MANGO AND CITRUS TRESS GROWN AS CASHCROPS AND FOR SOIL FERTILITY IMPROVEMENT [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: betty adoch
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson
- 审查者: Drake Mubiru, Nicole Harari, Stephanie Jaquet, Udo Höggel
Gwoko nyig yen igang
technologies_2319 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Okello Vincent
0782954875
okellovincent7@gmail.com
Pagwari Fruit Farmers Association
Pader district, Acoro Sub-County , Acoro parish, Pagwari East village
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
CDE Centre for Development and Environment (CDE Centre for Development and Environment) - 瑞士1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
09/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
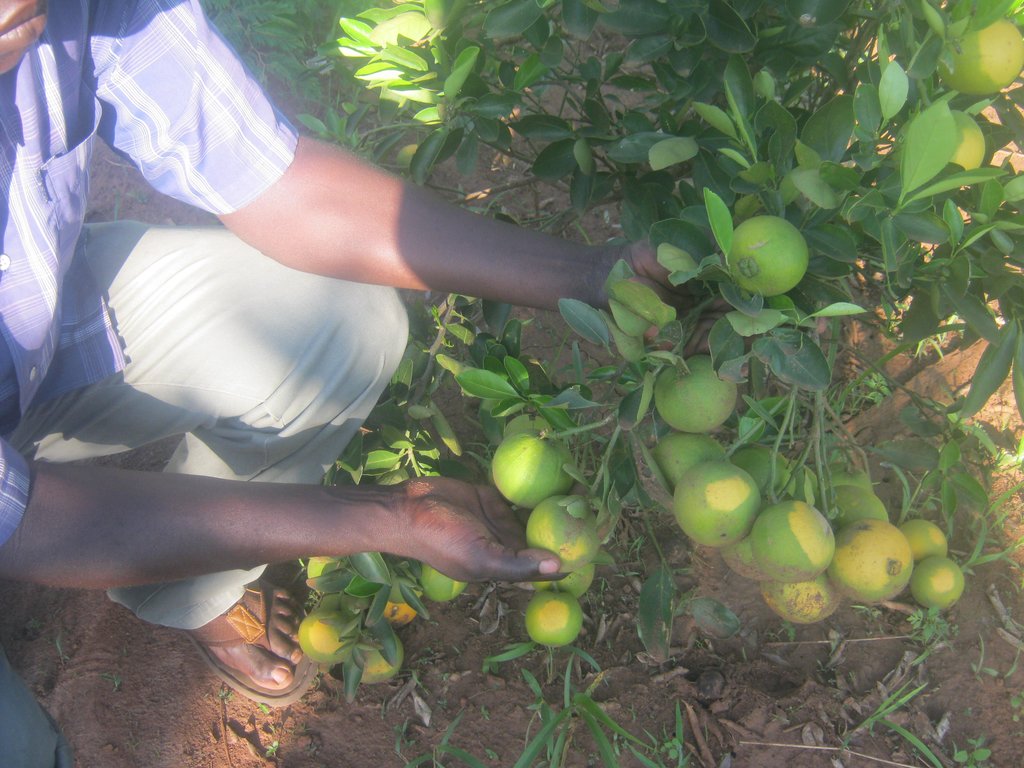
Different varieties of mangoes such as Banganapalle, Alphonso, Kesar, Haden, Bombay, Kent, Keitt, oranges such as Washington Navel, Valencies, Tangarine, jack fruits and avacados are grown for purposes of household income and soil fertility improvement.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
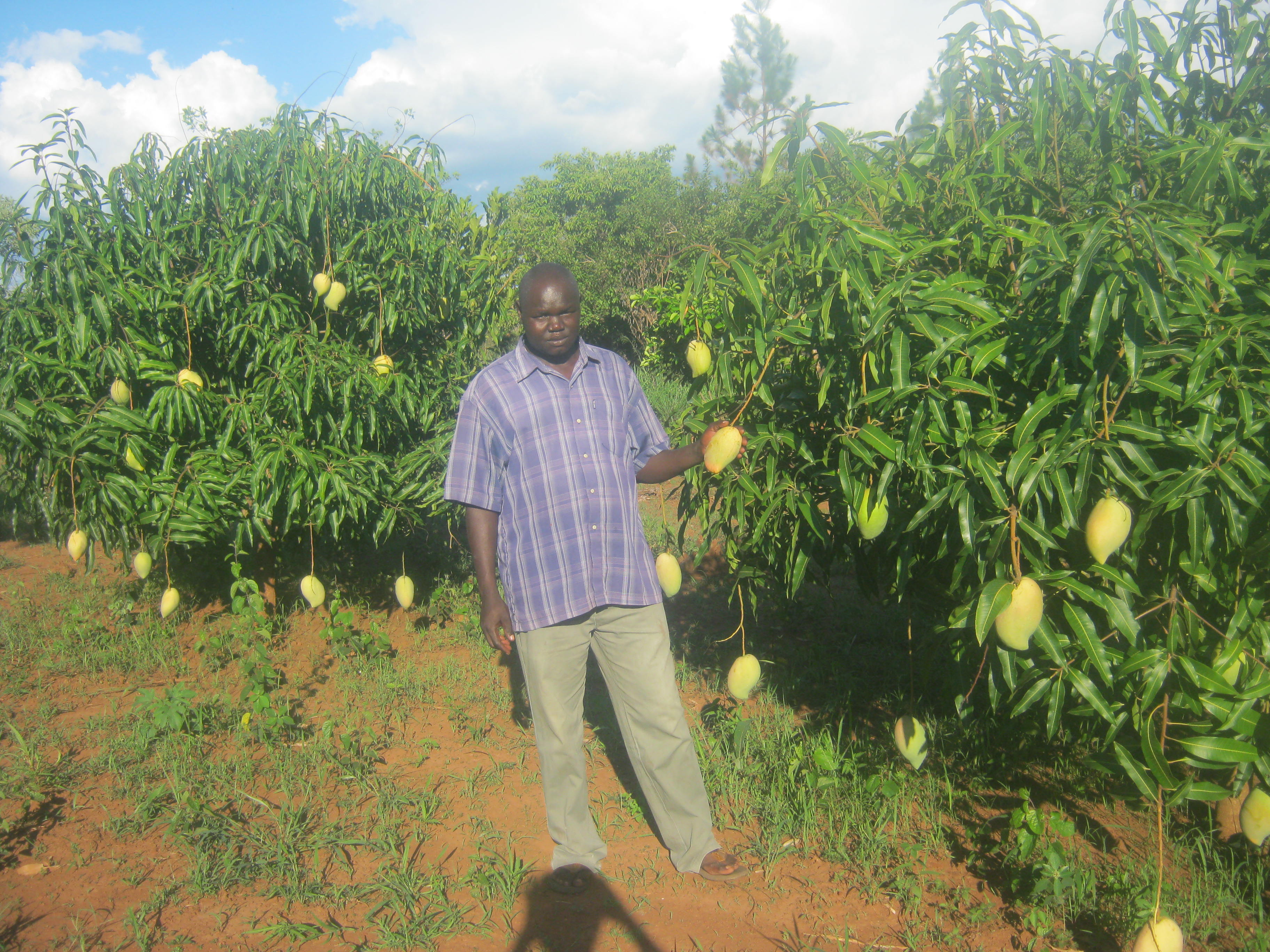
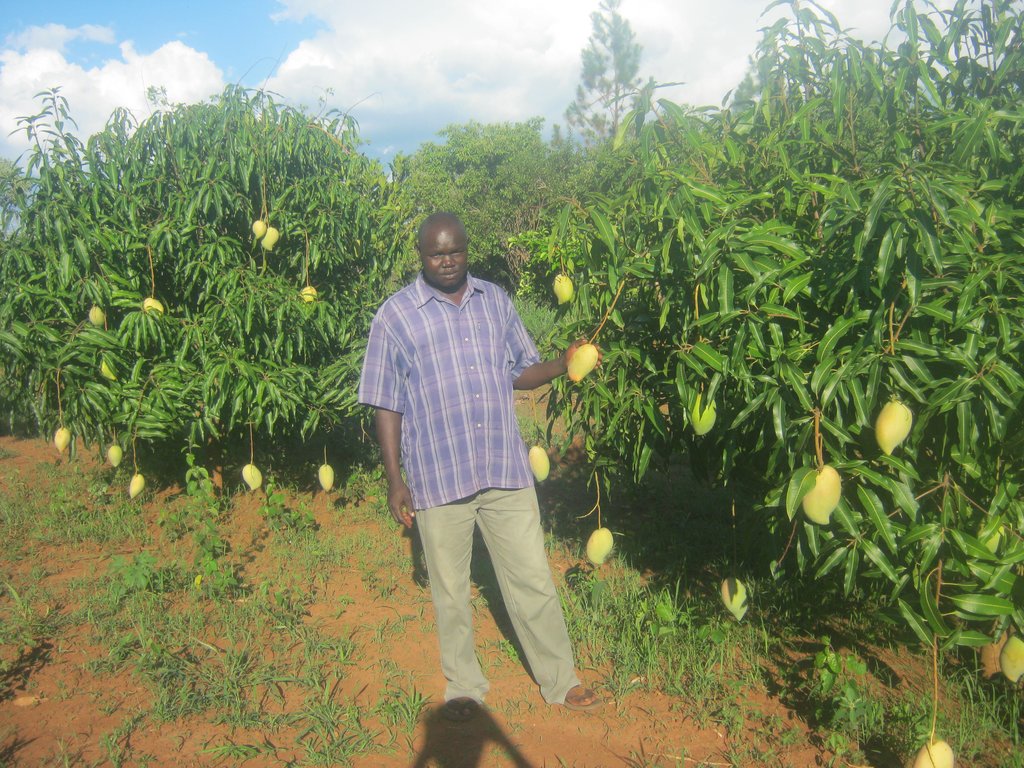
Home fruit tree groves of grafted mango (mangifera indica) and citrus (citrus aurantium) is a farming practice that farmers practice in Northern Uganda to diversify their economic activity, for soil fertility improvement and household income.
Northern Uganda has tropical savanna climate which receives moderate amount of rainfall ranging from 750-1000mm per annum. The soils are moderately fertile with less organic matters coupled with soil erosion, which leads to low crop productions hence low incomes. The moderate rainfall is also unreliable which makes the region to experience drought. Farmers grow fruits as an alternative source of income.
This land user generates over 90% of his household income from fruit growing. The planted fruit trees increase the organic matter content in the soil when dry leaves decompose, rooting prevents soil erosion, pruned brunches are a source of fuel wood and trees acts as wind breaks. Major fruits grown include jack fruits, grafted mangoes, oranges and avocados.
For all these fruits, seeds are first planted in a nursery bed for a period for about two months with the following required inputs: hoes, pangas, spades, wheelbarrows, and shovels. Afterwards, transplanting into the gardens is done. Selection and clearing of the field is done and the planting holes are marked. Excavation is done in accordance to the slope direction: the top soil is put on the hillward side of the planting hole then the sub-soil is put on the downward side of the planting hole. The planting holes are dug in a square shape at 60*60 cm. Composite manure is mixed with top soil and applied into the hole to speed up the seedling establishment and to enhance growth. When planting, the hole is not fully filled but ends 5 cm below the surface so to enable water harvesting, moisture retentions and infiltration. This ensures ample soil moisture and water supply to plants.
The spacing for avocados is 8 × 8 m (65 seedlings/acre), jack fruits is 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre), mangoes 10 × 10 m (44 seedlings/acre) and oranges 4 × 5 m (200 seedlings/acre). After planting, mulching is done by saw dust, kitchen waste like groundnut husks, vegetables and so on. 75 mangoes, 150 oranges, 20 avocados, 20 jack fruits and 4 grapes trees are spread evenly over the planting area. To realize maximum production, the land user needs to have constant water for irrigation.
On the other side, fruit tree growing has brought negative feelings from neighbors who don't promote this practice. Fruit farmers' lifestyle has changed due to revenues realised from growing fruit trees. To maintain this technology, weeding, pruning and creating fire lines during dry seasons to protect the farm is very critical . The technology is highly susceptible to pests and diseases that may require support from the local extension worker from time to time to be able to obtain high yields.
2.3 技术照片
关于照片的一般说明:
Fruit trees protect the soil from environmental degradation and its effects such as soil erosion and landslides.
2.4 技术视频
日期:
19/05/2017
位置:
Pader District, Acoro parish, Pagwari East village.
摄影师的名字:
Betty Adoch
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda.
有关地点的进一步说明:
Pader District, Acoro parish,Pagwari East village.
注释:
GPS point indicating the land user fruits garden
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2013
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
注释(项目类型等):
Land user needs to generate income.
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 适应气候变化/极端天气及其影响
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 乔木与灌木的种植

森林/林地
植树造林:
- 混交品种
产品和服务:
- 水果和坚果
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
The land was use for brick making
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
注释:
Drip irrigation is done during dry seasons
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
牲畜密度(如相关):
Cows: 5, Goats:7. Improved breeds of goat and cattle which are high yielding
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 改良植物品种/动物品种
- 家庭花园
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 均匀地分布在一个区域
如果该技术均匀地分布在一个区域上,请注明覆盖的大致区域。:
- < 0.1 平方千米(10 公顷)
注释:
The fruits gardens covers 2 acres of land.
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

植物措施
- V1:乔木和灌木覆盖层

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
注释:
Fruit growing promotes soil conversation.
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

土壤风蚀
- Et:表土流失

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)
注释:
Fruit growing conserves the environment by preventing tree cutting.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 减少土地退化
注释:
The area initially was severly degraded by brick making work but after putting it under fruit growing, it became very fertile.
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
作者:
Betty Adoch
日期:
19/05/2017
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
The fruit trees are planted on a generally flat average land size of 2 acres of land with following spacing: mangoes 10X10msq, jack fruits 10X10msq because it forms a big canopy, oranges 5X5 msq.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
2 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3500.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3000 UGX
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing for nursery bed | 农业学的 | dry season |
| 2. | Raising the nursery | 农业学的 | dry season |
| 3. | Digging planting holes | 农业学的 | dry season |
| 4. | Applying composite manure | 农业学的 | dry season |
| 5. | Transplanting at 15 to 30cm seedling high | 农业学的 | onset of rain |
注释:
Different fruit species have different nursery beds
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Site clearing for nursery bed | Meters | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Raising the nursery | Meters | 2.0 | 10000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Transplanting | Acres | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Pitting for fruit tree planting | Acres | 2.0 | 50000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Pangas | Pieces | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | Pieces | 15.0 | 10000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Axes | Pieces | 5.0 | 10000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheelbarrows | Pieces | 4.0 | 95000.0 | 380000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | String | Pieces | 4.0 | 5000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Dipper | Pieces | 4.0 | 45000.0 | 180000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Watering can | Pieces | 2.0 | 25000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Spray pump | Pieces | 4.0 | 75000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Bamboo | Pieces | 10.0 | 10000.0 | 100000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Dry grass | Bundles | 5.0 | 3000.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 1535000.0 | |||||
注释:
The technology is technically easy to maintain once established and can be replicated by other land users.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Weeding | 农业学的 | after every 3 months |
| 2. | Pest control | 农业学的 | dry season use cow dung and driny use season pesticide |
| 3. | Stray animal control | 农业学的 | dry season |
| 4. | Thieves control | 农业学的 | rainy season |
| 5. | Prunning branches | 农业学的 | rainy season |
| 6. | Buying pesticides | 农业学的 | rainy season |
| 7. | Transportation to market | 农业学的 | season of harvest |
| 8. | Buying mulching materials | 农业学的 | onset of rain |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Hired labour | Man day | 4.0 | 3000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spray pump | Piece | 4.0 | 75000.0 | 300000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Irrigation during dry season | Litres | 10000.0 | 200.0 | 2000000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Syringe pipe | Piece | 1.0 | 2500.0 | 2500.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Seedings | Pieces | 269.0 | 3500.0 | 941500.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Composite manures | Wheelbarrows | 1.0 | 5000.0 | 5000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Stringes for making holes in a stright line | Rolls | 4.0 | 5000.0 | 20000.0 | 100.0 |
| 植物材料 | Peg for setting holes | Boundle | 1.0 | 10000.0 | 10000.0 | 100.0 |
| 肥料和杀菌剂 | Pesticides (dythen m45) | kg | 1.0 | 40000.0 | 40000.0 | |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 3331000.0 | |||||
注释:
The land user has knowledge on agronomic practices.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
High costs of labor
High transportation cost
Purchase of pesticides
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
950.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Heavy rains in April, May, August and September
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Pader weather station
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Savanna climate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
如有可能,附上完整的土壤描述或具体说明可用的信息,例如土壤类型、土壤酸碱度、阳离子交换能力、氮、盐度等。:
Loamy, silty soil at the top and deep down there is gravel. Soil pH is neutral and less saline.
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
中等
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
关于水质和水量的注释和进一步规范:
Very low water table
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 中等
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 畜力牵引
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 中年人
说明土地使用者的其他有关特征:
The land user is a typical farmer who is contented with his lifestyle as a fruit grower due to the income derived from sale of fruits.
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
注释:
The land user bought the land from the community members.
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,有命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
注释:
The land user has fenced his land and put marked stones.
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Due to the litter from the leaves, increased soil fertility leading to increased production.
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Due to the nutrients from the soil.
饲料生产
注释/具体说明:
Especially from the jack fruits wastes
生产故障风险
注释/具体说明:
Increased level of nutrients in the soil.
产品多样性
注释/具体说明:
Because of the different fruit trees species planted.
生产区域
注释/具体说明:
The land user recently acquired additional plot of land (0.5 acres) from the sale of fruit trees.
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Fruit trees reduce soil erosion and increase soil fertility due to leaves litter.
收入和成本
农业投入费用
注释/具体说明:
Fruit trees dont require alot of inputs once established; minimal costs for reducing pests and diseases; minimized by the role of extension workers during trainings.
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
From the sale of fruits and reduced expenses on farm in puts
收入来源的多样性
注释/具体说明:
From the sale of diverse fruit types (mangoes, oranges, jack fruits and others)
工作量
注释/具体说明:
Only labour for maintenance and monitoring against thieves
社会文化影响
食品安全/自给自足
注释/具体说明:
Income from sale of fruits is used to buy other household income.
健康状况
注释/具体说明:
Daily portion of fruits within diet.
土地使用权/用水权
注释/具体说明:
Community bye-laws on controlled grazing and encroachment were put in place.
社区机构
注释/具体说明:
Local bye-law committee (LBC) was put in place and supported by the Sub-County and District Council.
Bye-law on controlled grazing and encroachment passed at Sub-County Level.
SLM/土地退化知识
注释/具体说明:
Trainings conducted by extension workers and fellow champion farmers, also integrating exposure learning events.
冲突缓解
注释/具体说明:
The presence of the local bye-law committee and bye-laws reduced conflicts: no encroachment, no grazing on fruit gardens and no thieves.
社会经济弱势群体的情况
注释/具体说明:
Integrating people with disabilities (PWDs) in fruit tree growing trainings and exposure learning events.
生态影响
水循环/径流
地表径流
注释/具体说明:
Planted fruit trees control soil run off/soil erosion.
土壤
土壤覆盖层
注释/具体说明:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
土壤流失
注释/具体说明:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees.
土壤堆积
注释/具体说明:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
土壤压实
注释/具体说明:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
土壤有机物/地下C
注释/具体说明:
Due to vegetation litter, plant growth and reduced cutting of trees
减少气候和灾害风险
滑坡/泥石流
注释/具体说明:
Due to planted fruit trees and soil&water conservation bye-law on tree planting.
干旱影响
注释/具体说明:
Planted trees reduce drought.
火灾风险
注释/具体说明:
Due to firelines to control bush burning during dry season.
6.2 该技术的场外影响已经显现
对邻近农田的破坏
注释/具体说明:
Due to presence of strict community bye-laws.
有关影响评估的意见:
The technology is rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by any farmer in any climatic region especially tropical regions.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 减少 | 非常好 | |
| 季节性温度 | 湿季/雨季 | 减少 | 非常好 |
| 年降雨量 | 增加 | 好 | |
| 季雨量 | 湿季/雨季 | 增加 | 非常好 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
气候灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 干旱 | 非常好 |
| 森林火灾 | 非常好 |
| 陆地火灾 | 适度 |
水文灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 滑坡 | 非常好 |
注释:
This technology is drought resistant and manageable by any farmer who has the interest to practice it.
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
稍微积极
长期回报:
非常积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
非常积极
注释:
The fruits are locally sold expensively at 1000 UGX@ and raise much income to the farmer.
6.5 技术采用
- 10-50%
如若可行,进行量化(住户数量和/或覆盖面积):
20 household
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
注释:
The land user uses the little resources he has to establish the technology.
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
否
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| Constant supply of fruits provides high income to the land user. To realize maximum production, there is need for irrigation to have a constant fruit supply with support from extension workers who are readily available with the extension workers for technical advice. |
| The fruit trees modify the micro-environment making it conducive. |
| The technology is very rewarding, cost effective once established and can easily be replicated by other land users. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is good for small , medium and large scale farmers due to its ability to improve soil fertility, increase production and household income. |
| Can easily be replicated by other land users. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Before establishment the technology requires some knowledge and skills on fruit growing which can be extended by the extension worker who are located far from the land user. Associated with high costs in terms of transport and allowances to the land user. |
Training and capacity building of local land users / experts. Training champion farmers. Establishment of learning sites / demonstrations. |
| Prone to climate change | Irrigation during the dry season |
| Requires water supply | Irrigation during dry seasons |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| High establishment costs associated with reduced maintenance costs both in the short, medium and long term. | Adapt low cost practices for those starting and integrate with time and for those with low incomes. |
| Associated with high prevalence of pests and diseases. Risky to spray during flowering season. |
Close monitoring of the field all the time. Seek technical advice from the extension worker. |
| Labour intensive at the time of establishment. | Supplement with family labour. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
- 与SLM专业人员/专家的访谈
1
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
Do Trees on Farms Improve Household Well-Being? Evidence From National Panel Data in Uganda, Daniel, C.Miller,September 2020.2020.0010
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
On-line. Free of cost.
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块