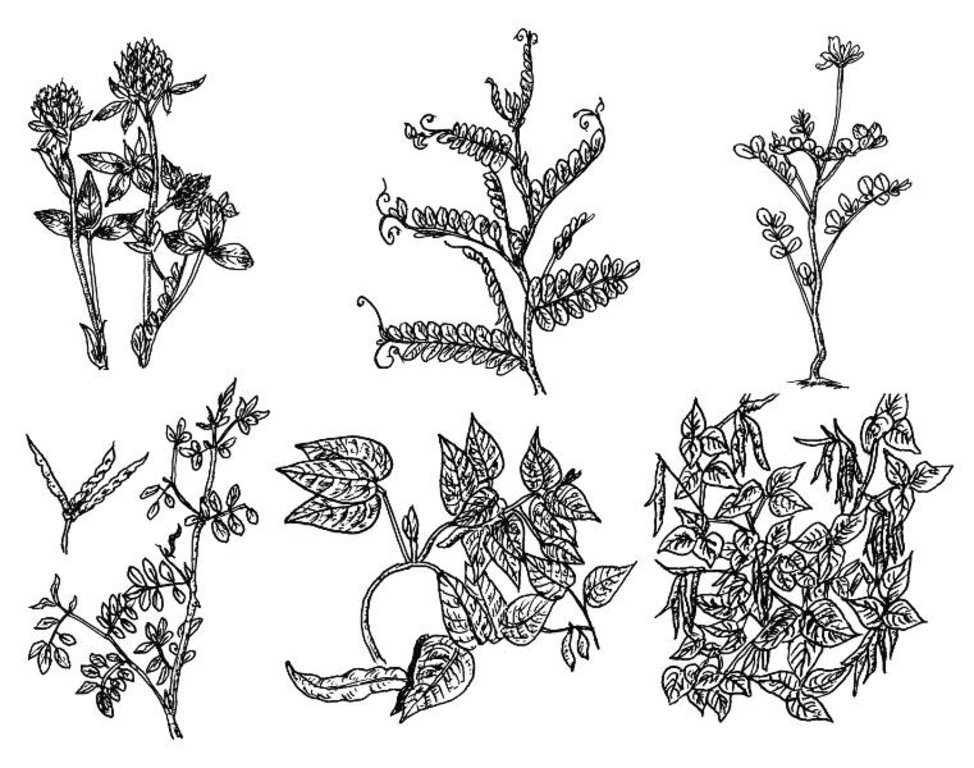
A number of species are presented
in the legume integration decision
support guide (SSMP, PARDYP, SSDNARC 2000). Here only a selection of useful legume species are presented (from top left corner to lower right corner):
- red clover (Trifolium pratense)
- hairy vetch (Vicia villosa Roth)
- Chinese milk vetch (Astragalus sinicus)
- rice bean (Vigna umbellata)
- velvet bean (Mucuna pruriens)
- tephrosia (Tephrosia spp.
Technical knowledge required for field staff / advisors: low
Technical knowledge required for land users: low
Main technical functions: increase in soil fertility (nitrogen in particular), increase in soil productivity & decrease in soil erosionon terrace bunds, nutritius and high value crops
Secondary technical functions: fodder and green manure availability & income
4.2 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术单元
具体说明成本计算所用货币:
- 美元
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
2.00
4.4 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | Persons/day | 2.5 | 2.0 | 5.0 | |
| 植物材料 | Seeds | unit | 1.0 | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 6.5 | |||||
| 技术建立总成本,美元 | 6.5 | |||||
4.5 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|
| 1. | Depending on the type of farm niche - broadcast, line sow, or spot |
4.6 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
注释:
Cost as in January 2007
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Annual rainfall: Also 2000-3000 mm
农业气候带
- 潮湿的
Thermal climate class: subtropics
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
关于地形的注释和进一步规范:
Slopes on average:Also moderate (6-10%), rolling (11-15%) and hilly (16-30%)
Landforms: Also footslopes
Altitudinal zone: Also 1000-1500 m a.s.l., 1500-2000 m a.s.l. and 2000-2500 m a.s.l.
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
生产系统的市场定位:
- 生计(自给)
- 商业/市场
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
Off-farm income specification: In most farm households, off-farm income plays at least a minor and increasingly a major role. Occasional opportunities for off-farm income present themselves in the form of daily labour wages. Some households’ members receive regular salaries whilst an increasing number of Nepalis are working in India, the Middle East, Malaysia and elsewhere and sending remittance incomes home.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者使用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 租赁
- 个人
注释:
sharecropping between owner and tenant
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Reduced expenses for nitrogen fertilizers
其它社会经济效应
Livestock fodder nutritiousness
Value and nutritiousness of crops
Crop in terms of main yield
生态影响
土壤
土壤流失
土壤有机物/地下C
生物多样性:植被、动物
害虫/疾病控制
注释/具体说明:
Highly susceptible to diseases and pests
其它生态影响
Application of fertilizer
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
地下水/河流污染
注释/具体说明:
Reduced nutrient flux into water bodies
Dependence on outside
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
注释:
On average a benefi t of US$ 40 to 50 per ropani can be expected from the production of legume species
6.5 技术采用
注释:
Comments on spontaneous adoption: About 80% of participating farmers used/had adopted the technolog. It has also been adopted by farmers who have not directly participated in SSMP activities.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Cost effective in terms of inputs and management practices in comparison with other commodities |
| Needs less agronomic practices and care (i.e. can be cultivated in zero or reduced tillage) |
| Has multiple uses: food crop, feed crop, fodder, soil building |
| Can be integrated in varying niches on farms and therefore does not need additional land |
| Rich indigenous knowledge exists |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Highly vulnerable to diseases and pests | Skip planting time (i.e. preponing planting of crops to get around life cycle of pests) , use location specifi c species, resistant varieties |
| Very susceptible to waterlogging | Only plant in well-drained soils |
| In high fertility conditions, nitrogen fixing rhizobium does not work leading to less nitrogen fixation | For very specifi c and new species, the soil needs to be inoculated with the correct strain of bacteria |
| Legumes generally do not respond to nitrogen fertiliser | Do not apply nitrogen fertiliser to legumes |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SSMP (2005) Legume Integration Manual (in Nepali). Kathmandu: Sustainable Soil Management Programme
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SSMP
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
SSMP; PARDYP; SSD-NARC (2000) LegumeIntegration into Hill Farming Systems, Decision Support Guide Kathmandu: Sustainable Soil Management Programme, People and Resource Dynamics Project and Soil Science Division-Nepal Agricultural Research Council
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
SSMP
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接

Farmer field schools on integrated plant nutrient systems [尼泊尔]
Participatory and collaborative learning through the farmer field school approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-led experimentation [尼泊尔]
Participatory technology testing and adaptation through farmer-led experiments
- 编制者: Richard Allen

Farmer-to-farmer diffusion [尼泊尔]
Wider diffusion of sustainable soil management technologies through a demand responsive farmer-to-farmer diffusion approach
- 编制者: Richard Allen
模块
无模块