Local Rabbit Keeping for Manure Production and Household Income [អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា]
- ការបង្កើត៖
- បច្ចុប្បន្នភាព
- អ្នកចងក្រង៖ betty adoch
- អ្នកកែសម្រួល៖ JOY TUKAHIRWA, Kamugisha Rick Nelson, Bernard Fungo
- អ្នកត្រួតពិនិត្យច្រើនទៀត៖ Drake Mubiru, Udo Höggel
Gwoko Apwoyo pi cetgi me medo moc ngom
technologies_2890 - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ពិនិត្យមើលគ្រប់ផ្នែក
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់1. ព័ត៌មានទូទៅ
1.2 ព័ត៌មានលម្អិតពីបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ និងស្ថាប័នដែលចូលរួមក្នុងការវាយតម្លៃ និងចងក្រងឯកសារនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បុគ្គលសំខាន់ម្នាក់ (ច្រើននាក់)
អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
Onen Geoffrey
0793874904 / 0776492280
onen@yahoorocket.com
Ongako Farmers group
Omoro District, Ongako Subcounty, Kal Parish, Kal Village
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
ឈ្មោះគម្រោងដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃលើបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Scaling-up SLM practices by smallholder farmers (IFAD)ឈ្មោះអង្គភាពមួយ (ច្រើន) ដែលបានចងក្រងឯកសារ/ វាយតម្លៃបច្ចេកទេស (បើទាក់ទង)
Uganda Landcare Network (ULN) - អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា1.3 លក្ខខណ្ឌទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈ វ៉ូខេត
តើពេលណាដែលទិន្នន័យបានចងក្រង (នៅទីវាល)?
24/05/2017
អ្នកចងក្រង និង(បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ)យល់ព្រមទទួលយកនូវលក្ខខណ្ឌនានាទាក់ទងទៅនឹងការប្រើប្រាស់ទិន្នន័យដែលបានចងក្រងតាមរយៈវ៉ូខេត:
បាទ/ចា៎
1.4 សេចក្តីប្រកាសស្តីពីចីរភាពនៃការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស
តើបច្ចេកទេសដែលបានពណ៌នានេះមានបញ្ហាដែលផ្តោតលើការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី, បើដូច្នេះវាមិនអាចត្រូវបានប្រកាសថាជាបច្ចេកទេសនៃការគ្រប់គ្រងប្រកបដោយចីរភាពទេ?
ទេ
2. ការពណ៌នាពីបច្ចេកទេស SLM
2.1 ការពណ៌នាដោយសង្ខេបពីបច្ចេកទេស
និយមន័យបច្ចេកទេស:
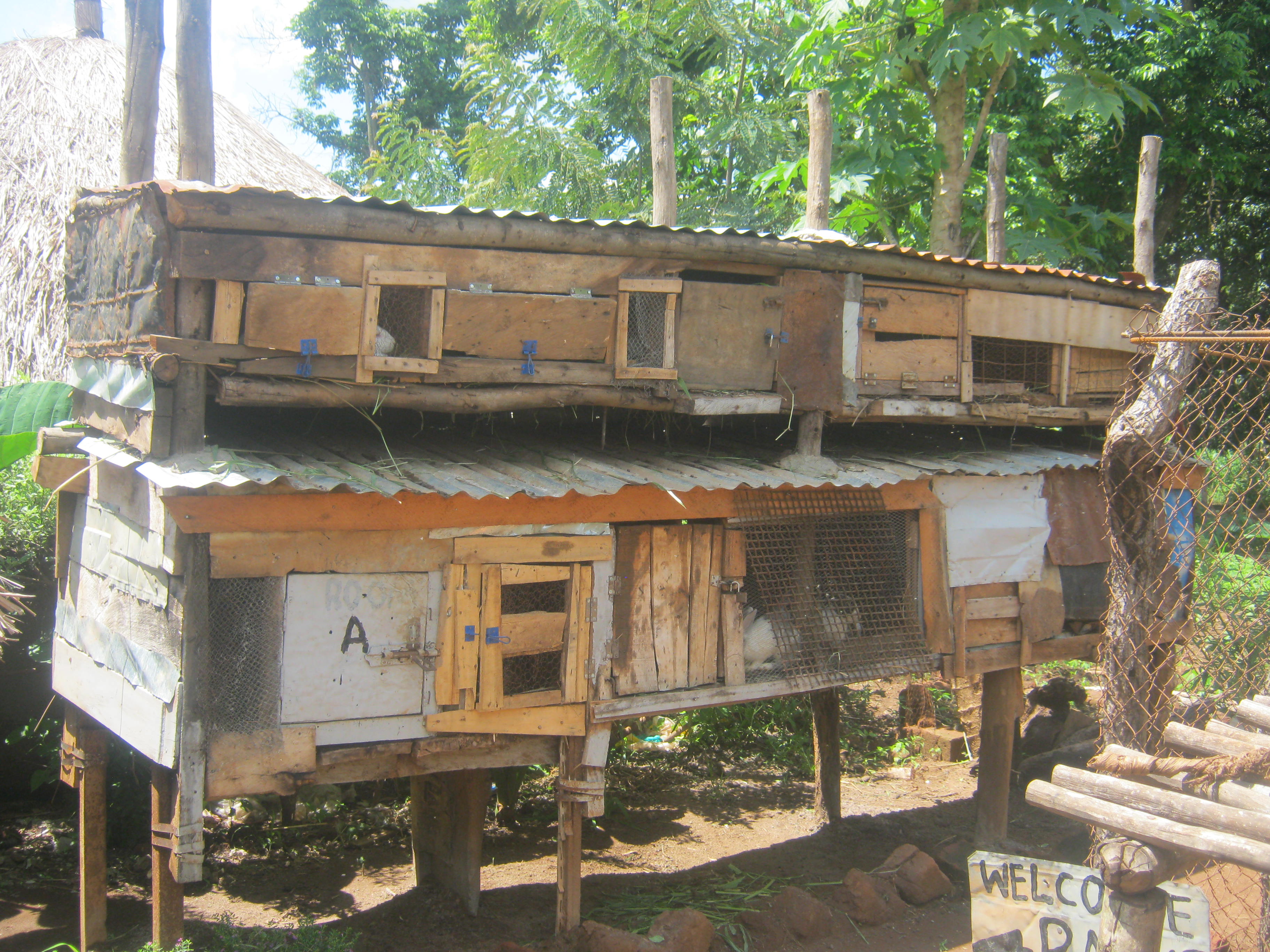
Local rabbits are kept in a shade made of wood, iron sheet and wire mesh for manure production with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement thus increasing vegetable and fruits production and household income.
2.2 ការពណ៌នាលម្អិតពីបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នា:
Local rabbit keeping for manure production is a common practice promoted by farmers in Northern Uganda with the aim of obtaining animal manure for soil fertility improvement, increasing agricultural production and for securing household income.
Through the promotion of this technology the farmer uses animal manure because soils have low fertility, coupled with low productivity and hence low crop yields caused by degradation due to mono-culture, overgrazing and bush burning.
To obtain animal manure, local rabbits are kept within the compound for easy monitoring, minimum protection against predators and easy collection of manure. After manure is collected, it is filled into a decomposing pit. From there the manure is later applied to agricultural fields, vegetable and fruit gardens.
Important to note is that this technology is appropriate for small scale farmers with land size holding of 0.5-2 acres. it requires little amount of money at the time of establishment, it is not labour intensive and provides high nutrient manure since the rabbits are fed mainly on local feeds.
Usually manure is collected around the rabbit house on a weekly basis to be used as compost manure which is then applied to the garden. Following steps are required : Site clearing, collecting manure and digging compost pits for manure decomposition and manure application to the garden. Material required is timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails, wire mesh and iron sheets. The compost manure pit is dug to 1 meter depth and 1 meter width. Rabbit dung is collected to fill up the pit.
To maintain the technology, land users need to clear the bush around the house for easy collection of the dung and turning the decomposing manure weekly for proper decomposition.
Usually it takes one month for a pit to fill up and the decomposition period is three months. The compost manure is then collected using a wheelbarrow and spread into the vegetables and fruits gardens of lemon grass, green peas, green pepper and fruits (tangerine, oranges).
After applying on his garden, the farmer continues to collect the surplus manure which he sells to other farmers at a rate of 2,000 shillings per spade of organic manure. This practice is usually appreciated by land users because it enhances soil fertility, increases crop production and rehabilitates badly degraded land by adding manure nutrients to the soil.
What is not liked about this technology is that the manure takes somewhat a long time to accumulate due to the small number of rabbits kept in addition to long time to decompose for application on the garden.
2.3 រូបភាពនៃបច្ចេកទេស
2.4 វីដេអូនៃបច្ចេកទេស
ការពណ៌នាសង្ខេប:
Video showing rabbit keeping for increased manure production and household income.
កាលបរិច្ឆេទ:
24/05/2017
ទីតាំង:
Kal Village , Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
ឈ្មោះអ្នកថតវីឌីអូ:
Betty Adoch
2.5 ប្រទេស/តំបន់/ទីតាំងកន្លែង ដែលបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានអនុវត្ត និងបានគ្រប់ដណ្តប់ដោយការវាយតម្លៃនេះ
ប្រទេស:
អ៊ូហ្គង់ដា
តំបន់/រដ្ឋ/ខេត្ត:
Northern Uganda.
បញ្ជាក់បន្ថែមពីលក្ខណៈនៃទីតាំង:
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty,Omoro District, Northern Uganda
មតិយោបល់:
Kal Village, Kal Parish, Ongako Subcounty, Omoro District, Northern Uganda
Map
×2.6 កាលបរិច្ឆេទនៃការអនុវត្ត
បង្ហាញឆ្នាំនៃការចុះអនុវត្ត:
2016
2.7 ការណែនាំពីបច្ចេកទេស
សូមបញ្ជាក់តើបច្ចេកទេសត្រូវបានណែនាំឱ្យអនុវត្តដោយរបៀបណា:
- តាមរយៈការបង្កើតថ្មីរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
- តាមរយៈគម្រោង / អន្តរាគមន៍ពីខាងក្រៅ
មតិយោបល់ (ប្រភេទនៃគម្រោង ។ល។):
Local rabbit keeping project for animal manure
3. ចំណាត់ថ្នាក់នៃបច្ចេកទេស SLM
3.1 គោលបំណងចម្បង (១ ឬច្រើន) នៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
- ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងនូវផលិតកម្ម
- កាត់បន្ថយ, បង្ការ, ស្តារឡើងវិញនូវការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- អភិរក្ស/ធ្វើឱ្យប្រសើរឡើងជីវចម្រុះ
- បង្កើតផលប្រយោជន៍សេដ្ឋកិច្ច
3.2 ប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់មួយប្រភេទ (ច្រើនប្រភេទ) ដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស

ដីដាំដំណាំ
- ដំណាំប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- ដំណាំរយៈពេលវែង (មិនមែនឈើ)
- ប្រភេទដើមឈើធំៗ និងដើមឈើតូចៗ
ដំណាំចម្បង (ដំណាំកសិ-ឧស្សាហកម្ម និងដំណាំស្បៀង) :
Vegetables, fruits

ដីខ្សោះជីជាតិ
សូមបញ្ជាក់:
Degraded lands
ប្រសិនបើដីមានការប្រែប្រួលបន្ទាប់ពីការអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស សូមបញ្ជាក់ពីការប្រើប្រាស់ដីមុនពេលអនុវត្តន៍បច្ចេកទេស:
Cereals cropland and grazing fields.
3.3 ព័ត៌មានបន្ថែមអំពីអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
ការផ្គត់ផ្គង់ទឹកនៅកន្លែងអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស:
- ទឹកភ្លៀង
ចំនួនសារដែលដាំដំណាំក្នុងមួយឆ្នាំ:
- 1
3.4 ក្រុម SLM ដែលបច្ចេកទេសស្ថិតនៅក្នុង
- ការគ្រប់គ្រងដោយរួមបញ្ចូលការដាំដំណាំ និងការចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ
- ការចិញ្ចឹមឃ្មុំ, វារីវប្បកម្ម, ការចិញ្ចឹមបសុបក្សី, ទន្សាយ, ដង្កូវនាង ។ល។
3.5 ការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស
បញ្ជាក់ពីការសាយភាយនៃបច្ចេកទេស:
- អនុវត្តនៅកន្លែងជាក់លាក់មួយ/ ប្រមូលផ្តុំនៅតំបន់តូចៗ
3.6 វិធានការ SLM ដែលបញ្ចូលនូវបច្ចេកទេស

វិធានការក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ
- A2: សារធាតុសរីរាង្គ/ជីជាតិដី

វិធានការរចនាស័ម្ពន្ធ
- S9: រោងដំណាំ និងរោងចិញ្ចឹមសត្វ

វិធានការគ្រប់គ្រង
- M1: ការផ្លាស់ប្តូរប្រភេទដីប្រើប្រាស់
3.7 កំណត់ប្រភេទនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដីសំខាន់ៗដែលបច្ចេកទេសនេះបានដោះស្រាយ

ការហូរច្រោះដីដោយសារទឹក
- Wt: ការបាត់ដីស្រទាប់លើដោយការហូរច្រោះ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះសារធាតុគីមីក្នុងដី
- Cn: ការថយចុះជីជាតិ និងកាត់បន្ថយបរិមាណសារធាតុសរីរាង្គ (មិនកើតឡើងដោយការហូរច្រោះទេ)

ការបាត់បង់រូបសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Pu: បាត់បង់នូវផលិតភាពជីវៈដោយសារសកម្មភាពផ្សេងៗ

ការធ្លាក់ចុះជីវសាស្ត្រនៃដី
- Bc: ការថយចុះនូវគម្របរុក្ខជាតិ
- Bh: ការបាត់បង់ទីជំរក
- Bq: ការថយចុះនូវជីវម៉ាស/ បរិមាណ
មតិយោបល់:
The application of this technology helps repairing the soil from human-induced degradation.
3.8 ការពារ កាត់បន្ថយ ឬស្តារឡើងវិញនៃការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
បញ្ជាក់ពីគោលដៅរបស់បច្ចេកទេស ដែលផ្តោតទៅការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី:
- ការការពារការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
- ការកាត់បន្ថយការធ្លាក់ចុះគុណភាពដី
4. បច្ចេកទេសជាក់លាក់ សកម្មភាពអនុវត្ត ធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
4.1 គំនូសបច្ចេកទេសនៃបច្ចេកទេសនេះ
4.2 លក្ខណៈពិសេសនៃបច្ចេកទេស/ ពណ៌នាពីគំនូរបច្ចេកទេស
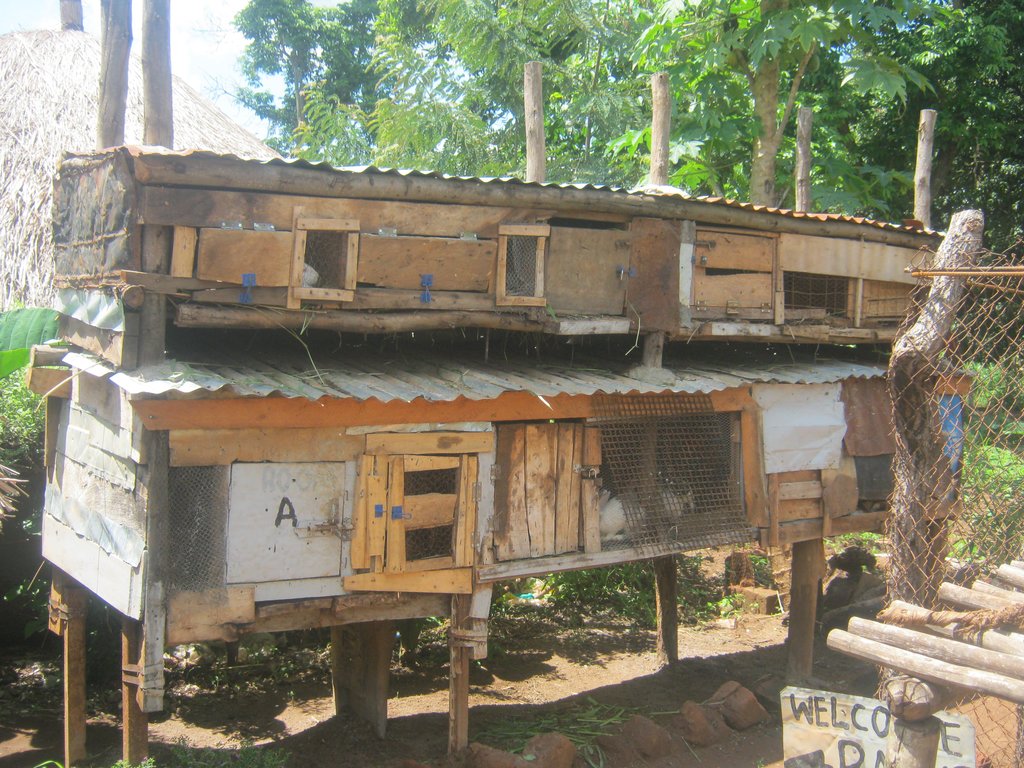
The technical drawing shows a rabbit house (hutch). This hutch was made simple and affordable to the farmer. The hutch was constructed around the compound for easy monitoring from danger by the farmer. The farmer constructed the hutch out of wood, iron sheets for the roofing and a wire mesh door that can be opened and closed.
However, when constructing a hutch, the measurements tend to vary depending on the number of rabbits a farmer wants to rear.
The technical drawing shows that the width of the hutch is six (6) meters and having a depth of 1,5 metres. The wall of the hutch is made of wood of about 1 meter high supported by a raised platform. That platform offers protection against dangerous reptiles such as snakes that prey on rabbits.
The hutch has lower and upper levels, partitioned into smaller rooms big enough to accommodate a pair of rabbits. The sizes of the rooms are four times bigger than the size of the rabbit's length. This is to provide ample space for the rabbit to run around and stretch as well as a place to hide while playing.
A hutch is constructed in a way that protects the rabbit from adverse weather conditions such a too windy weather that usually kills or makes the rabbit to become too sick as well as to provide shade to the rabbits.
However, hutches can be difficult to clean and also rabbits may be able to escape if the wire mesh isn't tightly secured.
4.3 ព័ត៌មានទូទៅដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធនឹងការគណនាធាតុចូល និងថ្លៃដើម
កំណត់របៀបនៃការគណនាថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូល:
- ក្នុងតំបន់អនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
កំណត់ទំហំ និងឯកត្តាផ្ទៃដី:
2 acres
ផ្សេងៗ/ រូបិយប័ណ្ណជាតិ (បញ្ជាក់):
UGX
កំណត់អត្រាប្តូរប្រាក់ពីដុល្លាទៅរូបិយប័ណ្ណតំបន់ (បើទាក់ទង)៖ 1 ដុល្លារ =:
3500,0
កំណត់ថ្លៃឈ្នួលជាមធ្យមនៃការជួលកម្លាំងពលកម្មក្នុងមួយថ្ងៃ:
3000shs
4.4 សកម្មភាពបង្កើត
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Site clearing | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Dry and wet season |
| 2. | Digging pits | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Dry and wet season |
| 3. | Collecting rabbit dung | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Dry and Wet season |
| 4. | Pilling the dung in the pit | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | Dry and Wet season |
| 5. | Applying manures to the garden | ក្សេត្រសាស្ត្រ | Wet season |
| 6. | Constructing the hutch | រចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ | Dry and Wet season |
មតិយោបល់:
Easy to establish the technology because it requires less capital.
4.5 ថ្លៃដើម និងធាតុចូលដែលត្រូវការសម្រាប់ការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Labour | persons day | 2,0 | 3500,0 | 7000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hoes | piece | 3,0 | 12000,0 | 36000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Wheelbarrows | piece | 1,0 | 90000,0 | 90000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Spade | piece | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Nails | pics | 30,0 | 500,0 | 15000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Poles | pics | 10,0 | 5000,0 | 50000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Wire mesh | Roll | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Iron sheets | pics | 2,0 | 32000,0 | 64000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈសាងសង់ | Timber | pics | 10,0 | 12000,0 | 120000,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបក្នុងការបង្កើតបច្ចេកទេស | 442000,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Land user can afford to pay the workers during during construction, compost manure making and labour for transporting the manures to the garden.
4.6 សកម្មភាពថែទាំ
| សកម្មភាព | ប្រភេទវិធានការ | ពេលវេលា/ ភាពញឹកញាប់ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Turning the compost | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | During dry and wet season |
| 2. | Cleaning the hutch | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | During dry and wet season |
| 3. | Digging around the hutch | ការគ្រប់គ្រង | During dry and wet season |
4.7 កំណត់ថ្លៃដើមសម្រាប់ការថែទាំ/ សកម្មភាពរបស់បច្ចេកទេស (ក្នុងរយៈពេលមួយឆ្នាំ)
| បញ្ជាក់ពីធាតុចូល | ឯកតា | បរិមាណ | ថ្លៃដើមក្នុងមួយឯកតា | ថ្លៃធាតុចូលសរុប | % នៃថ្លៃដើមដែលចំណាយដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Clearing around the hutch | perso per dayn | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Cleaning the hutch | person per day | 4,0 | 3000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Clearing around the manure pit | person per day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| កម្លាំងពលកម្ម | Adding manure to the garden | persons per day | 1,0 | 3000,0 | 3000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hoe | pic | 1,0 | 12000,0 | 12000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Spade | pic | 1,0 | 30000,0 | 30000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Wheelbarrow | pic | 1,0 | 150000,0 | 150000,0 | 100,0 |
| សម្ភារៈ | Hard broom | pic | 1,0 | 500,0 | 500,0 | 100,0 |
| ថ្លៃដើមសរុបសម្រាប់ការថែទាំដំណាំតាមបច្ចេកទេស | 213500,0 | |||||
មតិយោបល់:
Maintenance activities do not require much capital.
4.8 កត្តាសំខាន់បំផុតដែលមានឥទ្ធិពលដល់ការចំណាយ
ពណ៌នាពីកត្តាប៉ះពាល់ចម្បងៗទៅលើថ្លៃដើម:
Inputs such as timber, wheel barrows, hoes, nails , wire mesh and iron sheets affect costs most.
5. លក្ខណៈបរិស្ថានធម្មជាតិ និងមនុស្ស
5.1 អាកាសធាតុ
បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ
- < 250 មម
- 251-500 មម
- 501-750 មម
- 751-1,000 មម
- 1,001-1,500 មម
- 1,501-2,000 មម
- 2,001-3,000 មម
- 3,001-4,000 មម
- > 4,000 មម
កំណត់បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀង (បើដឹង) ជា មីលីម៉ែត្រ:
1500,00
លក្ខណៈពិសេស/ មតិយោបល់លើរដូវភ្លៀង:
Rainy seasons from april, may, june, july, august, september and october. Dry seasons from november, december, january, febuary and march.
បញ្ជាក់ឈ្មោះឯកសារយោងនៃស្ថានីយឧតុនិយម:
Gulu weather station.
តំបន់កសិអាកាសធាតុ
- មានភ្លៀងមធ្យម
Tropical savanna climate
5.2 សណ្ឋានដី
ជម្រាលជាមធ្យម:
- រាបស្មើ (0-2%)
- ជម្រាលតិចតួច (3-5%)
- មធ្យម (6-10%)
- ជម្រាលខ្ពស់បន្តិច (11-15%)
- ទីទួល (16-30%)
- ទីទួលចោត (31-60%)
- ទីទួលចោតខ្លាំង (>60%)
ទម្រង់ដី:
- ខ្ពង់រាប
- កំពូលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលភ្នំ
- ជម្រាលទួល
- ជម្រាលជើងភ្នំ
- បាតជ្រលងភ្នំ
តំបន់តាមរយៈកម្ពស់ :
- 0-100 ម
- 101-500 ម
- 501-1,000 ម
- 1,001-1,500 ម
- 1,501-2,000 ម
- 2,001-2,500 ម
- 2,501-3,000 ម
- 3,001-4,000 ម
- > 4,000 ម
បញ្ជាក់ថាតើបច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានអនុវត្តន៍នៅក្នុង:
- មិនពាក់ព័ន្ធទាំងអស់
5.3 ដី
ជម្រៅដីជាមធ្យម:
- រាក់ខ្លាំង (0-20 សម)
- រាក់ (21-50 សម)
- មធ្យម (51-80 សម)
- ជ្រៅ (81-120 សម)
- ជ្រៅខ្លាំង (> 120 សម)
វាយនភាពដី (ស្រទាប់លើ):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
វាយនភាពដី (> 20 សម ស្រទាប់ក្នុង):
- មធ្យម (ល្បាយ, ល្បាប់)
សារធាតុសរីរាង្គនៅស្រទាប់ដីខាងលើ:
- មធ្យម (1-3%)
5.4 ទឹកដែលអាចទាញមកប្រើប្រាស់បាន និងគុណភាពទឹក
នីវ៉ូទឹកក្រោមដី:
5-50 ម
ទឹកលើដីដែលអាចទាញយកប្រើប្រាស់បាន:
ល្អ
គុណភាពទឹក (មិនបានធ្វើប្រត្តិកម្ម):
ទឹកពិសារដែលមានគុណភាពល្អ
តើមានបញ្ហាភាពទឹកប្រៃហូរចូលមកដែរឬទេ?
ទេ
តើទឹកជំនន់កំពុងកើតមាននៅតំបន់នេះដែររឺទេ?
ទេ
5.5 ជីវៈចម្រុះ
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃប្រភេទ:
- ខ្ពស់
ភាពសម្បូរបែបនៃទីជម្រក:
- ខ្ពស់
5.6 លក្ខណៈនៃអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដីដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
នៅមួយកន្លែង ឬពនេចរ :
- នៅមួយកន្លែង
ទីផ្សារនៃប្រព័ន្ធផលិតកម្ម:
- ពាក់កណ្តាលពាណិជ្ជកម្ម (ផ្គត់ផ្គង់ខ្លួនឯង/ ពាណិជ្ជកម្ម
ចំណូលក្រៅកសិកម្ម:
- តិចជាង 10% នៃចំណូល
កម្រិតជីវភាព:
- មធ្យម
ឯកជន ឬក្រុម:
- ធ្វើខ្លួនឯង/ គ្រួសារ
កម្រិតប្រើប្រាស់គ្រឿងយន្ត:
- ប្រើកម្លាំងពលកម្ម
យេនឌ័រ:
- ស្ត្រី
- បុរស
អាយុរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- យុវវ័យ
- វ័យកណ្តាល
5.7 ទំហំផ្ទៃដីជាមធ្យមនៃដីផ្ទាល់ខ្លួន ឬជួលគេដែលបានអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស
- < 0.5 ហិកតា
- 0.5-1 ហិកតា
- 1-2 ហិកតា
- 2-5 ហិកតា
- 5-15 ហិកតា
- 15-50 ហិកតា
- 50-100 ហិកតា
- 100-500 ហិកតា
- 500-1,000 ហិកតា
- 1,000-10,000 ហិកតា
- > 10,000 ហិកតា
តើផ្ទៃដីនេះចាត់ទុកជាទំហំកម្រិតណាដែរ ខ្នាតតូច មធ្យម ឬខ្នាតធំ (ធៀបនឹងបរិបទតំបន់)?
- ខ្នាតតូច
5.8 ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ដី និងកម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក
ភាពជាម្ចាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន មិនមានកម្មសិទ្ធ
កម្មសិទ្ធិប្រើប្រាស់ដី:
- ឯកជន
កម្មសិទ្ធប្រើប្រាស់ទឹក:
- ជាក្រុម (មានដែនកំណត់)
5.9 ការប្រើប្រាស់សេវាកម្ម និងហេដ្ឋារចនាសម្ព័ន្ធ
សុខភាព:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការអប់រំ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ជំនួយបច្ចេកទេស:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ការងារ (ឧ. ការងារក្រៅកសិដ្ឋាន):
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទីផ្សារ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ថាមពល:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ផ្លូវ និងការដឹកជញ្ជូន:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
ទឹកផឹក និងអនាម័យ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
សេវាកម្មហិរញ្ញវត្ថុ:
- មិនល្អ
- មធ្យម
- ល្អ
6. ផលប៉ះពាល់ និងការសន្និដ្ឋាន
6.1 ផលប៉ះពាល់ក្នុងបរិវេណអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេសដែលកើតមាន
ផលប៉ះពាល់លើសេដ្ឋកិច្ចសង្គម
ផលិតផល
ផលិតកម្មដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Manure adds nutrients into the soil thus increasing crop productions
គុណភាពដំណាំ
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Manure add nutrients to the soil fertile soils improving crop quality
ការគ្រប់គ្រងដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Due to application of manure which is locally obtained.
ចំណូល និងថ្លៃដើម
ចំណូលក្នុងកសិដ្ឋាន
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Some of the surplus manure is sold to generate income @ spade at UGX 2000 to the neighbourhood
ផលប៉ះពាល់ទៅលើអេកូឡូស៊ី
ជីវចម្រុះ៖ ដំណាំ, សត្វ
ដំណាំគម្រប
គុណភាពមុន SLM:
low quantity before SLM
គុណភាពក្រោយ SLM:
high quantity after SLM
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Vegetable crop growing improved due to manure applications into the soil.
ជីវម៉ាស/ កាបូនលើដី
មតិយោបល់/ ការបញ្ជាក់:
Dense vegetation cover provides above ground carbon sink.
6.3 ភាពប្រឈម និងភាពរួសនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ និងគ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ/ គ្រោះមហន្តរាយ (ដែលដឹងដោយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
ការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ
| រដូវកាល | ប្រភេទនៃការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ/ព្រឹត្តិការណ៍ | លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|---|---|
| សីតុណ្ហភាពប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | កើនឡើង | មធ្យម | |
| បរិមាណទឹកភ្លៀងប្រចាំឆ្នាំ | ថយចុះ | មធ្យម |
គ្រោះអាកាសធាតុ (មហន្តរាយ)
គ្រោះមហន្តរាយជីវៈសាស្ត្រ
| លក្ខណៈឆ្លើយតបនៃបច្ចេកទេសទៅនឹងការប្រែប្រួលអាកាសធាតុ | |
|---|---|
| ការរាតត្បាតនៃជំងឺ | មិនល្អ |
6.4 ការវិភាគថ្លៃដើម និងអត្ថប្រយោជន៍
តើផលចំណេញ និងថ្លៃដើមត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
តើផលចំណេញ និងការថែទាំ/ ជួសជុលត្រូវបានប្រៀបធៀបគ្នាយ៉ាងដូចម្តេច (ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី)?
រយៈពេលខ្លី:
វិជ្ជមាន
រយៈពេលវែង:
វិជ្ជមាន
6.5 ការទទួលយកបច្ចេកទេស
- តែមួយករណី /ពិសោធន៍
ក្នុងចំណោមគ្រួសារទាំងអស់ដែលអនុវត្តបច្ចេកទេស តើមានប៉ុន្មានគ្រួសារដែលចង់ធ្វើដោយខ្លួនឯង ដោយមិនទទួលបានសម្ភារៈលើកទឹកចិត្ត/ប្រាក់ឧបត្ថម្ភ?:
- 90-100%
6.6 ការបន្សុំា
តើថ្មីៗនេះ បច្ចេកទេសនេះត្រូវបានកែតម្រូវដើម្បីបន្ស៊ាំទៅនឹងស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលដែរឬទេ?
បាទ/ចា៎
បើឆ្លើយបាទ/ ចា៎ សូមកំណត់ថាតើស្ថានភាពប្រែប្រួលមួយណាត្រូវបានបន្ស៊ាំ:
- បម្រែបម្រួលទីផ្សារ
បញ្ជាក់ពីការបន្ស៊ាំនៃបច្ចេកទេស (ការរៀបចំ, ឧបករណ៍/ប្រភេទ ។ល។):
Improved rabbit species being reared by the farmers that fetch high market prices.
6.7 ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៃបច្ចេកទេស
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាសនៅកន្លែងរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី |
|---|
| The technology is good at providing locally available materials such rabbit dung/animal manure that is less cost intensive and locally obtained. |
| Good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, rewarding in the short, medium and long term and can be replicated by other small scale farmers in other areas. |
| Provides income after sale of manure. |
| Very appropriate for men and children/youth since it does not involve a lot of moving from one place to another for feeds. |
| ភាពខ្លាំង/ គុណសម្បត្តិ/ ឱកាស ទស្សនៈរបស់បុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ |
|---|
| The technology is multipurpose (good at improving soil fertility by applying manure, provides income after sale of manure). |
| Easy to replicate. |
6.8 ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យនៃបច្ចេកទេស និងវិធីសាស្ត្រដោះស្រាយ
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Leaching due to excessive rainfall. | Dig the manure pit under shade/shelter. |
| Liked by thieves. | Fencing, provision of security. |
| Rabbits consume lots of feeds. | Grow relevant local feeds near the homestead such as grass, maize plant. |
| ភាពខ្សោយ/ គុណវិបត្តិ/ ហានិភ័យ ទស្សនៈរបស់អ្នកចងក្រងឬបុគ្គលសំខាន់ៗ | តើបច្ចេកទេសទាំងនោះបានដោះស្រាយបញ្ហាដូចម្តេច? |
|---|---|
| Negative attitude by other community members. | Involve them in the process of manure preparation and hutch constructions. |
| Long period required for manure to decompose. | Dig pit under shade for fast cooling of the compost and enhancement of decomposition. |
| Low rabbit dung collection for manure since they are kept in less numbers. | Expand the number of rabbits to generate manure. |
7. ឯកសារយោង និងវេបសាយ
7.1 វិធីសាស្ត្រ/ ប្រភពនៃព័ត៌មាន
- តាមការចុះទីវាល ការស្រាវជ្រាវនៅទីវាល
1
- ការសម្ភាសន៍ជាមួយអ្នកប្រើប្រាស់ដី
1
7.2 ឯកសារយោងដែលបានចេញផ្សាយ
ចំណងជើង អ្នកនិពន្ធ ឆ្នាំ ISBN:
The potential of rabbit production in improving household incomes in Nankoma Sub-county, Bugiri District, Uganda E K Ndyomugyenyi and O D Otiengino
មានប្រភពមកពីណា? ថ្លៃដើមប៉ុន្មាន?
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/289674867_Ndyomugyenyi_E_K_and_Otiengino_O_D_2013_The_potential_of_rabbit_production_in_improving_household_incomes_in_Nankoma_Sub-county_Bugiri_District_Uganda_Livestock_Research_for_Rural_Development_25_8_htt
7.3 ចូលទៅទាញយកឯកសារដែលពាក់ព័ន្ធតាមបណ្តាញអ៊ិនធឺណែត
ចំណងជើង/ ពណ៌នា:
Rabbit Farming In Uganda, Rearing Tips, Farmers Association, Market, Urine, Feeds & Cages
វេបសាយ:
https://www.aboutuganda.com/agriculture/rabbit-farming-in-uganda
ការតភ្ជាប់ និងម៉ូឌុល
ពង្រីកមើលទាំងអស់ បង្រួមទាំងអស់ការតភ្ជាប់
គ្មានការតភ្ជាប់
ម៉ូឌុល
គ្មានម៉ូឌុល