Local Rabbit Keeping for Manure Production and Household Income [乌干达]
- 创建:
- 更新:
- 编制者: betty adoch
- 编辑者: JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson, Bernard Fungo
- 审查者: Drake Mubiru, Udo Höggel
Gwoko Apwoyo pi cetgi me medo moc ngom
technologies_2890 - 乌干达
查看章节
全部展开 全部收起1. 一般信息
1.2 参与该技术评估和文件编制的资源人员和机构的联系方式
关键资源人
土地使用者:
Onen Geoffrey
0793874904 / 0776492280
onen@yahoorocket.com
Ongako Farmers group
Omoro District, Ongako Subcounty, Kal Parish, Kal Village
乌干达
有助于对技术进行记录/评估的项目名称(如相关)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)有助于对技术进行记录/评估的机构名称(如相关)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - 乌干达1.3 关于使用通过WOCAT记录的数据的条件
(现场)数据是什么时候汇编的?:
24/05/2017
编制者和关键资源人员接受有关使用通过WOCAT记录数据的条件。:
是
1.4 所述技术的可持续性声明
这里所描述的技术在土地退化方面是否存在问题,导致无法被认为是一种可持续的土地管理技术?:
否
2. SLM技术的说明
2.1 技术简介
技术定义:
Local rabbits are kept in a shade made of wood, iron sheet and wire mesh for manure production with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement thus increasing vegetable and fruits production and household income.
2.2 技术的详细说明
说明:
Local rabbit keeping for manure production is a common practice promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement, increasing agricultural production and for securing household income.
Through the promotion of this technology the farmer uses animal manure because soils have low fertility, coupled with low productivity and hence low crop yields caused by degradation due to mono-culture, overgrazing and bush burning.
To obtain animal manure, local rabbits are kept within the compound for easy monitoring, minimum protection against predators and easy collection of manure. After manure is collected, it is filled into a decomposing pit. From there the manure is later applied to agricultural fields, vegetable and fruit gardens.
Important to note is that this technology is appropriate for small scale farmers with land size holding of 0.5-2 acres. it requires little amount of money at the time of establishment, it is not labour intensive and provides high nutrient manure since the rabbits are fed mainly on local feeds.
Usually manure is collected around the rabbit house on a weekly basis to be used as compost manure which is then applied to the garden. Following steps are required : Site clearing, collecting manure and digging compost pits for manure decomposition and manure application to the garden. Material required is timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails, wire mesh and iron sheets. The compost manure pit is dug to 1 meter depth and 1 meter width. Rabbit dung is collected to fill up the pit.
To maintain the technology, land users need to clear the bush around the house for easy collection of the dung and turning the decomposing manure weekly for proper decomposition.
Usually it takes one month for a pit to fill up and the decomposition period is three months. The compost manure is then collected using a wheelbarrow and spread into the vegetables and fruits gardens of lemon grass, green peas, green pepper and fruits (tangerine, oranges).
After applying on his garden, the farmer continues to collect the surplus manure which he sells to other farmers at a rate of 2,000 shillings per spade of organic manure. This practice is usually appreciated by land users because it enhances soil fertility, increases crop production and rehabilitates badly degraded land by adding manure nutrients to the soil.
What is not liked about this technology is that the manure takes somewhat a long time to accumulate due to the small number of rabbits kept in addition to long time to decompose for application on the garden.
2.3 技术照片
2.4 技术视频
注释、简短说明:
Video showing rabbit keeping for increased manure production and household income.
日期:
24/05/2017
位置:
Kal Village , Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
摄影师的名字:
Betty Adoch
2.5 已应用该技术的、本评估所涵盖的国家/地区/地点
国家:
乌干达
区域/州/省:
Northern Uganda.
有关地点的进一步说明:
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
注释:
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty, Omoro District, Northern Uganda
Map
×2.6 实施日期
注明实施年份:
2016
2.7 技术介绍
详细说明该技术是如何引入的:
- 通过土地使用者的创新
- 通过项目/外部干预
注释(项目类型等):
Local rabbit keeping project for animal manure
3. SLM技术的分类
3.1 该技术的主要目的
- 改良生产
- 减少、预防、恢复土地退化
- 保持/提高生物多样性
- 创造有益的经济影响
3.2 应用该技术的当前土地利用类型

农田
- 一年一作
- 多年一作(非木材)
- 乔木与灌木的种植
主要农作物(经济作物及粮食作物):
Vegetables, fruits

不毛之地
具体说明:
Degraded lands
如果由于技术的实施而导致土地用途发生变化,则在技术实施前说明土地利的用途。:
Cereals cropland and grazing fields.
3.3 有关土地利用的更多信息
该技术所应用土地的供水:
- 雨养
每年的生长季节数:
- 1
3.4 该技术所属的SLM组
- 农畜综合管理
- 养蜂、养殖业、家禽业、养兔业、养蚕业等
3.5 技术传播
具体说明该技术的分布:
- 适用于特定场所/集中在较小区域
3.6 包含该技术的可持续土地管理措施

农艺措施
- A2:有机质/土壤肥力

结构措施
- S9:动植物庇护所

管理措施
- M1:改变土地使用类型
3.7 该技术强调的主要土地退化类型

土壤水蚀
- Wt:表土流失/地表侵蚀

化学性土壤退化
- Cn:肥力下降和有机质含量下降(非侵蚀所致)

物理性土壤退化
- Pu:由于其他活动而导致生物生产功能的丧失

生物性退化
- Bc:植被覆盖的减少
- Bh:栖息地丧失
- Bq:数量/生物量减少
注释:
The application of this technology helps repairing the soil from human-induced degradation.
3.8 防止、减少或恢复土地退化
具体数量名该技术与土地退化有关的目标:
- 防止土地退化
- 减少土地退化
4. 技术规范、实施活动、投入和成本
4.1 该技术的技术图纸
4.2 技术规范/技术图纸说明
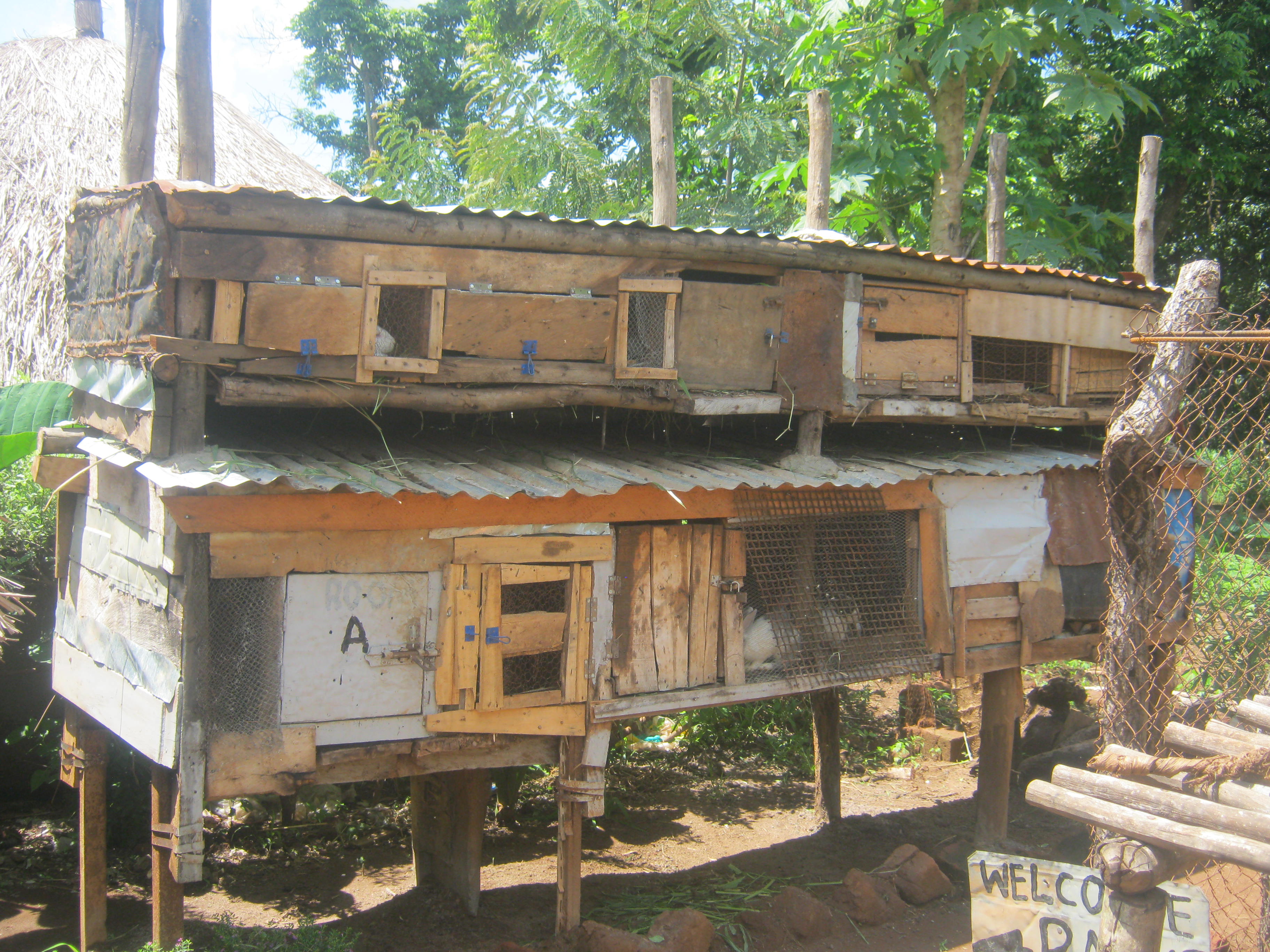
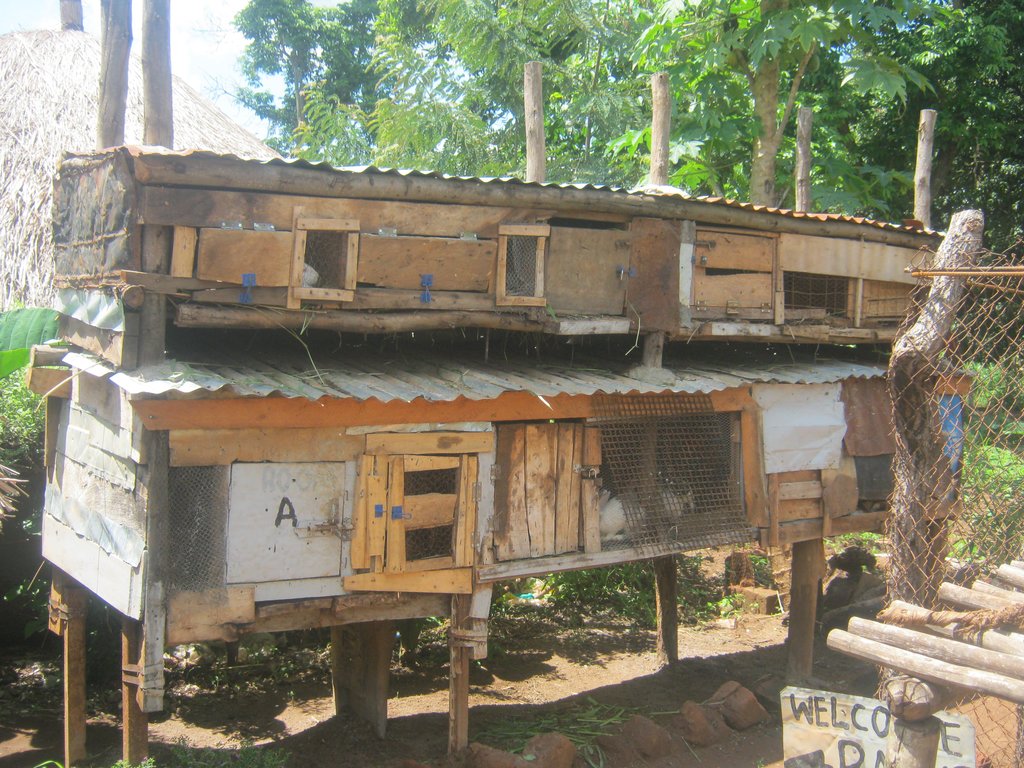
The technical drawing shows a rabbit house (hutch). This hutch was made simple and affordable to the farmer. The hutch was constructed around the compound for easy monitoring from danger by the farmer. The farmer constructed the hutch out of wood, iron sheets for the roofing and a wire mesh door that can be opened and closed.
However, when constructing a hutch, the measurements tend to vary depending on the number of rabbits a farmer wants to rear.
The technical drawing shows that the width of the hutch is six (6) meters and having a depth of 1,5 metres. The wall of the hutch is made of wood of about 1 meter high supported by a raised platform. That platform offers protection against dangerous reptiles such as snakes that prey on rabbits.
The hutch has lower and upper levels, partitioned into smaller rooms big enough to accommodate a pair of rabbits. The sizes of the rooms are four times bigger than the size of the rabbit's length. This is to provide ample space for the rabbit to run around and stretch as well as a place to hide while playing.
A hutch is constructed in a way that protects the rabbit from adverse weather conditions such a too windy weather that usually kills or makes the rabbit to become too sick as well as to provide shade to the rabbits.
However, hutches can be difficult to clean and also rabbits may be able to escape if the wire mesh isn't tightly secured.
4.3 有关投入和成本计算的一般信息
具体说明成本和投入是如何计算的:
- 每个技术区域
注明尺寸和面积单位:
2 acres
其它/国家货币(具体说明):
UGX
注明美元与当地货币的汇率(如相关):1美元=:
3500.0
注明雇用劳工的每日平均工资成本:
3000shs
4.4 技术建立活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing | 农业学的 | Dry and wet season |
| 2. | Digging pits | 结构性的 | Dry and wet season |
| 3. | Collecting rabbit dung | 管理 | Dry and Wet season |
| 4. | Pilling the dung in the pit | 管理 | Dry and Wet season |
| 5. | Applying manures to the garden | 农业学的 | Wet season |
| 6. | Constructing the hutch | 结构性的 | Dry and Wet season |
注释:
Easy to establish the technology because it requires less capital.
4.5 技术建立所需要的费用和投入
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Labour | persons day | 2.0 | 3500.0 | 7000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoes | piece | 3.0 | 12000.0 | 36000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheelbarrows | piece | 1.0 | 90000.0 | 90000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spade | piece | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Nails | pics | 30.0 | 500.0 | 15000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Poles | pics | 10.0 | 5000.0 | 50000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Wire mesh | Roll | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Iron sheets | pics | 2.0 | 32000.0 | 64000.0 | 100.0 |
| 施工材料 | Timber | pics | 10.0 | 12000.0 | 120000.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术建立所需总成本 | 442000.0 | |||||
注释:
Land user can afford to pay the workers during during construction, compost manure making and labour for transporting the manures to the garden.
4.6 维护/经常性活动
| 活动 | 措施类型 | 时间/频率 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turning the compost | 管理 | During dry and wet season |
| 2. | Cleaning the hutch | 管理 | During dry and wet season |
| 3. | Digging around the hutch | 管理 | During dry and wet season |
4.7 维护/经常性活动所需要的费用和投入(每年)
| 对投入进行具体说明 | 单位 | 数量 | 单位成本 | 每项投入的总成本 | 土地使用者承担的成本% | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 劳动力 | Clearing around the hutch | perso per dayn | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Cleaning the hutch | person per day | 4.0 | 3000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Clearing around the manure pit | person per day | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 劳动力 | Adding manure to the garden | persons per day | 1.0 | 3000.0 | 3000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hoe | pic | 1.0 | 12000.0 | 12000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Spade | pic | 1.0 | 30000.0 | 30000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Wheelbarrow | pic | 1.0 | 150000.0 | 150000.0 | 100.0 |
| 设备 | Hard broom | pic | 1.0 | 500.0 | 500.0 | 100.0 |
| 技术维护所需总成本 | 213500.0 | |||||
注释:
Maintenance activities do not require much capital.
4.8 影响成本的最重要因素
描述影响成本的最决定性因素:
Inputs such as timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails , wire mesh and iron sheets affect costs most.
5. 自然和人文环境
5.1 气候
年降雨量
- < 250毫米
- 251-500毫米
- 501-750毫米
- 751-1,000毫米
- 1,001-1,500毫米
- 1,501-2,000毫米
- 2,001-3,000毫米
- 3,001-4,000毫米
- > 4,000毫米
指定年平均降雨量(若已知),单位为mm:
1500.00
有关降雨的规范/注释:
Rainy seasons from april, may, june, july, august, september and october. Dry seasons from november, december, january, febuary and march.
注明所考虑的参考气象站名称:
Gulu weather station.
农业气候带
- 半湿润
Tropical savanna climate
5.2 地形
平均坡度:
- 水平(0-2%)
- 缓降(3-5%)
- 平缓(6-10%)
- 滚坡(11-15%)
- 崎岖(16-30%)
- 陡峭(31-60%)
- 非常陡峭(>60%)
地形:
- 高原/平原
- 山脊
- 山坡
- 山地斜坡
- 麓坡
- 谷底
垂直分布带:
- 0-100 m a.s.l.
- 101-500 m a.s.l.
- 501-1,000 m a.s.l.
- 1,001-1,500 m a.s.l.
- 1,501-2,000 m a.s.l.
- 2,001-2,500 m a.s.l.
- 2,501-3,000 m a.s.l.
- 3,001-4,000 m a.s.l.
- > 4,000 m a.s.l.
说明该技术是否专门应用于:
- 不相关
5.3 土壤
平均土层深度:
- 非常浅(0-20厘米)
- 浅(21-50厘米)
- 中等深度(51-80厘米)
- 深(81-120厘米)
- 非常深(> 120厘米)
土壤质地(表土):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
土壤质地(地表以下> 20厘米):
- 中粒(壤土、粉土)
表土有机质:
- 中(1-3%)
5.4 水资源可用性和质量
地下水位表:
5-50米
地表水的可用性:
好
水质(未处理):
良好饮用水
水的盐度有问题吗?:
否
该区域正在发生洪水吗?:
否
5.5 生物多样性
物种多样性:
- 高
栖息地多样性:
- 高
5.6 应用该技术的土地使用者的特征
定栖或游牧:
- 定栖的
生产系统的市场定位:
- 混合(生计/商业
非农收入:
- 低于全部收入的10%
相对财富水平:
- 平均水平
个人或集体:
- 个人/家庭
机械化水平:
- 手工作业
性别:
- 女人
- 男人
土地使用者的年龄:
- 青年人
- 中年人
5.7 应用该技术的土地使用者拥有或租用的平均土地面积
- < 0.5 公顷
- 0.5-1 公顷
- 1-2 公顷
- 2-5公顷
- 5-15公顷
- 15-50公顷
- 50-100公顷
- 100-500公顷
- 500-1,000公顷
- 1,000-10,000公顷
- > 10,000公顷
这被认为是小规模、中规模还是大规模的(参照当地实际情况)?:
- 小规模的
5.8 土地所有权、土地使用权和水使用权
土地所有权:
- 个人,未命名
土地使用权:
- 个人
用水权:
- 社区(有组织)
5.9 进入服务和基础设施的通道
健康:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
教育:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
技术援助:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
就业(例如非农):
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
市场:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
能源:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
道路和交通:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
饮用水和卫生设施:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
金融服务:
- 贫瘠
- 适度的
- 好
6. 影响和结论性说明
6.1 该技术的现场影响
社会经济效应
生产
作物生产
注释/具体说明:
Manure adds nutrients into the soil thus increasing crop productions
作物质量
注释/具体说明:
Manure add nutrients to the soil fertile soils improving crop quality
土地管理
注释/具体说明:
Due to application of manure which is locally obtained.
收入和成本
农业收入
注释/具体说明:
Some of the surplus manure is sold to generate income @ spade at UGX 2000 to the neighbourhood
生态影响
生物多样性:植被、动物
植被覆盖
SLM之前的数量:
low quantity before SLM
SLM之后的数量:
high quantity after SLM
注释/具体说明:
Vegetable crop growing improved due to manure applications into the soil.
生物量/地上C
注释/具体说明:
Dense vegetation cover provides above ground carbon sink.
6.3 技术对渐变气候以及与气候相关的极端情况/灾害的暴露和敏感性(土地使用者认为的极端情况/灾害)
渐变气候
渐变气候
| 季节 | 气候变化/极端天气的类型 | 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 年温度 | 增加 | 适度 | |
| 年降雨量 | 减少 | 适度 |
气候有关的极端情况(灾害)
生物灾害
| 该技术是如何应对的? | |
|---|---|
| 流行病 | 不好 |
6.4 成本效益分析
技术收益与技术建立成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
技术收益与技术维护成本/经常性成本相比如何(从土地使用者的角度看)?
短期回报:
积极
长期回报:
积极
6.5 技术采用
- 单例/实验
在所有采用这项技术的人当中,有多少人是自发地采用该技术,即未获得任何物质奖励/付款?:
- 90-100%
6.6 适应
最近是否对该技术进行了修改以适应不断变化的条件?:
是
若是,说明它适应了哪些变化的条件:
- 不断变化的市场
具体说明技术的适应性(设计、材料/品种等):
Improved rabbit species being reared by the farmers that fetch high market prices.
6.7 该技术的优点/长处/机会
| 土地使用者眼中的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is good at providing locally available materials such rabbit dung/animal manure that is less cost intensive and locally obtained. |
| Good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by other small scale farmers in other areas. |
| Provides income after sale of manure. |
| Very appropriate for men and children/youth since it does not involve a lot of moving from one place to another for feeds. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的长处/优势/机会 |
|---|
| The technology is multipurpose (good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, provides income after sale of manure). |
| Easy to replicate. |
6.8 技术的弱点/缺点/风险及其克服方法
| 土地使用者认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Leaching due to excessive rainfall. | Dig the manure pit under shade/shelter. |
| Liked by thieves. | Fencing, provision of security. |
| Rabbits consume lots of feeds. | Grow relevant local feeds near the homestead such as grass, maize plant. |
| 编制者或其他关键资源人员认为的弱点/缺点/风险 | 如何克服它们? |
|---|---|
| Negative attitude by other community members. | Involve them in the process of manure preparation and hutch constructions. |
| Long period required for manure to decompose. | Dig pit under shade for fast cooling of the compost and enhancement of decomposition. |
| Low rabbit dung collection for manure since they are kept in less numbers. | Expand the number of rabbits to generate manure. |
7. 参考和链接
7.1 信息的方法/来源
- 实地考察、实地调查
1
- 与土地使用者的访谈
1
7.2 参考可用出版物
标题、作者、年份、ISBN:
The potential of rabbit production in improving household incomes in Nankoma Sub-county, Bugiri District, Uganda E K Ndyomugyenyi and O D Otiengino
可以从哪里获得?成本如何?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289674867_Ndyomugyenyi_E_K_and_Otiengino_O_D_2013_The_potential_of_rabbit_production_in_improving_household_incomes_in_Nankoma_Sub-county_Bugiri_District_Uganda_Livestock_Research_for_Rural_Development_25_8_htt
7.3 链接到网络上可用的相关信息
标题/说明:
Rabbit Farming In Uganda, Rearing Tips, Farmers Association, Market, Urine, Feeds & Cages
URL:
https://www.aboutuganda.com/agriculture/rabbit-farming-in-uganda
链接和模块
全部展开 全部收起链接
无链接
模块
无模块